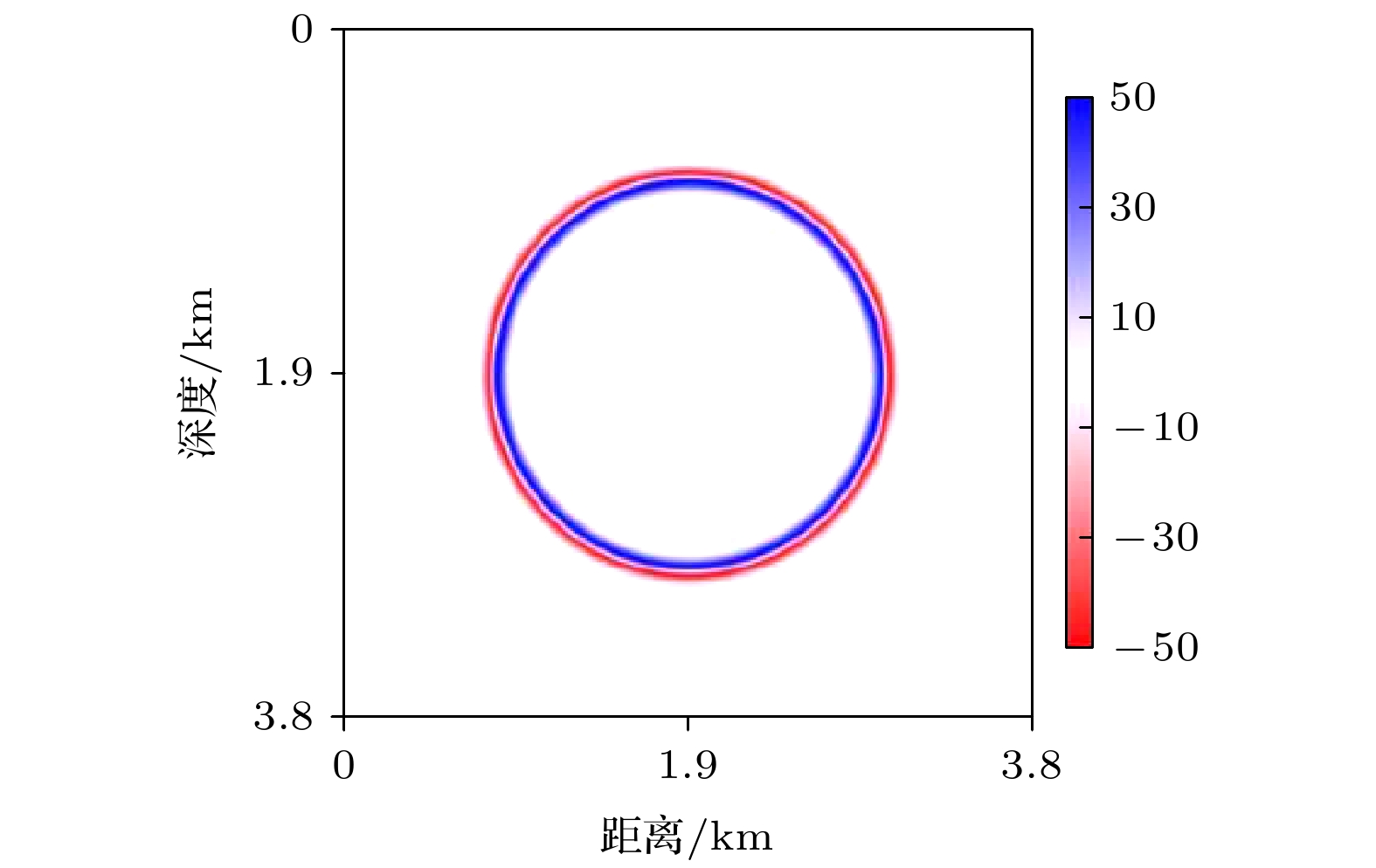
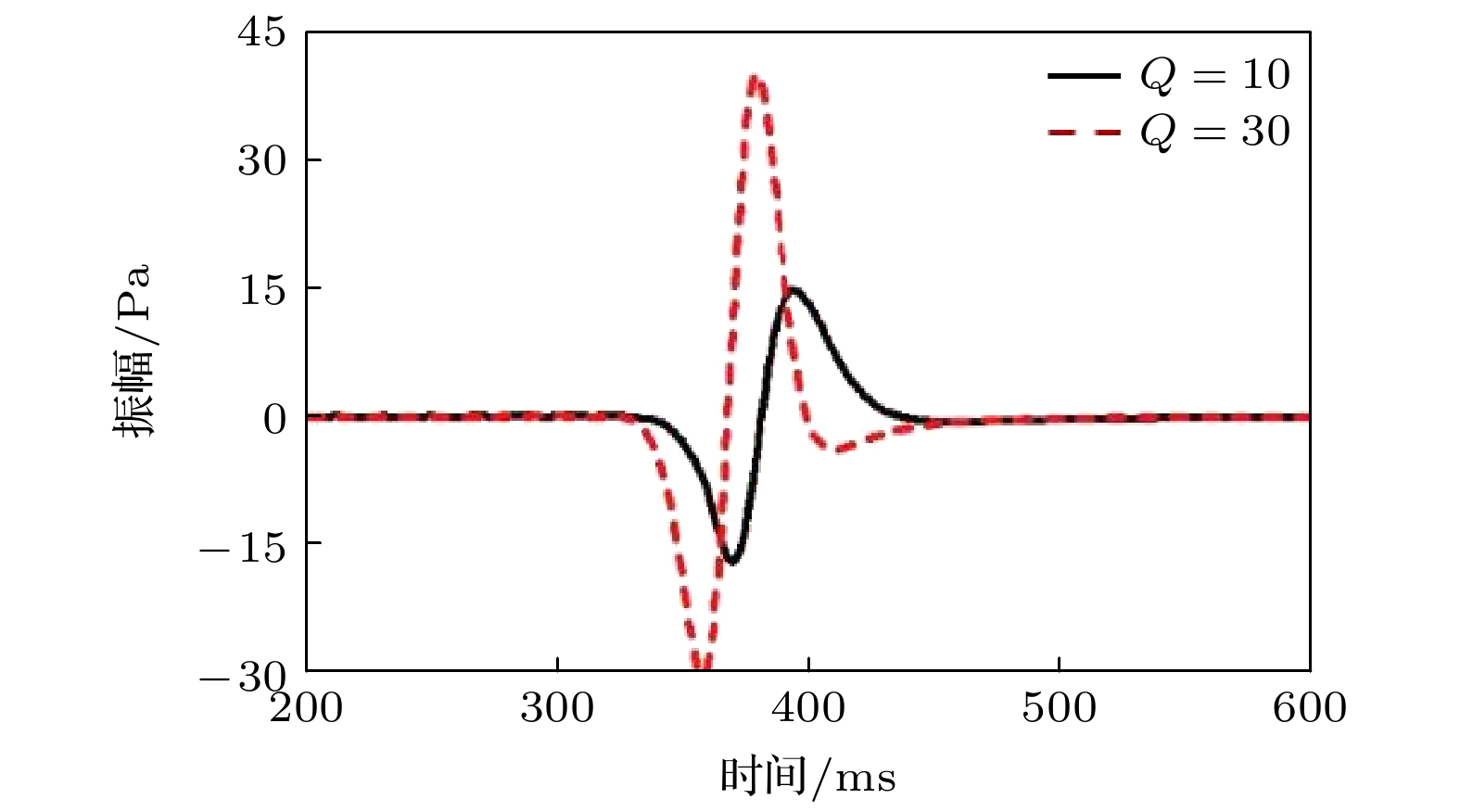
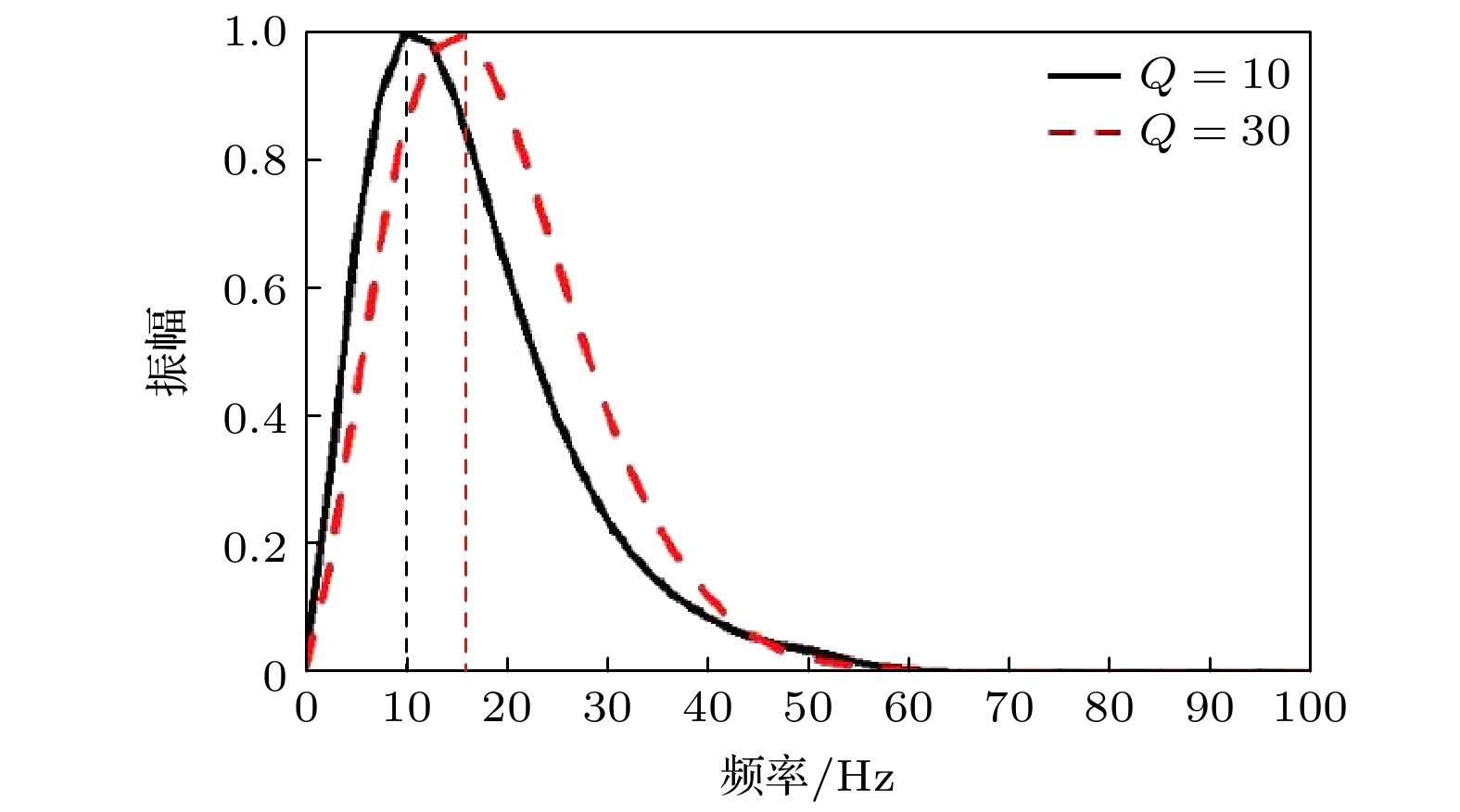
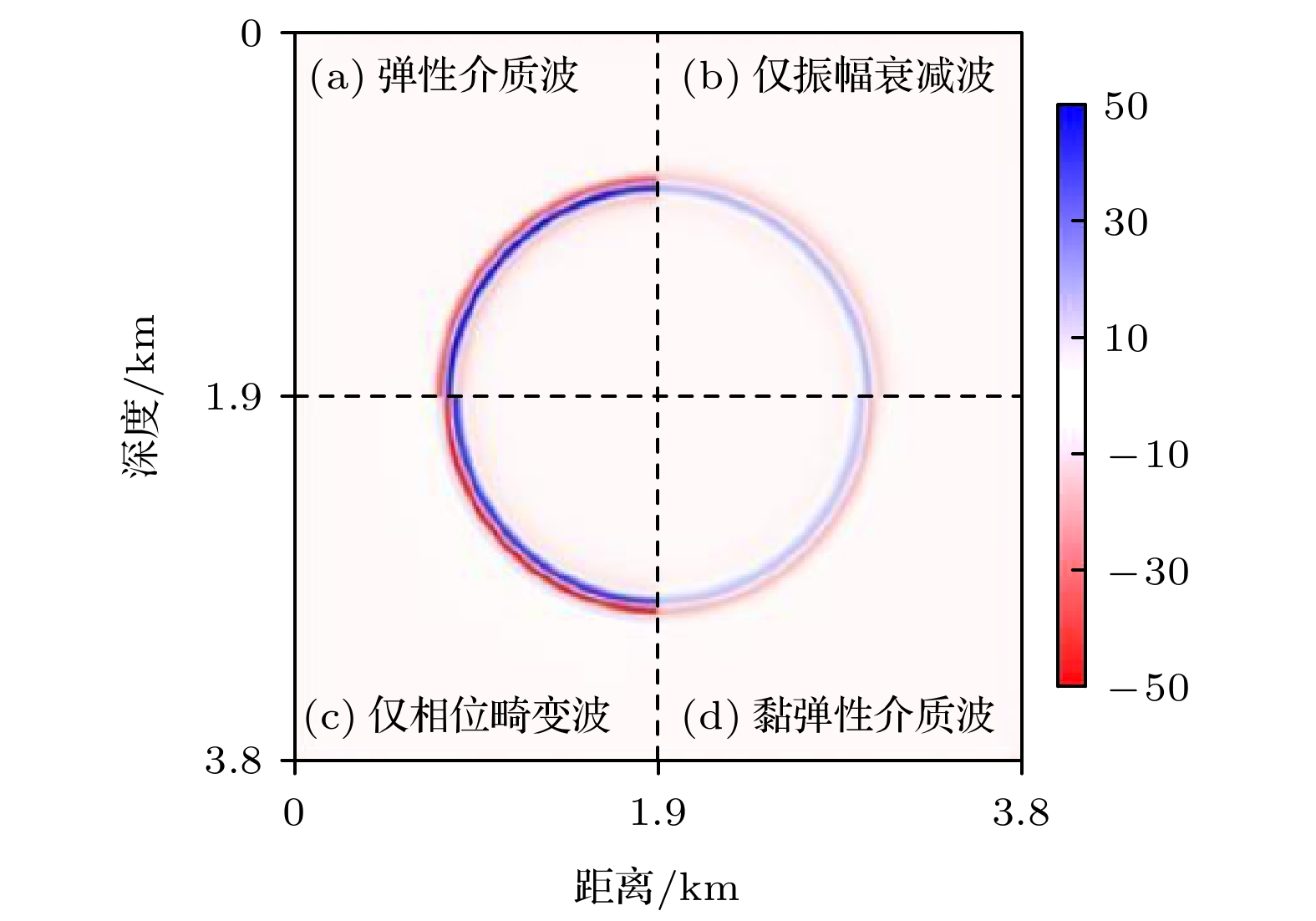
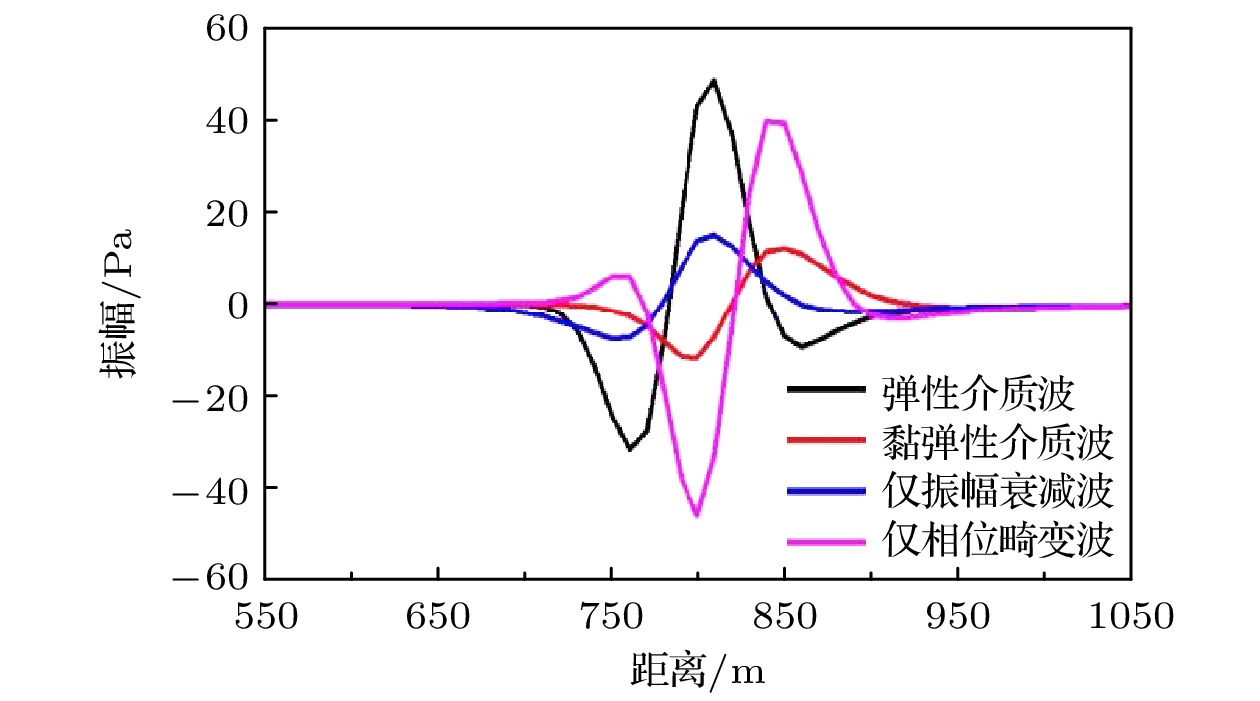
-
实际介质普遍具有黏弹性, 波在传播过程中常伴有能量的耗散、相位畸变和频带变窄等, 对于含有液体和气体的介质, 衰减现象尤为突出. 由于经典的波动理论未考虑介质的黏弹性效应, 基于完全弹性假设的模拟波场和实际传播特征之间的差异明显, 波动理论在工程技术中的应用效果还有提升的空间. 在岩石物理中, 品质因子Q是量化地震衰减强度的参数, 为了研究波在地下介质中的传播规律, 本文从常Q理论出发, 在黏弹性介质频散关系中, 利用多项式拟合和Taylor展开法将频率的分数阶转化为整数阶, 进而推导了时间域复数形式的地下黏弹性介质波动方程. 该近似处理避免了频散关系经域转换后出现分数阶时间微分项, 能有效地降低计算成本. 最后, 采用有限差分法联合伪谱法对均质模型实现了波场的数值模拟, 验证了方程的有效性.The energy of wavefield is gradually attenuated in all real materials, which is a fundamental feature and more obvious in the media containing liquid and gas. Because the viscosity effect is not considered in the classical wave theory, the actual wavefield is different from the simulated scenario based on the assumption of complete elasticity so that the application of wavefield does not meet the expectations in engineering technology, such as geophysical exploration. In the rock physics field, the well-known constant-Q theory gives a linear description of attenuation and Q is regarded as independent of the frequency. The quality factor Q is a parameter for calculating the phase difference between stress and strain of the media, which, as an index of wavefield attenuation behavior, is inversely proportional to the viscosity. Based on the constant-Q theory, a wave equation can be directly obtained by the Fourier transform of the dispersion relation, in which there is a fractional time differential operator. Therefore, it is difficult to perform the numerical simulation due to memory for all historical wavefields. In this paper, the dispersion relation is approximated by polynomial fitting and Taylor expansion method to eliminate the fractional power of frequency which is uncomfortably treated in the time domain. And then a complex-valued wave equation is derived to characterize the propagation law of wavefield in earth media. Besides the superiority of numerical simulation, the other advantage of this wave equation is that the dispersion and dissipation effects are decoupled. Next, a feasible numerical simulation strategy is proposed. The temporal derivative is solved by the finite-difference approach, moreover, the fractional spatial derivative is calculated in the spatial frequency domain by using the pseudo-spectral method. In the process of numerical simulation, only two-time slices, instead of the full-time wavefields, need to be saved, so the demand for data memory significantly slows down compared with solving the operator of the fractional time differential. Following that, the numerical examples prove that the novel wave equation is capable and efficient for the homogeneous model. The research work contributes to the understanding of complex wavefield phenomena and provides a basis for treating the seismology problems.
-
Keywords:
- viscoelastic media /
- wave equation /
- numerical simulation /
- pseudo-spectral method
[1] Yang P, Brossier R, Metivier L 2018 SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40 B1101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen H, Zhou H, Yao Y 2020 Geophysics 85 S169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Keating S, Innanen K 2020 Geophysics 85 R397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang, W, Shi Y 2019 Geophysics 84 S95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu H P, Anderson D L, Kanamori H 1976 Geophys. J. Int. 47 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Emmerich H, Korn M 1987 Geophysics 52 1252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhu T, Carcione J M, Harris J M 2013 Geophys. Prospect. 61 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kjartansson E 1979 Geophys. Prospect. 84 4737
[9] Carcione J M 2008 Geophysics 74 T1
[10] Carcione J M, Cavallini F, Mainardi F, Hanyga A 2002 Pure Appl. Geophys. 159 1719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lu J F, Hanyga A 2004 Geophys. J. Int. 159 688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Podlubny I 1999 Fractional Differential Equations (California: Academic Press) pp270−217
[13] Yang J, Zhu H 2018 Geophys. J. Int. 215 1064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen X W, Zhang R C, Mei F X 2000 Acta Mech. Sin. 16 282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dorodnitsyn V, Kozlov R 2010 J. Eng. Math. 66 253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 方刚, 张斌 2013 62 154502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang G, Zhang B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 154502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li H X, Tao C H, Liu C, Huang G N, Yao Z A 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 064301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 周聪, 王庆良 2015 64 239101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou C, Wang Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 239101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Z J, Wang G J, Harris J M 1999 Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 114 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 董良国, 马在田, 曹景忠 2000 地球 43 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong L G, Ma Z T, Cao J Z 2000 Chin. J. Geophys 43 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 孟路稳, 程广利, 张明敏, 尚建华 2017 海军工程大学学报 29 57
Meng L W, Cheng G L, Zhang M M, Shang J H 2017 J. Naval Univ. Eng. 29 57
[22] 杜启振, 刘莲莲, 孙晶波 2007 56 6143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du Q, Liu L, Sun J 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 6143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 唐春安 1997 岩石力学与工程学报 4 75
Tang C A 1997 Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 4 75
[24] Carcione J M 2014 Wave Fields in Real Media (Amsterdam: Elsevier Science) p75
[25] Chen W, Holm S 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115 1424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Carcione J M 2010 Geophysics 75 A53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同Q值拟合系数
Table 1. Fitting coefficients of different Q values.
Q 5 10 20 30 60 100 5000 a1 0.8144 0.9081 0.9545 0.9698 0.9850 0.991 0.9998 a2 58.452 30.728 15.662 10.499 5.276 3.1716 0.0636 a3 –2078.2 –1133.1 –587.58 –396.08 –200.14 –120.57 –2.4255 -
[1] Yang P, Brossier R, Metivier L 2018 SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40 B1101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen H, Zhou H, Yao Y 2020 Geophysics 85 S169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Keating S, Innanen K 2020 Geophysics 85 R397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang, W, Shi Y 2019 Geophysics 84 S95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu H P, Anderson D L, Kanamori H 1976 Geophys. J. Int. 47 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Emmerich H, Korn M 1987 Geophysics 52 1252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhu T, Carcione J M, Harris J M 2013 Geophys. Prospect. 61 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kjartansson E 1979 Geophys. Prospect. 84 4737
[9] Carcione J M 2008 Geophysics 74 T1
[10] Carcione J M, Cavallini F, Mainardi F, Hanyga A 2002 Pure Appl. Geophys. 159 1719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lu J F, Hanyga A 2004 Geophys. J. Int. 159 688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Podlubny I 1999 Fractional Differential Equations (California: Academic Press) pp270−217
[13] Yang J, Zhu H 2018 Geophys. J. Int. 215 1064
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen X W, Zhang R C, Mei F X 2000 Acta Mech. Sin. 16 282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dorodnitsyn V, Kozlov R 2010 J. Eng. Math. 66 253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 方刚, 张斌 2013 62 154502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang G, Zhang B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 154502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li H X, Tao C H, Liu C, Huang G N, Yao Z A 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 064301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 周聪, 王庆良 2015 64 239101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou C, Wang Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 239101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Z J, Wang G J, Harris J M 1999 Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 114 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 董良国, 马在田, 曹景忠 2000 地球 43 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong L G, Ma Z T, Cao J Z 2000 Chin. J. Geophys 43 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 孟路稳, 程广利, 张明敏, 尚建华 2017 海军工程大学学报 29 57
Meng L W, Cheng G L, Zhang M M, Shang J H 2017 J. Naval Univ. Eng. 29 57
[22] 杜启振, 刘莲莲, 孙晶波 2007 56 6143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du Q, Liu L, Sun J 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 6143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 唐春安 1997 岩石力学与工程学报 4 75
Tang C A 1997 Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 4 75
[24] Carcione J M 2014 Wave Fields in Real Media (Amsterdam: Elsevier Science) p75
[25] Chen W, Holm S 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115 1424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Carcione J M 2010 Geophysics 75 A53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12259
- PDF下载量: 318
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: