-
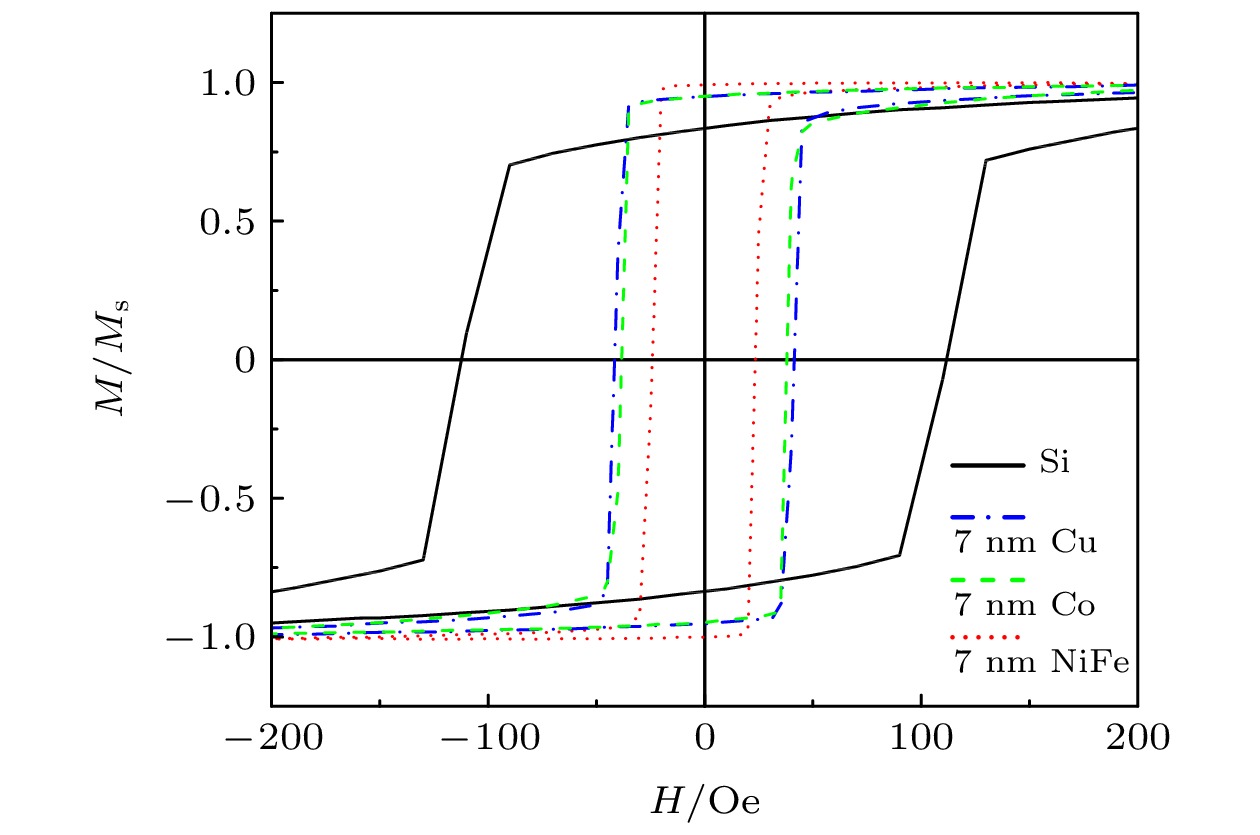
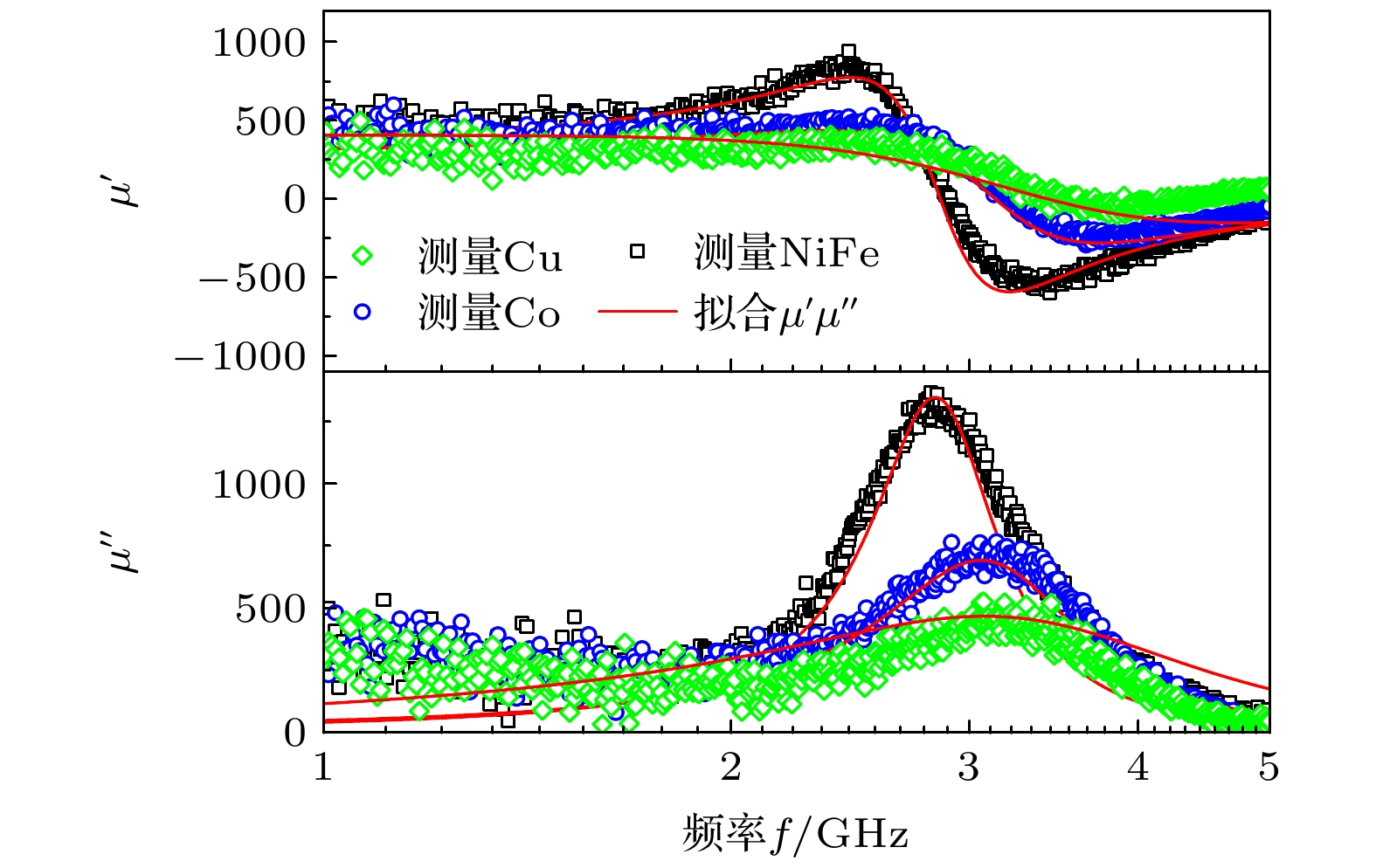
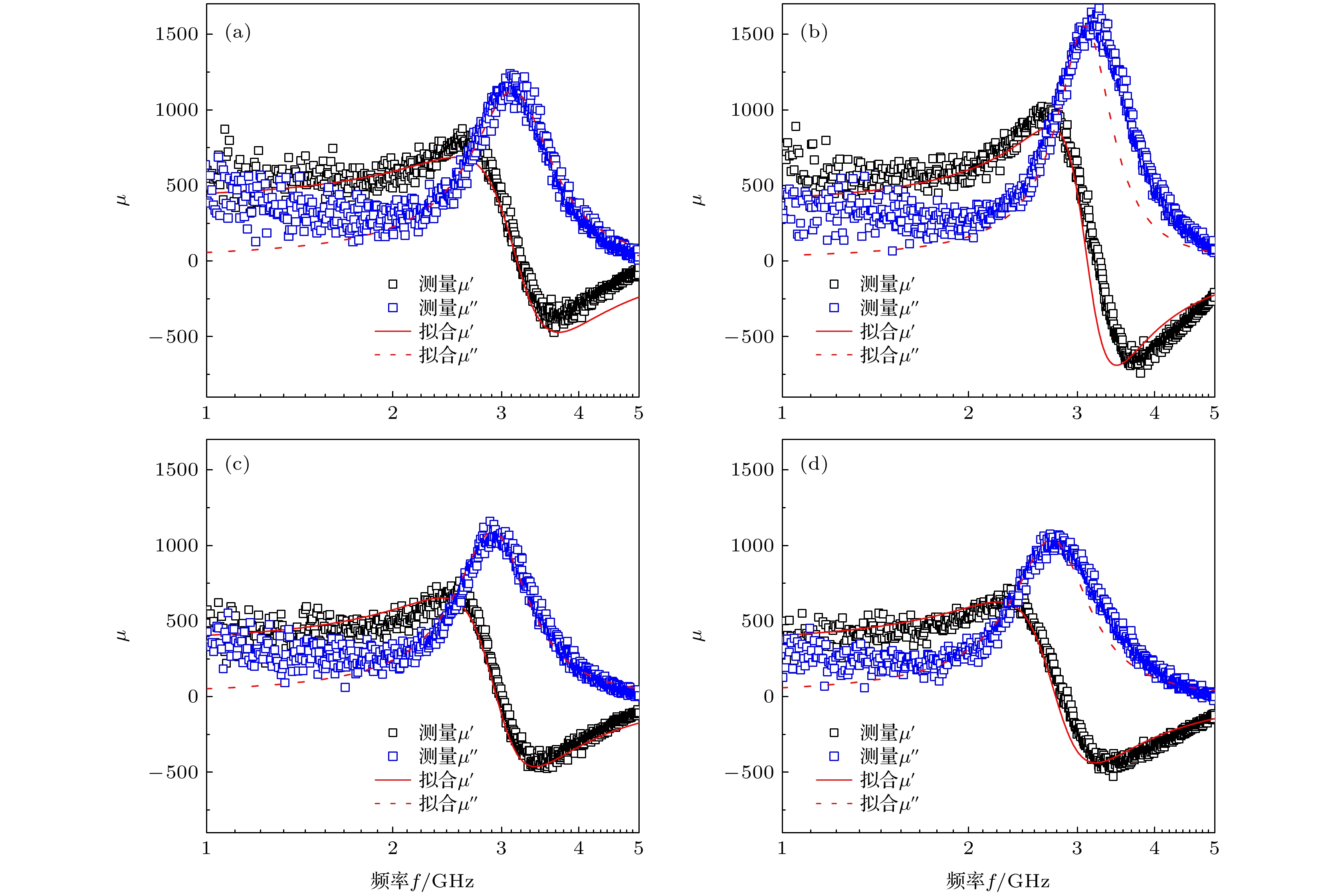
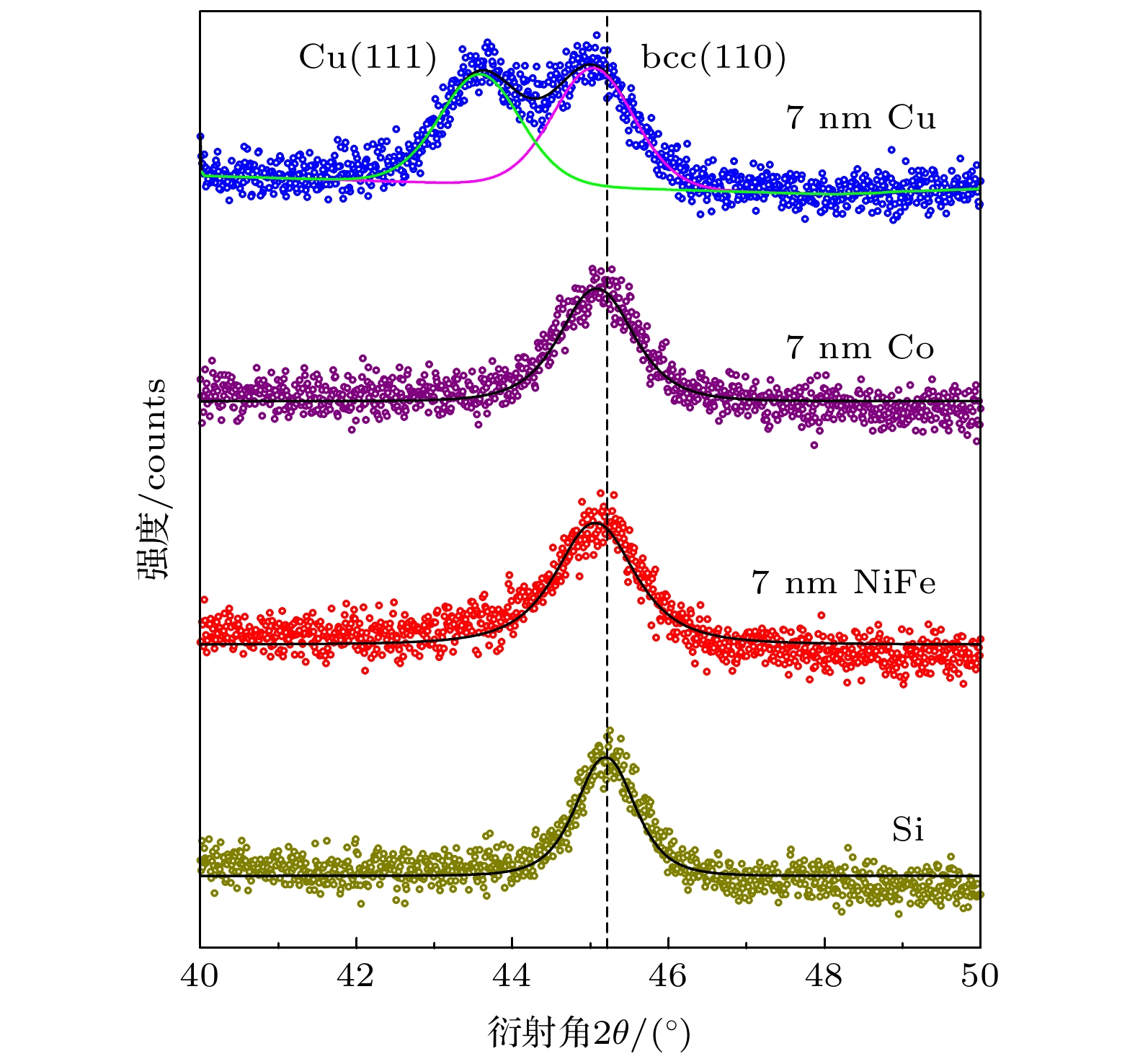
采用磁控溅射法制备了具有不同衬底层(Cu, Co和Ni80Fe20)的Fe65Co35双层合金薄膜. 研究了不同衬底材料以及NiFe衬底层厚度对FeCo合金薄膜结构与磁性的影响. 研究结果表明: 衬底层的引入可以增加薄膜的面内单轴各向异性, 且薄膜的软磁性能显著提升, 获得良好软磁性的原因归结为晶粒的细化、层间的偶极相互作用以及表面粗糙度的降低, 并且对于相同厚度的不同衬底层, NiFe衬底层对FeCo薄膜软磁性能的提升最为明显; 通过改变NiFe衬底层厚度, 实现了对薄膜各向异性的调控, NiFe/FeCo表现出良好的高频响应和低的阻尼系数, 同时较小的薄膜厚度能够减小涡流损耗, 因此, 促进了其在高频微波磁性器件方面的应用.Fe100-xCox (x = 30–40) alloys have the highest saturation magnetizations, 4πMs ≥ 24 kG (1 G = 10–4 T). Therefore, FeCo thin flms have been widely used in microwave magnetic devices. However, the as-deposited FeCo film has a large coercivity, which is attributed to the large saturation magnetostriction and high magneto-crystalline anisotropy. On the basis of maintaining high saturation magnetization, adding an appropriate underlayer is a simple and effective method to reduce the coercivity of the film and facilitate the magnetic field-induced in-plane uniaxial magnetic anisotropy. Since these kinds of films are used in a high-frequency environment, the eddy current loss in GHz band must be considered. For a certain film material, the thinner the film, the lower the eddy current loss is. However, at present, the thickness of ferromagnetic layer is generally tens of nanometers or even hundreds of nanometers, which will not help to suppress the eddy current loss at high frequency. In the present study, to obtain FeCo films with good soft magnetic properties and excellent high-frequency characteristics, Fe65Co35 alloy films with a thickness of 13 nm and different underlayers (Cu, Co and Ni80Fe20) are prepared by magnetron sputtering. The effects of different underlayer materials and different NiFe underlayer thickness values on the structures and magnetic properties of FeCo films are studied. The results show that the introduction of underlayers can increase the in-plane uniaxial magnetic anisotropies of films, and the soft magnetic properties of films are significantly improved. The reason why the good soft magnetic properties can be achieved is attributed to the grain refinement, the dipolar interaction between layers, and the reduction of surface roughness. For different underlayer materials with the same thickness, NiFe underlayer can obviously improve the soft magnetic properties of FeCo films: the covercivity of easy axis is 23 Oe. By changing the thickness of NiFe underlayer, the dynamic magnetic properties of films can be adjusted. The resonance frequency changes from 3.13 GHz for NiFe(1 nm)/FeCo(13 nm) film to 2.78 GHz for NiFe(9.3 nm)/ FeCo(13 nm) film. For all NiFe/FeCo bilayer films, the real part of the permeability μ′ at low frequency has a large value of 350–450, and the damping coefficient α shows a small value of 0.01–0.02. In addition, the smaller film thickness can reduce eddy current loss, which contributes to its application in high-frequency microwave magnetic devices.
-
Keywords:
- FeCo alloy films /
- underlayers /
- soft magnetic properties /
- high-frequency characteristics
[1] Li T Y, Liu X Y, Li J W, Pan L N, He A N, Dong Y Q 2022 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 547 168777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cronin D, Lordan D, Wei G, McCloskey P, Mathúna C O, Masood A 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 243903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tang X L, Yu Y, Su H, Zhang H W, Zhong Z Y, Jing Y L 2018 J. Mater. Sci. 53 3573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chai G, Phuoc N N, Ong C K 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Masood A, McCloskey P, Mathúna C Ó, Kulkarni S 2017 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 903 012050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kurlyandskaya G V, Shcherbinin S V, Volchkov S O, Bhagat S M, Calle E, Pérez R, Vazquez M 2018 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 459 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zheng F, Ma Z, Gao H, Pan F C, Li S T, Cao J W, Bai J M, Wei F L 2017 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28 17448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang F J, Min J J, Hui J H, Chen H B, Degao L, Li W J, Chen X Q, Yang C P 2017 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28 11733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Baco S, Abbas Q A, Hayward T J, Morley N A 2021 J. Alloy. Compd. 881 160549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Cabral L, Aragon F H, Villegas-Lelovsky L, Lima M P, Macedo W A A, Da Silva J L F 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11 1529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Vopsaroiu M, Georgieva M, Grundy P J, Fernandez G V, Manzoor S, Thwaites M J, O’Grady K 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 10N303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vas’ko V A, Rantschler J O, Kief M T 2004 IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 2335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xi L, Du J H, Zhou J J, Ma J H, Li X Y, Wang Z, Zuo Y L, Xue D S 2012 Thin Solid Films 520 5421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王璇, 郑富, 卢佳, 白建民, 王颖, 魏福林 2011 60 017505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Zheng F, Lu J, Bai J M, Wang Y, Wei F L 2011 Acta. Phys. Sin. 60 017505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X, Zheng F, Liu Z Y, Liu X X, Wei D, Wei F L 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 105 07B714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wu Y P, Yang Y, Yang Z H, Ma F S, Zong B Y, Ding J 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 093905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xu F, Liao Z Q, Huang Q J, Ong C K, Li S D 2011 IEEE Trans. Magn. 47 3921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Acosta A, Fitzell K, Schneider J D, Dong C Z, Yao Z, Wang Y E, Carman G P, Sun N X, Chang J P 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 222404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Acosta A, Fitzell K, Schneider J D, Dong C Z, Yao Z, Sheil R, Wang Y E, Carman G P, Sun N X, Chang J P 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 128 013903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fu Y, Miyao T, Cao J W, Yang Z, Matsumoto M, Liu X X, Morisako A 2007 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Y B, Li Z H, Liu X, Fu Y, Wei F L, Kamzin A S, Wei D 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 09A325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sun N X, Wang S X 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 92 1477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shimatsu T, Katada H, Watanabe I, Muraoka H, Nakamura Y 2003 IEEE Trans. Magn. 39 2365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Langford J I, Wilson A J C 1978 J. Appl. Cryst. 11 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Scherrer P 1918 Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26 98
[26] Herzer G 1990 IEEE Trans. Magn. 26 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jiang H, Chen Y J, Chen L F, Huai Y M 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 91 6821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Inturi V R, Barnard J A 1996 J. Appl. Phys. 79 5904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu X X, Kanda H, Morisako A 2011 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 266 012037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Jung H S, Doyle W D, Wittig J E, Al-Sharab J F, Bentley J 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 2415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] O'Grady K, Laidler H 1999 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200 616
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wohlfarth E P 1958 J. Appl. Phys. 29 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Henkel O 1964 Phys. Stat. Sol. 7 919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Gilbert T L 2004 IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 3443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Ge S H, Yao D S, Yamaguchi M, Yang X L, Zuo H P, Ishii T, Zhou D, Li F 2007 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40 3660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Kuanr B K, Camley R E, Celinski Z 2005 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 286 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Ben Youssef J, Vukadinovic N, Billet D, Labrune M 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 174402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Wu Y P, Han G C, Kong L B 2010 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322 3223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Zhong X X, Soh W T, Phuoc N N, Liu Y, Ong C K 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 013906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Fu Y, Cheng X F, Yang Z 2006 Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 203 963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Phuoca N N, Hungb L T, Ongb C K 2011 J. Alloy. Compd. 509 4010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 10 (a) NiFe/FeCo薄膜的各向异性场和共振频率与NiFe衬底层厚度的关系; (b) NiFe/FeCo薄膜的阻尼系数和频率线宽与NiFe衬底层厚度的关系
Fig. 10. (a) Dependence of anisotropic field and resonance frequency of NiFe/FeCo films on thickness of NiFe underlayers; (b) dependence of damping coefficient and frequency linewidth of NiFe/FeCo films on thickness of NiFe underlayers.
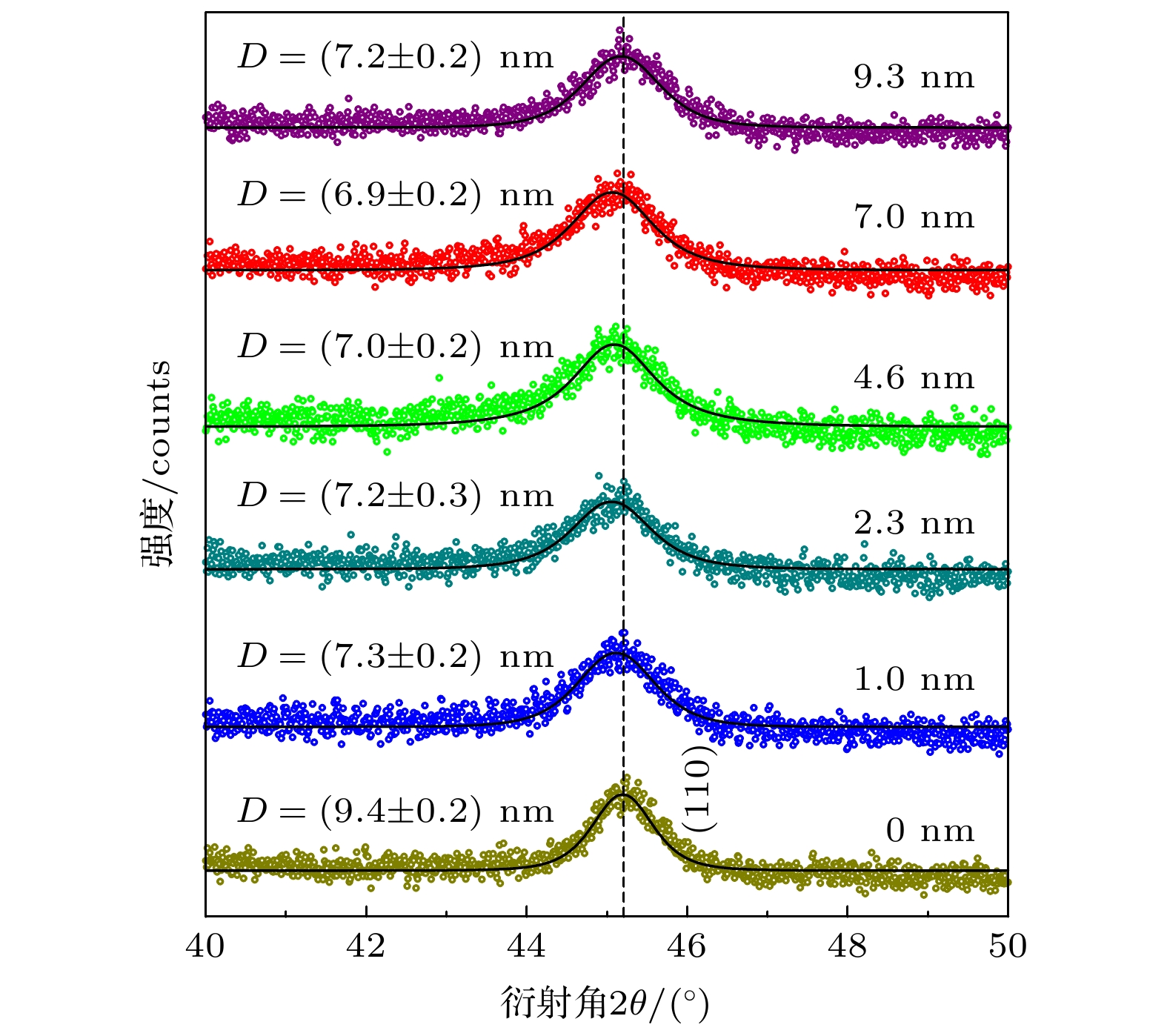
表 1 Si基底和不同衬底上沉积的FeCo薄膜的易轴矫顽力、剩磁比、应变、晶粒尺寸以及阻尼系数
Table 1. Coercivity of easy axis, remanent magnetization ratio, strain, grain size, and damping coefficient of FeCo films deposited on Si substrate and different underlayers.
衬底层
材料易轴矫顽力
Hc/Oe剩磁比
Mr/Ms应变
∆ε/%晶粒尺寸
D/nm阻尼
αSi 112 0.834 — 9.4±0.2 — Cu 41 0.949 0.59 7.5±0.6 0.045 Co 38 0.951 0.27 7.5±0.2 0.025 NiFe 23 0.991 0.29 6.9±0.2 0.015 表 2 不同衬底上沉积的FeCo薄膜的磁性总结
Table 2. Summary of magnetic properties of FeCo films deposited on different underlayers.
-
[1] Li T Y, Liu X Y, Li J W, Pan L N, He A N, Dong Y Q 2022 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 547 168777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cronin D, Lordan D, Wei G, McCloskey P, Mathúna C O, Masood A 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 243903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tang X L, Yu Y, Su H, Zhang H W, Zhong Z Y, Jing Y L 2018 J. Mater. Sci. 53 3573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chai G, Phuoc N N, Ong C K 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Masood A, McCloskey P, Mathúna C Ó, Kulkarni S 2017 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 903 012050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kurlyandskaya G V, Shcherbinin S V, Volchkov S O, Bhagat S M, Calle E, Pérez R, Vazquez M 2018 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 459 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zheng F, Ma Z, Gao H, Pan F C, Li S T, Cao J W, Bai J M, Wei F L 2017 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28 17448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang F J, Min J J, Hui J H, Chen H B, Degao L, Li W J, Chen X Q, Yang C P 2017 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28 11733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Baco S, Abbas Q A, Hayward T J, Morley N A 2021 J. Alloy. Compd. 881 160549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Cabral L, Aragon F H, Villegas-Lelovsky L, Lima M P, Macedo W A A, Da Silva J L F 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11 1529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Vopsaroiu M, Georgieva M, Grundy P J, Fernandez G V, Manzoor S, Thwaites M J, O’Grady K 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 10N303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vas’ko V A, Rantschler J O, Kief M T 2004 IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 2335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xi L, Du J H, Zhou J J, Ma J H, Li X Y, Wang Z, Zuo Y L, Xue D S 2012 Thin Solid Films 520 5421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王璇, 郑富, 卢佳, 白建民, 王颖, 魏福林 2011 60 017505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Zheng F, Lu J, Bai J M, Wang Y, Wei F L 2011 Acta. Phys. Sin. 60 017505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X, Zheng F, Liu Z Y, Liu X X, Wei D, Wei F L 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 105 07B714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wu Y P, Yang Y, Yang Z H, Ma F S, Zong B Y, Ding J 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 093905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xu F, Liao Z Q, Huang Q J, Ong C K, Li S D 2011 IEEE Trans. Magn. 47 3921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Acosta A, Fitzell K, Schneider J D, Dong C Z, Yao Z, Wang Y E, Carman G P, Sun N X, Chang J P 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 222404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Acosta A, Fitzell K, Schneider J D, Dong C Z, Yao Z, Sheil R, Wang Y E, Carman G P, Sun N X, Chang J P 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 128 013903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fu Y, Miyao T, Cao J W, Yang Z, Matsumoto M, Liu X X, Morisako A 2007 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Y B, Li Z H, Liu X, Fu Y, Wei F L, Kamzin A S, Wei D 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 09A325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sun N X, Wang S X 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 92 1477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shimatsu T, Katada H, Watanabe I, Muraoka H, Nakamura Y 2003 IEEE Trans. Magn. 39 2365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Langford J I, Wilson A J C 1978 J. Appl. Cryst. 11 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Scherrer P 1918 Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26 98
[26] Herzer G 1990 IEEE Trans. Magn. 26 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jiang H, Chen Y J, Chen L F, Huai Y M 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 91 6821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Inturi V R, Barnard J A 1996 J. Appl. Phys. 79 5904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu X X, Kanda H, Morisako A 2011 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 266 012037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Jung H S, Doyle W D, Wittig J E, Al-Sharab J F, Bentley J 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 2415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] O'Grady K, Laidler H 1999 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200 616
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wohlfarth E P 1958 J. Appl. Phys. 29 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Henkel O 1964 Phys. Stat. Sol. 7 919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Gilbert T L 2004 IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 3443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Ge S H, Yao D S, Yamaguchi M, Yang X L, Zuo H P, Ishii T, Zhou D, Li F 2007 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40 3660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Kuanr B K, Camley R E, Celinski Z 2005 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 286 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Ben Youssef J, Vukadinovic N, Billet D, Labrune M 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 174402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Wu Y P, Han G C, Kong L B 2010 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322 3223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Zhong X X, Soh W T, Phuoc N N, Liu Y, Ong C K 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 013906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Fu Y, Cheng X F, Yang Z 2006 Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 203 963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Phuoca N N, Hungb L T, Ongb C K 2011 J. Alloy. Compd. 509 4010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7613
- PDF下载量: 120
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: