-
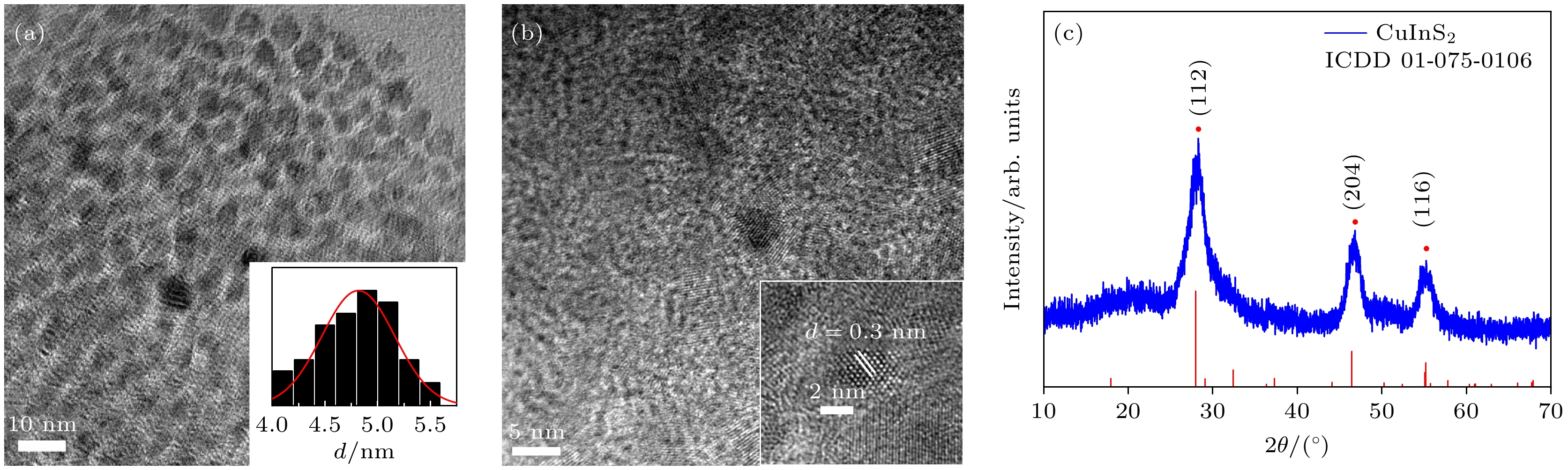
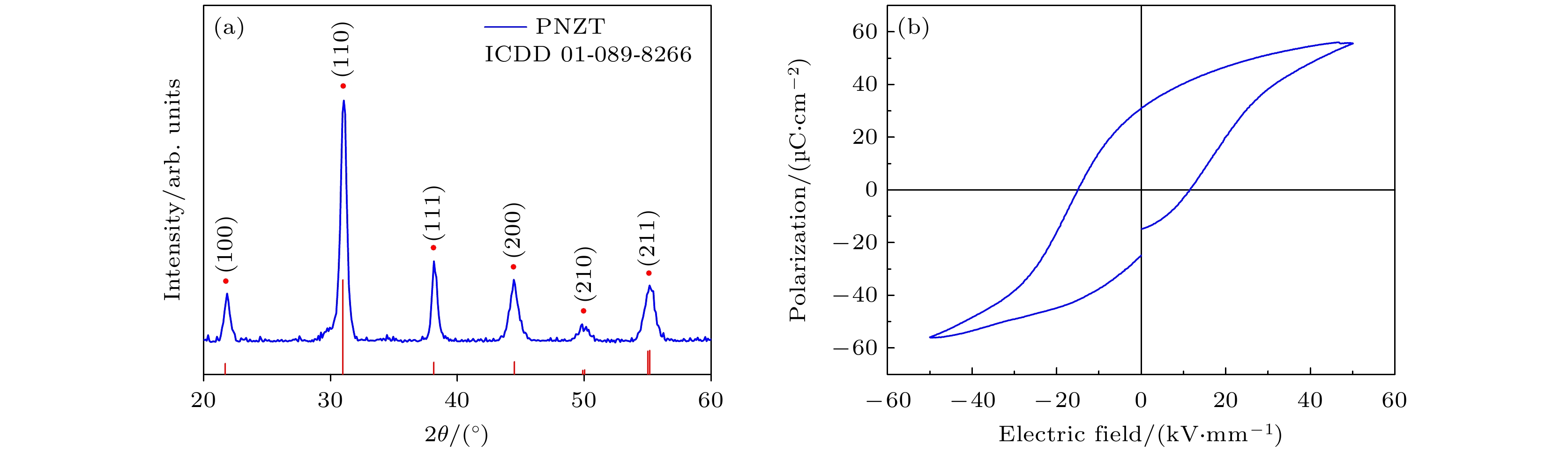
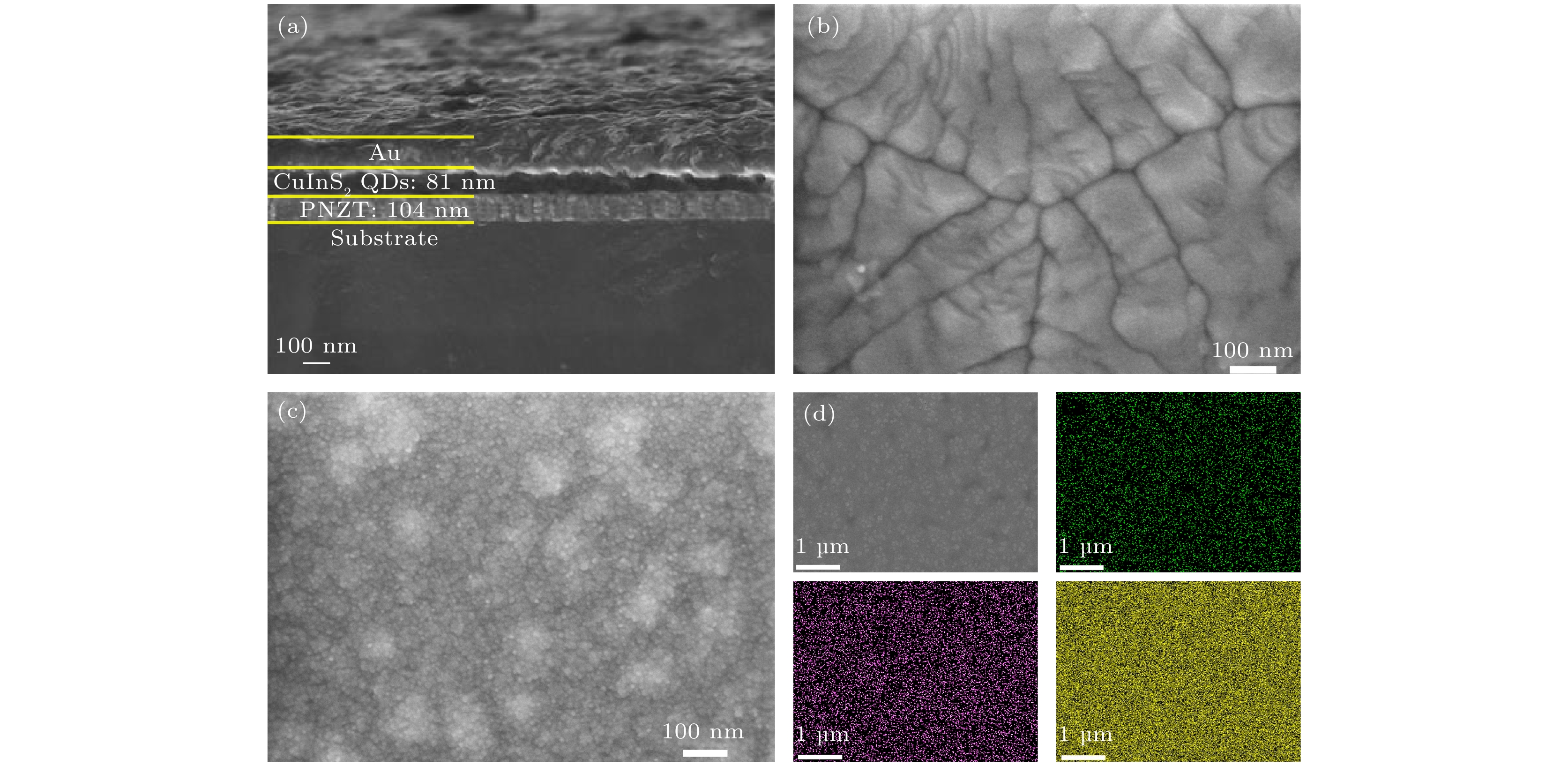
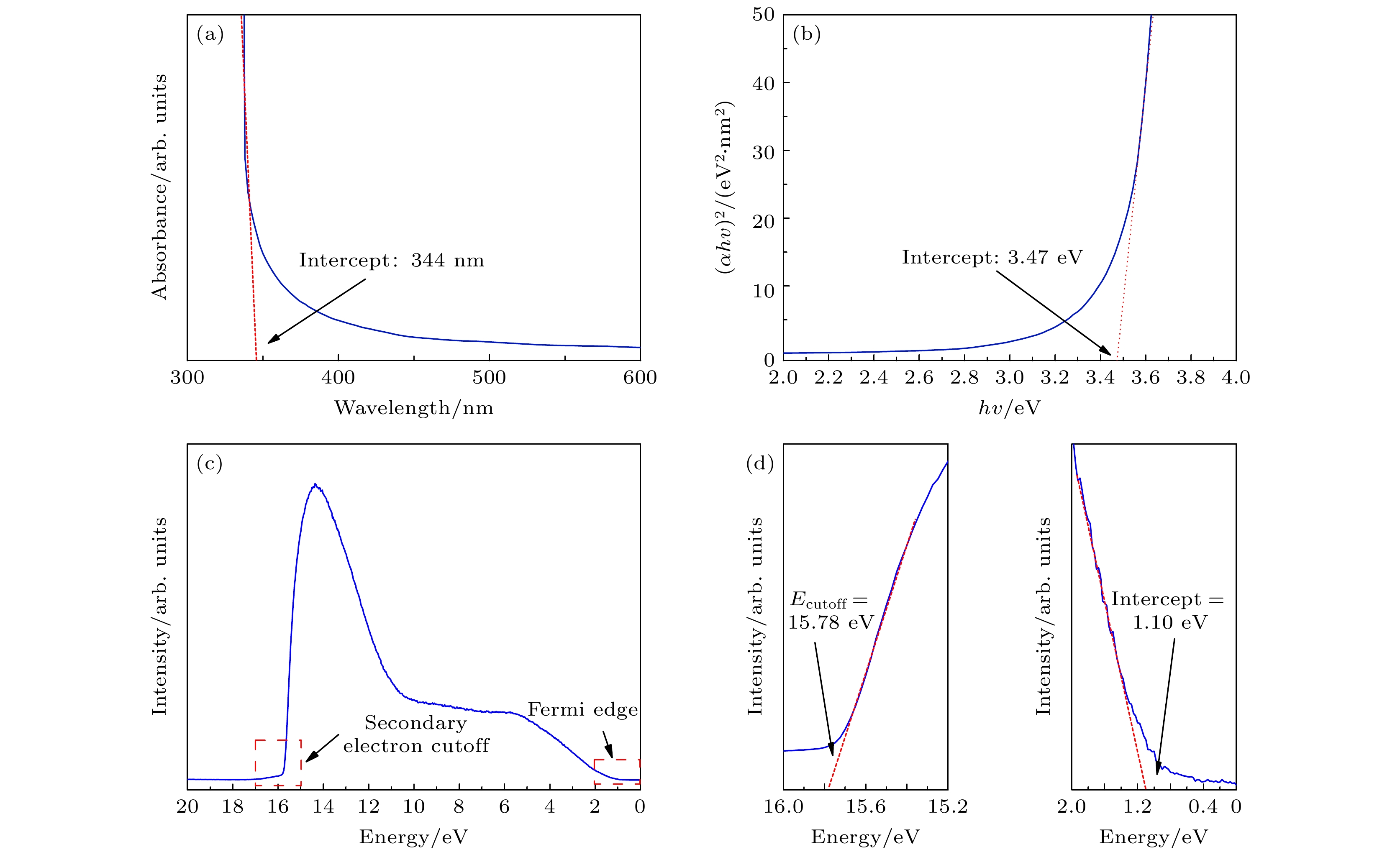
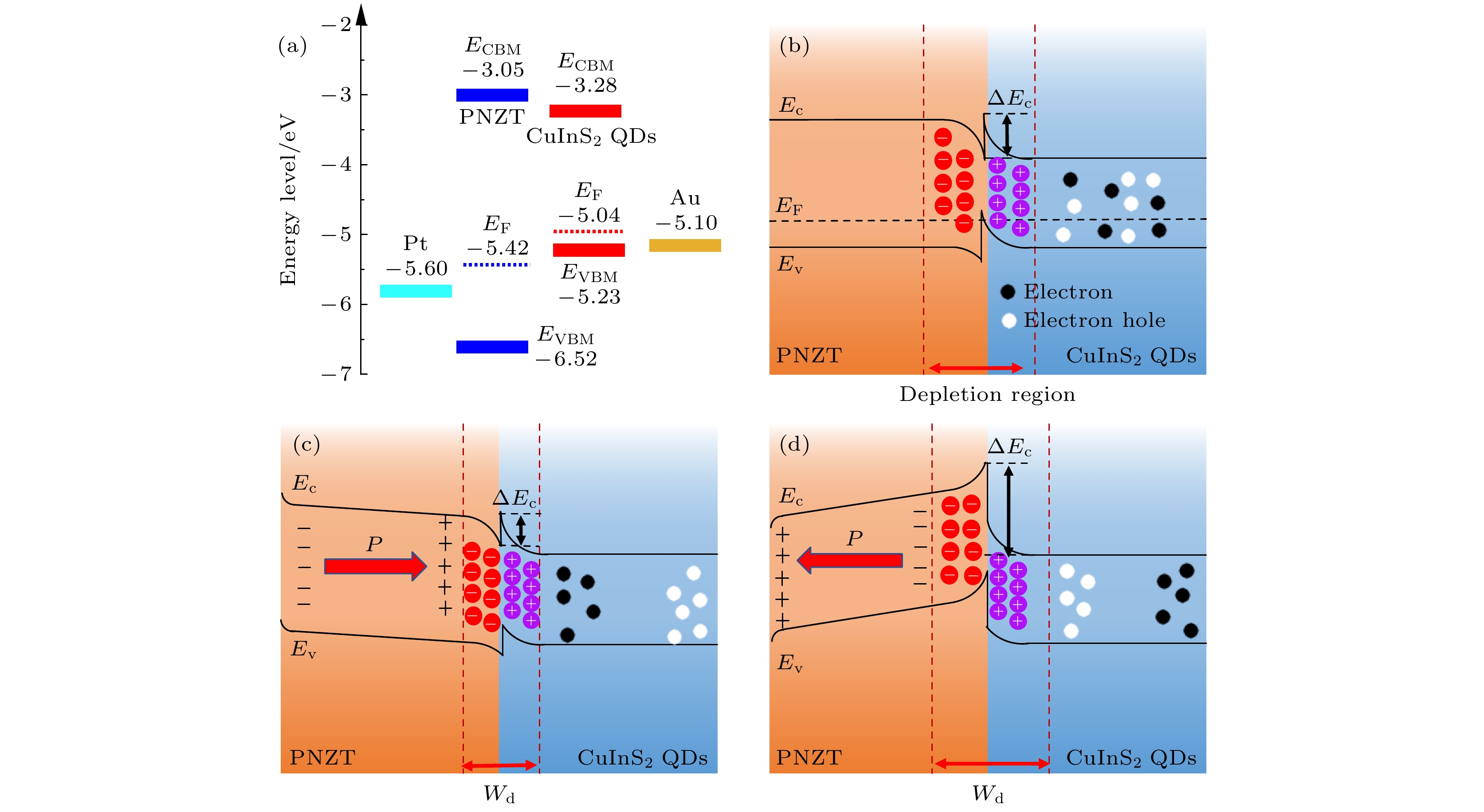
CuInS2量子点 (quantum dots, QDs)具有宽尺寸调节范围 (2—20 nm)、丰富的电子俘获位点、高光吸收系数、较高的载流子迁移率和制备工艺简单等优势, 可应用于下一代非易失性存储器, 但其开关电压(–4.5/4.5 V)和阻变开关比 (103)还达不到实际使用要求. 本文引入铌掺杂锆钛酸铅 (Nb:Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3, PNZT)制备CuInS2 QDs/PNZT复合薄膜, 发现PNZT的引入可以明显改善QDs的阻变性能, 开关电压降至–4.1/3.4 V, 阻变开关比提升至106, 在103次的循环耐久性测试中始终保持良好的稳定性. 切换PNZT薄膜的铁电极化方向可以改变CuInS2 QDs/PNZT复合薄膜界面势垒高度和耗尽区宽度, 以此调控CuInS2 QDs/PNZT复合薄膜的阻变性能.
-
关键词:
- CuInS2 量子点 /
- Nb:Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 /
- 阻变存储器 /
- 界面调控
As a new type of non-volatile memory, quantum dot resistive random access memory (RRAM) has attracted much attention for its easy preparation, fast responding time, high storage density, and smaller device size. CuInS2 quantum dot (CuInS2 QD) is a kind of excellent resistive functional material with abundant electron capture sites, high optical absorption coefficient, and high carrier mobility. In this work, CuInS2 QDs/Nb:Pb (Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 (PNZT) films are prepared by spin-coating CuInS2 QDs on PNZT films. The results show that the resistive properties of CuInS2 QDs RRAMs can be effectively improved by introducing PNZT films and can be controlled by changing the polarization direction. The CuInS2 QDs/PNZT film in the negative polarization state promotes the interfacial electrons to enter into the PNZT film, which will reduce the height of the interfacial barrier and the thickness of the interfacial depletion region. And it will reduce the resistance of the composite film at the low resistance state (LRS). Compared with the switching voltage and resistive switching ratio of the pure CuInS2 QDs film (103), the switching voltage of the device decreases to –4.1/3.4 V and the resistive switching ratio increases to 106. Furthermore, it maintains good stability in the 103 cycle durability test. In contrast, the CuInS2 QDs/PNZT film interface has a larger barrier height and depletion-layer thickness when the PNZT is in the positive polarization state, which increases the resistance of the composite film in the LRS state. As a result, the switching voltage of the device increases to –6.4/5.7 V with a resistive switching ratio of 104. The resistive properties of the CuInS2 QDs/PNZT film can be tuned by changing the polarization direction, as the polarization direction of the PNZT changes the interfacial energy band structure and affects the conduction mechanism. This work reveals the feasibility of using ferroelectric thin films to improve the resistive properties of quantum dots RRAMs and thus providing an approach to further developing RRAMs.-
Keywords:
- CuInS2 quantum dots /
- Nb:Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 /
- resistive random access memory /
- interface regulation
[1] Wang Z J, Bai Y 2019 Small 15 1805088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 曾凡菊, 谭永前, 唐孝生, 张小梅, 尹海峰 2021 70 157301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng F J, Tan Y Q, Tang X S, Zhang X M, Yin H F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 157301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lü Z Y, Wang Y, Chen J G, Wang J J, Zhou Y, Han S T 2020 Chem. Rev. 120 3941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yan X B, Pei Y F, Chen H W, et al. 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1805284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Han S T, Hu L, Wang X, Zhou Y, Zeng Y J, Ruan S, Pan C, Peng Z 2017 Adv. Sci. 4 1600435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kim T W, Yang Y, Li F, Kwan W L 2012 NPG Asia Mater. 4 e18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Y, Lü Z, Chen J, Wang Z, Zhou Y, Zhou L, Chen X, Han S T 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1802883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Thomas A, Resmi A, Ganguly A, Jinesh K 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 12450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chen Z, He L, Zhang F, Jiang J, Meng J, Zhao B, Jiang A 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 184106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 贾林楠, 黄安平, 郑晓虎, 肖志松, 王玫 2012 21 217306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia L N, Huang A P, Zheng X H, Xiao Z S, Wang Z 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 21 217306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fan Z, Fan H, Yang L, Li P, Lu Z, Tian G, Huang Z, Li Z, Yao J, Luo Q 2017 J. Mater. Chem. C 5 7317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Peng Z, Liu Y, Chen K, Yang G, Chen W 2014 Chem. Eng. J. 244 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang M, Jing Y, Zhang J, Sheng Z, Hou Y, Xu J, Chen B, Liu J, Wang M, Hou X 2022 Interdiscip. Mater. 1 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 高小钦, 卓宁泽, 王海波, 崔一平, 张家雨 2015 64 137801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao X Q, Zhuo N Z, Wang H B, Cui Y P, Zhang J Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 137801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu L, Li H, Liu Z, Xie Y H 2018 Mater. Des. 149 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang H, Yan X 2019 Phys. Status Solidi-Rapid Res. Lett. 13 1900073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lee Y C, Tsai C C, Liou Y C, Hong C S, Chu S Y 2021 ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 10 063010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Onlaor K, Thiwawong T, Tunhoo B 2014 Org. Electron. 15 1254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma Z, Wu C, Lee D U, Li F, Kim T W 2016 Org. Electron. 28 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang X G, Pantelides S T 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 266602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Feng Y, Lin S, Huang S, Shrestha S, Conibeer G 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 125701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Durruthy-Rodríguez M, Gervacio-Arciniega J, Hernández-García M, Yáñez-Limón J 2018 J. Adv. Ceram. 7 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 邵雅洁, 沈杰, 龚少康, 陈文, 周静 2020 无机化学学报 36 2093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao Y J, Shen J, Gong S K, Chen W, Zhou J 2020 Inorg. Chim. Acta. 36 2093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Adamu B I, Falak A, Tian Y, Tan X, Meng X, Chen P, Wang H, Chu W 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 8411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 郝国强, 张瑞, 张文静, 陈娜, 叶晓军, 李红波 2022 71 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao G Q, Zhang R, Zhang W J, Chen N, Ye X J, Li H B 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
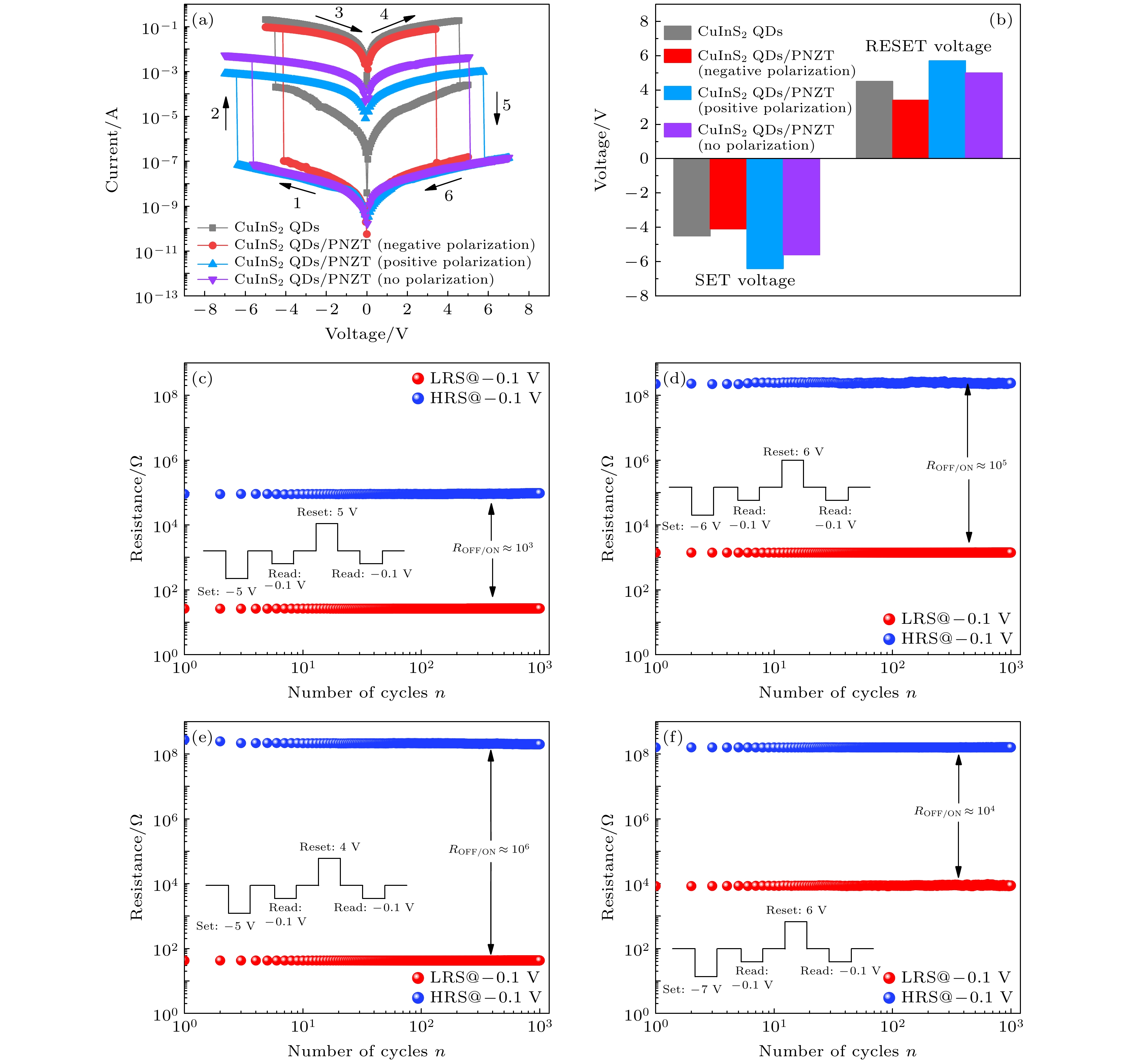
图 5 CuInS2 QDs RRAM与正负向和无极化下CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM的 (a) I-V曲线与 (b) 开关电压直方图; (c) CuInS2 QDs RRAM循环稳定性测试; (d) 无极化, (e) 负向极化和 (f) 正向极化的CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM循环稳定性测试(插图为施加的脉冲电压)
Fig. 5. (a) I-V curves and (b) SET/RESET voltage histograms of CuInS2 QDs RRAM and CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM with the different polarization orientations; (c) cycling stability test of CuInS2 QDs RRAM; cycling stability test of (d) no polarized, (e) negative polarized and (f) positive polarized CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM (Inset is the applied pulse voltage).
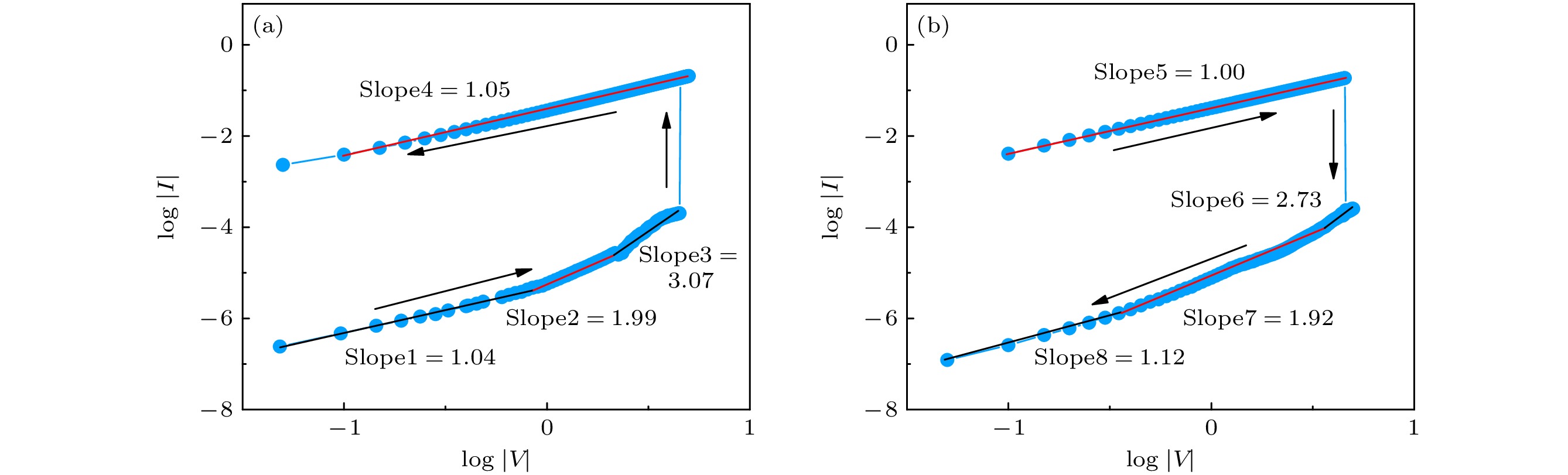
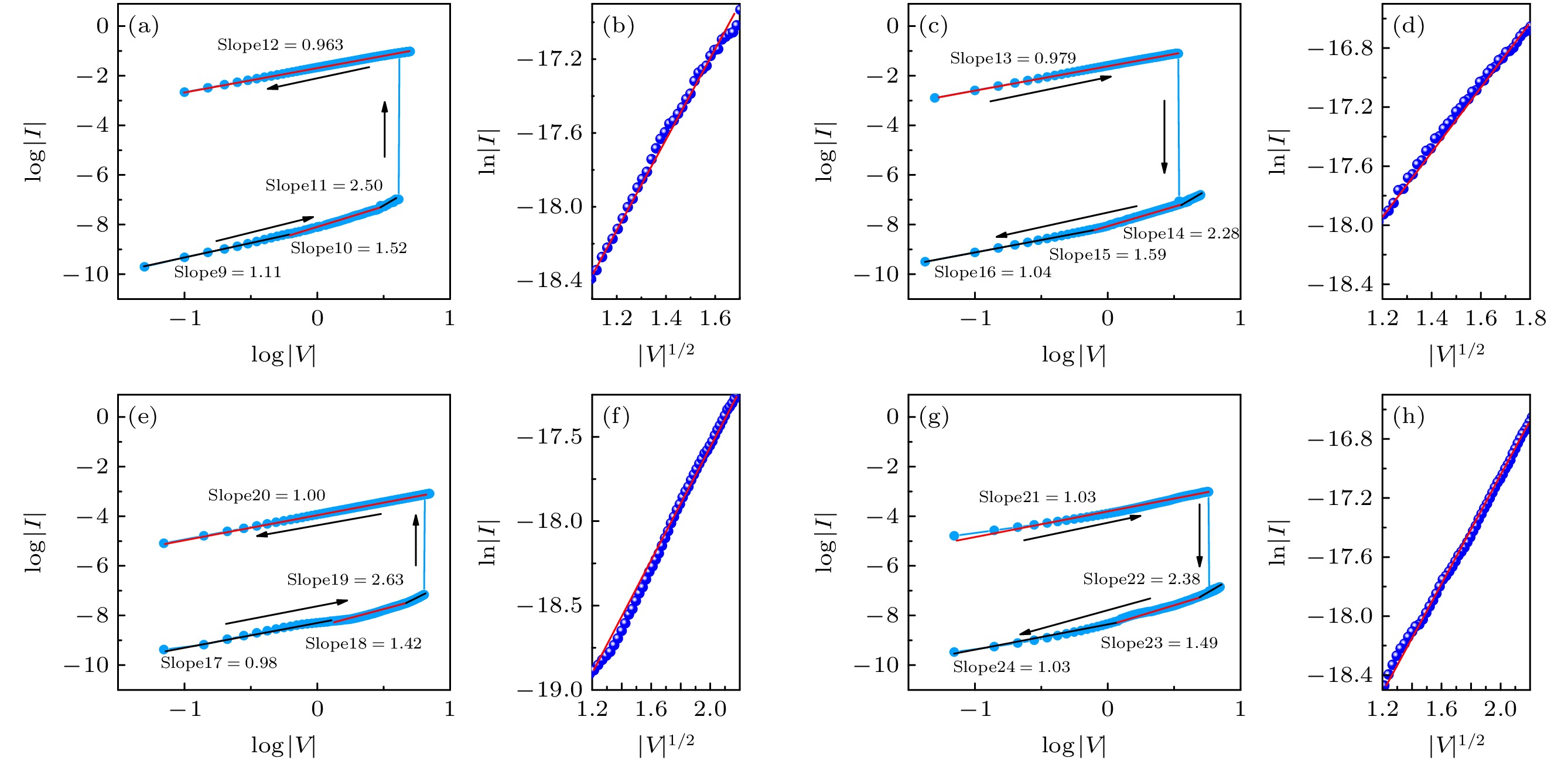
图 7 负向极化下CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM (a) 设置过程及(b) Slope10阶段的拟合曲线, (c) 复位过程及(d) Slope15阶段的拟合曲线; 正向极化下CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM (e) 设置过程及(f) Slope18阶段的拟合曲线, (g) 复位过程及(h) Slope23阶段的拟合曲线
Fig. 7. Fitting curves of CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM under negative polarization in (a) set process and (b) Slope10 stage, (c) reset process and (d) Slope15 stage; fitting curves of CuInS2 QDs/PNZT RRAM under positive polarization in (e) set process and (f) Slope18 stage, (g) reset process and (h) Slope23 stage.
表 1 不同器件的阻变性能
Table 1. Resistance switching performance of the different devices.
测试单元 工作电
压/V阻变开
关比CuInS2 QDs RRAM –4.5/4.5 3.4×103 无极化PNZT/CuInS2 QDs RRAM –5.6/5.0 1.7×105 正向极化PNZT/CuInS2 QDs RRAM –6.4/5.7 1.8×104 负向极化PNZT/CuInS2 QDs RRAM –4.1/3.4 4.8×106 -
[1] Wang Z J, Bai Y 2019 Small 15 1805088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 曾凡菊, 谭永前, 唐孝生, 张小梅, 尹海峰 2021 70 157301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng F J, Tan Y Q, Tang X S, Zhang X M, Yin H F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 157301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lü Z Y, Wang Y, Chen J G, Wang J J, Zhou Y, Han S T 2020 Chem. Rev. 120 3941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yan X B, Pei Y F, Chen H W, et al. 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1805284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Han S T, Hu L, Wang X, Zhou Y, Zeng Y J, Ruan S, Pan C, Peng Z 2017 Adv. Sci. 4 1600435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kim T W, Yang Y, Li F, Kwan W L 2012 NPG Asia Mater. 4 e18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Y, Lü Z, Chen J, Wang Z, Zhou Y, Zhou L, Chen X, Han S T 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1802883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Thomas A, Resmi A, Ganguly A, Jinesh K 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 12450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chen Z, He L, Zhang F, Jiang J, Meng J, Zhao B, Jiang A 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 184106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 贾林楠, 黄安平, 郑晓虎, 肖志松, 王玫 2012 21 217306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia L N, Huang A P, Zheng X H, Xiao Z S, Wang Z 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 21 217306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fan Z, Fan H, Yang L, Li P, Lu Z, Tian G, Huang Z, Li Z, Yao J, Luo Q 2017 J. Mater. Chem. C 5 7317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Peng Z, Liu Y, Chen K, Yang G, Chen W 2014 Chem. Eng. J. 244 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang M, Jing Y, Zhang J, Sheng Z, Hou Y, Xu J, Chen B, Liu J, Wang M, Hou X 2022 Interdiscip. Mater. 1 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 高小钦, 卓宁泽, 王海波, 崔一平, 张家雨 2015 64 137801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao X Q, Zhuo N Z, Wang H B, Cui Y P, Zhang J Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 137801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu L, Li H, Liu Z, Xie Y H 2018 Mater. Des. 149 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang H, Yan X 2019 Phys. Status Solidi-Rapid Res. Lett. 13 1900073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lee Y C, Tsai C C, Liou Y C, Hong C S, Chu S Y 2021 ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 10 063010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Onlaor K, Thiwawong T, Tunhoo B 2014 Org. Electron. 15 1254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma Z, Wu C, Lee D U, Li F, Kim T W 2016 Org. Electron. 28 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang X G, Pantelides S T 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 266602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Feng Y, Lin S, Huang S, Shrestha S, Conibeer G 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 125701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Durruthy-Rodríguez M, Gervacio-Arciniega J, Hernández-García M, Yáñez-Limón J 2018 J. Adv. Ceram. 7 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 邵雅洁, 沈杰, 龚少康, 陈文, 周静 2020 无机化学学报 36 2093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao Y J, Shen J, Gong S K, Chen W, Zhou J 2020 Inorg. Chim. Acta. 36 2093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Adamu B I, Falak A, Tian Y, Tan X, Meng X, Chen P, Wang H, Chu W 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 8411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 郝国强, 张瑞, 张文静, 陈娜, 叶晓军, 李红波 2022 71 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao G Q, Zhang R, Zhang W J, Chen N, Ye X J, Li H B 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5511
- PDF下载量: 71
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: