-
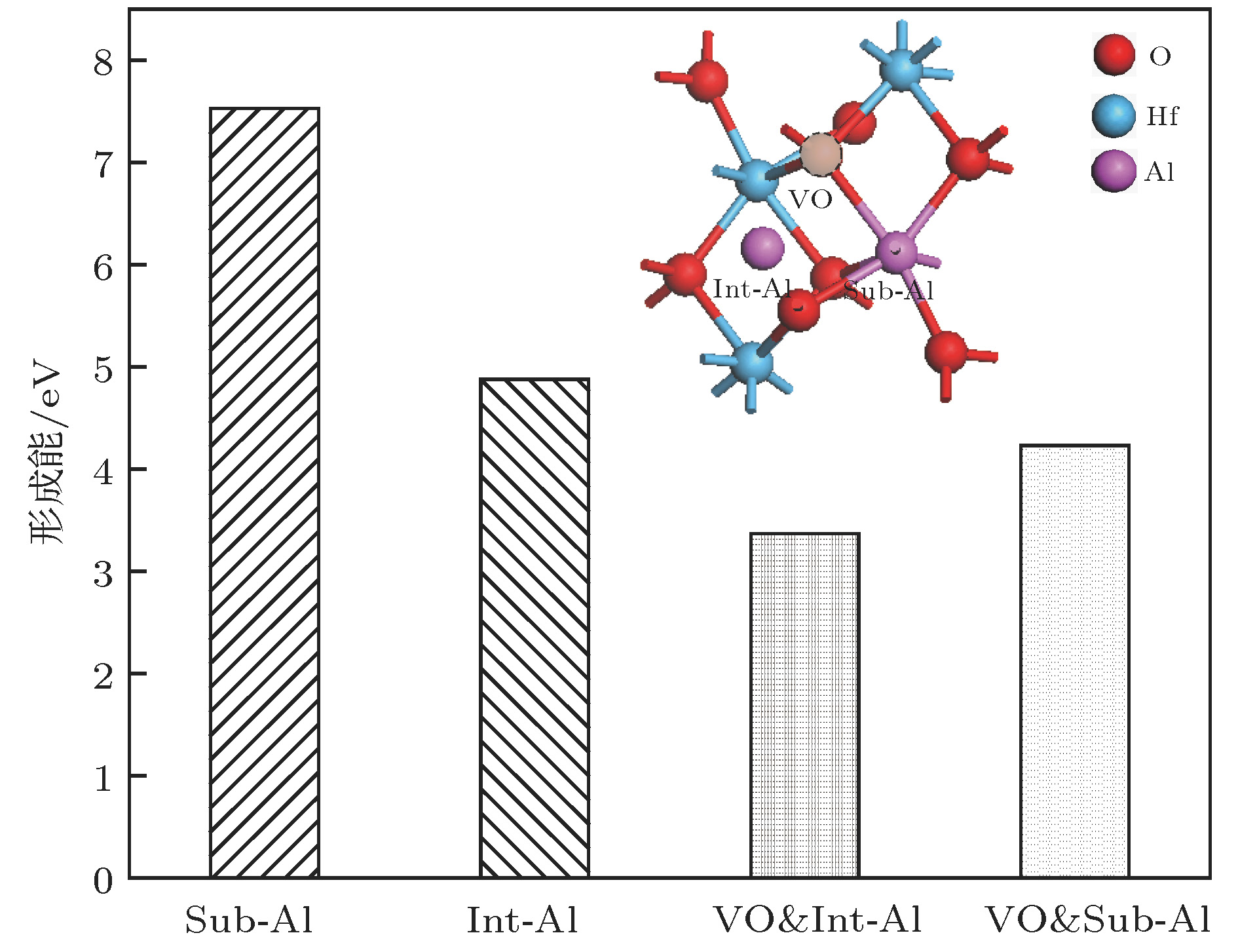
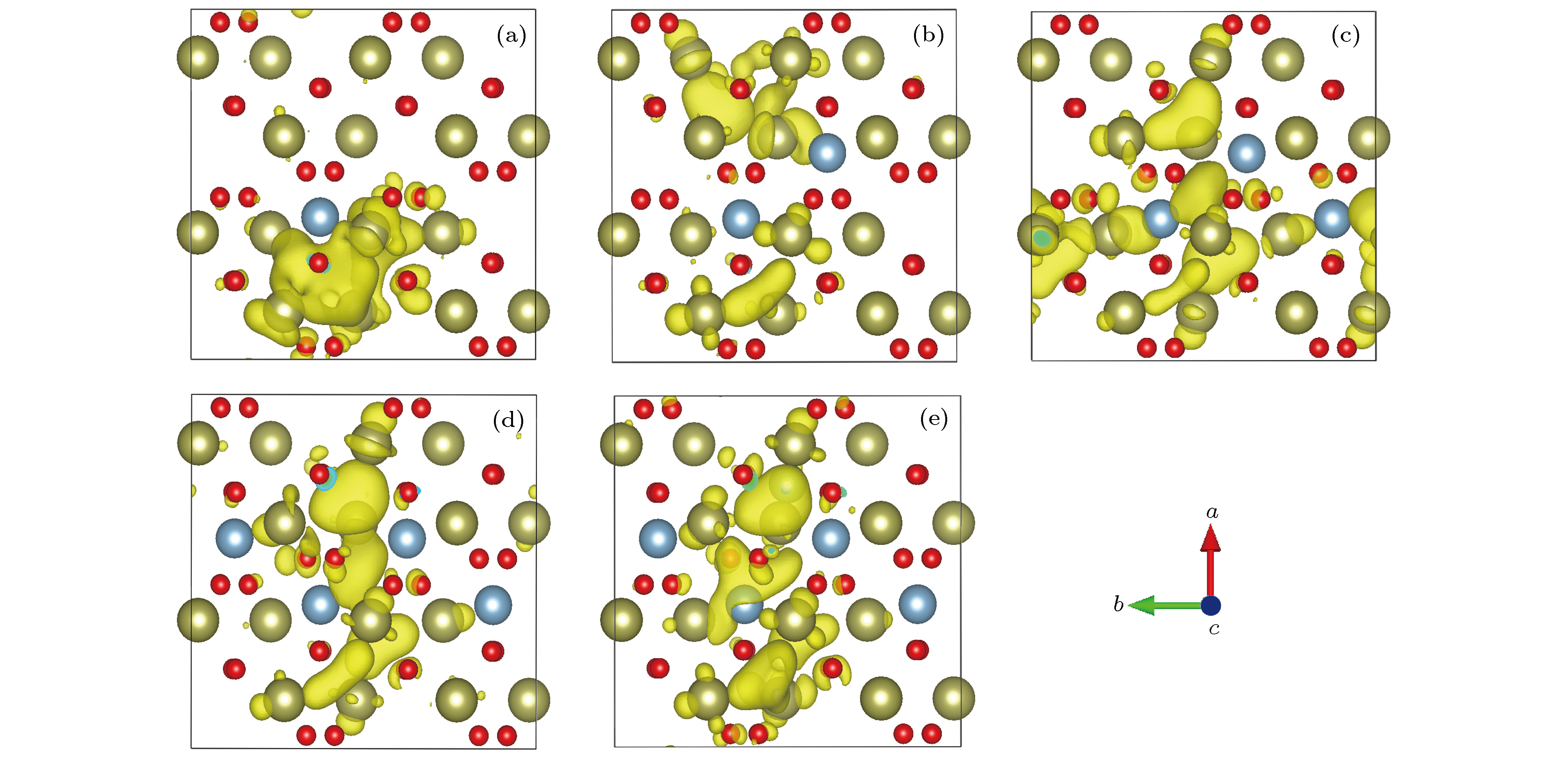
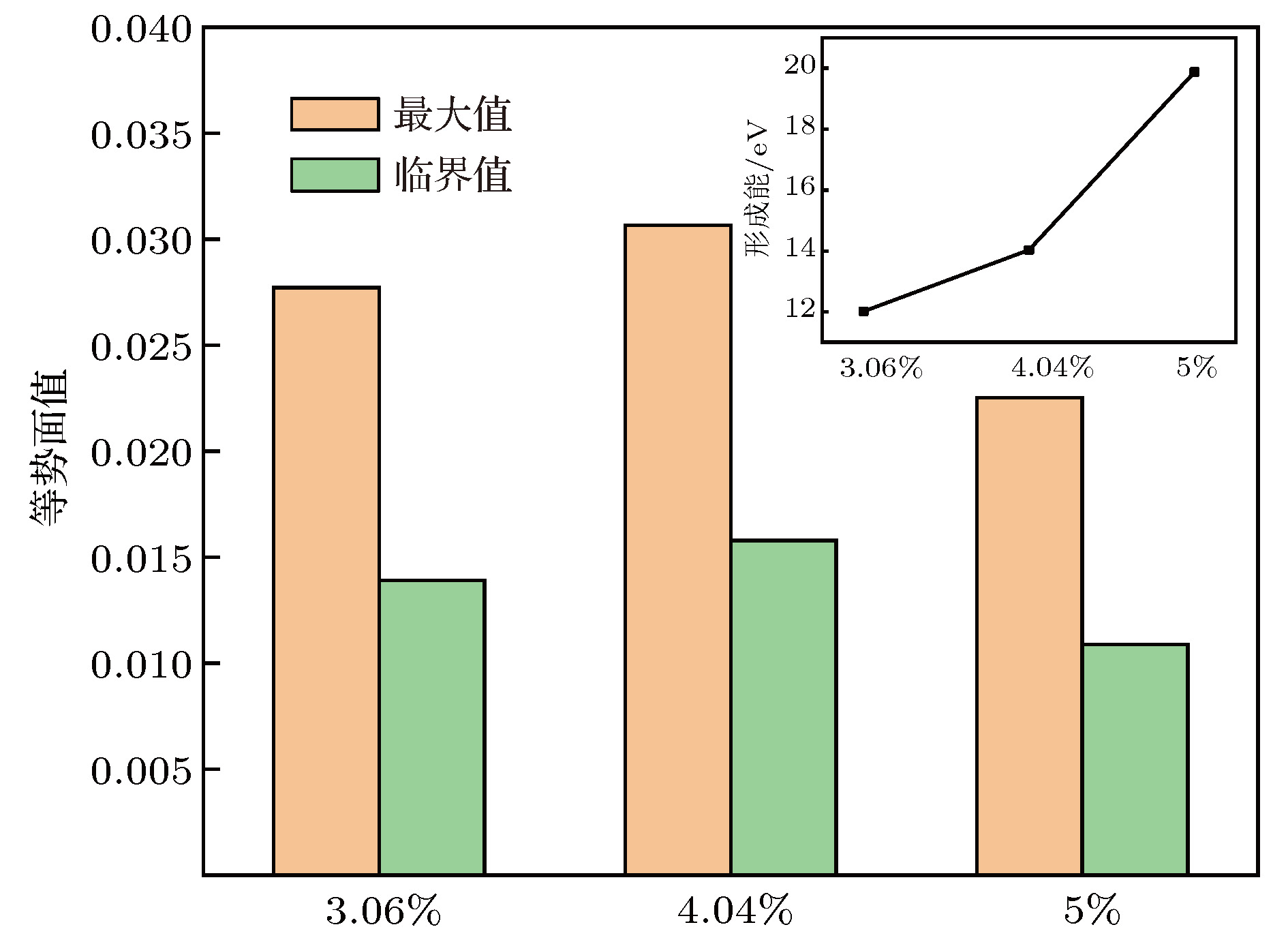
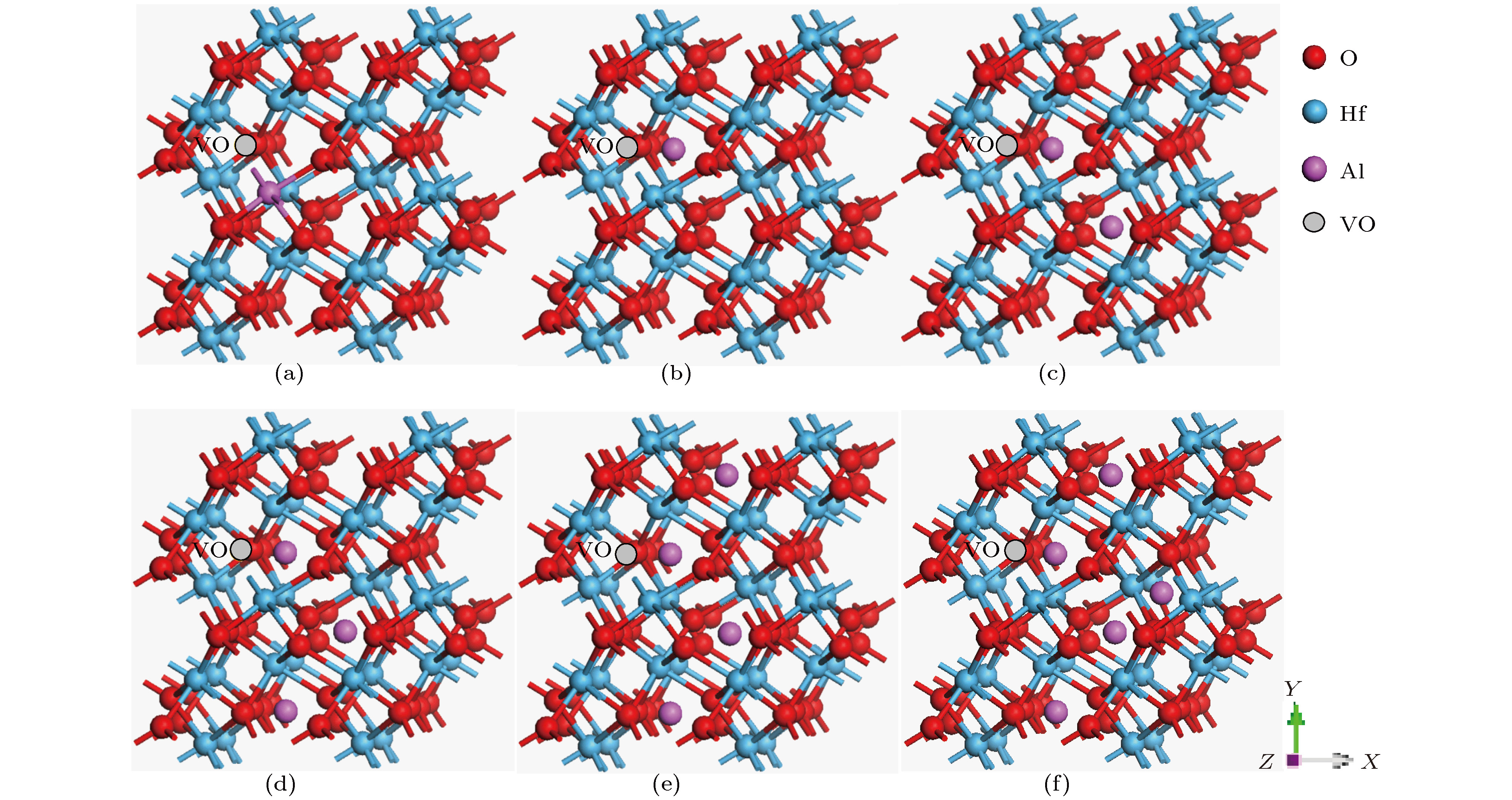
为了改善HfO2的阻变特性, 提高氧空位(VO)导电细丝形成的一致性和均匀性, 采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算方法研究了掺杂Al的HfO2阻变材料的微观特性. 结果表明, 间隙Al (Int-Al)更适合掺入到HfO2中, 并且Int-Al与VO相对位置越近, 阻变材料趋于稳定的收敛速度越快, 形成能越小. 不同Int-Al浓度对含有VO缺陷的HfO2超胞的影响结果显示, 当掺杂Int-Al浓度为4.04%时, 分波电荷态密度图能够形成相对较好的电荷通道, 最大等势面和临界等势面值均为最高, 有利于改善HfO2阻变材料中导电细丝形成的一致性和均匀性; 形成能计算结果显示, 当Int-Al浓度低于4.04%时形成能变化缓慢, 当高于4.04%时则异常增大, 表明缺陷体系随Int-Al浓度增大越来越难以形成; 进一步研究掺杂Int-Al浓度为4.04%时晶格结构的变化, 结果显示缺陷形成能显著降低, 有利于形成完美的导电通道. 该研究为改善基于HfO2阻变存储材料的性能有一定的借鉴意义.
In order to improve the resistance properties of HfO2 and increase the consistency and uniformity of conductive filaments formed by oxygen vacancies (VO), the first-principles calculation method based on density functional theory is used to study the micro-properties of Al-doped HfO2 resistive materials. The results show that the interval Al (Int-Al) is more suitable for being incorporated into HfO2, and the closer to the relative position of VO the Int-Al, the faster the convergence rate of the resistive material tends to be stable, and the smaller the formation energy. The effects of different Int-Al concentrations on the formation of HfO2 supercells with VO defects show that when the concentration of doped Int-Al is 4.04%, the fractional charge state density map can form relatively good charge channels. The maximum and critical equipotential surface values are highest, which is conducive to improving the consistency and uniformity of the formation of conductive filaments in HfO2 resistive materials. The calculation of energy formation shows that the change is slow when the concentration of Int-Al is lower than 4.04%. When the concentration of Int-Al is higher than 4.04%, the abnormal increase occurs, which indicates that the defect system becomes more and more difficult to form with the increase of the concentration of Int-Al. The introduction of the impurity and the VO defect destroy the original complete crystal structure, which causes the position of the atoms around the impurity to shift, and the valence electron orbit and the energy level of the crystal are changed, and the distribution of the internal charges of the HfO2 defect system is affected. In order to study the effect of the change of the lattice structure on the formation of the VO conductive filament, the VASP software package is used to calculate the relative ratio of the atoms in the lattice structure of the HfO2 defect system as the reference and the relative ratio of the HfO2 defect system after the optimizing the lattice structure. Further study of the change of lattice structure, when the concentration of doped Int-Al is 4.04%, shows that the defect formation energy decreases significantly, which is conducive to the formation of perfect conductive channel. The conductive channel has a certain reference significance for improving the performance of HfO2 based resistive variable memory materials. -
Keywords:
- HfO2 /
- first principles /
- interval Al /
- lattice structure
[1] 赵强 2013 硕士学位论文 (安徽: 安徽大学)
Zhao Q 2013 M. S. Thesis (Anhui: Anhui University) (in Chinese)
[2] 张文博, 王华, 许积文, 刘国保, 谢航, 杨玲 2018 材料导报 32 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W B, Wang H, Xu J W, Liu G B, Xie H, Yang L 2018 Mater. Rev. 32 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 杨龙康 2014 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Yang L K 2014 M. S. Thesis (Xian: Xi'an University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[4] 王源, 贾嵩, 甘学温 2011 北京大学学报 47 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Jia S, Gan X W 2011 Acta Sci. Natur. Univ. Pekinensis 47 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Frascaroli J, Volpe F G, Brivio S, Spiga S 2015 Microelectron. Eng. 147 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hou T H, Lin K L, Shieh J, Lin J H, Chou C T, Lee Y J 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 771
[7] 李晓燕, 李颖弢, 高晓平, 陈传兵, 韩根亮 2018 科学通报 63 2954
Li X Y, Li Y T, Gao X P, Chen C B, Han G L 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 63 2954
[8] 郭家俊, 董静雨, 康鑫, 陈伟, 赵旭 2018 67 063101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo J J, Dong J Y, Kang X, Chen W, Zhao X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 063101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 殷一民, 程海峰, 刘东青, 张朝阳 2016 电子元件与材料 35 9
Yin Y M, Cheng H F, Liu D Q, Zhang Z Y 2016 Electron. Compon. Mater. 35 9
[10] 张志超, 王芳, 吴仕剑, 李毅, 弭伟, 赵金石, 张楷亮 2018 67 057301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z C, Wang F, Wu S J, Li Y, Mi W, Zhao J S, Zhang K L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 057301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张颖, 龙世兵, 刘明 2017 物理 46 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Long S B, Liu M 2017 Physics 46 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 赵远洋 2015 硕士学位论文 (安徽: 安徽大学)
Zhao Y Y 2015 M. S. Thesis (Anhui: Anhui University) (in Chinese)
[13] Xue K H, Blaise P, Fonseca L R C, Nishi Y 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 065502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘森, 刘琦 2016 国防科技 37 4
Liu S, Liu Q 2016 Natl. Def. Sci. Technol. 37 4
[15] Wang Z, Zhu W G, Du A Y, Wu L, Fang Z, Tran X A 2012 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59 1203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wei W, Chuai X, Lu N, Wang Y, Li M, Ye C, Liu M 2017 International Conference on Simulation of Semiconductor Processes and Devices Kamakura, Japan, September 7−9, 2017 p21
[17] Magyari-Köpe B, Dan D, Liang Z, Nishi Y 2016 International Symposium on Vlsi Technology, Systems and Application Hsinchu, Taiwan, April 25−27, 2016 p1
[18] Yang J, Dai Y, Lu S, Jiang X, Wang F, Chen J 2017 J. Semicond. 38 100
[19] Zhao Q, Zhou M X, Zhang W, Liu Q, Li X F, Liu M, Dai Y H 2013 J. Semicond. 34 032001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wei X D, Huang H, Ye C, Wei W, Zhou H, Chen Y, Zhang R L, Zhang L, Xia Q 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 775 1301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 代广珍, 罗京, 汪家余, 杨金, 蒋先伟, 刘琦, 代月花, 陈军宁 2014 功能材料 45 15023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai G Z, Luo J, Wang J Y, Yang J, Jiang X W, Liu Q, Dai Y H, Chen J N 2014 J. Funct. Mater. 45 15023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Alayan M, Vianello E, Padovani A, Salvo B D, Larcher L, Perniola L 2017 IEEE Des. Test 34 23
[23] Gao B, Zhang H W, Yu S, Sun B, Liu L F, Liu X Y, Wang Y, Han R Q, Kang J F, Yu B, Wang Y Y 2009 Vlsi Technology Symposium on Kamakura Japan, September 7-9, 2009 p30
[24] 杨金 2014 博士学位论文 (安徽: 安徽大学)
Yang J 2014 Ph. D. Dissertation (Anhui: Anhui University) (in Chinese)
[25] Xie H W, Wang M, Kurunczi P, Erokhin Y, Liu Q, Lv H B, Li Y T, Long S B, Liu S, Liu M 2012 Am. Inst. Phys. 1496 26
[26] Zhang H, Liu L, Gao B, Qiu Y 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 093509
[27] Tan T T, Gao A, Zha G Q 2018 Superlattices Microstruct. 121 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhao L, Clima S, Magyariköpe B, Jurczak M, Nishi Y 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 013504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李丛飞, 傅兴华, 李良荣, 赵海臣 2014 微纳电子技术 51 24
Li C F, Fu X H, Li L R, Zhao H C 2014 Micronanoelectronic Technol. 51 24
[30] Lu L, Liu Y H, Dai G Z, Zhang Y, Ding G G, Liu Q 2018 Optik 164 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 代广珍, 蒋先伟, 徐太龙, 刘琦, 陈军宁, 代月花 2015 64 033101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai G Z, Jiang X W, Xu T L, Liu Q, Chen J N, Dai Y H 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 033101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 庞华, 邓宁 2014 63 147301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pang H, Deng N 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 147301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 罗岚, 熊志华, 周耐根 2016 材料导报 30 149
Luo L, Xiong Z H, Zhou N G 2016 Mater. Rev. 30 149
[34] 蒋先伟, 陈军宁, 金波, 王菲菲, 鲁世斌 2016 合肥工业大学学报 39 934
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X W, Chen J N, Jin B, Wang F F, Lu S B 2016 J. Hefei Univ. Tech. 39 934
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 汪家余, 赵远洋, 徐建彬, 代月花 2014 63 053101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J Y, Zhao Y Y, Xu J B, Dai Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 053101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 蒋先伟, 鲁世斌, 代广珍, 汪家余, 金波, 陈军宁 2015 64 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X W, Lu S B, Dai G Z, Wang J Y, Jin B, Chen J N 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] 代月花, 潘志勇, 陈真, 王菲菲, 李宁, 金波, 李晓风 2016 65 073101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Y H, Pan Z Y, Chen Z, Wang F F, Li N, Jin B, Li X F 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 073101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhang H W, Gao B, Yu S M, Lai L, Zeng L, Sun B, Liu L F, Liu X Y, Lu J, Han R Q, Kang J F 2009 International Conference on Simulation of Semiconductor Processes & Devices San Diego, California, September 9−11, 2009 p155
[39] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Comput. Mater. Sci. 6 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 贾晓伟, 王敏 2018 材料导报 32 500
Jia X W, Wang M 2018 Mater. Rev. 32 500
[41] 李春萍, 陈鑫, 张宝林 2015 材料导报 39 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C P, Chen X, Zhang B L 2015 Mater. Rev. 39 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 侯清玉, 赵春旺, 李继军, 王钢 2011 60 047104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou Q Y, Zhao C W, Li J J, Wang G 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 047104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Dai Y H, Zhao Y Y, Wang J Y, Xu J B, Yang F 2015 AIP Adv. 5 017133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Zhao Y Y, Wang J Y, Xu J B, Yang F, Liu Q, Dai Y H 2014 J. Semicond. 35 25
[45] 蒋先伟, 代广珍, 鲁世斌, 汪家余, 代月花, 陈军宁 2015 64 091301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X W, Dai G Z, Lu S B, Wang J Y, Dai Y H, Chen J N 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 091301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 m-HfO2晶格参数
Table 1.
m-HfO2 lattice constants. -
[1] 赵强 2013 硕士学位论文 (安徽: 安徽大学)
Zhao Q 2013 M. S. Thesis (Anhui: Anhui University) (in Chinese)
[2] 张文博, 王华, 许积文, 刘国保, 谢航, 杨玲 2018 材料导报 32 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W B, Wang H, Xu J W, Liu G B, Xie H, Yang L 2018 Mater. Rev. 32 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 杨龙康 2014 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Yang L K 2014 M. S. Thesis (Xian: Xi'an University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[4] 王源, 贾嵩, 甘学温 2011 北京大学学报 47 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Jia S, Gan X W 2011 Acta Sci. Natur. Univ. Pekinensis 47 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Frascaroli J, Volpe F G, Brivio S, Spiga S 2015 Microelectron. Eng. 147 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hou T H, Lin K L, Shieh J, Lin J H, Chou C T, Lee Y J 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 771
[7] 李晓燕, 李颖弢, 高晓平, 陈传兵, 韩根亮 2018 科学通报 63 2954
Li X Y, Li Y T, Gao X P, Chen C B, Han G L 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 63 2954
[8] 郭家俊, 董静雨, 康鑫, 陈伟, 赵旭 2018 67 063101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo J J, Dong J Y, Kang X, Chen W, Zhao X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 063101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 殷一民, 程海峰, 刘东青, 张朝阳 2016 电子元件与材料 35 9
Yin Y M, Cheng H F, Liu D Q, Zhang Z Y 2016 Electron. Compon. Mater. 35 9
[10] 张志超, 王芳, 吴仕剑, 李毅, 弭伟, 赵金石, 张楷亮 2018 67 057301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z C, Wang F, Wu S J, Li Y, Mi W, Zhao J S, Zhang K L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 057301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张颖, 龙世兵, 刘明 2017 物理 46 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Long S B, Liu M 2017 Physics 46 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 赵远洋 2015 硕士学位论文 (安徽: 安徽大学)
Zhao Y Y 2015 M. S. Thesis (Anhui: Anhui University) (in Chinese)
[13] Xue K H, Blaise P, Fonseca L R C, Nishi Y 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 065502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘森, 刘琦 2016 国防科技 37 4
Liu S, Liu Q 2016 Natl. Def. Sci. Technol. 37 4
[15] Wang Z, Zhu W G, Du A Y, Wu L, Fang Z, Tran X A 2012 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59 1203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wei W, Chuai X, Lu N, Wang Y, Li M, Ye C, Liu M 2017 International Conference on Simulation of Semiconductor Processes and Devices Kamakura, Japan, September 7−9, 2017 p21
[17] Magyari-Köpe B, Dan D, Liang Z, Nishi Y 2016 International Symposium on Vlsi Technology, Systems and Application Hsinchu, Taiwan, April 25−27, 2016 p1
[18] Yang J, Dai Y, Lu S, Jiang X, Wang F, Chen J 2017 J. Semicond. 38 100
[19] Zhao Q, Zhou M X, Zhang W, Liu Q, Li X F, Liu M, Dai Y H 2013 J. Semicond. 34 032001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wei X D, Huang H, Ye C, Wei W, Zhou H, Chen Y, Zhang R L, Zhang L, Xia Q 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 775 1301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 代广珍, 罗京, 汪家余, 杨金, 蒋先伟, 刘琦, 代月花, 陈军宁 2014 功能材料 45 15023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai G Z, Luo J, Wang J Y, Yang J, Jiang X W, Liu Q, Dai Y H, Chen J N 2014 J. Funct. Mater. 45 15023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Alayan M, Vianello E, Padovani A, Salvo B D, Larcher L, Perniola L 2017 IEEE Des. Test 34 23
[23] Gao B, Zhang H W, Yu S, Sun B, Liu L F, Liu X Y, Wang Y, Han R Q, Kang J F, Yu B, Wang Y Y 2009 Vlsi Technology Symposium on Kamakura Japan, September 7-9, 2009 p30
[24] 杨金 2014 博士学位论文 (安徽: 安徽大学)
Yang J 2014 Ph. D. Dissertation (Anhui: Anhui University) (in Chinese)
[25] Xie H W, Wang M, Kurunczi P, Erokhin Y, Liu Q, Lv H B, Li Y T, Long S B, Liu S, Liu M 2012 Am. Inst. Phys. 1496 26
[26] Zhang H, Liu L, Gao B, Qiu Y 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 093509
[27] Tan T T, Gao A, Zha G Q 2018 Superlattices Microstruct. 121 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhao L, Clima S, Magyariköpe B, Jurczak M, Nishi Y 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 013504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李丛飞, 傅兴华, 李良荣, 赵海臣 2014 微纳电子技术 51 24
Li C F, Fu X H, Li L R, Zhao H C 2014 Micronanoelectronic Technol. 51 24
[30] Lu L, Liu Y H, Dai G Z, Zhang Y, Ding G G, Liu Q 2018 Optik 164 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 代广珍, 蒋先伟, 徐太龙, 刘琦, 陈军宁, 代月花 2015 64 033101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai G Z, Jiang X W, Xu T L, Liu Q, Chen J N, Dai Y H 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 033101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 庞华, 邓宁 2014 63 147301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pang H, Deng N 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 147301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 罗岚, 熊志华, 周耐根 2016 材料导报 30 149
Luo L, Xiong Z H, Zhou N G 2016 Mater. Rev. 30 149
[34] 蒋先伟, 陈军宁, 金波, 王菲菲, 鲁世斌 2016 合肥工业大学学报 39 934
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X W, Chen J N, Jin B, Wang F F, Lu S B 2016 J. Hefei Univ. Tech. 39 934
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 汪家余, 赵远洋, 徐建彬, 代月花 2014 63 053101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J Y, Zhao Y Y, Xu J B, Dai Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 053101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 蒋先伟, 鲁世斌, 代广珍, 汪家余, 金波, 陈军宁 2015 64 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X W, Lu S B, Dai G Z, Wang J Y, Jin B, Chen J N 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] 代月花, 潘志勇, 陈真, 王菲菲, 李宁, 金波, 李晓风 2016 65 073101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Y H, Pan Z Y, Chen Z, Wang F F, Li N, Jin B, Li X F 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 073101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhang H W, Gao B, Yu S M, Lai L, Zeng L, Sun B, Liu L F, Liu X Y, Lu J, Han R Q, Kang J F 2009 International Conference on Simulation of Semiconductor Processes & Devices San Diego, California, September 9−11, 2009 p155
[39] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Comput. Mater. Sci. 6 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 贾晓伟, 王敏 2018 材料导报 32 500
Jia X W, Wang M 2018 Mater. Rev. 32 500
[41] 李春萍, 陈鑫, 张宝林 2015 材料导报 39 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C P, Chen X, Zhang B L 2015 Mater. Rev. 39 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 侯清玉, 赵春旺, 李继军, 王钢 2011 60 047104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou Q Y, Zhao C W, Li J J, Wang G 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 047104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Dai Y H, Zhao Y Y, Wang J Y, Xu J B, Yang F 2015 AIP Adv. 5 017133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Zhao Y Y, Wang J Y, Xu J B, Yang F, Liu Q, Dai Y H 2014 J. Semicond. 35 25
[45] 蒋先伟, 代广珍, 鲁世斌, 汪家余, 代月花, 陈军宁 2015 64 091301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X W, Dai G Z, Lu S B, Wang J Y, Dai Y H, Chen J N 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 091301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9731
- PDF下载量: 84
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: