-
超导-冷原子复合系统因能够实现快速门操控、长寿命存储和光纤中长距离传输等特点, 被认为是实现两台超导量子计算机光互联的最有潜力的复合体系之一. 本文综述了近年来基于超导-冷原子复合系统实现两台超导量子计算机光互联的研究进展, 包括超导芯片与冷原子相干耦合、微波光波相干转换和超导量子比特与量子转换器长程微波互联. 对该复合量子系统的研究将为超导量子计算机之间的实用化光纤互联奠定物理和技术基础, 有望在分布式超导量子计算机和杂化量子网络中获得广泛应用.
-
关键词:
- 超导-冷原子复合系统 /
- 相干耦合 /
- 微波光波转换 /
- 长程微波互联
The hybrid quantum system composed of superconductor and cold atoms is expected to achieve fast quantum gates, long-life quantum storage and long-distance transmission through optical fibers, making it one of the most promising hybrid quantum systems to realize optical interconnection between two superconducting quantum computers. In this paper, we comprehensively review the recent research advancements in the optical interconnection of two superconducting quantum computers, based on the superconductor and cold atoms hybrid quantum system, specifically the review covers the coherent coupling between superconducting chips and cold atoms, the coherent microwave-to-optics conversion, and the long-range microwave interconnection between superconducting qubits and quantum converters. The system is expected to provide a physical and technical foundation for practical optical-fiber interconnection of two superconducting quantum computers, and have broad applications in distributed superconducting quantum computation and hybrid quantum networks.-
Keywords:
- superconductor and cold atoms hybrid quantum system /
- coherent coupling /
- microwave-to-optics conversion /
- long-distance microwave interconnection
[1] Arute F, Arya K, Babbush R, et al. 2019 Nature 574 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhu Q L, Cao S R, Chen F S, et al. 2022 Sci. Bull. 67 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ye Y, Cao S, Wu Y, et al. 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett. 38 100301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu S, Sun Z Z, Wang K, et al. 2023 Chin. Phys. Lett. 40 060301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Monroe C, Raussendorf R, Ruthven A, Brown K R, Maunz P, Duan L M, Kim J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 022317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Nickerson N H, Fitzsimons J F, Benjamin S C 2014 Phys. Rev. X 4 041041
[7] Wehner S, Elkouss D, Hanson R 2018 Science 362 303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李颖, 孙昌璞 2019 物理 48 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Sun C P 2019 Physics 48 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Awschalom D, Berggren K K, Bernien H, Bhave S, Carr L, Davids P, Economou S, Englund D, Faraon A, Fejer M 2021 PRX Quantum 2 017002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhong Y P, Chang H S, Bienfait A, Dumur É, Chou M H, Conner C R, Grebel J, Povey R G, Yan H X, Schuster D I, Cleland A N 2021 Nature 590 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Niu J J, Zhang L B, Liu Y, et al. 2023 Nat. Electron. 6 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Magnard P, Storz S, Kurpiers P, et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 260502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Storz S, Schär J, Kulikov A, et al. 2023 Nature 617 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lambert N J, Rueda A, Sedlmeir F, Schwefel H G 2020 Adv. Quantum Technol. 3 1900077
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lauk N, Sinclair N, Barzanjeh S, Covey J P, Saman M, Spiropulu M, Simon C 2020 Quantum Sci. Technol. 5 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kurizki G, Bertet P, Kubo Y, Mølmer K, Petrosyan D, Rabl P, Schmiedmayer J 2015 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 3866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Verdú J, Zoubi H, Koller C, Majer J, Ritsch H, Schmiedmayer J 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 043603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Beck M A, Isaacs J A, Booth D, Pritchard J D, Saffman M, McDermott R 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 092602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bernon S, Hattermann H, Bothner D, Knufinke M, Weiss P, Jessen F, Cano D, Kemmler M, Kleiner R, Koelle D, Fortágh J 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hattermann H, Bothner D, Ley L Y, Ferdinand B, Wiedmaier D, Sárkány L, Kleiner R, Koelle D, Fortágh J 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 2254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kaiser M, Glaser C, Li Y L, Grimmel J, Hattermann H, Bothner D, Koelle D, Kleiner R, Petrosyan D, Günther A, Fortágh J 2022 Phys. Rev. Res. 4 013207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Morgan A, Hogan S 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 193604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Andrews R W, Peterson R W, Purdy T P, Cicak K, Simmonds R W, Regal C A, Lehnert K W 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Higginbotham A P, Burns P S, Urmey M D, Peterson R W, Kampel N S, Brubaker B M, Smith G, Lehnert K W, Regal C A 2018 Nat. Phys. 14 1038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Forsch M et al. 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sahu R, Hease W, Rueda A, Arnold G, Qiu L, Fink J M 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 1276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Fan L, Zou C L, Cheng R, Guo X, Han X, Gong Z, Tang H X 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaar4994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kumar A, Suleymanzade A, Stone M, Taneja L, Anferov A, Schuster D I, Simon J 2023 Nature 615 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Smith B D, Babaei B, Narayanan A, LeBlanc L J 2023 arXiv: 2305.19221v1
[30] Tu H T, Liao K Y, Zhang Z X, Liu X H, Zheng S Y, Yang S Z, Zhang X D, Yan H, Zhu S L 2022 Nat. Photonics 16 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Vogt T, Gross C, Han J, Pal S B, Lam M, Kiffner M, Li W 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 023832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fernandez-Gonzalvo X, Horvath S P, Chen Y H, Longdell J J 2019 Phys. Rev. A 10 033807
[33] Hisatomi R, Osada A, Tabuchi Y, Ishikawa T, Noguchi A, Usami K, Yamazaki R, Nakamura Y 2016 Phys. Rev. B 93 174427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Shen Z, Xu G T, Zhang M, Zhang Y L, Wang Y, Chai C Z, Zou C L, Guo G C, Dong C H 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 243601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kiffner M, Feizpour A, Kaczmarek K T, Jaksch D, Nunn J 2016 New J. Phys. 18 093030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Mirhosseini M, Sipahigil A, Kalaee M, Painter O 2020 Nature 588 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Delaney R D, Urmey M D, Mittal S, Brubaker B M, Kindem J M, Burns P S, Regal C A, Lehnert K W 2022 Nature 606 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Han X, Fu W, Zhong C C, Zou C L, Xu Y T, Sayem A A, Xu M R, Wang S H, Cheng R S, Jiang L, Tang H X 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 3237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Xu M R, Han X, Zou C L, Fu W, Xu Y T, Zhong C C, Jiang L, Tang H X 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 033602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Liang Z T, Zhang G Q, Yuan J H, Ye Q Z, Liao K Y, Xue Z Y, Yan H, Zhu S L 2022 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 65 240362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Zhu S L, Wang Z D, Zanardi P 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 100502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Zhu S L, Wang Z D 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 187902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Liang Y, Shen P, Ji L N, Xue Z Y 2023 Phys. Rev. Appl. 19 024051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Ji L N, Liang Y, Shen P, Xue Z Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 044034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Chen T, Xue Z Y, Wang Z D 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 014062
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Liang M J, Xue Z Y 2022 Phys. Rev. A 106 012603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] McKenzie-Sell L, Xie J, Lee C M, Robinson J W, Ciccarelli C, Haigh J A 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 140414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Sarabi B, Huang P, Zimmerman N M 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 11 014001
[49] Stockklauser A, et al. 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 011030
[50] Wang C H, Zhang M, Jiang L 2022 Phys. Rev. Res. 4 L042023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Xiang Z L, Zhang M, Jiang L, Rabl P 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 011035
[52] Vermersch B, Guimond P O, Pichler H, Zoller P 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 133601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
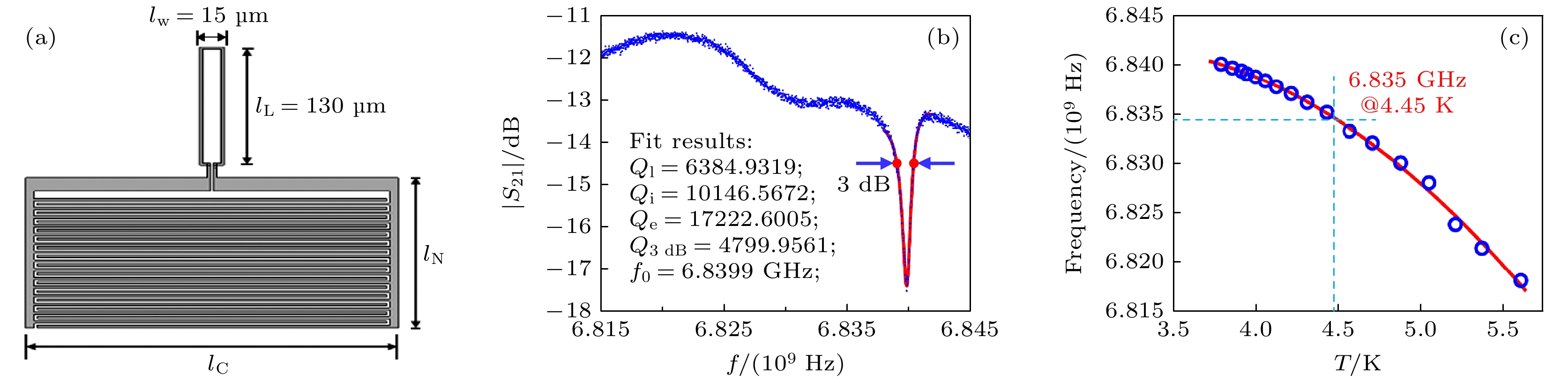
图 2 超导LC谐振腔芯片设计与测试 (a) 超导LC谐振腔COMSOL模型; (b) 在3.8 K温度下腔频为6.84 GHz的超导LC谐振腔芯片的|S21|曲线及其Q值; (c) 超导LC谐振腔频率随温度变化, 当温度为4.45 K时, 可以实现LC谐振腔与冷原子的共振耦合
Fig. 2. Design and test results of superconducting LC resonator: (a) Model of superconducting LC resonator by COMSOL software; (b) microwave transmission |S21| at 3.8 K of superconducting LC resonator with center frequency of 6.84 GHz and its corresponding Q factor; (c) the frequencies of superconducting LC resonator varies with temperature. When the temperature is 4.45 K, the resonant coupling between LC resonator and cold atoms can be realized.
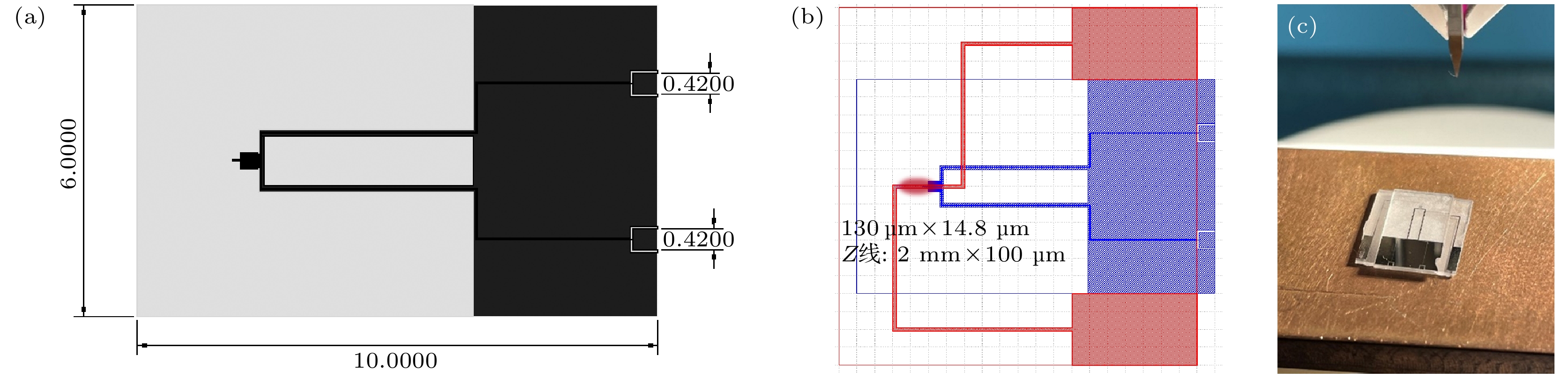
图 3 超导LC谐振腔芯片与冷原子相干耦合 (a) 超导LC谐振腔芯片尺寸(单位为mm); (b), (c) Z型超导原子芯片与超导LC谐振腔定位原理图与实物图
Fig. 3. Coherent coupling between superconducting LC resonator and cold atoms: (a) Size of superconducting LC resonator (in mm); (b), (c) positioning schematic diagram and physical diagram of Z-type superconducting atom chip and superconducting LC resonator
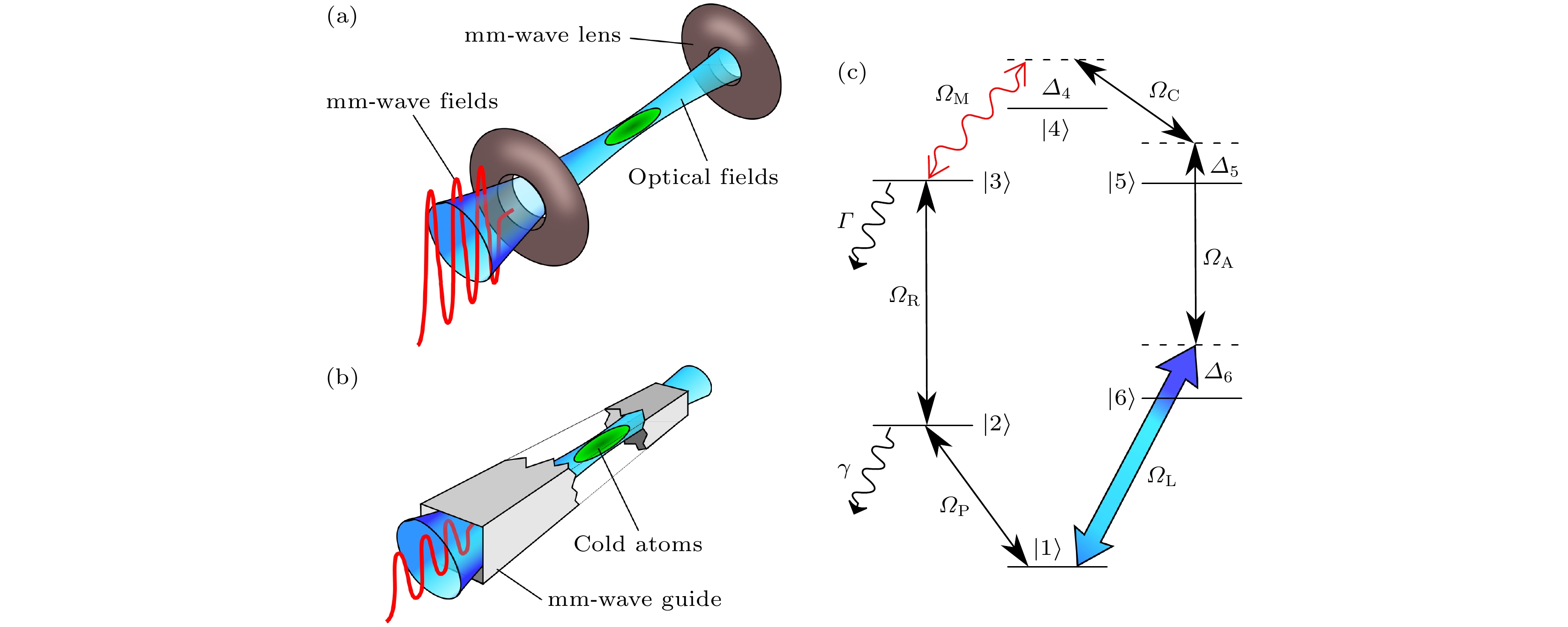
图 4 基于冷87Rb原子系综六波混频的毫米波-光波转换方案 (a) 毫米波透镜聚焦毫米波的毫米波-光波转换方案; (b) 波导收束毫米波的毫米波-光波转换方案; (c) 毫米波-光波转换方案原子能级图[35]
Fig. 4. Millimeter-wave-to-optics conversion via six-wave mixing based on cold 87Rb atomic ensembles: (a) Millimeter-wave-to-optics conversion with mm-wave fields focused by dielectric lenses; (b) millimeter-wave-to-optics conversion with mm-wave fields confined by waveguide; (c) six-level system of millimeter-wave-to-optics conversion[35].
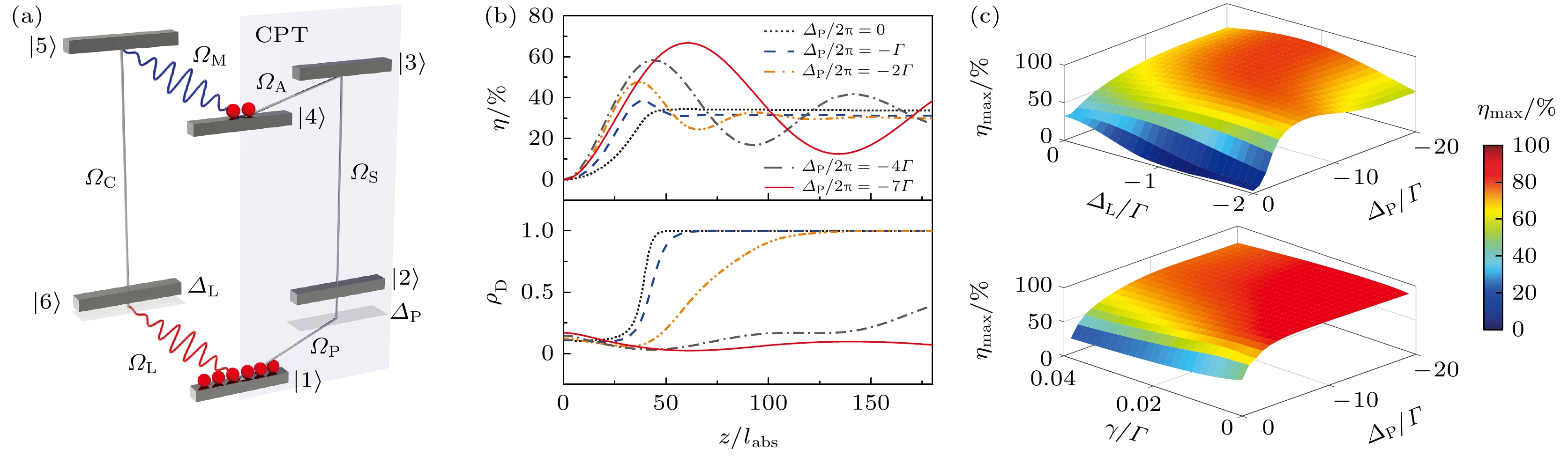
图 5 基于非共振散射的微波-光波转换 (a) 六能级系统; (b) 转换效率和原子暗态布局数随光学厚度的变化; (c) 最大转换效率与激光失谐、里德伯退相率的依赖关系[30]
Fig. 5. Microwave-to-optics conversion via off-resonant scattering: (a) Six-level system; (b) conversion efficiency and dark-state probability versus optical density; (c) maximum conversion efficiency versus detunings of probe laser and dephasing rates of Rydberg state[30].
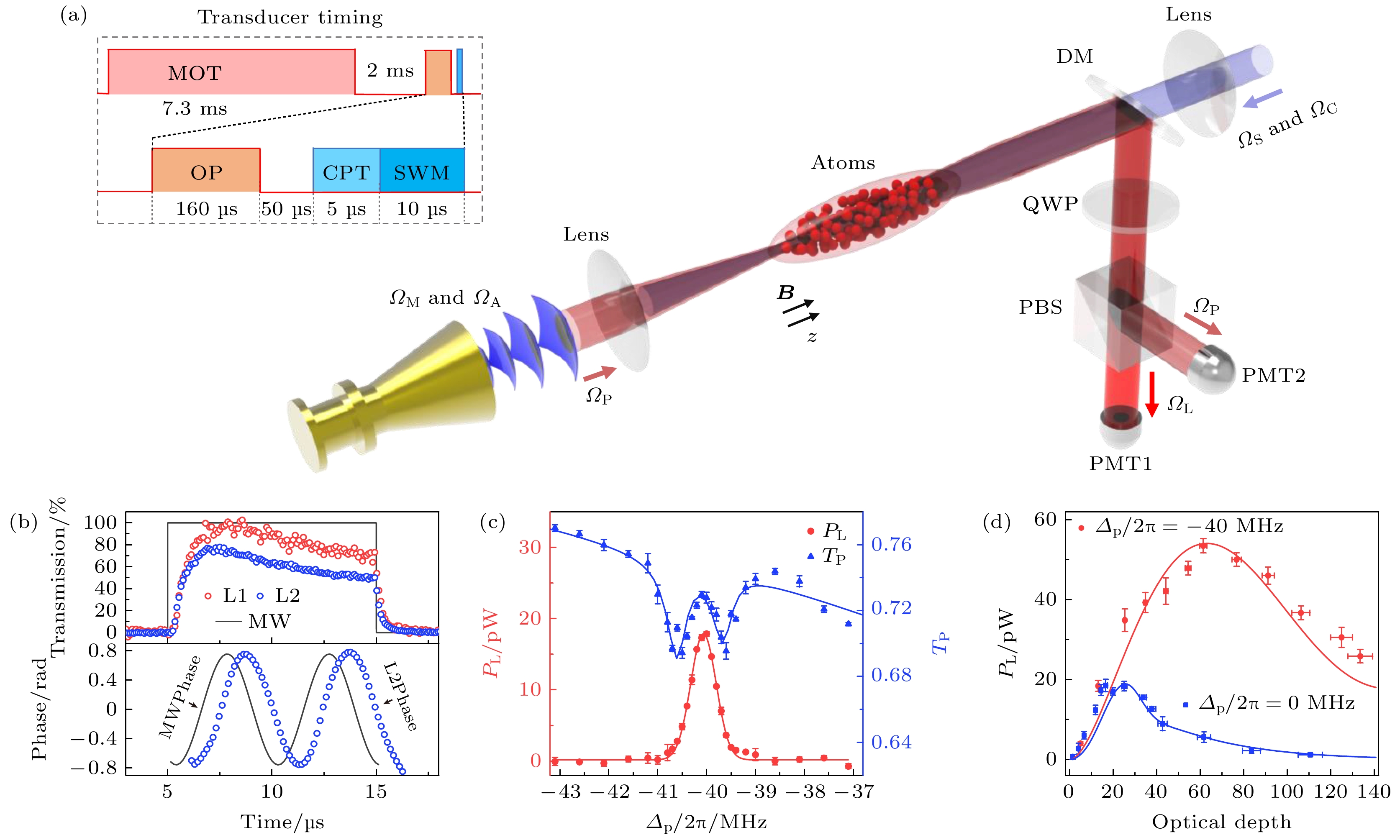
图 6 微波光波相干转换实验结果 (a) 实验构架与时序; (b) 微波光波的波形以及光外差检测结果; (c) 探测光与产生光的谱线; (d) 全共振及非共振的微波频率上转换随光学厚度的变化[30]
Fig. 6. Experimental results of microwave-to-optics conversion: (a) Experimental setup and time sequence; (b) temporal waveforms of the input microwave pulse and output optical pulses, and the relative phase of a heterodyne signal for the phase-modulated microwave; (c) spectra of transmission and generated optical power; (d) power PL of output optical pulses versus optical depth for off-resonant and near-resonant scatterings[30].
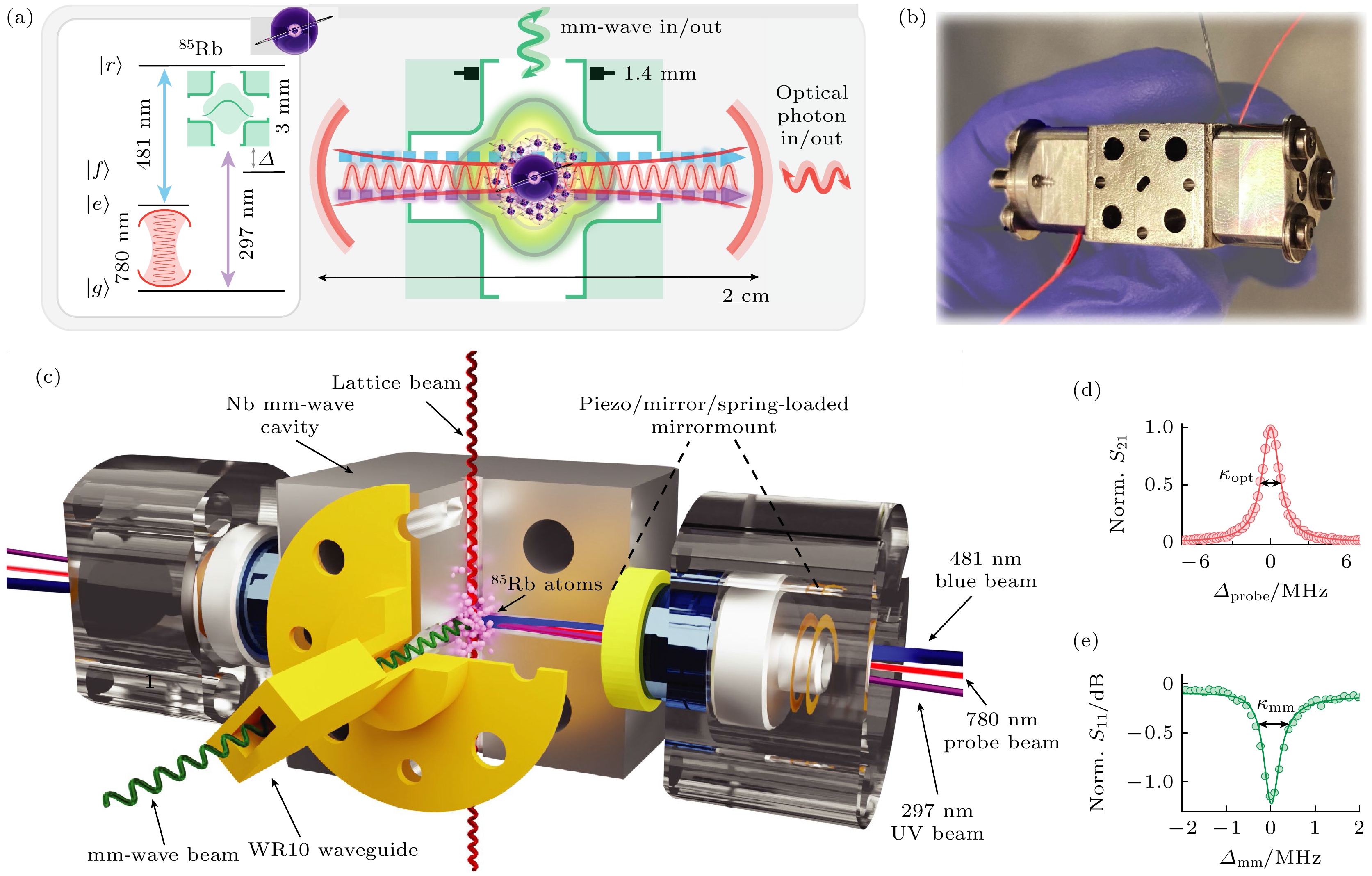
图 7 基于四波混频的光学光子与毫米波光子相干转换 (a) 实验方案, 左图为转换所需的原子能级和波长, 右图为毫米波光波转换接口的内部结构; (b) 实物图; (c) 超导腔和光腔的横截面图; (d) 空光腔的传输特性曲线, 半高全宽
$ {\kappa }_{{\rm{o}}{\rm{p}}{\rm{t}}} $ = 2π × 1.7 MHz; (e) 在5 K温区的超导毫米波谐振腔的反射谱, 半高全宽$ {\kappa }_{{\rm{m}}{\rm{m}}} $ = 2π × 800 kHz[28]Fig. 7. Millimeter-wave-to-optics conversion via four-wave mixing: (a) Schematic of the system, atomic energy levels and wavelengths of light involved in transduction (left), internal structure of the optical and mmwave interface (right); (b) image of the physical hybrid cavity; (c) expanded view of the main assembly; (d) bare optical cavity transmission with full-width half-maximum (FWHM) linewidth
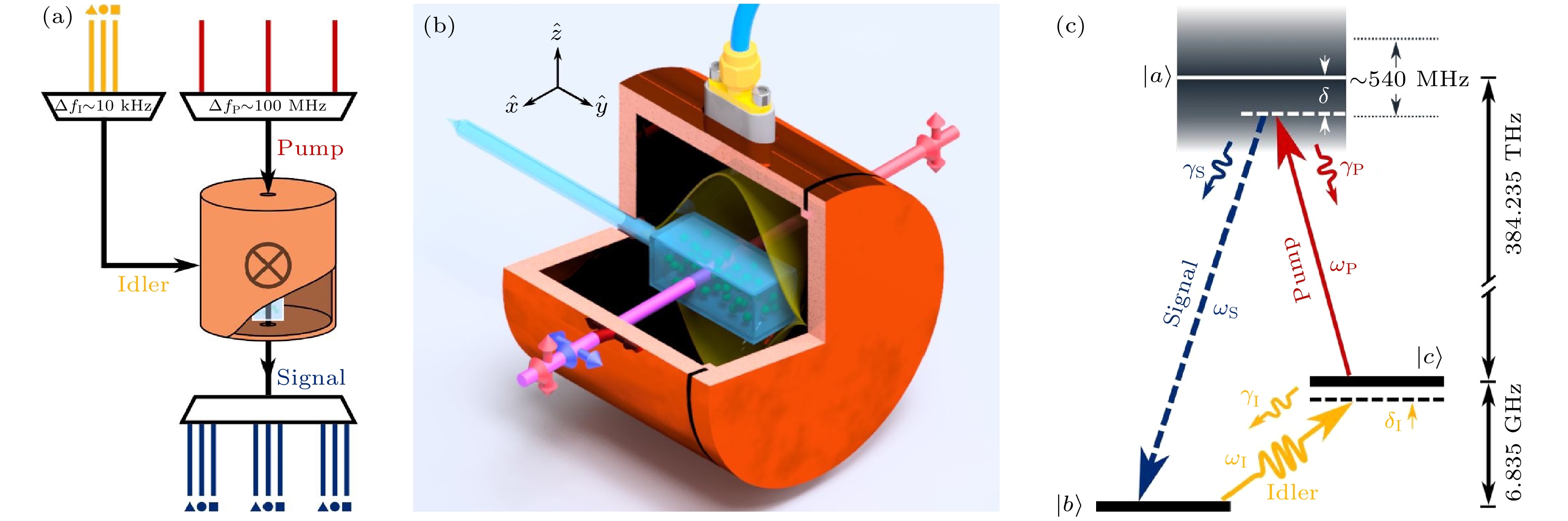
$ {\kappa }_{{\rm{o}}{\rm{p}}{\rm{t}}} $ = 2π × 1.7 MHz; (e) reflection spectrum of the superconducting mm wave cavity at 5 K with FWHM linewidth$ {\kappa }_{{\rm{m}}{\rm{m}}} $ = 2π × 800 kHz[28].图 8 基于热87Rb原子系综三波混频的微波-光波转换 (a) 频分多路复用原子转换器方案; (b) 微波腔-铷泡复合系统示意图; (c) 微波-光波转换能级图[29]
Fig. 8. Microwave-to-optics conversion via three-wave mixing based on thermal 87Rb atomic ensembles: (a) Schematic of the atomic frequency-division multiplexing scheme; (b) the microwave cavity-vapor cell hybrid system; (c) three-level system of microwave-to-optics conversion[29].
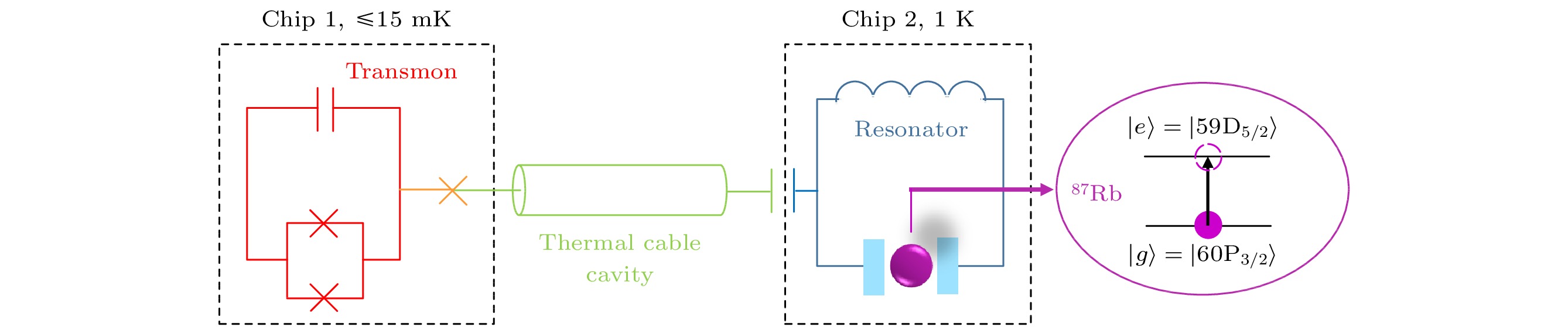
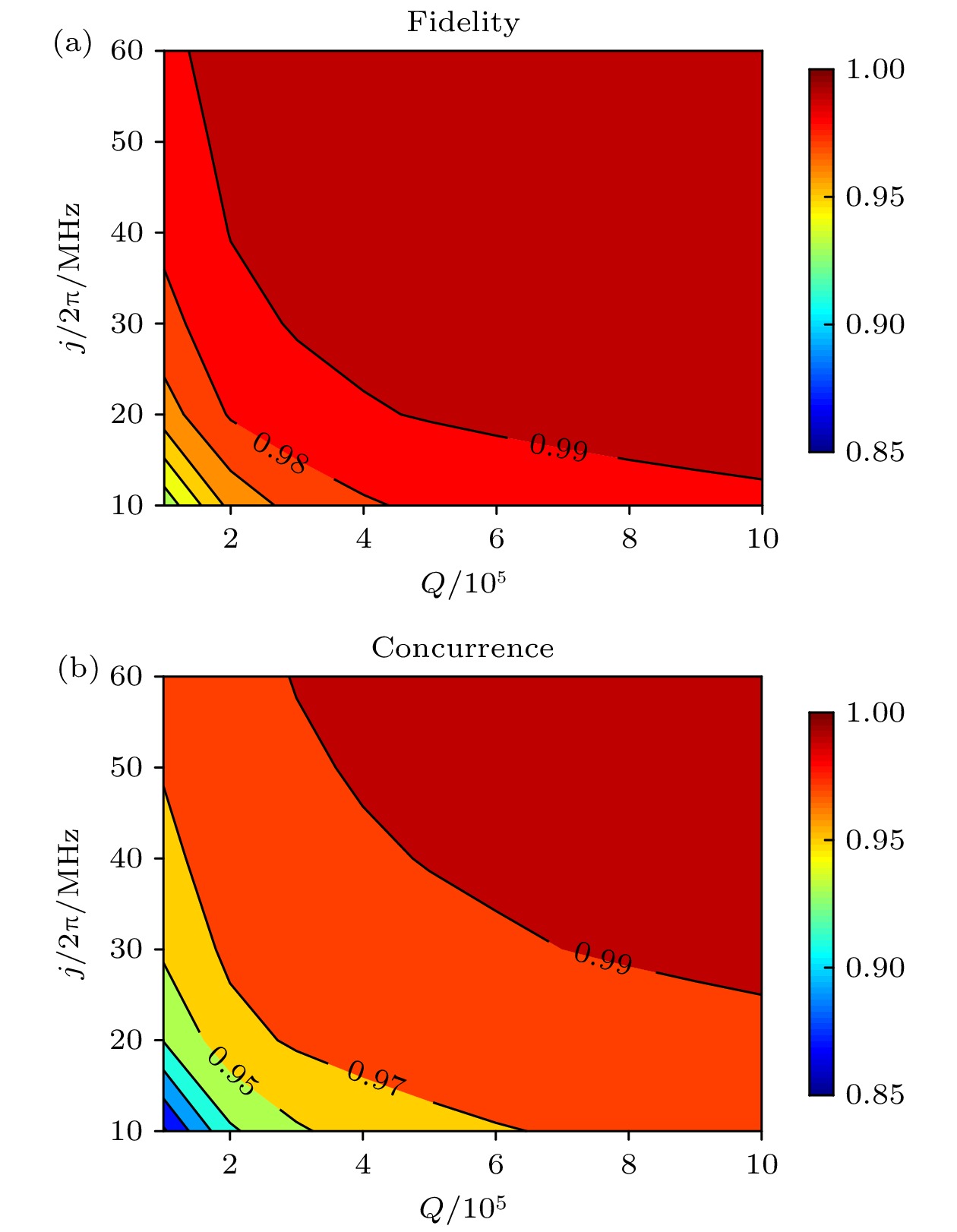
图 9 15 mK超导量子比特与1 K冷台附近里德伯冷原子基于1 K热耦合腔长程互联的实验装置示意图[40]
Fig. 9. Schematic of the hybrid system. A superconducting transmon qubit (red) on chip 1 anchored to a 15 mK plate resonantly couples with a standing mode of a superconducting coaxial-cable cavity (green) via a tunable coupler (orange cross). A superconducting LC resonator (blue) on chip 2 anchored to a 1 K plate resonantly couples with the same coaxial-cable cavity and a Rydberg-atom qubit (purple)[40].
表 1 超导芯片微波腔与冷原子相干耦合的实验研究进展
Table 1. Experimental research progress on coherent coupling of superconducting-chip microwave resonators and cold atoms.
表 2 基于中性原子微波光波相干转换的实验研究进展
Table 2. Experimental research progress of microwave-to-optics conversion based on neutral atoms.
-
[1] Arute F, Arya K, Babbush R, et al. 2019 Nature 574 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhu Q L, Cao S R, Chen F S, et al. 2022 Sci. Bull. 67 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ye Y, Cao S, Wu Y, et al. 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett. 38 100301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu S, Sun Z Z, Wang K, et al. 2023 Chin. Phys. Lett. 40 060301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Monroe C, Raussendorf R, Ruthven A, Brown K R, Maunz P, Duan L M, Kim J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 022317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Nickerson N H, Fitzsimons J F, Benjamin S C 2014 Phys. Rev. X 4 041041
[7] Wehner S, Elkouss D, Hanson R 2018 Science 362 303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李颖, 孙昌璞 2019 物理 48 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Sun C P 2019 Physics 48 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Awschalom D, Berggren K K, Bernien H, Bhave S, Carr L, Davids P, Economou S, Englund D, Faraon A, Fejer M 2021 PRX Quantum 2 017002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhong Y P, Chang H S, Bienfait A, Dumur É, Chou M H, Conner C R, Grebel J, Povey R G, Yan H X, Schuster D I, Cleland A N 2021 Nature 590 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Niu J J, Zhang L B, Liu Y, et al. 2023 Nat. Electron. 6 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Magnard P, Storz S, Kurpiers P, et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 260502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Storz S, Schär J, Kulikov A, et al. 2023 Nature 617 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lambert N J, Rueda A, Sedlmeir F, Schwefel H G 2020 Adv. Quantum Technol. 3 1900077
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lauk N, Sinclair N, Barzanjeh S, Covey J P, Saman M, Spiropulu M, Simon C 2020 Quantum Sci. Technol. 5 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kurizki G, Bertet P, Kubo Y, Mølmer K, Petrosyan D, Rabl P, Schmiedmayer J 2015 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 3866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Verdú J, Zoubi H, Koller C, Majer J, Ritsch H, Schmiedmayer J 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 043603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Beck M A, Isaacs J A, Booth D, Pritchard J D, Saffman M, McDermott R 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 092602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bernon S, Hattermann H, Bothner D, Knufinke M, Weiss P, Jessen F, Cano D, Kemmler M, Kleiner R, Koelle D, Fortágh J 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hattermann H, Bothner D, Ley L Y, Ferdinand B, Wiedmaier D, Sárkány L, Kleiner R, Koelle D, Fortágh J 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 2254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kaiser M, Glaser C, Li Y L, Grimmel J, Hattermann H, Bothner D, Koelle D, Kleiner R, Petrosyan D, Günther A, Fortágh J 2022 Phys. Rev. Res. 4 013207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Morgan A, Hogan S 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 193604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Andrews R W, Peterson R W, Purdy T P, Cicak K, Simmonds R W, Regal C A, Lehnert K W 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Higginbotham A P, Burns P S, Urmey M D, Peterson R W, Kampel N S, Brubaker B M, Smith G, Lehnert K W, Regal C A 2018 Nat. Phys. 14 1038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Forsch M et al. 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sahu R, Hease W, Rueda A, Arnold G, Qiu L, Fink J M 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 1276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Fan L, Zou C L, Cheng R, Guo X, Han X, Gong Z, Tang H X 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaar4994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kumar A, Suleymanzade A, Stone M, Taneja L, Anferov A, Schuster D I, Simon J 2023 Nature 615 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Smith B D, Babaei B, Narayanan A, LeBlanc L J 2023 arXiv: 2305.19221v1
[30] Tu H T, Liao K Y, Zhang Z X, Liu X H, Zheng S Y, Yang S Z, Zhang X D, Yan H, Zhu S L 2022 Nat. Photonics 16 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Vogt T, Gross C, Han J, Pal S B, Lam M, Kiffner M, Li W 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 023832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fernandez-Gonzalvo X, Horvath S P, Chen Y H, Longdell J J 2019 Phys. Rev. A 10 033807
[33] Hisatomi R, Osada A, Tabuchi Y, Ishikawa T, Noguchi A, Usami K, Yamazaki R, Nakamura Y 2016 Phys. Rev. B 93 174427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Shen Z, Xu G T, Zhang M, Zhang Y L, Wang Y, Chai C Z, Zou C L, Guo G C, Dong C H 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 129 243601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kiffner M, Feizpour A, Kaczmarek K T, Jaksch D, Nunn J 2016 New J. Phys. 18 093030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Mirhosseini M, Sipahigil A, Kalaee M, Painter O 2020 Nature 588 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Delaney R D, Urmey M D, Mittal S, Brubaker B M, Kindem J M, Burns P S, Regal C A, Lehnert K W 2022 Nature 606 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Han X, Fu W, Zhong C C, Zou C L, Xu Y T, Sayem A A, Xu M R, Wang S H, Cheng R S, Jiang L, Tang H X 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 3237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Xu M R, Han X, Zou C L, Fu W, Xu Y T, Zhong C C, Jiang L, Tang H X 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 033602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Liang Z T, Zhang G Q, Yuan J H, Ye Q Z, Liao K Y, Xue Z Y, Yan H, Zhu S L 2022 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 65 240362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Zhu S L, Wang Z D, Zanardi P 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 100502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Zhu S L, Wang Z D 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 187902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Liang Y, Shen P, Ji L N, Xue Z Y 2023 Phys. Rev. Appl. 19 024051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Ji L N, Liang Y, Shen P, Xue Z Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 044034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Chen T, Xue Z Y, Wang Z D 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 014062
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Liang M J, Xue Z Y 2022 Phys. Rev. A 106 012603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] McKenzie-Sell L, Xie J, Lee C M, Robinson J W, Ciccarelli C, Haigh J A 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 140414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Sarabi B, Huang P, Zimmerman N M 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 11 014001
[49] Stockklauser A, et al. 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 011030
[50] Wang C H, Zhang M, Jiang L 2022 Phys. Rev. Res. 4 L042023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Xiang Z L, Zhang M, Jiang L, Rabl P 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 011035
[52] Vermersch B, Guimond P O, Pichler H, Zoller P 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 133601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6920
- PDF下载量: 380
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: