-
针对软物质的激光微纳加工技术, 通过激光辅助机械注射和可控自组装来实现装配软物质微滴球体结构的目的, 相较于传统的液滴微流控技术具有显著的优势. 本文研究了激光能量、光束尺寸、曝光位置等激光参数对激光辅助机械注射的影响, 得到了最佳的激光参数条件范围, 发现过高的激光强度(如0.365 mW)可诱发液晶材料的对流而不注入子液滴. 研究了表面活性剂浓度、液晶种类和相态等材料因素对注射机械力, 以及注入子液滴尺寸的影响. 证实表面活性剂浓度影响的实质是不同的离子浓度会改变相同升温条件下所形成的界面张力梯度值(注射机械力提高3.1倍); 发现液晶的相态对激光注射没有影响, 而液晶的种类会改变注入难度(弹性常数K值越高越难注入). 此外, 引入液晶微滴的拓扑相错线作为子液滴的自组装模板, 分析了注入子液滴在拓扑相错线上的自组装动力学过程. 软物质激光微纳加工技术可应用于光电子、生物医药等领域的三维球体结构的极端加工与应用开发.Laser micro/nanomachining technology for soft matter achieves the purpose of fabricating the spherical structures of soft matter by combing laser-assisted mechanical injection and controllable self-assembly, which has significant advantages in comparison with conventional methods like droplet microfluidics. In this study, the effects of laser parameters such as laser energy, beam size, and irradiation position on the injection are investigated. It is found that there also exists one upper limit of the laser energy, and if the laser irradiation is too strong, it can introduce a convection flow of liquid crystal rather than trigger off the injection of guest microdroplets. Thus, the laser injection can be achieved in a specific energy range of the laser irradiation. By manipulating the laser beam with a smaller size, the guest water microdroplets can be injected at the preselected location on the surface of a host liquid crystal droplet. In addition, the influences of material parameters such as the surfactant concentration, the material type and phase state of liquid crystal on the laser-assisted mechanical injection, and the size of the injected guest droplet are investigated. It is found that the liquid crystal droplet with higher surfactant concentration requires less energy from the laser irradiation to generate enough mechanical force to trigger off the injection. Because under the same temperature increment, the liquid crystal droplet with higher ion concentration enjoys a stronger surface tension gradient. By comparing several different types of liquid crystals, it is found the injection of guest droplets into a host with a higher elastic constant liquid crystal can be more difficult. The influences of the material type of liquid crystal and the concentration of surfactant on the critical size of guest microdroplets are summarized. Finally, the defect lines of liquid crystal are introduced as the self-assembly template, through which microdroplets of liquid crystal with the sophisticated spherical structure are fabricated. The self-assembly kinetic behaviors of guest droplets in the defect line are analyzed. The laser micro/nanomachining technology of soft matter can be applied to the extreme processing and application development of 3D spherical structures in the fields of optoelectronics, photonics, and biomedicine.
-
Keywords:
- laser micro/nanomachining /
- laser injection /
- soft matter /
- liquid crystal
[1] Ouyang Z C 2009 Encyclopedia of China (Vol. 74) (Encyclopedia of China Publishing House) p389 (in Chinese) [欧阳钟灿 2009 中国大百科全书 (第74卷) (中国大百科全书出版社) 第389页
[2] Lin P, Chen H, Li A, Zhuang H, Chen Z, Xie Y, Zhou H, Mo S, Chen Y, Lu X, Cheng Z 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 46788
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lin P, Yan Q, Wei Z, Chen Y, Chen S, Wang H, Huang Z, Wang X, Cheng Z 2018 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10 18289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lee S S, Kim S K, Won J C, Kim Y H, Kim S H 2015 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 54 15266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Park S, Lee S S, Kim S H 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 2002166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lee S S, Kim J B, Kim Y H, Kim S H 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaat8276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Che K J, Yang Y J, Lin Y L, Shan Y W, Ge Y H, Li S S, Chen L J, Yang C J 2019 Lab. Chip. 19 3116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 王磊, 肖芮文, 葛士军, 沈志雄, 吕鹏, 胡伟, 陆延青 2019 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L, Xiao R W, Ge S J, Shen Z X, Lu P, Hu W, Lu Y Q 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王志鹏, 张峰, 杨嘉炜, 李鹏涛, 关宝璐 2020 69 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z P, Zhang F, Yang J W, Li P T, Guan B L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shan Y W, You L Q, Bisoyi H K, Yang Y J, Ge Y H, Che K J, Li S S, Chen L J, Li Q 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 2000692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Schwartz M, Lenzini G, Geng Y, Ronne P B, Ryan P Y A, Lagerwall J P F 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 e1707382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Martino C, deMello A J 2016 Interface Focus 6 20160011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Iglesias W, Abbott N L, Mann E K, Jakli A 2012 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4 6884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yelleswarapu V, Buser J R, Haber M, Baron J, Inapuri E, Issadore D 2019 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 116 4489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kang Y, Yao Y P, Kang Z H, Ma L, Zhang T Y 2015 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 32 1063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim Y J, Park S Y 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 47342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang X L, Ju X J, Mu X T, Wang W, Xie R, Liu Z, Chu L Y 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 10524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Mahler L, Niehs S P, Martin K, Weber T, Scherlach K, Hertweck C, Roth M, Rosenbaum M A 2021 Elife 10 64774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dickinson E 2011 Food Biophys. 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Grigoriev D O, Miller R 2009 Curr. Opin. Colloid In 14 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lorber N, Sarrazin F, Guillot P, Panizza P, Colin A, Pavageau B, Hany C, Maestro P, Marre S, Delclos T 2011 Lab. Chip. 11 779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chu L Y, Utada A S, Shah R K, Kim J W, Weitz D A 2007 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 46 8970
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li Y, Khuu N, Prince E, Alizadehgiashi M, Galati E, Lavrentovich O D, Kumacheva E 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 eaav1035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo J K, Hong S H, Yoon H J, Babakhanova G, Lavrentovich O D, Song J K 2019 Adv. Sci. 6 1900785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yoshioka J, Fukao K 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 022702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yan X, Xu J, Meng Z, Xie J, Wang H, 2020 Small 16 e2001548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Verneuil E, Cordero M, Gallaire F, Baroud C N 2009 Langmuir. 25 5127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Poulin P, Stark H, Lubensky T C, Weitz D A 1997 Science 275 1770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Muševič I, Škarabot M, Tkalec U, Ravnik M, Žumer S 2006 Science 313 954
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Loudet J C, Barois P, Poulin P 2000 Nature 407 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guo J K, Song J K 2016 Opt. Express 24 7381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Guo J K, Vij J K, Song J K 2017 Adv. Opt. Mater. 5 1700119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yoshida H, Asakura K, Fukuda J, Ozaki M 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 7180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 激光光束参量对激光注射的影响 (a) 激光辅助机械注射在特定能量区间内可行; (b), (c) 超出最高能量的激光会诱发液晶发生流动; (d)—(g) 光束尺寸和曝光位置对激光注入的影响(标尺20 μm)
Fig. 2. The impact of parameters of laser beam on the laser injection: (a) Laser injection is feasible within a specific energy range; (b), (c) laser irradiation with the energy above the maximum range would induce the flow of liquid crystal; (d)–(g) the impact of beam size and irradiation location on the laser injection (Scale bars, 20 μm).
图 3 离子浓度对激光注射机械力的影响 (a) 水溶液中SDS浓度会影响激光注射所需的最低能量阈值; (b) 相同升温条件下, 更高的SDS浓度形成的界面张力梯度值更大, 进而形成更强的注射机械力; (c) 升温形成不同界面张力梯度的原因是溶液中离子浓度的差异
Fig. 3. The impact of ion concentration on the mechanical force of laser injection: (a) SDS concentration in water solution can change the minimum laser energy required to inject guest droplets; (b) it can generate higher interfacial tension gradient in a solution with higher SDS concentration under the same temperature increment, resulting a stronger mechanical force for injection; (c) the ionic concentration is the key factor to drive the difference in thermal induced interfacial tension gradient.
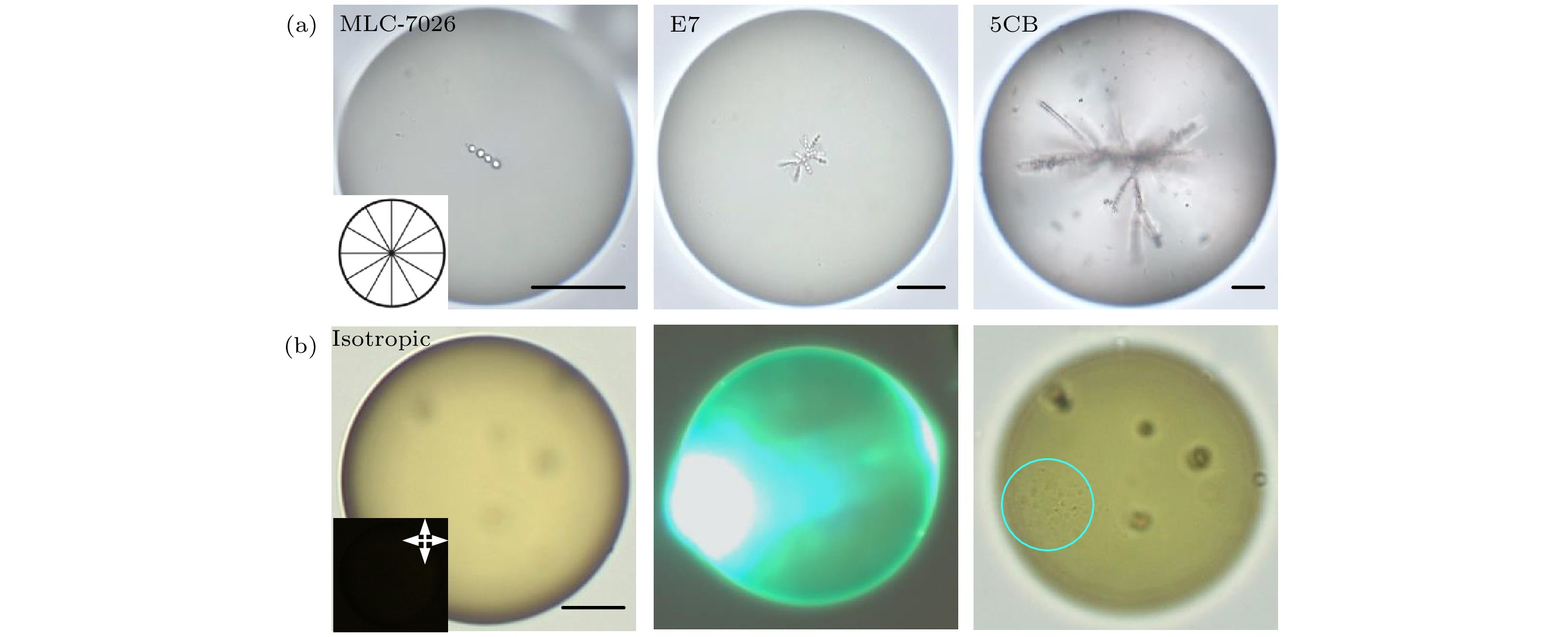
图 4 液晶种类和相态对激光注射的影响 (a) 液晶材料弹性系数K值越高, 注入难度越大; (b) 激光辅助机械注射针对各向同性的材料依然有效 (标尺20 μm)
Fig. 4. The impact of material type and phase state of liquid crystal on the laser injection: (a) It could be harder to inject guest droplets into a host liquid crystal droplet with higher elastic constant K; (b) the laser assisted mechanical injection remains effective for the processing of isotropic materials (Scale bars, 20 μm).
图 5 注入水溶液在液晶微滴内的自组装 (a)—(c) 被注入水溶液自发合并为均匀尺寸的子液滴, 并自组装为子液滴链; (d) 液晶介质中子液滴的偏振显微纹理图; (e) SDS浓度可以控制注入子液滴的尺寸(标尺10 μm)
Fig. 5. The self-assembly of injected water within the host liquid crystal droplet: (a)–(c) The injected water spontaneously merges into guest droplets with uniform size which subsequently self-assemble into droplet chains; (d) the cross-polarized microscopic texture of guest droplets in a liquid crystal medium; (e) the critical size of guest droplets can be tuned by varying the SDS concentration (Scale bars, 10 μm).
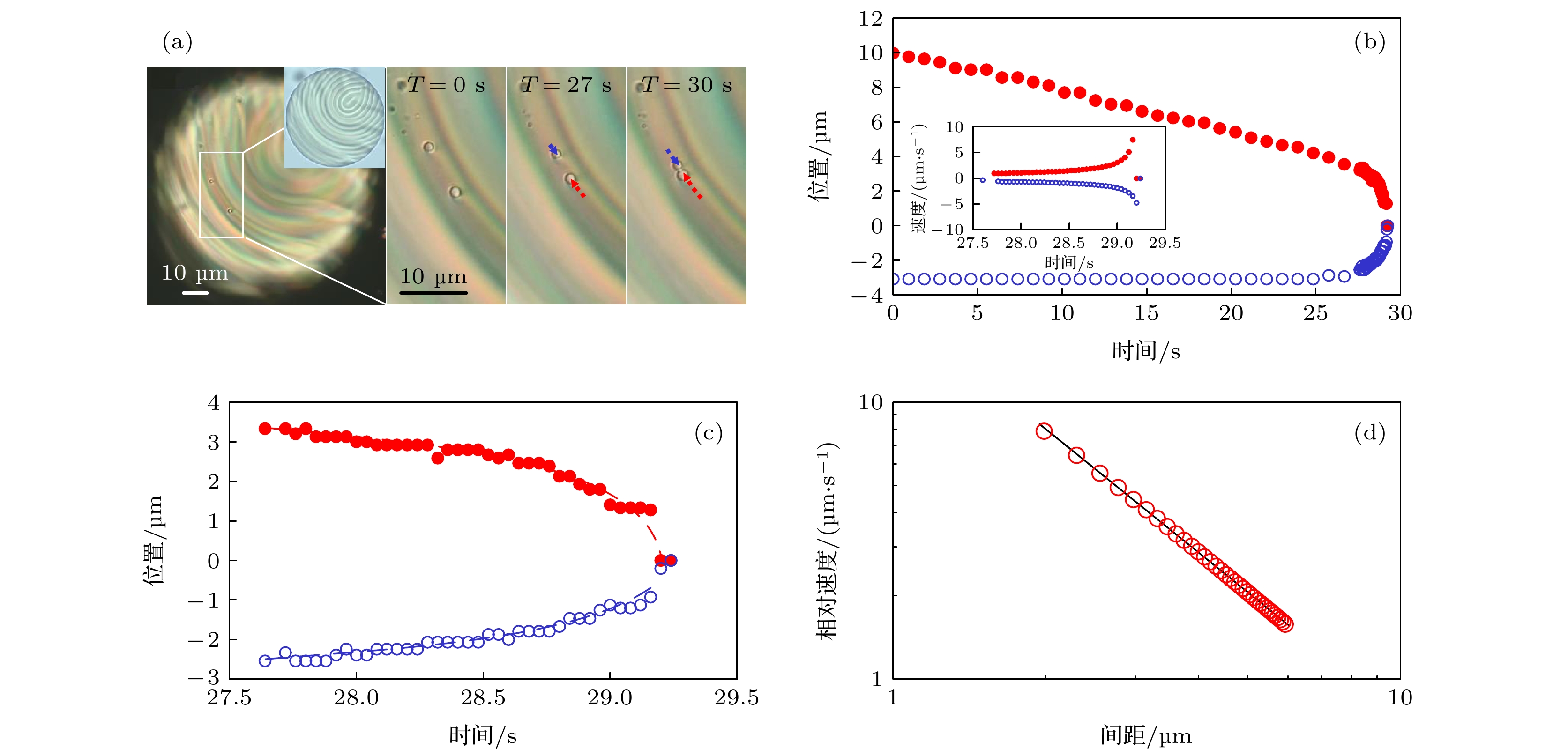
图 6 子液滴在相错线上的自组装动力学过程 (a)—(c)两个子液滴在相错线上相向运动, 最终组成一个液滴链; (d)两个子液滴的相对速度与间距服从幂律
Fig. 6. Self-assembly kinetics of guest droplet in the defect line: (a)–(c) Two guest droplets move in opposite direction in the defect line and eventually attach into a droplet chain; (d) their relative velocity and separation distance follow a power law dependence.
图 7 借助微滴内的拓扑相错线装配液晶微滴球体结构 (a)操控激光将子液滴注入液晶微滴内的拓扑相错线上; (b)注入的子液滴沿着相错线的几何结构排列
Fig. 7. Processing of microdroplet structure of liquid crystal with the help of the defect line: (a) Inject and load guest droplets in the topological defect line of a host liquid crystal microdroplet; (b) the injected guest droplets arrange along the geometric structure of the defect line.
-
[1] Ouyang Z C 2009 Encyclopedia of China (Vol. 74) (Encyclopedia of China Publishing House) p389 (in Chinese) [欧阳钟灿 2009 中国大百科全书 (第74卷) (中国大百科全书出版社) 第389页
[2] Lin P, Chen H, Li A, Zhuang H, Chen Z, Xie Y, Zhou H, Mo S, Chen Y, Lu X, Cheng Z 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 46788
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lin P, Yan Q, Wei Z, Chen Y, Chen S, Wang H, Huang Z, Wang X, Cheng Z 2018 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10 18289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lee S S, Kim S K, Won J C, Kim Y H, Kim S H 2015 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 54 15266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Park S, Lee S S, Kim S H 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 2002166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lee S S, Kim J B, Kim Y H, Kim S H 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaat8276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Che K J, Yang Y J, Lin Y L, Shan Y W, Ge Y H, Li S S, Chen L J, Yang C J 2019 Lab. Chip. 19 3116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 王磊, 肖芮文, 葛士军, 沈志雄, 吕鹏, 胡伟, 陆延青 2019 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L, Xiao R W, Ge S J, Shen Z X, Lu P, Hu W, Lu Y Q 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王志鹏, 张峰, 杨嘉炜, 李鹏涛, 关宝璐 2020 69 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z P, Zhang F, Yang J W, Li P T, Guan B L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shan Y W, You L Q, Bisoyi H K, Yang Y J, Ge Y H, Che K J, Li S S, Chen L J, Li Q 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 2000692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Schwartz M, Lenzini G, Geng Y, Ronne P B, Ryan P Y A, Lagerwall J P F 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 e1707382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Martino C, deMello A J 2016 Interface Focus 6 20160011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Iglesias W, Abbott N L, Mann E K, Jakli A 2012 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4 6884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yelleswarapu V, Buser J R, Haber M, Baron J, Inapuri E, Issadore D 2019 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 116 4489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kang Y, Yao Y P, Kang Z H, Ma L, Zhang T Y 2015 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 32 1063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim Y J, Park S Y 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 47342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang X L, Ju X J, Mu X T, Wang W, Xie R, Liu Z, Chu L Y 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 10524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Mahler L, Niehs S P, Martin K, Weber T, Scherlach K, Hertweck C, Roth M, Rosenbaum M A 2021 Elife 10 64774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dickinson E 2011 Food Biophys. 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Grigoriev D O, Miller R 2009 Curr. Opin. Colloid In 14 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lorber N, Sarrazin F, Guillot P, Panizza P, Colin A, Pavageau B, Hany C, Maestro P, Marre S, Delclos T 2011 Lab. Chip. 11 779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chu L Y, Utada A S, Shah R K, Kim J W, Weitz D A 2007 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 46 8970
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li Y, Khuu N, Prince E, Alizadehgiashi M, Galati E, Lavrentovich O D, Kumacheva E 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 eaav1035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo J K, Hong S H, Yoon H J, Babakhanova G, Lavrentovich O D, Song J K 2019 Adv. Sci. 6 1900785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yoshioka J, Fukao K 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 022702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yan X, Xu J, Meng Z, Xie J, Wang H, 2020 Small 16 e2001548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Verneuil E, Cordero M, Gallaire F, Baroud C N 2009 Langmuir. 25 5127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Poulin P, Stark H, Lubensky T C, Weitz D A 1997 Science 275 1770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Muševič I, Škarabot M, Tkalec U, Ravnik M, Žumer S 2006 Science 313 954
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Loudet J C, Barois P, Poulin P 2000 Nature 407 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guo J K, Song J K 2016 Opt. Express 24 7381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Guo J K, Vij J K, Song J K 2017 Adv. Opt. Mater. 5 1700119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yoshida H, Asakura K, Fukuda J, Ozaki M 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 7180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5601
- PDF下载量: 101
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: