-
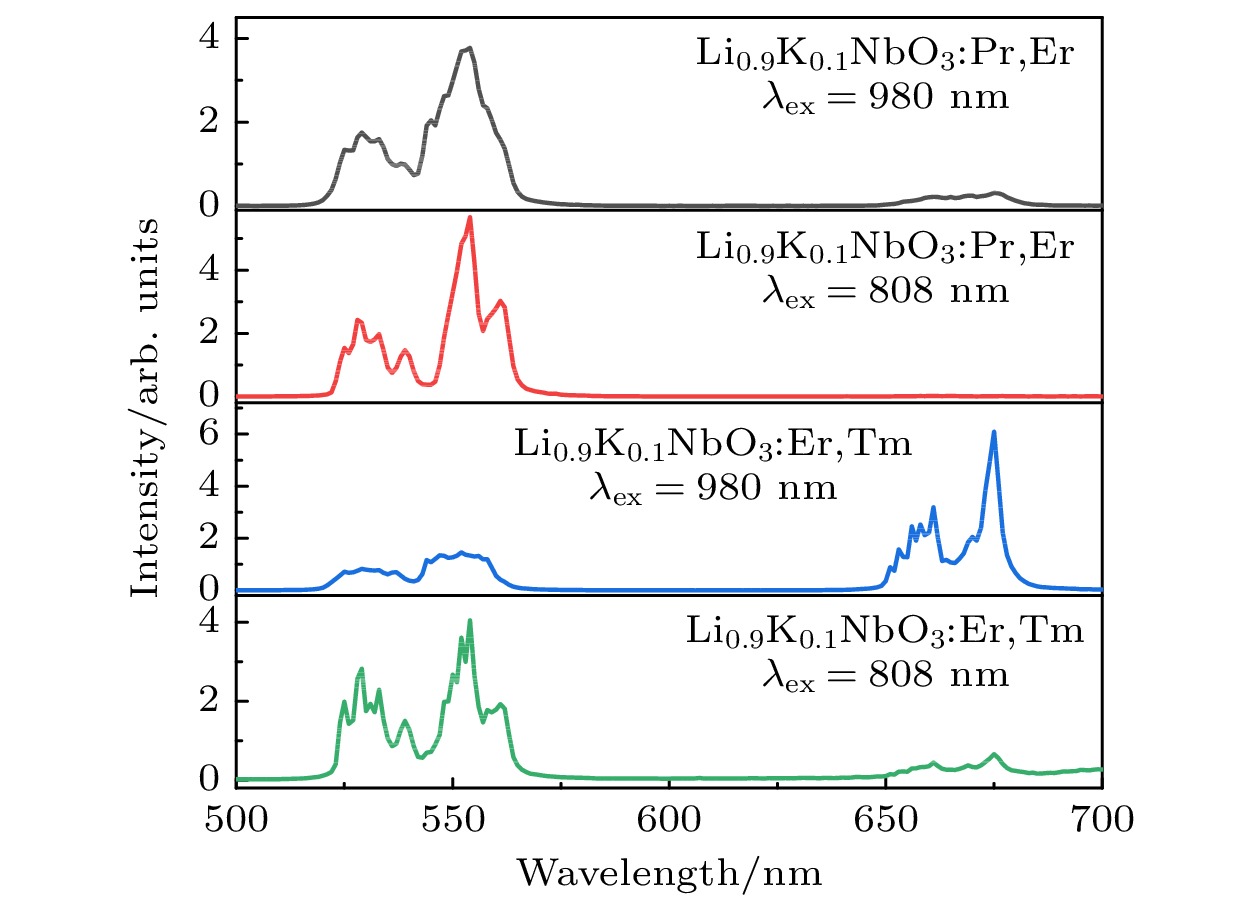
多色多模荧光材料在信息安全加密领域具有重要的应用价值, 然而目前多色多模荧光材料的设计合成仍然是一个挑战. 本文采用高温固相法制备了一系列Li1–xKxNbO3:Pr3+/Er3+/Tm3+单掺及双掺荧光粉. 通过X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜、荧光光谱仪以及自搭建的加热装置, 对其结构、形貌、光谱学特性以及热释光性能进行表征. 研究了Li0.9K0.1NbO3基质中Pr3+, Er3+, Tm3+单掺及共掺调控的多色多模荧光特性与上/下转换、余辉和光激励荧光机理. 基于优异的光谱特性, 将三基色荧光粉设计成蝴蝶图案, 采用不同波长光选择激发, 展现了图案和色彩的动态变化, 具有高阶多色多模防伪能力.Multicolor and multimode luminescence materials have important applications in the field of information security encryption. However, the design and synthesis of multicolor multimode luminescent materials is still a challenge, and only several materials have been reported. In this paper, a series of single doped and double doped Li1–xKxNbO3:Pr3+/Er3+/Tm3+ phosphors are prepared by high temperature solid state method. The structure, morphology, optical properties and thermoluminescence (TL) spectra are characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), luminescence spectrometer and self-made heating device. Firstly, the effects of different values of K+ content on the luminescence and trap distribution of LiNbO3 materials are studied. The results show that the ionic lattice is distorted when a small quantity of K+ ions replace Li+. With the addition of K+, the photoluminescence excitation (PLE) spectra monitored emission of 620 nm shows that the ratios of the absorption peaks from matrix (200–310 nm) to absorption peaks from the intrinsic transition of Pr3+ ions 4f→5d (310–430 nm) change significantly, showing a double-peak characteristic. When the concentration of K+ ions is 0.5, the absorption peak from the matrix disappears, which may be due to the phase transition of the matrix lattice caused by excessive K+ ions or the introduction of a large number of defect energy levels into the matrix lattice. Moreover, K+ ion doping can regulate the density and distribution of traps. TL curves show that a small quantity of K+ doping increases the trap density of shallow traps. When a large quantity of K+ is doped, the phase changes of matrix lattice and the defect density decrease. Secondly, the doping of Li0.9K0.1NbO3 matrix by different luminescent centers (Pr3+/Er3+/Tm3+) is studied. The results show that the multicolor luminescence emission in red, blue and green bands and the tunable multimode luminescence (up/down conversion luminescence, afterglow luminescence and photo-stimulated luminescence) are realized by the selective excitation. According to the multicolor and multimode characteristics of the phosphors, a butterfly-shaped anti-counterfeiting pattern is designed. Owing to the different energy level positions of the luminescence centers, dynamic multicolor photoluminescence is realized by selective excitation at different wavelengths. Based on the upconversion luminescence characteristics of Er3+ and the excellent afterglow characteristics of Pr3+ in Li0.9K0.1NbO3 material, the designed anti-counterfeiting pattern shows the dynamic color change and multicolor, multimode high-order anti-counterfeiting application.
-
Keywords:
- lanthanide ions doped /
- alkali metal ions doped /
- upconversion /
- multimode and multicolor luminescence /
- anti-counterfeiting
[1] Liu X M, Chen C, Li S L, Dai Y H, Guo H Q, Tang X H, Xie Y, Yan L S 2016 Inorg. Chem. 55 10383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tu D, Xu C N, Yoshida A, Fujihala M, Hirotsu J, Zheng X G 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1606914
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Park J, Kim Y J 2017 J. Korean. Ceram. Soc. 54 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xue J, Guo Y, Moon B K, Park S H, Jeong J H, Kim J H, Wang L L 2017 Opt. Mater. 66 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Baran M, Belikov K N, Kissabekova A, Krasnikov A, Lushchik A, Mihokova E, Tsiumra V, Vasylechko L, Zazubovich S, Zhydachevskyy Y 2021 J. Alloy Compd. 859 157800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Weis R S, Gaylord T K 1985 Appl. Phys. A 37 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Zheng H R, Shi P, Li L, Ling Y W 2013 Dalton Trans. 42 1834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Y J, Feng P, Ding S S, Tian S L, Wang Y H 2021 Inorg. Chem. Front. 8 3748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li M T, Wang X J, Zhu Q, Li J G, Kim B N 2021 J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Zou J, Shi M M, Yang B B 2020 RSC Adv. 10 13076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yantake R, Kaiheriman M, Yusufu T, Sidike A 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 5123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sun H C, Zhu Q, Li J G 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 9640
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gao D L, Ma K W, Wang P, Zhang X Y, Pang Q, Xin H, Zhang Z H, Jiao H 2022 Dalton Trans. 51 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Maurya A, Bahadur A, Dwivedi A, Choudhary A K, Yadav T P, Vishwakarma P K, Rai S B 2018 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 119 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang X Y, Wang M Q, Ding J J, Gao D L, Shi Y H, Song X H 2012 CrystEngComm 14 8357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Du P, Sun X, Zhu Q, Li J G 2020 Scripta Mater. 185 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sang J K, Zhou J Y, Zhang J C, Zhou H, Li H H, Ci Z P, Peng S L, Wang Z F 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 20150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Luo F, Xing J H, Qin Y Y, Gao Z X, Shang F, Chen G H 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 34483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] do Carmo F F, do Nascimento J P, Facanha M X, Sales T O, Santos, W Q, Gouveia-Neto A S, Jacinto C, Sombra A S 2018 J. Lumin. 204 676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang J C, Pan C, Zhu Y F, Zhao L Z, He H W, Liu X F, Qiu J R 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1804644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sun L L, Wang B, Xing G C, Liang C, Ma W, Yang S C 2023 Chem. Eng. J. 455 140752
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li Y, Gecevicius M, Qiu J R 2016 Chem. Soc. Rev. 45 2090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liang L L, Chen J Y, Shao K, Qin X, Pan Z F, Liu X G 2023 Nat. Mater. 22 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 李辰琳, 赵习宇, 郭彤, 刘峰, 王笑军, 廖川, 张家骅 2022 71 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C L, Zhao X Y, Guo T, Liu F, Wang X J, Liao C, Zhang J H 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xiong P X, Peng M Y, Qin K X, Xu F F, Xu X Y 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 7 1901107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Feng L, Wang Z B, Cao C, Zhang T, Zhang J C, Ci Z P, Zhao Z Y, Wang Y H 2017 J. Rare Earth 35 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen Y F, Spinelli S, Gu Z J, Pan Z W 2022 Chem. Eng. J. 446 137473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang P F, Li N, Wei Z T, Wang Z Q, Gou M W, Zhao L, Chen W B, Qiang Q P 2021 New J. Chem. 45 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li L Y, Castaing V, Rytz D, Sontakke A D, Katayama Y, Tanabe S, Peng M Y, Viana B 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Jia Q N, Zhang Q W, Sun H Q, Li Y, Hao X H 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 873 159852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 梁爱华, 王旭升, 李国荣, 郑嘹赢, 江向平, 胡锐 2022 71 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang A H, Wang X S, Li G R, Zheng L Y, Jiang X P, Hu R 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gao D L, Gao J, Gao F, Kuang Q Q, Pan Y, Chen Y F, Pan Z W 2021 J. Mater. Chem. C 9 16634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Guo H J, Wang Y H, Chen W B, Zeng W, Han S C, Li G, Li Y Y 2015 J. Mater. Chem. C 3 11212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang C L, Jin Y H, Lü Y, Ju G F, Liu D, Chen L, Li Z Z, Hu Y H 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 6058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Fan X T, Xu X H, Yu X, Chen W B, Zhou D C, Qiu J B 2018 Mater. Res. Bull. 99 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wang Z B, Pei P X, Bai D J, Zhao S S, Ma X Y, Liu W S 2020 Inorg. Chem. Front. 7 2506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Pei P X, Wei R P, Wang B B, Su J X, Zhang Z C, Liu W S 2021 Adv. Funct. Mater. 31 2102479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
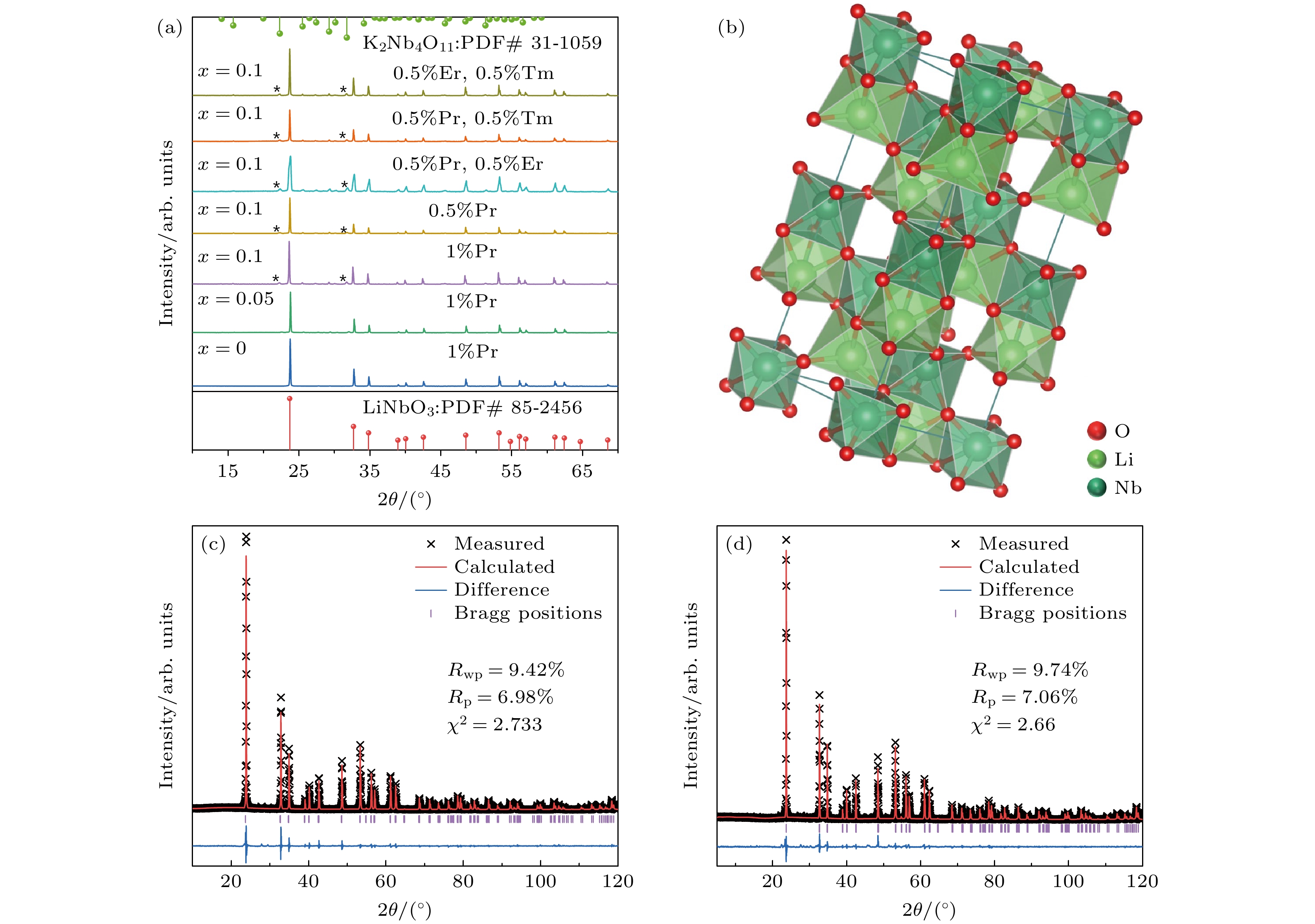
图 2 Ln3+掺杂系列Li1–xKxNbO3样品的SEM图片和Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+的EDX能谱图以及元素谱图 (a) LiNbO3:Pr3+; (b) Li0.95K0.05NbO3:Pr3+; (c) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+; (d) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+, Er3+; (e) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:1% Pr3+荧光粉的EDX能谱图(纵轴表示能谱计数频率); (f) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:1% Pr3+荧光粉的EDX元素谱
Fig. 2. SEM images of a series of lanthanide ions doped Li1–xKxNbO3 phosphors and EDX spectra and element mappings of Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+: (a) LiNbO3:Pr3+; (b) Li0.95K0.05NbO3:Pr3+; (c) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+; (d) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+, Er3+; (e) EDX spectrum of Li0.9K0.1NbO3:1% Pr3+ phosphors (The vertical axis shows the counting frequency of energy spectrum); (f) EDX elemental mappings of Li0.9K0.1NbO3:1%Pr3+ phosphors.
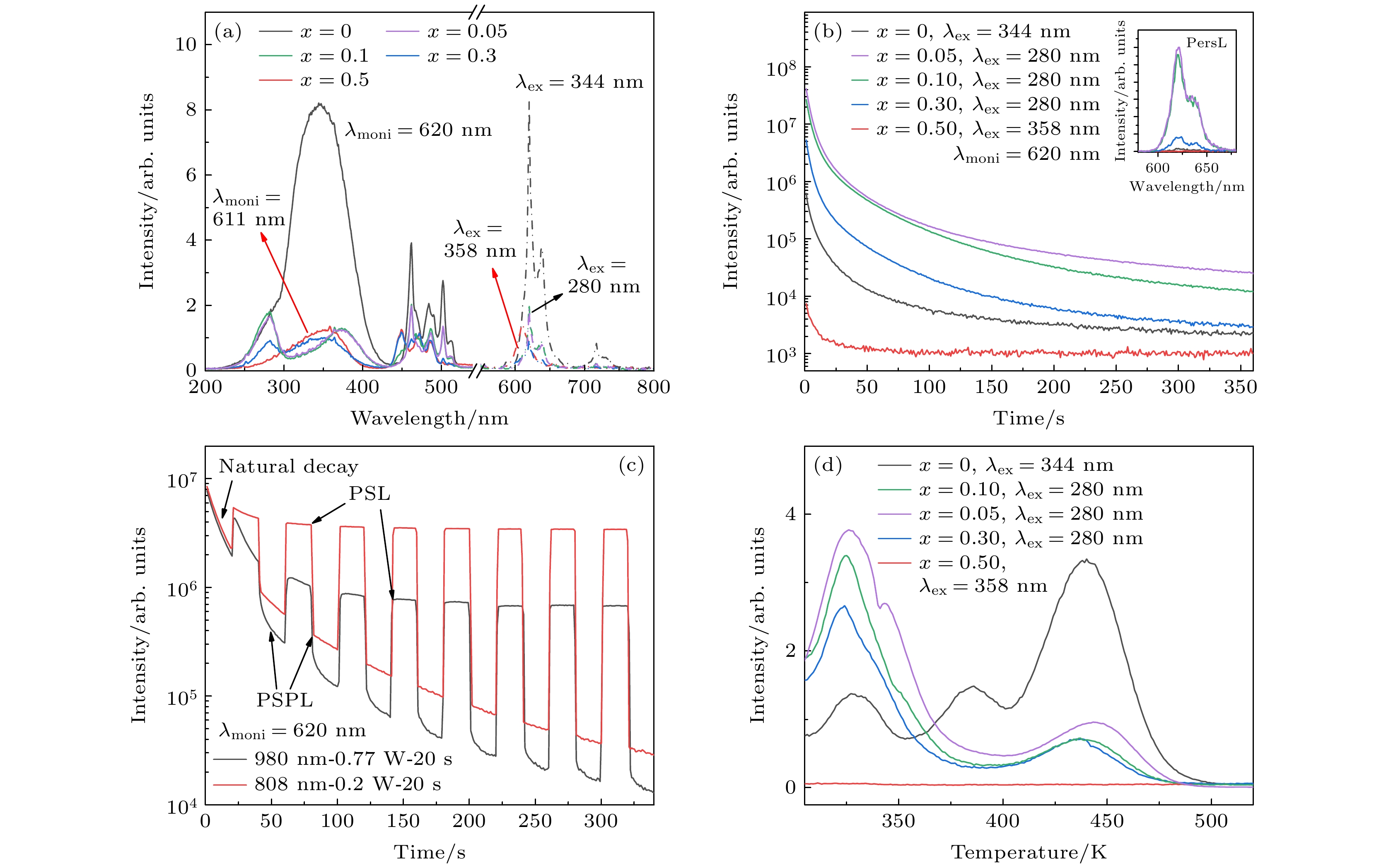
图 3 Li1–xKxNbO3:1% Pr3+ (x = 0—0.5)的荧光性能 (a) 激发和发射谱; (b) 紫外预辐照样品的余辉衰减曲线, 内插图为余辉发射谱; (c) Li0.9K0.1NbO3:0.5% Pr3+样品在280 nm辐照6 min后, 重复间断地在980/808 nm激发下的光激励荧光和光激励余辉荧光衰减曲线; (d) TL谱
Fig. 3. Luminescence properties of Li1–xKxNbO3:1% Pr3+ (x = 0–0.5) samples: (a) Excitation and emission spectra; (b) afterglow decay curves of UV preirradiated samples, the inset is their afterglow emission spectra; (c) repeated PSL and PSPL decay curve of Li0.9K0.1NbO3:0.5% Pr3+ sample under 980/808 nm excitation, after irradiation at 280 nm for 6 min; (d) TL spectra.
图 4 Li0.9K0.1NbO3:y% Pr3+ (y = 0.1—1.5)样品的激发、发射谱和余辉衰减曲线 (a) 激发和发射谱; (b) 280 nm紫外灯辐照后的余辉衰减曲线, 内插图为余辉发射谱
Fig. 4. Excitation, emission spectra and the afterglow decay curve of Li0.9K0.1NbO3:y% Pr3+ (y = 0.1–1.5) samples: (a) Excitation and emission spectra; (b) afterglow decay curve after 280 nm UV light irradiation and the inset is the afterglow emission spectra.
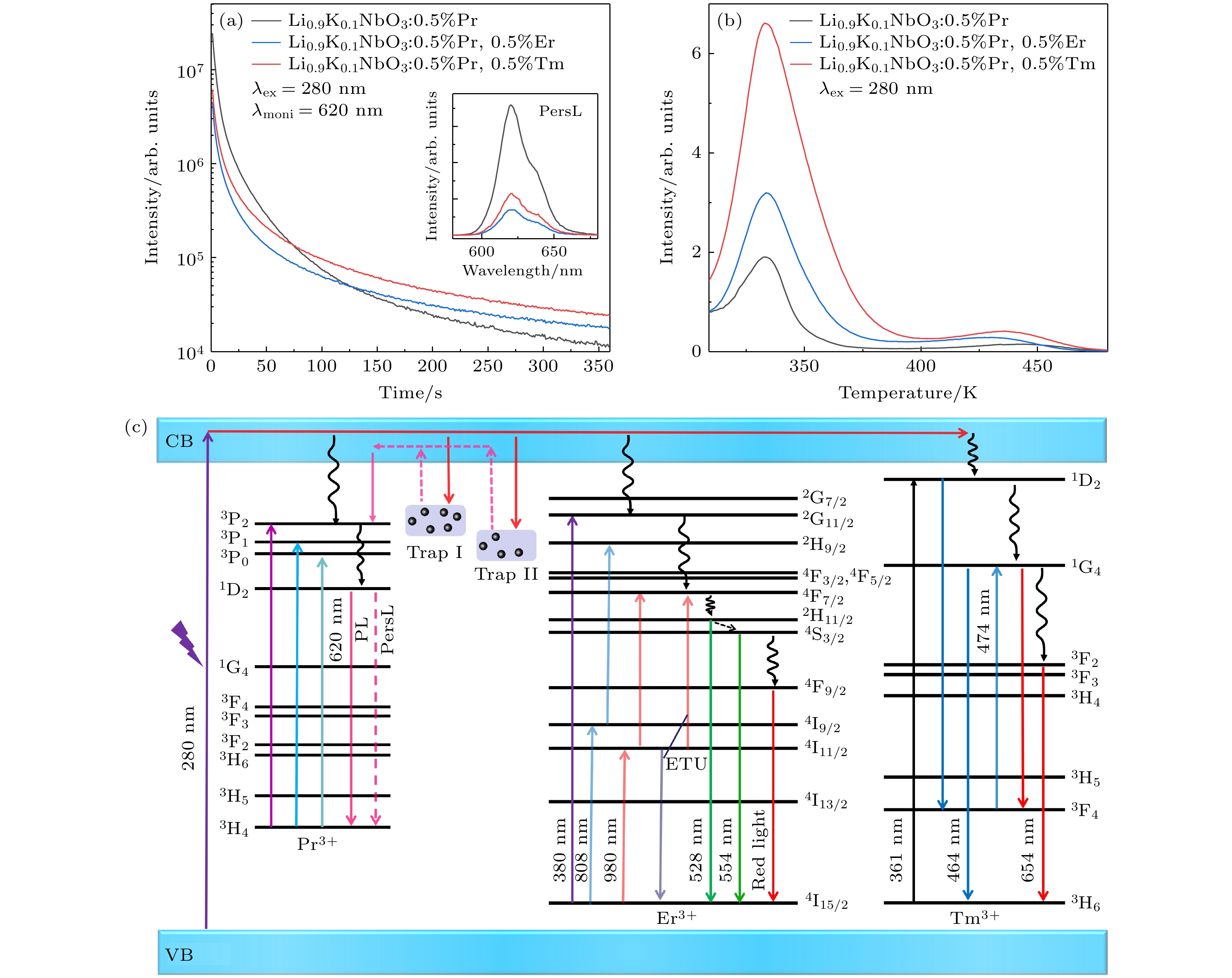
图 7 Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+, Er3+ (或Tm3+)样品的余辉衰减曲线、余辉发射谱、TL谱及余辉机理图 (a) 在280 nm辐照6 min后监控620 nm的余辉衰减曲线, 内插图为余辉发射谱; (b) TL图谱; (c) 多色荧光调控以及红色长余辉的机理图
Fig. 7. Afterglow decay curves, afterglow emission spectra, TL spectra and luminescence mechanism diagram of Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+, Er3+ (or Tm3+) sample: (a) Afterglow decay curve of 620 nm measured after the sample is irradiated at 280 nm for 6 min, the inset is afterglow emission spectra; (b) TL spectra; (c) mechanism diagram of multicolor luminescence regulation and red long afterglow luminescence.
-
[1] Liu X M, Chen C, Li S L, Dai Y H, Guo H Q, Tang X H, Xie Y, Yan L S 2016 Inorg. Chem. 55 10383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tu D, Xu C N, Yoshida A, Fujihala M, Hirotsu J, Zheng X G 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1606914
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Park J, Kim Y J 2017 J. Korean. Ceram. Soc. 54 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xue J, Guo Y, Moon B K, Park S H, Jeong J H, Kim J H, Wang L L 2017 Opt. Mater. 66 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Baran M, Belikov K N, Kissabekova A, Krasnikov A, Lushchik A, Mihokova E, Tsiumra V, Vasylechko L, Zazubovich S, Zhydachevskyy Y 2021 J. Alloy Compd. 859 157800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Weis R S, Gaylord T K 1985 Appl. Phys. A 37 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Zheng H R, Shi P, Li L, Ling Y W 2013 Dalton Trans. 42 1834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Y J, Feng P, Ding S S, Tian S L, Wang Y H 2021 Inorg. Chem. Front. 8 3748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li M T, Wang X J, Zhu Q, Li J G, Kim B N 2021 J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Zou J, Shi M M, Yang B B 2020 RSC Adv. 10 13076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yantake R, Kaiheriman M, Yusufu T, Sidike A 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 5123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sun H C, Zhu Q, Li J G 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 9640
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gao D L, Ma K W, Wang P, Zhang X Y, Pang Q, Xin H, Zhang Z H, Jiao H 2022 Dalton Trans. 51 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Maurya A, Bahadur A, Dwivedi A, Choudhary A K, Yadav T P, Vishwakarma P K, Rai S B 2018 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 119 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang X Y, Wang M Q, Ding J J, Gao D L, Shi Y H, Song X H 2012 CrystEngComm 14 8357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Du P, Sun X, Zhu Q, Li J G 2020 Scripta Mater. 185 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sang J K, Zhou J Y, Zhang J C, Zhou H, Li H H, Ci Z P, Peng S L, Wang Z F 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 20150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Luo F, Xing J H, Qin Y Y, Gao Z X, Shang F, Chen G H 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 34483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] do Carmo F F, do Nascimento J P, Facanha M X, Sales T O, Santos, W Q, Gouveia-Neto A S, Jacinto C, Sombra A S 2018 J. Lumin. 204 676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang J C, Pan C, Zhu Y F, Zhao L Z, He H W, Liu X F, Qiu J R 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1804644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sun L L, Wang B, Xing G C, Liang C, Ma W, Yang S C 2023 Chem. Eng. J. 455 140752
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li Y, Gecevicius M, Qiu J R 2016 Chem. Soc. Rev. 45 2090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liang L L, Chen J Y, Shao K, Qin X, Pan Z F, Liu X G 2023 Nat. Mater. 22 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 李辰琳, 赵习宇, 郭彤, 刘峰, 王笑军, 廖川, 张家骅 2022 71 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C L, Zhao X Y, Guo T, Liu F, Wang X J, Liao C, Zhang J H 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xiong P X, Peng M Y, Qin K X, Xu F F, Xu X Y 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 7 1901107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Feng L, Wang Z B, Cao C, Zhang T, Zhang J C, Ci Z P, Zhao Z Y, Wang Y H 2017 J. Rare Earth 35 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen Y F, Spinelli S, Gu Z J, Pan Z W 2022 Chem. Eng. J. 446 137473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang P F, Li N, Wei Z T, Wang Z Q, Gou M W, Zhao L, Chen W B, Qiang Q P 2021 New J. Chem. 45 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li L Y, Castaing V, Rytz D, Sontakke A D, Katayama Y, Tanabe S, Peng M Y, Viana B 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Jia Q N, Zhang Q W, Sun H Q, Li Y, Hao X H 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 873 159852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 梁爱华, 王旭升, 李国荣, 郑嘹赢, 江向平, 胡锐 2022 71 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang A H, Wang X S, Li G R, Zheng L Y, Jiang X P, Hu R 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gao D L, Gao J, Gao F, Kuang Q Q, Pan Y, Chen Y F, Pan Z W 2021 J. Mater. Chem. C 9 16634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Guo H J, Wang Y H, Chen W B, Zeng W, Han S C, Li G, Li Y Y 2015 J. Mater. Chem. C 3 11212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang C L, Jin Y H, Lü Y, Ju G F, Liu D, Chen L, Li Z Z, Hu Y H 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 6058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Fan X T, Xu X H, Yu X, Chen W B, Zhou D C, Qiu J B 2018 Mater. Res. Bull. 99 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wang Z B, Pei P X, Bai D J, Zhao S S, Ma X Y, Liu W S 2020 Inorg. Chem. Front. 7 2506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Pei P X, Wei R P, Wang B B, Su J X, Zhang Z C, Liu W S 2021 Adv. Funct. Mater. 31 2102479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5083
- PDF下载量: 70
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: