-
在考虑光学微腔中二阶和三阶非线性效应的情况下, 引入了可同时描述腔内基频和倍频光场的演化过程的Lugiato-Lefeve方程, 分析了SiN微腔中二次谐波的产生, 并讨论了各参数对腔内基频和倍频光场的影响. 理论分析结果表明, 失谐参量为0时, 稳定后的基频光场为平顶脉冲的形式, 而倍频光场呈正弦分布; 失谐参量增加, 将导致腔内基频和倍频光功率在演化过程中出现振荡, 且最终稳定的光功率变弱, 稳定后的光场分布为周期性变化; 失谐参量的值过大, 会使得微腔光场处于混沌状态. 抽运光强较弱时, 腔内可形成稳定的光场分布; 抽运光强较强时, 会导致腔内色散以及非线性效应过强, 最终稳定的光场仍然呈周期性变化, 且抽运光功率越强, 光功率的演化曲线振荡越强. 此外, 选取特定的微腔尺寸, 微腔可工作于“图灵环”状态. 理论分析结果对研究光学微腔中二次谐波的产生有重要意义.With the consideration of the second and the third order nonlinear effect, the Lugiato-Lefeve equation which describes the field evolution of the fundamental frequency wave and the second harmonic wave is introduced. Based on the Lugiato-Lefeve equation, the generation of the second harmonic wave in the SiN microresonator is analyzed, and the effect of the each parameter on the dual field is studied. Simulation results indicate that the stable field of the fundamental frequency wave is of flat top pulse, and the field of the second harmonic wave is of sinusoidal distribution. When the detuning parameter increases, the power of the dual wave inside the microresonator oscillates, and the stable power weakens, the stable light field is periodically varied. Moreover, the chaos emerges as detuning parameter becomes large. The stable field can be generated in the microresonator with the weak pump power. However, because of the high pump power, the dispersion and nonlinear effect are enhanced, resulting in the periodic light field. Furthermore, the oscillation of the dual power curve is aggravated, as the pump power increases. In addition, the turning patterns can be observed by choosing the special dimension of microresonator. Theoretical analysis results are significant for studying the generation of the second harmonic wave in the microresonator.
-
Keywords:
- nonlinear optics /
- optical microresonator /
- second harmonic waves
[1] 邢书剑, 张福民, 曹士英, 王高文, 曲兴华 2013 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xing S J, Zhang F M, Cao S Y, Wang G W, Qu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Niering M, Holzwarth R, Reichert J, Pokasov P, Udem T, Weitz M, Hansch T W, Lemonde P, Santarelli G, Abgrall M, Laurent P, Salomon C, Clairon A 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 孟飞, 曹士英, 蔡岳, 王贵重, 曹建平, 李天初, 方占军 2011 60 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng F, Cao S Y, Cai Y, Wang G Z, Cao J P, Li T C, Fang Z J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Swann W C, McFerran J J, Coddington I, Newbury N R, Hartl I, Fermann M E, Westbrook P S, Nicholson J W, Feder K S, Langrock C, Fejer M M 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3074
[5] Washburn B R, Fox R W, Newbury N R, Nicholson J W, Feder K, Westbrook P S, Jorgensen C G 2004 Opt. Express 12 4999
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 韩海年, 魏志义, 赵刚 2012 物理 41 249
Han H N, Wei Z Y, Zhao G 2012 Physics 41 249
[7] Herr T, Brasch V, Jost J D, Wang C Y, Kondratiev N M, Gorodetsky M L, Kippenberg T J 2013 Nat. Photon. 8 145
[8] Song Q H 2019 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 62 074231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang X Y, Cao Q T, Wang Z, Liu Y X, Qiu C W, Yang L, Gong Q H, Xiao Y F 2019 Nat. Photon. 13 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Godey C, Balakireva I V, Aurélien C, Chembo Y K 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 722
[11] Huang S W, Zhou H, Yang J, McMillan J F, Matsko A, Yu M, Kwong D L, Maleki L, Wong C W 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 053901
[12] Wang W Q, Lu Z Z, Zhang W F, Chu Sai T, Little B E, Wang L R, Xie X P, Liu M L, Yang Q H, Wang L, Zhao J G, Wang G X, Sun Q B, Liu Y S, Wang Y S, Zhao W 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 2002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xue X X, Xuan Y, Liu Y, Wang P H, Chen S, Wang J, Leaird D E, Qi M H, Weiner A M 2015 Nat. Photon. 9 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Coillet A, Balakireva I, Henriet R, Saleh K, Larger L, Dudley J M, Menyuk C R, Chembo Y K 2013 IEEE Photon. J. 5 6100409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Matsko A B, Liang W, Savchenkov A A, Maleki L 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Coen S, Randle H G, Sylvestre T, Erkintalo M 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xue X X, Leo F, Xuan Y, Villegas J A J, Wang P H, Leaird D E, Erkintalo M, Qi M H, Weiner Andrew M 2017 Light: Sci. Appl. 6 e16253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lin J T, Xu Y X, Ni J L, Wang M, Fang Z W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Cheng Y 2016 Phys. Rev. Appl. 6 014002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chembo Y K, Menyuk C R, 2014 Phys. Rev. A 87 053852
[20] Lin J T, Xu Y X, Fang Z W, Wang M, Song J X, Wang N W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Cheng Y 2015 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58 114209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Coen S, Haelterman M 2001 Opt. Lett. 26 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] And T, Boccaletti A, Grebogi C, Lai Y C, Mancini H, Maza D 2000 Phys. Rep. 329 2000
[23] Akhmediev N, Pelinovsky E 2010 Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 185 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
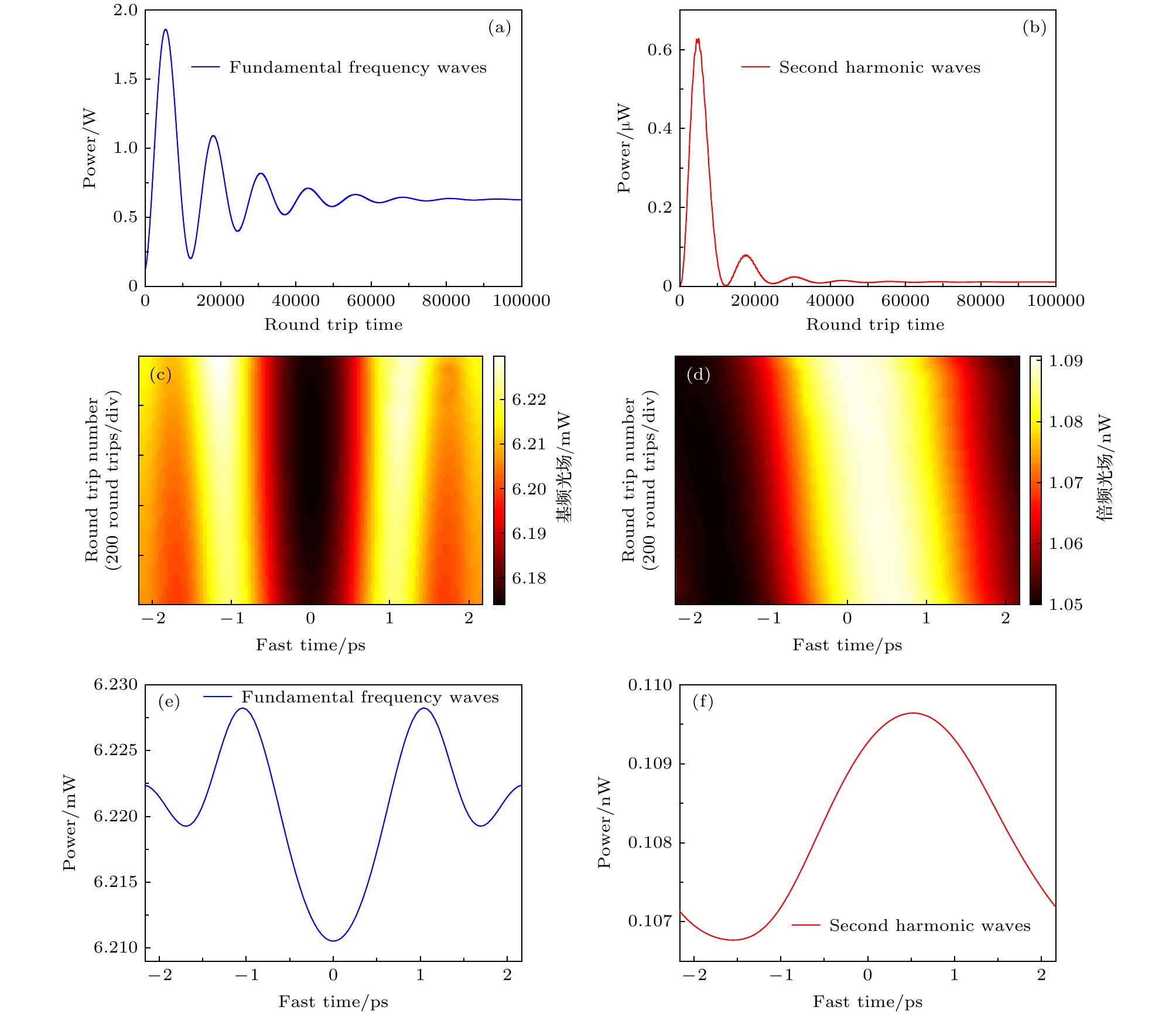
图 2 SiN光学微腔中二次谐波的产生 (δ1 = 0, Ein = 1 W1/2) (a) 倍频光场在腔内的演化过程; (b) 基频光功率随光在腔内循环次数的变化曲线; (c) 倍频光功率随光在腔内循环次数的变化曲线; (d)基频场的稳定分布; (e)倍频光场的稳定分布; (f)基频光的光谱; (g) 基频光的光谱
Fig. 2. Second harmonic waves generates inside the SiN microresonator (δ1 = 0, Ein = 1 W1/2): (a) Evolution of the second harmonic waves; (b) curves of the fundamental frequency waves power and (c) the second frequency waves power vary with the round trip number; (d) stationary distribution of the fundamental frequency waves light field and (e) the second frequency waves light field; (f) spectra of the fundamental frequency waves and (g) the second frequency waves.
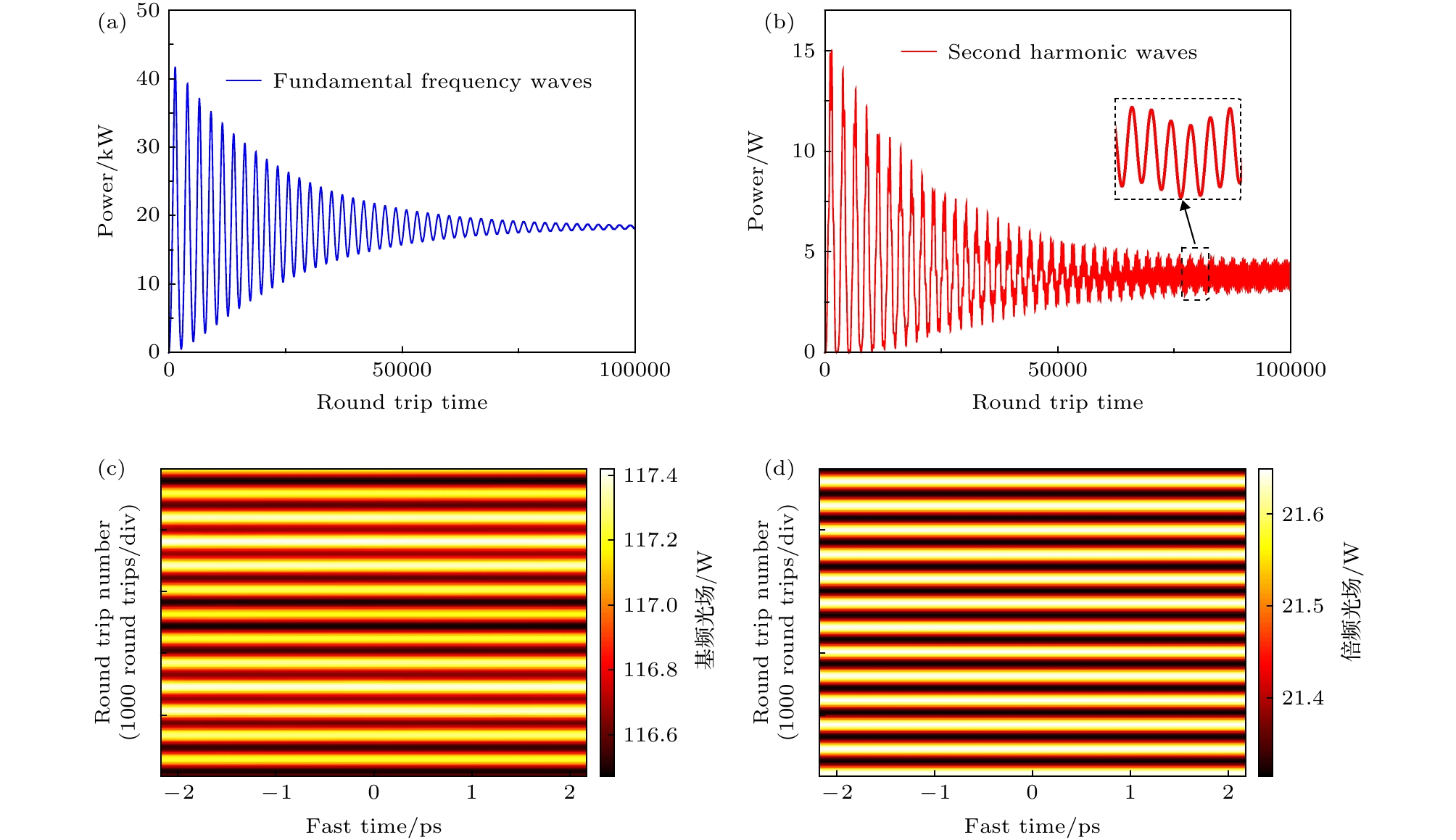
图 3 发生频率失谐后, 微腔内光场变化情况 (δ1 = 0.1, Ein = 1 W1/2) (a) 基频光功率和(b)倍频光功率随光在腔内循环次数的变化曲线; 光场稳定后, (c)基频光场和(d)倍频光场随时间的演化; (e) 基频光场和(f)倍频广场的稳定分布
Fig. 3. Light field evolution in the microresonator with the frequency detuning (δ1 = 0.1 and Ein = 1 W1/2): (a) Curves of the fundamental frequency waves power and (b) the second frequency waves power vary with the round trip number; evolution of (c) the fundamental frequency waves (d) the second frequency waves after the light fields are stable; stationary distribution of (e) the fundamental frequency waves light field and (f) the second frequency waves light field.
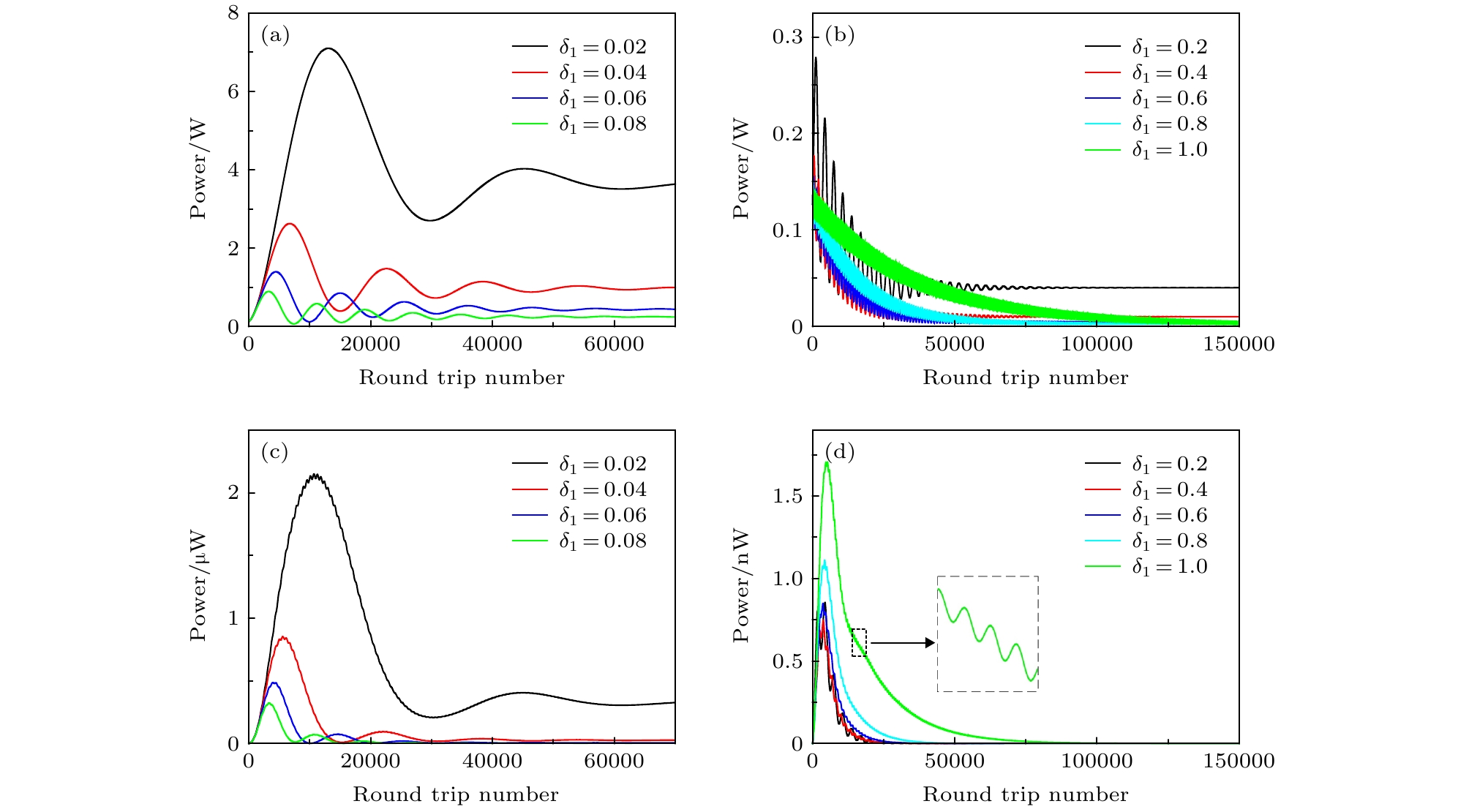
图 4 失谐参量δ1取不同值时, 微腔内基频光和倍频光功率变化曲线 (a) 0.02 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.08时, 基频光功率变化曲线; (b) 0.2 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.8时, 基频光功率变化曲线; (c) 0.02 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.08时, 倍频光功率变化曲线; (d) 0.2 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.8时, 倍频光功率变化曲线
Fig. 4. Influence of the frequency detuning δ1 on the power change curves: (a) Curves of the power variation for the fundamental frequency waves, 0.02 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.08; (b) curves of the power variation for the fundamental frequency waves, 0.2 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.8; (c) curves of the power variation for the second harmonic waves, 0.02 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.08; (d) curves of the power variation for the second harmonic waves, 0.2 ≤ δ1 ≤ 0.8.
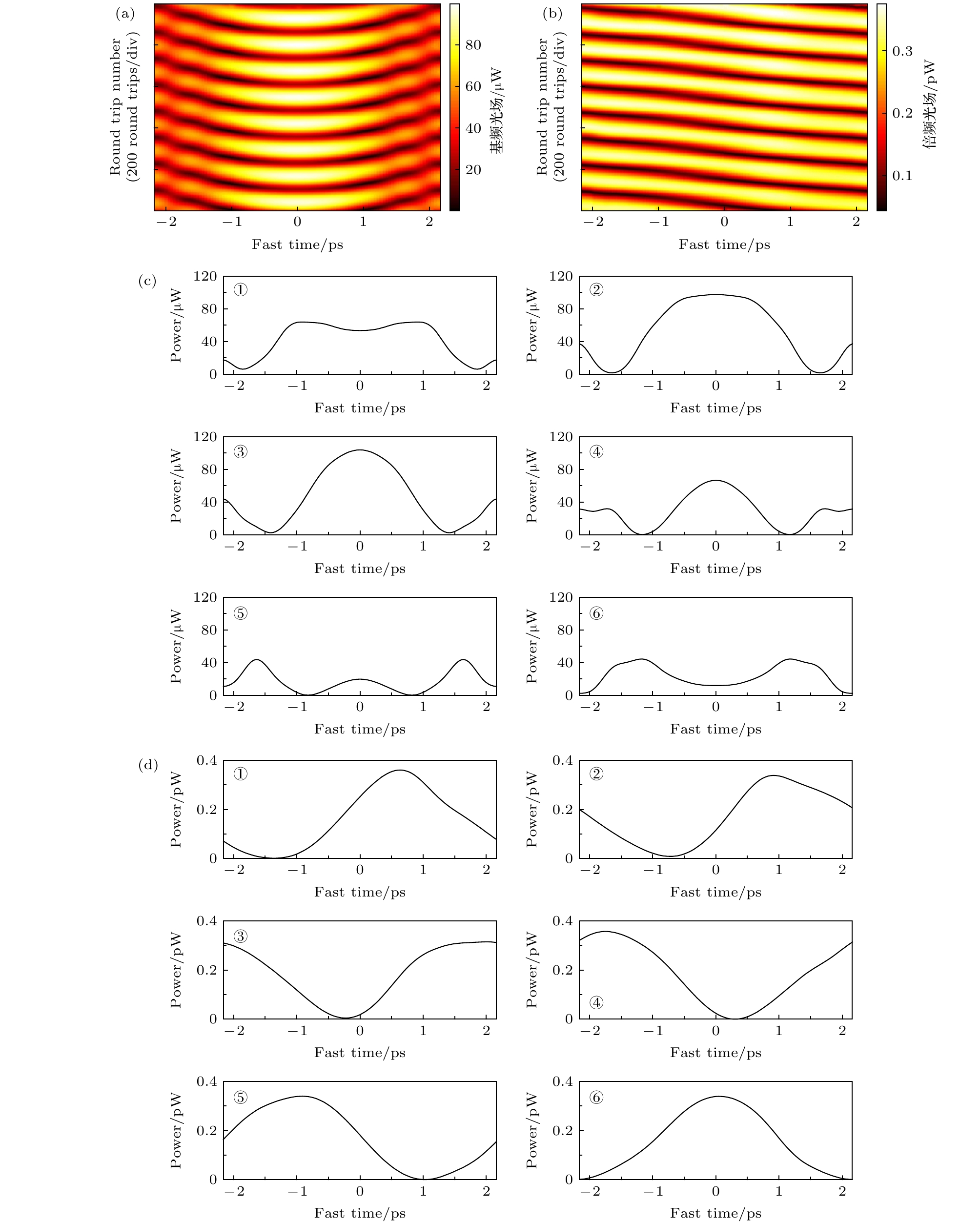
图 5 失谐参量δ1 = 1时, 腔内光场稳定后基频光和倍频光的光场演化 (a) 基频光场的演化; (b) 倍频光场的演化; (c) 基频光光场变化周期内, 光在腔内每循环100次, 绘制其波形; (d) 倍频光光场变化周期内, 光在腔内每循环100次, 绘制其波形
Fig. 5. Stable evolution of the dual light fields when δ1 = 1: (a) Evolution of the fundamental frequency waves; (b) evolution of the second harmonic waves; (c) intensity profiles of the fundamental frequency waves at six different moments within a period, the waveforms are plotted every hundred times; (d) intensity profiles of the second harmonic waves at six different moments within a period, the waveforms are plotted every hundred times.
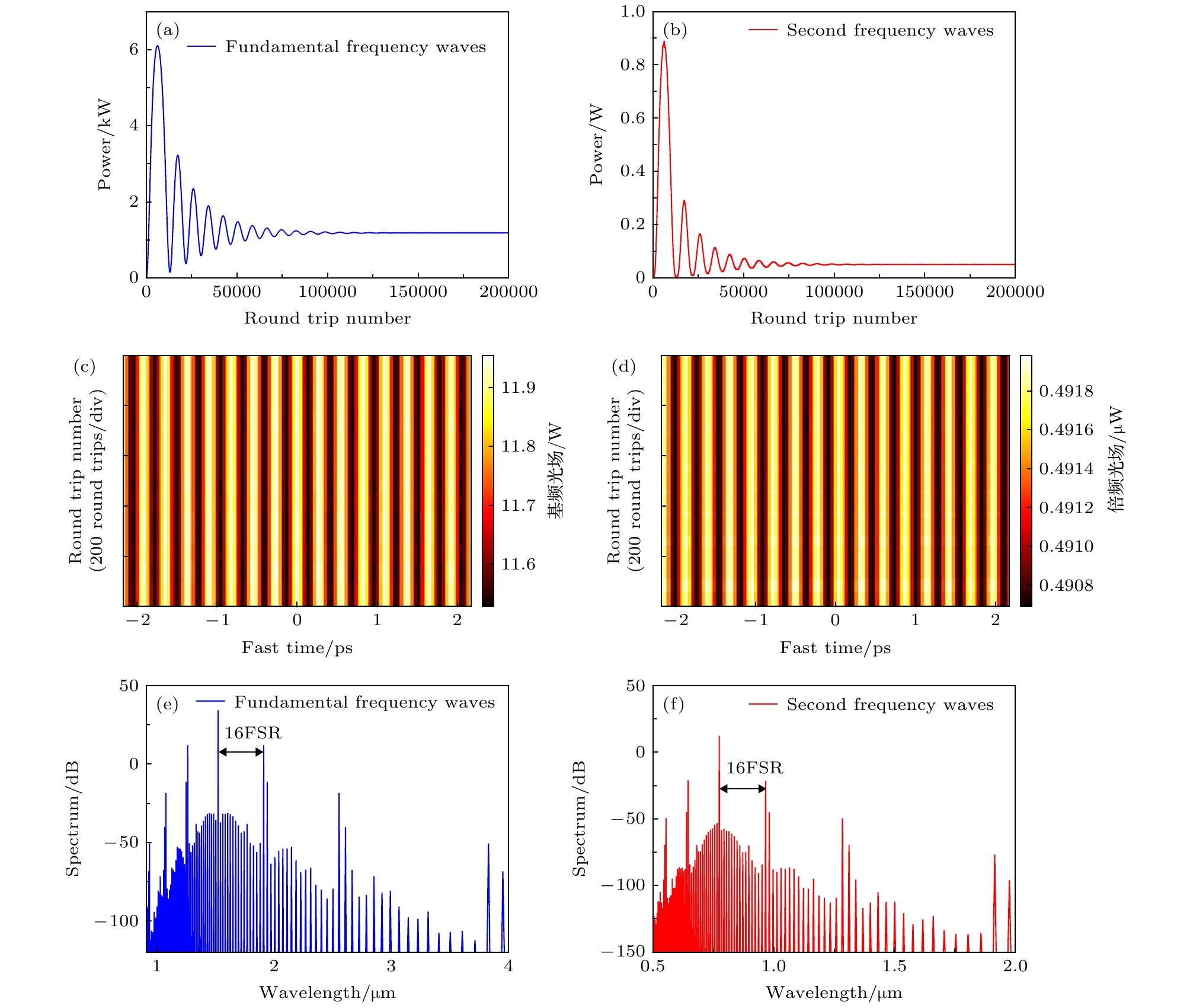
图 6 失谐参量δ1取值过大时, 腔内光场的混沌状态 (a) 基频光光场的混沌状态; (b) 倍频光光场的混沌状态; (c) 某一时刻基频光场的分布; (d) 某一时刻倍频光场的分布; (e) 与图(c)中光场对应的基频光光谱; (f) 与图(d)中光场对应的倍频光光谱
Fig. 6. Chaos inside the microresonator, when the value of detuning parameter is too large: (a) Chaos of the fundamental frequency waves; (b) chaos of the second harmonic waves; (c) intensity profile of the fundamental frequency waves in a moment; (d) intensity profile of the second harmonic waves in a moment; (e) spectrum of the fundamental frequency waves; (f) spectrum of the second harmonic waves.
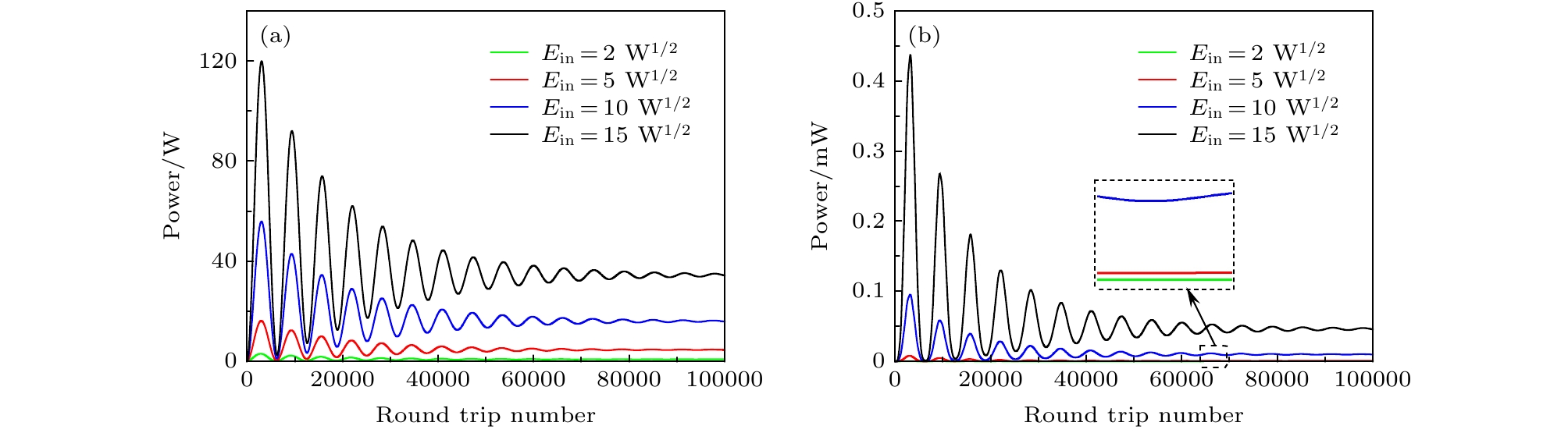
图 8 Ein = 100 W1/2时, 微腔内光场的演化 (a) 基频光功率的变化曲线; (b) 倍频光功率的变化曲线; (c) 光场稳定后, 腔内基频光光场的周期性演化; (d) 光场稳定后, 腔内倍频光光场的周期性演化
Fig. 8. Evolution of the light field in the microresonator at Ein = 100 W1/2: (a) Curve of power variation for the fundamental frequency waves; (b) curve of power variation for the second harmonic waves; (c) periodic evolution of the fundamental frequency waves; (d) periodic evolution of the second harmonic waves.
图 9 基频光和倍频光的功率变化曲线 Ein = 800 W1/2时(a)基频光和(b)倍频光的功率变化; Ein = 1000 W1/2时(c)基频光和(d) 倍频光的功率变化; Ein = 1200 W1/2时(e)基频光和(f)倍频光的功率变化
Fig. 9. Curves of the power variation for the fundamental frequency waves and the second harmonic waves: Power variation for (a) the fundamental frequency waves and (b) the second harmonic waves at Ein = 800 W1/2; power variation for (c) the fundamental frequency waves and (d) the second harmonic waves at Ein = 1000 W1/2; power variation for (e) the fundamental frequency waves and (f) the second harmonic waves at Ein = 1200 W1/2.
图 10 微腔FSR = 300 GHz时, 微腔内出现“图灵环”(Ein = 100 W1/2, δ1 = 0.1) (a)基频光功率变化曲线; (b)倍频光功率变化曲线; (c) 腔内光场稳定后, 基频光光场随时间的演化; (d) 腔内光场稳定后, 倍频光光场随时间的演化; (e) 腔内光场稳定后, 基频光的光谱; (f) 腔内光场稳定后, 倍频光的光谱
Fig. 10. Turning patterns in the microresonator, when FSR = 300 GHz (Ein = 100 W1/2, δ1 = 0.1): (a) Curves of the power variation for the fundamental frequency waves; (b) curves of the power variation for the second harmonic waves; (c) evolution of the fundamental frequency waves; (d) evolution of the second harmonic waves; (e)spectra of the fundamental harmonic waves; (f) spectra of the second harmonic waves.
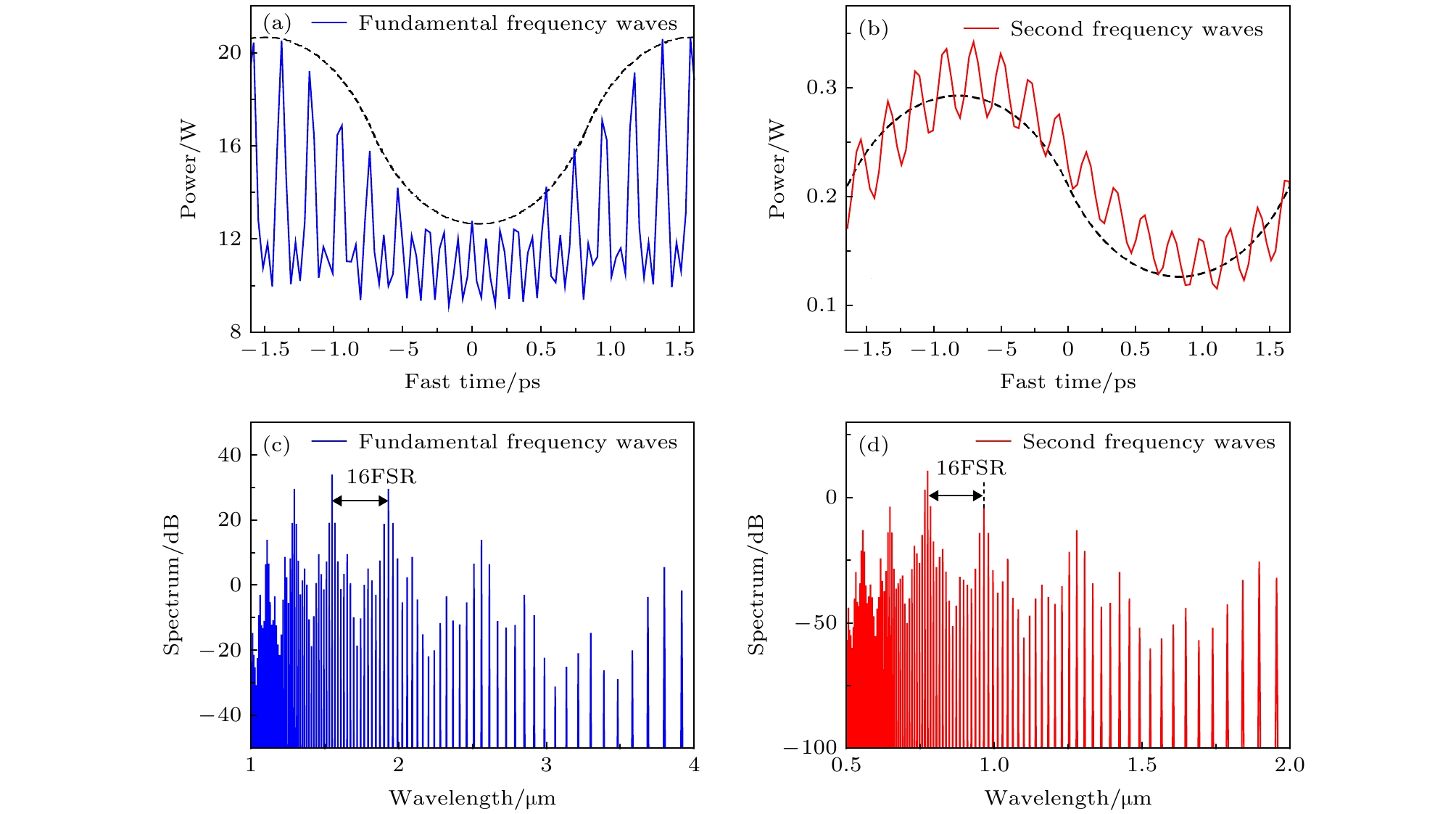
图 11 微腔FSR = 298 GHz时, 稳定后的光场分布及光谱 (a)基频光的光场分布; (b) 倍频光的光场分布; (c) 基频光光谱; (d) 倍频光光谱
Fig. 11. Stable intensity profile and spectra of the fundamental frequency waves for FSR = 298 GHz: (a) Intensity profile of the fundamental frequency waves; (c) spectrum of the fundamental frequency waves; (b) intensity profile of second harmonic waves; (d) spectrum of second harmonic waves.
图 12 微腔FSR = 295 GHz时, 稳定后的基频光和倍频光光场分布及光谱 (a) 基频光光场随时间的演化; (b) 倍频光光场随时间的演化; (c) 基频光场的瞬时分布; (d) 倍频光场的瞬时分布; (e) 基频光场的光谱; (f) 倍频光场的光谱
Fig. 12. Stable intensity profile and spectra of the fundamental frequency waves for FSR = 295 GH: (a) Evolution of the fundamental frequency waves; (b) evolution of the second frequency waves; (c) intensity profile of the fundamental frequency waves; (d) spectrum of the fundamental frequency waves; (e) intensity profile of the second harmonic waves; (f) spectrum of the second harmonic waves.
-
[1] 邢书剑, 张福民, 曹士英, 王高文, 曲兴华 2013 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xing S J, Zhang F M, Cao S Y, Wang G W, Qu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Niering M, Holzwarth R, Reichert J, Pokasov P, Udem T, Weitz M, Hansch T W, Lemonde P, Santarelli G, Abgrall M, Laurent P, Salomon C, Clairon A 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 5496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 孟飞, 曹士英, 蔡岳, 王贵重, 曹建平, 李天初, 方占军 2011 60 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng F, Cao S Y, Cai Y, Wang G Z, Cao J P, Li T C, Fang Z J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Swann W C, McFerran J J, Coddington I, Newbury N R, Hartl I, Fermann M E, Westbrook P S, Nicholson J W, Feder K S, Langrock C, Fejer M M 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3074
[5] Washburn B R, Fox R W, Newbury N R, Nicholson J W, Feder K, Westbrook P S, Jorgensen C G 2004 Opt. Express 12 4999
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 韩海年, 魏志义, 赵刚 2012 物理 41 249
Han H N, Wei Z Y, Zhao G 2012 Physics 41 249
[7] Herr T, Brasch V, Jost J D, Wang C Y, Kondratiev N M, Gorodetsky M L, Kippenberg T J 2013 Nat. Photon. 8 145
[8] Song Q H 2019 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 62 074231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang X Y, Cao Q T, Wang Z, Liu Y X, Qiu C W, Yang L, Gong Q H, Xiao Y F 2019 Nat. Photon. 13 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Godey C, Balakireva I V, Aurélien C, Chembo Y K 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 722
[11] Huang S W, Zhou H, Yang J, McMillan J F, Matsko A, Yu M, Kwong D L, Maleki L, Wong C W 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 053901
[12] Wang W Q, Lu Z Z, Zhang W F, Chu Sai T, Little B E, Wang L R, Xie X P, Liu M L, Yang Q H, Wang L, Zhao J G, Wang G X, Sun Q B, Liu Y S, Wang Y S, Zhao W 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 2002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xue X X, Xuan Y, Liu Y, Wang P H, Chen S, Wang J, Leaird D E, Qi M H, Weiner A M 2015 Nat. Photon. 9 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Coillet A, Balakireva I, Henriet R, Saleh K, Larger L, Dudley J M, Menyuk C R, Chembo Y K 2013 IEEE Photon. J. 5 6100409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Matsko A B, Liang W, Savchenkov A A, Maleki L 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Coen S, Randle H G, Sylvestre T, Erkintalo M 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xue X X, Leo F, Xuan Y, Villegas J A J, Wang P H, Leaird D E, Erkintalo M, Qi M H, Weiner Andrew M 2017 Light: Sci. Appl. 6 e16253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lin J T, Xu Y X, Ni J L, Wang M, Fang Z W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Cheng Y 2016 Phys. Rev. Appl. 6 014002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chembo Y K, Menyuk C R, 2014 Phys. Rev. A 87 053852
[20] Lin J T, Xu Y X, Fang Z W, Wang M, Song J X, Wang N W, Qiao L L, Fang W, Cheng Y 2015 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58 114209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Coen S, Haelterman M 2001 Opt. Lett. 26 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] And T, Boccaletti A, Grebogi C, Lai Y C, Mancini H, Maza D 2000 Phys. Rep. 329 2000
[23] Akhmediev N, Pelinovsky E 2010 Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 185 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11213
- PDF下载量: 181
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: