-
为补偿皮秒拍瓦激光系统中钕玻璃宽带放大引起的增益窄化, 提出了一种基于铌酸锂双折射晶体的高能量光谱整形方法. 在相同强度调制下, 对比了BBO、铌酸锂和石英3种晶体, 针对1053 nm激光, 选用了高双折射率、大口径且不易潮解的铌酸锂作为整形晶体. 理论分析了晶体厚度、倾斜角、面内旋转角对强度调制的影响, 发现它们分别决定调制的带宽、中心波长及深度. 并对整形过程中晶体引入的光谱相位进行了分析, 发现各阶色散量随晶体厚度、倾斜角、面内旋转角变化的规律, 因此可通过上述参数控制各阶色散量. 在此基础上, 开展了中心波长为1053 nm、带宽为10 nm、调制深度为80%的光谱整形实验和相位测量实验, 实验与理论分析相一致. 针对神光Ⅱ皮秒拍瓦激光系统, 利用上述整形方案, 国内首次实现了1700 J, 6 nm (FWHM)的高能宽带激光输出, 有效补偿了增益窄化. 研究结果对国内基于钕玻璃放大系统的宽频带激光装置的工程研制具有重要意义.In recent years, chirped pulse amplification (CPA) technology injects vitality into the development of ultra-strong and ultra-short lasers. However, in the CPA based gain media, the gain narrowing effect limits the higher output of ultrashort pulse in energy, power, signal-to-noise ratio. In order to compensate for the gain narrowing caused by the broadband amplification of Nb:glass in picosecond pewter laser system, a method of high-energy spectral shaping is proposed based on LiNbO3 birefringent crystal, and the spectral phase introduced by the crystal is analysed for the first time. Based on the strict Jones matrix, the transmittance function of birefringent crystal and the spectral phase introduced by the crystal are obtained. Further, three kinds of birefringent crystals are compared among each other, and the results show that the higher birefringence and the smaller thickness are required to achieve the same intensity modulation. For the laser pulse at 1053 nm, LiNbO3 is selected as the spectral shaping crystal due to its high birefringence, large diameter, and non-deliquescent. The influences of crystal thickness, tilt angle, and in-plane rotation angle on the spectral intensity modulation are simulated theoretically, and the results show the above parameters affect the modulation bandwidth, center wavelength, and modulation depth of the shaping. By analyzing the spectral phase introduced by the crystal, it is found that the dispersion of each order changes with the thickness of the crystal, the tilt angle, and the in-plane rotation angle, and it is the most sensitive to the change of thickness. In addition, by controlling the dispersion of each order, the influence on the pulse signal-to-noise ratio can be weakened during spectrum shaping. On the basis of theoretical analysis, the shaping experiment with a center wavelength of 1053 nm, modulation bandwidth of 10 nm, and modulation depth of 80% is carried out. And the phase introduced by the LiNbO3 is measured. The experimental results are consistent with the theoretical analysis. For the Shenguang Ⅱ high-energy petawatt laser system, by the above-mentioned shaping scheme, a high-energy broadband laser output of 1700 J and 6 nm (FWHM) is realized for the first time in China, which is 2 times that at 3.2 nm when it is not shaped. The research effectively compensates for the Nb:glass gain narrowing effect, and will provide references for the parameter design, material selection and spectral phase compensation in the birefringent spectral shaping.
-
Keywords:
- high-energy spectral shaping /
- birefringent crystal /
- spectral phase /
- high-energy petawatt laser system
[1] Strickland D, Mourou G 1985 Opt. Commun. 55 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sauteret C, Husson D, Thiell G, Seznec S, Gary S, Migus A, Mourou G 1991 Opt. Lett. 16 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Aoyama M, Yamakawa K, Akahane Y, Ma J, Inoue N, Ueda H, Kiriyama H 2003 Opt. Lett. 28 1594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Danson C N, Haefner C, Bromage J, et al. 2019 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 7 e54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stuart B C, Herman S, Perry M D 1994 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (California: Anaheim) pJFA3
[6] 曹东茂, 魏志义, 滕浩, 夏江帆, 张杰, 侯洵 2000 49 1202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao D M, Wei Z Y, Teng H, Xia J F, Zhang J, Hou X 2000 Acta Phys. Sin. 49 1202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 楚晓亮, 张彬, 蔡邦维, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 黄小军, 袁晓东, 曾小明, 刘兰琴, 王逍, 王晓东, 周凯南, 郭仪 2005 54 4696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei X L, Zhang B, Cai B W, Wei X F, Zhu Q H, Huang X J, Yuan X D, Zeng X M, Liu L Q, Wang X, Wang X D, Zhou K N, Guo Y 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 4696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 郭爱林, 杨庆伟, 谢兴龙, 高奇, 薛志玲, 李美荣 2007 光学学报 27 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo A L, Yang Q W, Xie X L, Gao Q, Xue Z L, Li M R 2007 Acta Optica Sinica 27 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 郭爱林, 杨庆伟, 张福领, 孙美智, 毕群玉, 谢兴龙, 朱健强 2009 光学学报 29 1582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo A L, Yang Q W, Zhang F L, Sun M Z, Bi Q Y, Xie X L, Zhu J Q 2009 Acta Optica Sinica 29 1582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 姚云华, 卢晨晖, 徐淑武, 丁晶新, 贾天卿, 张诗按, 孙真荣 2014 63 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao Y H, Lu C H, Xu S W, Ding J X, Jia T Q, Zhang S A, Sun Z R 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Xia G, Fan W, Huang D J, Cheng H, Guo J T, Wang X Q 2019 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 7 E9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘兰琴, 彭翰生, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 黄小军, 王晓东, 周凯南, 曾小明, 王逍, 郭仪, 袁晓东, 彭志涛, 唐晓东 2005 54 2764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chu L Q, Peng H S, Wei X F, Zhu Q H, Huang X J, Wang X D, Zhou K N, Zeng X M, Wang X, Guo Y, Yuan X D, Peng Z T, Tang X D 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 2764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rambo P 2008 International Conference on Ultrahigh Intensity Lasers (China: Shanghai) pp27−31
[14] Preuss D R, Gole J L 1980 Appl. Opt. 19 702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Barty C P, Korn G, Raksi F, Rose-Petruck C, Squier J, Tien A C, Wilson K R, Yakovlev V V, Yamakawa K 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lu X M, Li C, Leng Y X, Wang C, Zhang C M, Liang X Y, Li R X, Xu Z Z 2007 Chin. Opt. Lett. 5 493
[17] 张颖, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 谢旭东, 王凤蕊, 曾小明, 应纯同 2008 光学学报 28 1767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Wei X F, Zhu Q H, Xie X D, Wang F R, Zeng X M, Ying C T 2008 Acta Optica Sinica 28 1767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Heritage J P, Weiner A M, Thurston R N 1985 Opt. Lett. 10 609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Kalantar D H, et al. 2017 Fusion Sci. Technol. 69 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 朱鹏飞, 杨镜新, 薛绍林, 李美荣, 林尊琪 2003 中国激光 30 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu P F, Yang J X, Xue S L, Li M R, Lin Z Q 2003 Chinese J. Lasers 30 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu F, Wang C, Hu J, Zhang Z, Yang X, Liu X, Liu Y, Ji P, Bai P, Qian J, Gui J, Xu Y, Leng Y 2020 Opt. Express 28 31743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu X 1994 Appl. Opt. 33 3502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu G, Wang T, Li Z Y, Dai Y P, Lin Z Q, Gu Y, Zhu J Q 2008 Rev. Laser Eng. 36 1172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 杨庆伟 2009 博士学位论文 (上海: 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所)
Yang Q W 2009 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
-
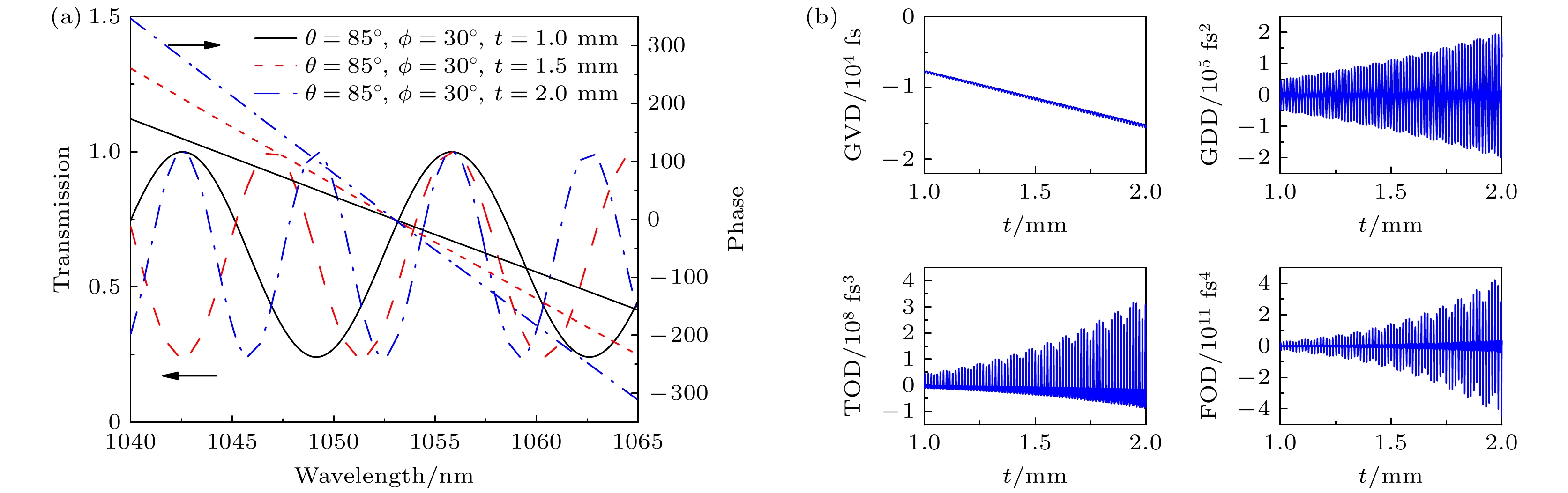
图 3 当θ = 85°, ϕ = 30°, t = 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 mm时, 透过率函数、晶体引入的光谱总相位及各阶色散的变化曲线 (a) t = 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 mm时, 透过率函数、光谱总相位随波长的变化曲线; (b) GVD, GDD, TOD, FOD随厚度t的变化
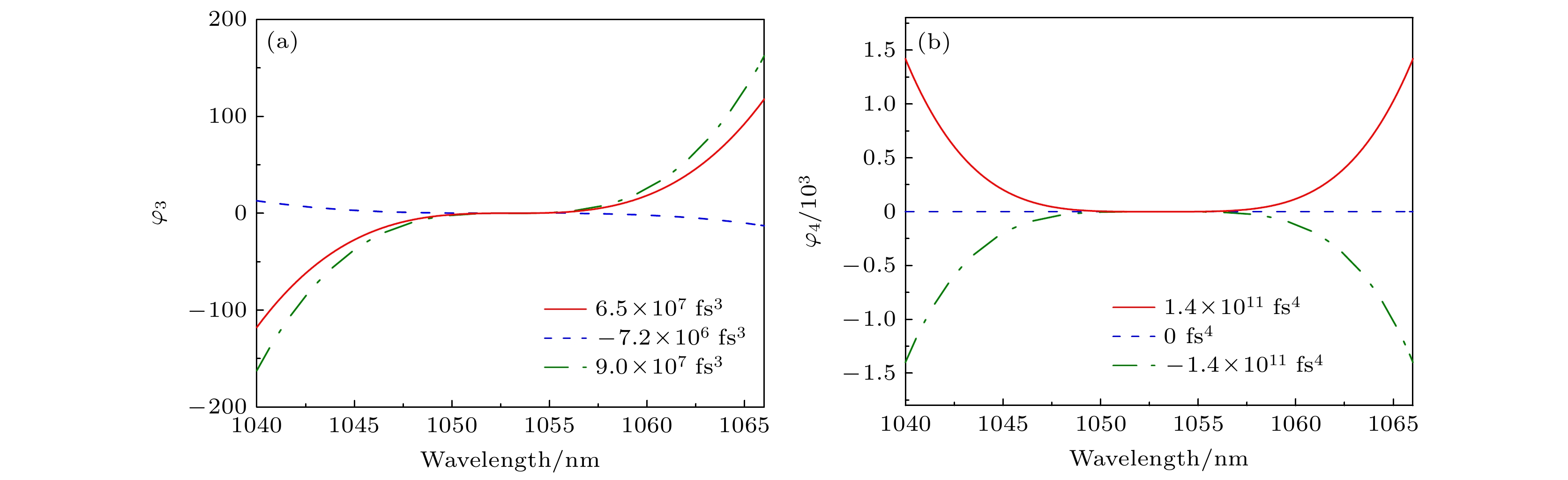
Fig. 3. The curve of transmittance function, total phase of the spectrum, and each order dispersion introduced by the crystal with θ = 85°, ϕ = 30°, t = 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 mm: (a) The transmittance function and total phase of spectrum changes with wavelength; (b) GVD, GDD, TOD, FOD changes with thickness t.
图 4 当ϕ = 30°, t = 1.5 mm, θ = 80°, 85°, 90°时, 透过率函数、晶体引入的光谱总相位及各阶色散的变化曲线 (a) 透过率函数、光谱总相位随波长的变化曲线; (b) GVD, GDD, TOD, FOD随厚度θ的变化
Fig. 4. The curve of transmittance function, total phase of the spectrum and each order dispersion introduced by the crystal with ϕ = 30°, t = 1.5 mm, θ = 80°, 85°, 90°: (a) The transmittance function and total phase of spectrum changes with wavelength; (b) GVD, GDD, TOD, FOD changes with thickness θ.
图 5 当θ = 85°, t = 1.5 mm, ϕ = 25°, 30°, 35°时, 透过率函数、晶体引入的光谱总相位及各阶色散的变化曲线 (a) 透过率函数、光谱总相位随波长的变化曲线; (b) GVD, GDD, TOD, FOD随厚度ϕ的变化
Fig. 5. The curve of transmittance function, total phase of the spectrum, and each order dispersion introduced by the crystal with θ = 85°, t = 1.5 mm, ϕ = 25°, 30°, 35°: (a) The transmittance function and total phase of spectrum changes with wavelength; (b) GVD, GDD, TOD, FOD changes with thickness ϕ.
图 8 皮秒拍瓦激光系统装置框图及注入钕玻璃放大系统前的预补偿光谱图 (a) 神光Ⅱ高能拍瓦激光系统装置框图[23]; (b) 强度调制前后注入钕玻璃放大系统前的预补偿光谱实验和模拟图
Fig. 8. Block diagram of picosecond petawatt laser system and pre-compensation spectrum before injection of Nb:glass amplifier system: (a) Block diagram of ShenguangⅡhigh-energy petawatt laser system[23]; (b) pre-compensation spectrum experiment and simulation diagram before and after intensity modulation before injection of Nb:glass amplifier system.
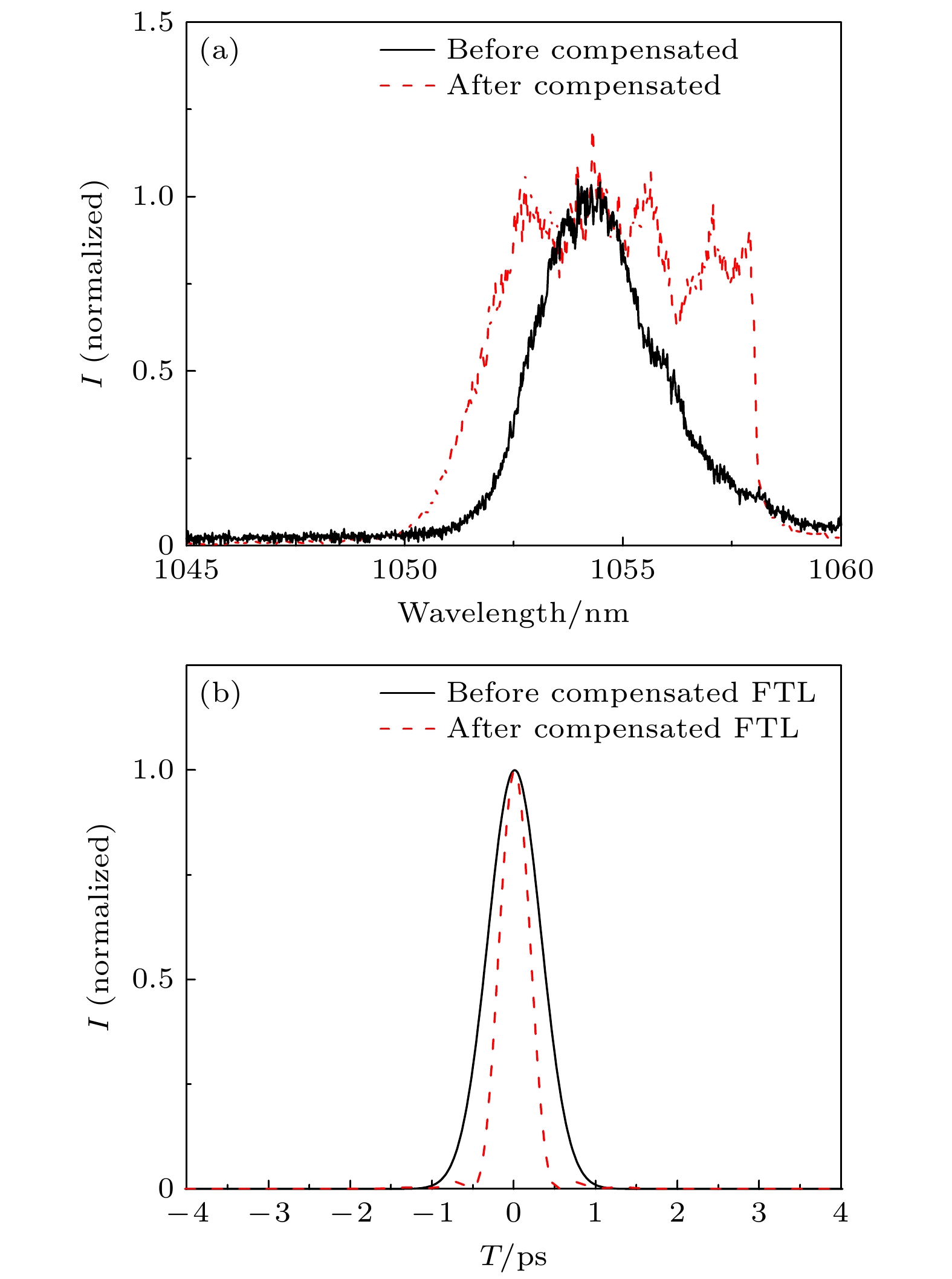
图 10 补偿增益窄化前后的输出光谱图与傅里叶变换极限脉冲比较图 (a) 补偿增益窄化与未补偿增益窄化的输出光谱实验图; (b) 补偿增益窄化与未补偿增益窄化的傅里叶变换极限脉冲
Fig. 10. Comparison of output spectrum and Fourier transform limit pulse before and after compensation gain narrowing: (a) Experimental graphs of output spectra of compensated gain narrowing and uncompensated gain narrowing; (b) the Fourier transform limit pulse with compensated gain narrowing and uncompensated gain narrowing.
-
[1] Strickland D, Mourou G 1985 Opt. Commun. 55 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sauteret C, Husson D, Thiell G, Seznec S, Gary S, Migus A, Mourou G 1991 Opt. Lett. 16 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Aoyama M, Yamakawa K, Akahane Y, Ma J, Inoue N, Ueda H, Kiriyama H 2003 Opt. Lett. 28 1594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Danson C N, Haefner C, Bromage J, et al. 2019 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 7 e54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stuart B C, Herman S, Perry M D 1994 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (California: Anaheim) pJFA3
[6] 曹东茂, 魏志义, 滕浩, 夏江帆, 张杰, 侯洵 2000 49 1202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao D M, Wei Z Y, Teng H, Xia J F, Zhang J, Hou X 2000 Acta Phys. Sin. 49 1202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 楚晓亮, 张彬, 蔡邦维, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 黄小军, 袁晓东, 曾小明, 刘兰琴, 王逍, 王晓东, 周凯南, 郭仪 2005 54 4696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei X L, Zhang B, Cai B W, Wei X F, Zhu Q H, Huang X J, Yuan X D, Zeng X M, Liu L Q, Wang X, Wang X D, Zhou K N, Guo Y 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 4696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 郭爱林, 杨庆伟, 谢兴龙, 高奇, 薛志玲, 李美荣 2007 光学学报 27 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo A L, Yang Q W, Xie X L, Gao Q, Xue Z L, Li M R 2007 Acta Optica Sinica 27 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 郭爱林, 杨庆伟, 张福领, 孙美智, 毕群玉, 谢兴龙, 朱健强 2009 光学学报 29 1582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo A L, Yang Q W, Zhang F L, Sun M Z, Bi Q Y, Xie X L, Zhu J Q 2009 Acta Optica Sinica 29 1582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 姚云华, 卢晨晖, 徐淑武, 丁晶新, 贾天卿, 张诗按, 孙真荣 2014 63 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao Y H, Lu C H, Xu S W, Ding J X, Jia T Q, Zhang S A, Sun Z R 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Xia G, Fan W, Huang D J, Cheng H, Guo J T, Wang X Q 2019 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 7 E9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘兰琴, 彭翰生, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 黄小军, 王晓东, 周凯南, 曾小明, 王逍, 郭仪, 袁晓东, 彭志涛, 唐晓东 2005 54 2764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chu L Q, Peng H S, Wei X F, Zhu Q H, Huang X J, Wang X D, Zhou K N, Zeng X M, Wang X, Guo Y, Yuan X D, Peng Z T, Tang X D 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 2764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rambo P 2008 International Conference on Ultrahigh Intensity Lasers (China: Shanghai) pp27−31
[14] Preuss D R, Gole J L 1980 Appl. Opt. 19 702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Barty C P, Korn G, Raksi F, Rose-Petruck C, Squier J, Tien A C, Wilson K R, Yakovlev V V, Yamakawa K 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lu X M, Li C, Leng Y X, Wang C, Zhang C M, Liang X Y, Li R X, Xu Z Z 2007 Chin. Opt. Lett. 5 493
[17] 张颖, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 谢旭东, 王凤蕊, 曾小明, 应纯同 2008 光学学报 28 1767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Wei X F, Zhu Q H, Xie X D, Wang F R, Zeng X M, Ying C T 2008 Acta Optica Sinica 28 1767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Heritage J P, Weiner A M, Thurston R N 1985 Opt. Lett. 10 609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Kalantar D H, et al. 2017 Fusion Sci. Technol. 69 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 朱鹏飞, 杨镜新, 薛绍林, 李美荣, 林尊琪 2003 中国激光 30 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu P F, Yang J X, Xue S L, Li M R, Lin Z Q 2003 Chinese J. Lasers 30 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu F, Wang C, Hu J, Zhang Z, Yang X, Liu X, Liu Y, Ji P, Bai P, Qian J, Gui J, Xu Y, Leng Y 2020 Opt. Express 28 31743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu X 1994 Appl. Opt. 33 3502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu G, Wang T, Li Z Y, Dai Y P, Lin Z Q, Gu Y, Zhu J Q 2008 Rev. Laser Eng. 36 1172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 杨庆伟 2009 博士学位论文 (上海: 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所)
Yang Q W 2009 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 7144
- PDF下载量: 89
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: