-
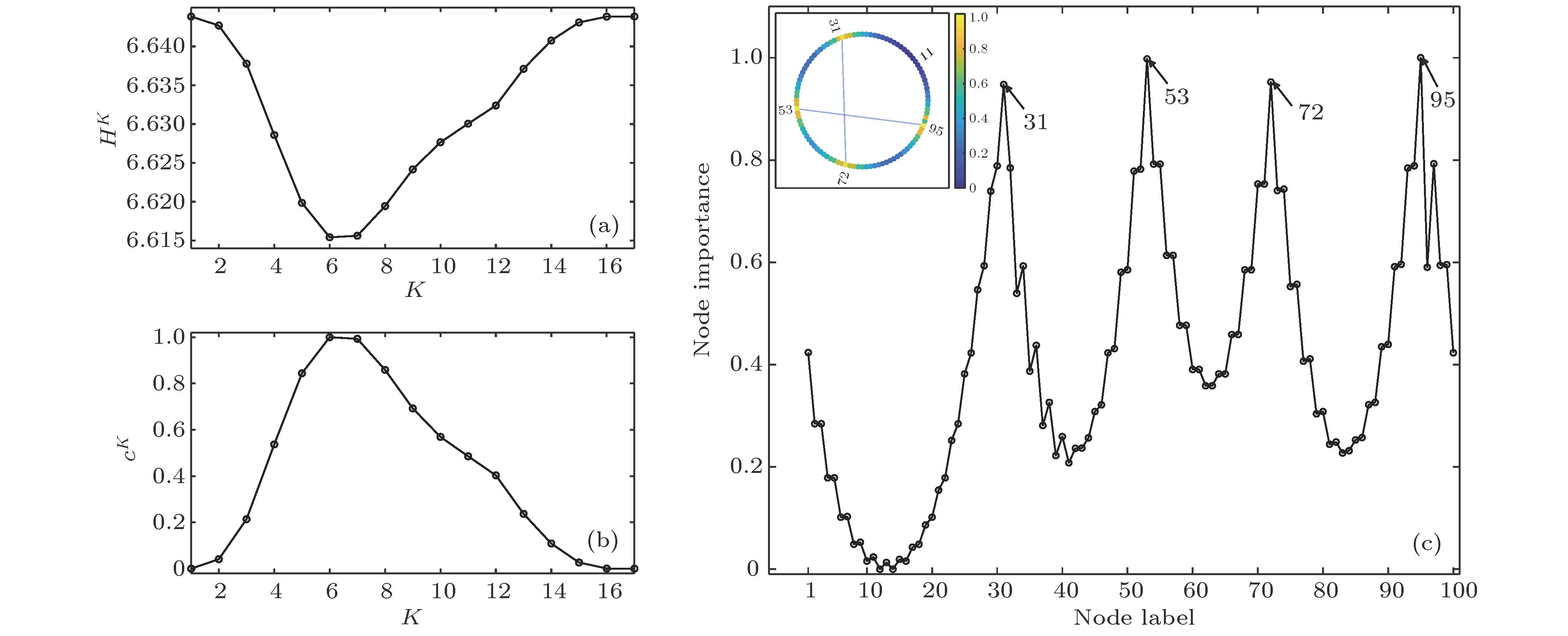
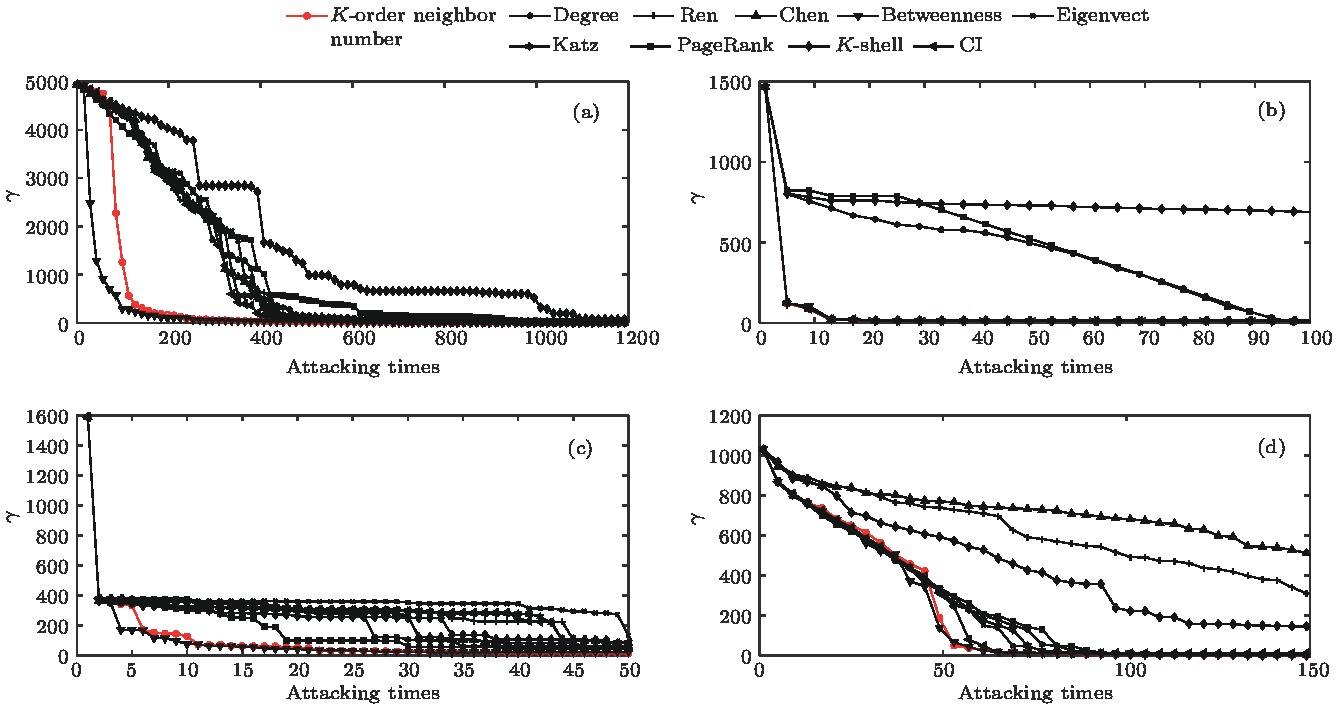
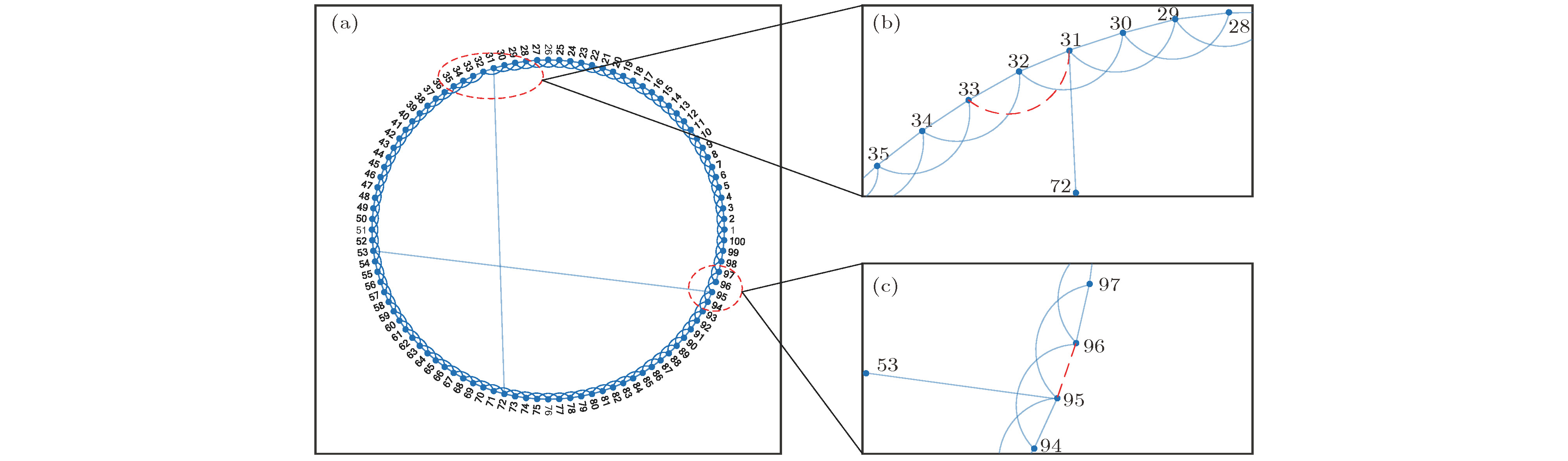
节点重要性对于分析网络结构具有重要意义. 为了充分刻画网络全局和局部特性, 本研究基于网络拓扑结构对疾病传播过程进行了抽象, 分别设置各个节点为传染源, 在经历传播时长K后, 将网络中已感染节点的数量定义为K-阶传播数, 最终基于不同K值下的K-阶传播数得到节点重要性结果. 对Watts-Strogatz小世界网络和海豚网络的仿真实验表明, 加权K-阶传播数法对节点重要性的评估较其他方法更为合理, 能够细致地刻画小世界网络中长程连接对信息传输的影响, 提高海豚网络中对社区交流起关键作用的节点的重视程度. 本文利用蓄意攻击策略对美国西部电网、芝加哥公路网络、网络科学家合著网络以及小鼠神经纤维束网络进行了研究, 即依照节点重要性由高到低的排序依次攻击网络. 结果显示, 相较于其他方法, 基于加权K-阶传播数法仅需移除少量重要节点便可实现对网络结构的充分破坏.The measurement of node importance is significant for analyzing a network structure. To comprehensively reflect the global and local network features, in this paper we abstract the propagating process of epidemic diseases based on the network topology structure, and then respectively sets each node as an infection source. After a certain dissemination time K, the number of infected nodes in the network is defined as the K-order propagation number, and the weighted sum of K-order propagation numbers under different values of K is taken as the important index of nodes. The simulation experiments of Watts-Strogatz small-world networks and a dolphin network show that the weighted K-order propagation number algorithm is more effective than the traditional method in evaluating the importance of nodes. For the Watts-Strogatz small-world networks, it can reflect the influence of long-distance connections on information transmission in detail. For the dolphin network, the weighted K-order propagation number algorithm significantly raises the profile of those nodes which play a key role in the information communication between different dolphin communities. In addition, in this paper we use a deliberate attacking method to analyze the western power grid of the United States, the road transportation network of the Chicago region, the co-authorship network in network science and the axonal tracts’ network between neurons of mouse. According to the specific order of the node importance from high to low, network nodes are attacked in turn, that is, all edges of the attacked nodes are removed. The analysis results of network parameters such as the network efficiency and the node number of the maximum sub-graph changing with the attacking times show that comparing with other evaluation indices of node importance such as degree, Ren method, Chen method, eigenvector method, Katz index, PageRank, CI method and K-shell, the weighted K-order propagation number algorithm focuses much on destroying the major structure, and all of the above four networks will break down if only a small number of important nodes are attacked. For example, after attacking only 100 nodes, the network efficiency of the western power grid of the United States is down by 90%, and after attacking 200 nodes, the network scale of the maximum sub-graph is nearly 3% of the original network.
-
Keywords:
- complex network /
- node importance /
- propagation model
[1] 周漩, 张凤鸣, 周卫平, 邹伟, 杨帆 2012 61 190201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou X, Zhang F M, Zhou W P, Zhou W, Yang F 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 190201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 周涛, 柏文洁, 汪秉宏, 刘之景, 严钢 2005 物理 34 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou T, Bai W J, Wang B H, Liu Z J, Yan G 2005 Physics 34 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu J G, Wang Z T, Dang Y Z 2005 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 19 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2006 复杂网络理论及其应用 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第8页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2006 Complex Network Theory and Application (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) p8 (in Chinese)
[5] Dunne J A, Williams R J, Martinez N D 2002 Ecol. Lett. 5 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Samant K, Bhattacharyya S 2004 Proceedings of the 37th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences Washington, USA, January 5–8, 2004 p289
[7] Newman M E J, Forrest S, Balthrop A 2002 Phys. Rev. E 66 035101
[8] Jeong H, Mason S, Barabasi A L 2001 Nature 411 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 任卓明, 邵凤, 刘建国, 郭强, 汪秉宏 2013 62 128901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren Z M, Shao F, Liu J G, Guo Q, Wang B H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 128901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen D B, Lü L Y, Shang M S, Zhang Y C, Zhou T 2012 Physica A 391 1777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sabidussi G 1966 Psyehometrika 31 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bavelas A 1950 J. Acoustical Soc. Amer. 22 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Stephenson K, Zelen M 1989 Soc. Netw. 1 11
[15] Borgatti S P 2005 Soc. Netw. 27 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Katz L 1953 Psychometrika 18 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang J, Xu X K, Li P, Zhang K, Small M 2011 Chaos 21 016107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zeng A, Zhang C J 2013 Phys. Lett. A 377 1031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bryan K, Leise T 2006 SIAM Rev. 48 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lü L Y, Zhang Y C, Yeung C H, Zhou T 2011 PLoS One 6 e 2120 2
[22] Zhong L F, Liu Q H, Wang W, Cai S M 2018 Physica A 511 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Allen L J S 1994 Math. Biosci. 124 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 黄丽亚, 霍宥良, 王青, 成谢锋 2019 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L Y, Huo Y L, Wang Q, Cheng X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau O J, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson S M 2003 Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lusseau D, Newman M E J 2004 Proc. Biol. Sci. 271 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Eash R W, Chon K S, Lee Y J, Boyce D E 1983 Transport. Res. Rec. 994 30
[29] Newman M E J 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ryan A R, Nesreen K A 2015 Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Austin, Texas, January 25–30, 2015 p4292
[31] 李鹏翔, 任玉晴, 席酉民 2004 系统工程 22 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li P X, Ren Y Q, Xi Y M 2004 Syst. Eng. 22 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 赫南, 李德毅, 淦文燕, 朱熙 2007 计算机科学 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He N, Li D Y, Gan W Y, Zhu X 2007 Comput. Sci. 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 赵志远, 孟相如, 孙瑞男 2018 计算机工程 44 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Z Y, Meng X R, Sun R N 2018 Comput. Eng. 44 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 基于若干传统算法的WS小世界网络节点重要性评价结果 (a) 度中心性; (b) Ren法; (c) Chen法; (d) 介数中心性; (e) 特征向量法; (f) Katz指标法; (g) PageRank算法; (h) CI法
Fig. 3. Node importance of the WS small-world network based on some traditional algorithms: (a) Degree centrality; (b) Ren method; (c) Chen method; (d) betweenness centrality; (e) eigenvector method; (f) Katz index; (g) PageRank; (h) CI method.
图 5 K-阶结构熵 (a) 美国西部电网; (b) 芝加哥公路网络; (c) 科学家合作网络; (d) 小鼠神经纤维束网络
Fig. 5. The K-order structure entropy: (a) The western power grid of the United States; (b) the road transportation network of the Chicago region; (c) the co-authorship network in network science; (d) the axonal tracts network between neurons of mouse.
图 6 网络效率下降率ε随攻击次数的变化情况 (a) 美国西部电网; (b) 芝加哥公路网络; (c) 网络科学家合著网络; (d) 小鼠神经纤维束网络
Fig. 6. Change of the network efficiency decrease rate ε with attacking times: (a) The western power grid of the United States; (b) the road transportation network of the Chicago region; (c) the co-authorship network in network science; (d) the axonal tracts network between neurons of mouse.
图 7 最大子图节点数γ随攻击次数的变化情况 (a) 美国西部电网; (b) 芝加哥公路网络; (c) 网络科学家合著网络; (d) 小鼠神经纤维束网络
Fig. 7. Change of the node number of the maximum sub-graph ε with attacking times: (a) The western power grid of the United States; (b) the road transportation network of the Chicago region; (c) the co-authorship network in network science; (d) the axonal tracts network between neurons of mouse.
表 1 WS小世界网络以及同规模随机网络的网络参数
Table 1. Network features of the WS small-world network and random networks.
网络类型 节点数 边数 平均聚类
系数特征路径
长度WS小世界网络 100 200 0.486 8.4891 随机网络 100 200 0.0254 3.4158 表 2 海豚网节点重要性排序结果
Table 2. Node importance ordering result of the dolphin network.
节点重要性 加权K-阶传播数法 Ren法 Chen法 介数中心性法 特征向量法 Katz指标法 PageRank算法 CI法 1 15 15 15 37 15 15 15 15 2 38 38 38 2 38 38 18 38 3 46 46 46 41 46 46 52 46 4 21 34 34 38 34 34 58 34 5 41 51 51 8 51 52 38 41 6 34 41 41 18 30 30 46 30 7 37 21 17 21 52 41 34 52 8 30 30 22 55 17 21 30 21 9 52 52 19 52 41 51 14 51 10 51 44 30 58 22 39 2 19 11 2 39 21 40 19 19 21 39 12 39 19 25 29 39 17 39 17 13 19 37 39 30 25 22 10 22 14 44 22 52 44 44 44 41 44 15 9 18 44 15 21 25 55 25 -
[1] 周漩, 张凤鸣, 周卫平, 邹伟, 杨帆 2012 61 190201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou X, Zhang F M, Zhou W P, Zhou W, Yang F 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 190201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 周涛, 柏文洁, 汪秉宏, 刘之景, 严钢 2005 物理 34 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou T, Bai W J, Wang B H, Liu Z J, Yan G 2005 Physics 34 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu J G, Wang Z T, Dang Y Z 2005 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 19 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2006 复杂网络理论及其应用 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第8页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2006 Complex Network Theory and Application (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) p8 (in Chinese)
[5] Dunne J A, Williams R J, Martinez N D 2002 Ecol. Lett. 5 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Samant K, Bhattacharyya S 2004 Proceedings of the 37th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences Washington, USA, January 5–8, 2004 p289
[7] Newman M E J, Forrest S, Balthrop A 2002 Phys. Rev. E 66 035101
[8] Jeong H, Mason S, Barabasi A L 2001 Nature 411 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 任卓明, 邵凤, 刘建国, 郭强, 汪秉宏 2013 62 128901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren Z M, Shao F, Liu J G, Guo Q, Wang B H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 128901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen D B, Lü L Y, Shang M S, Zhang Y C, Zhou T 2012 Physica A 391 1777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sabidussi G 1966 Psyehometrika 31 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bavelas A 1950 J. Acoustical Soc. Amer. 22 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Stephenson K, Zelen M 1989 Soc. Netw. 1 11
[15] Borgatti S P 2005 Soc. Netw. 27 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Katz L 1953 Psychometrika 18 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang J, Xu X K, Li P, Zhang K, Small M 2011 Chaos 21 016107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zeng A, Zhang C J 2013 Phys. Lett. A 377 1031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bryan K, Leise T 2006 SIAM Rev. 48 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lü L Y, Zhang Y C, Yeung C H, Zhou T 2011 PLoS One 6 e 2120 2
[22] Zhong L F, Liu Q H, Wang W, Cai S M 2018 Physica A 511 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Allen L J S 1994 Math. Biosci. 124 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 黄丽亚, 霍宥良, 王青, 成谢锋 2019 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L Y, Huo Y L, Wang Q, Cheng X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau O J, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson S M 2003 Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lusseau D, Newman M E J 2004 Proc. Biol. Sci. 271 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Eash R W, Chon K S, Lee Y J, Boyce D E 1983 Transport. Res. Rec. 994 30
[29] Newman M E J 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ryan A R, Nesreen K A 2015 Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Austin, Texas, January 25–30, 2015 p4292
[31] 李鹏翔, 任玉晴, 席酉民 2004 系统工程 22 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li P X, Ren Y Q, Xi Y M 2004 Syst. Eng. 22 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 赫南, 李德毅, 淦文燕, 朱熙 2007 计算机科学 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He N, Li D Y, Gan W Y, Zhu X 2007 Comput. Sci. 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 赵志远, 孟相如, 孙瑞男 2018 计算机工程 44 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Z Y, Meng X R, Sun R N 2018 Comput. Eng. 44 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 23075
- PDF下载量: 134
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: