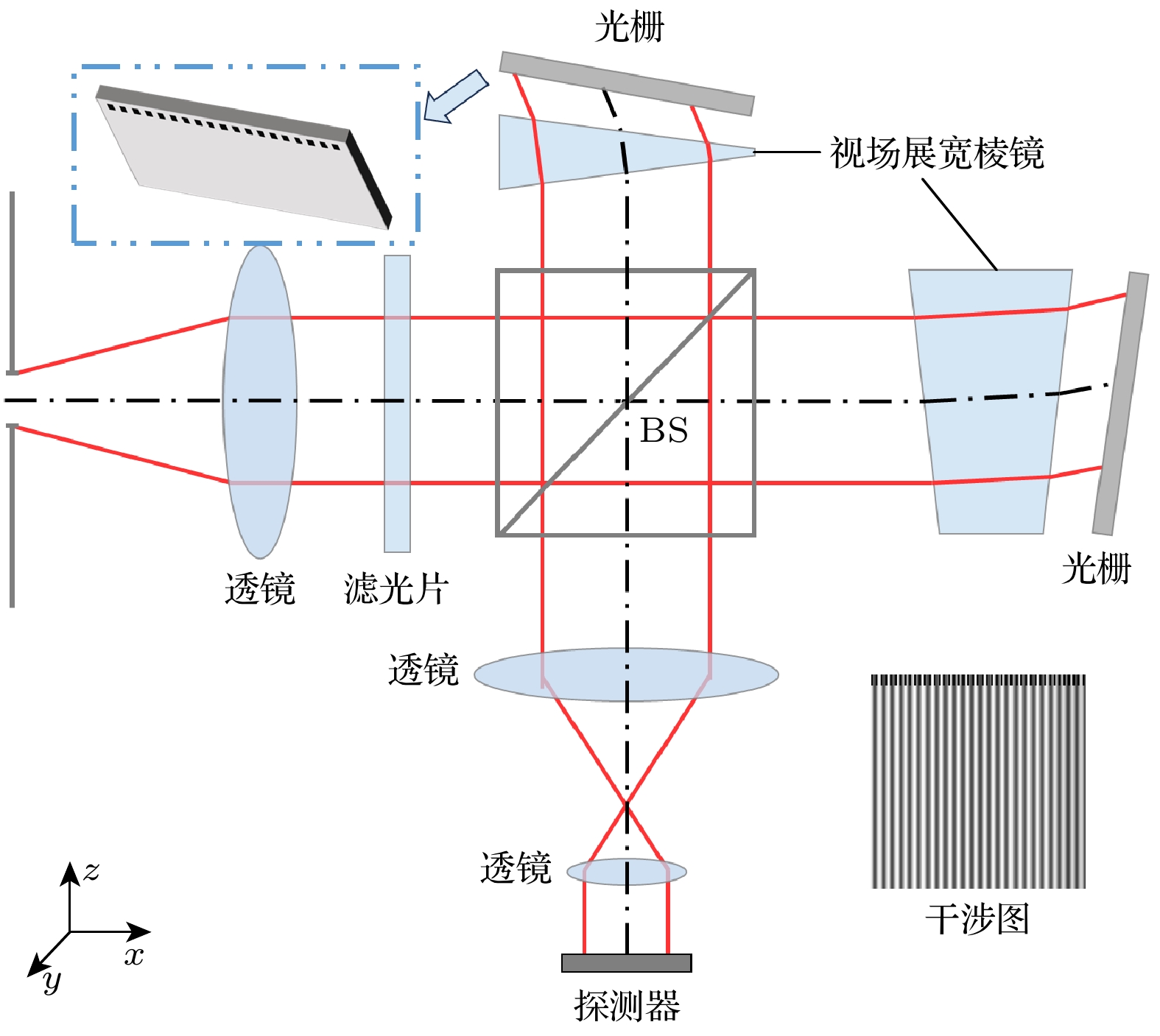
-
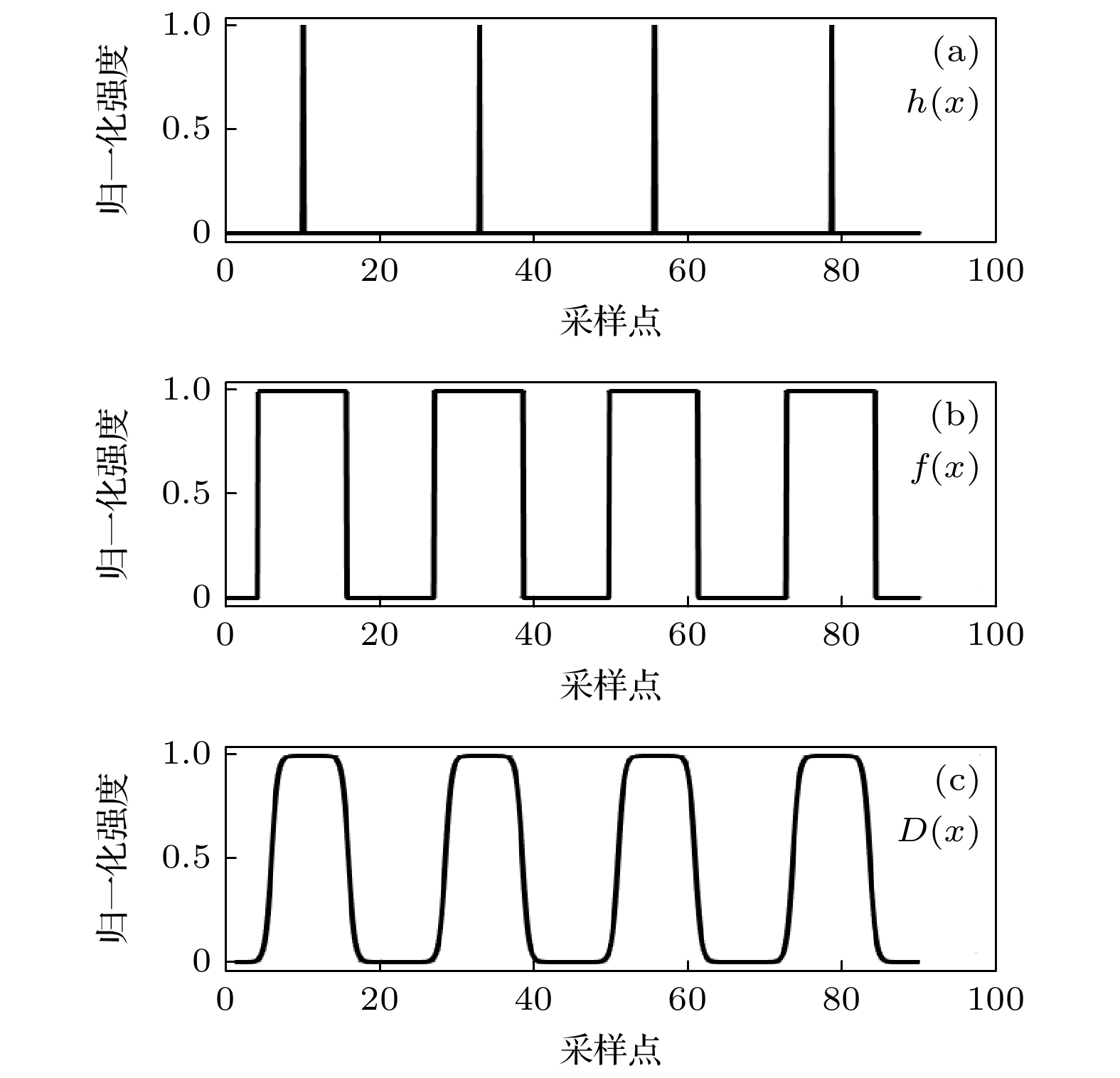
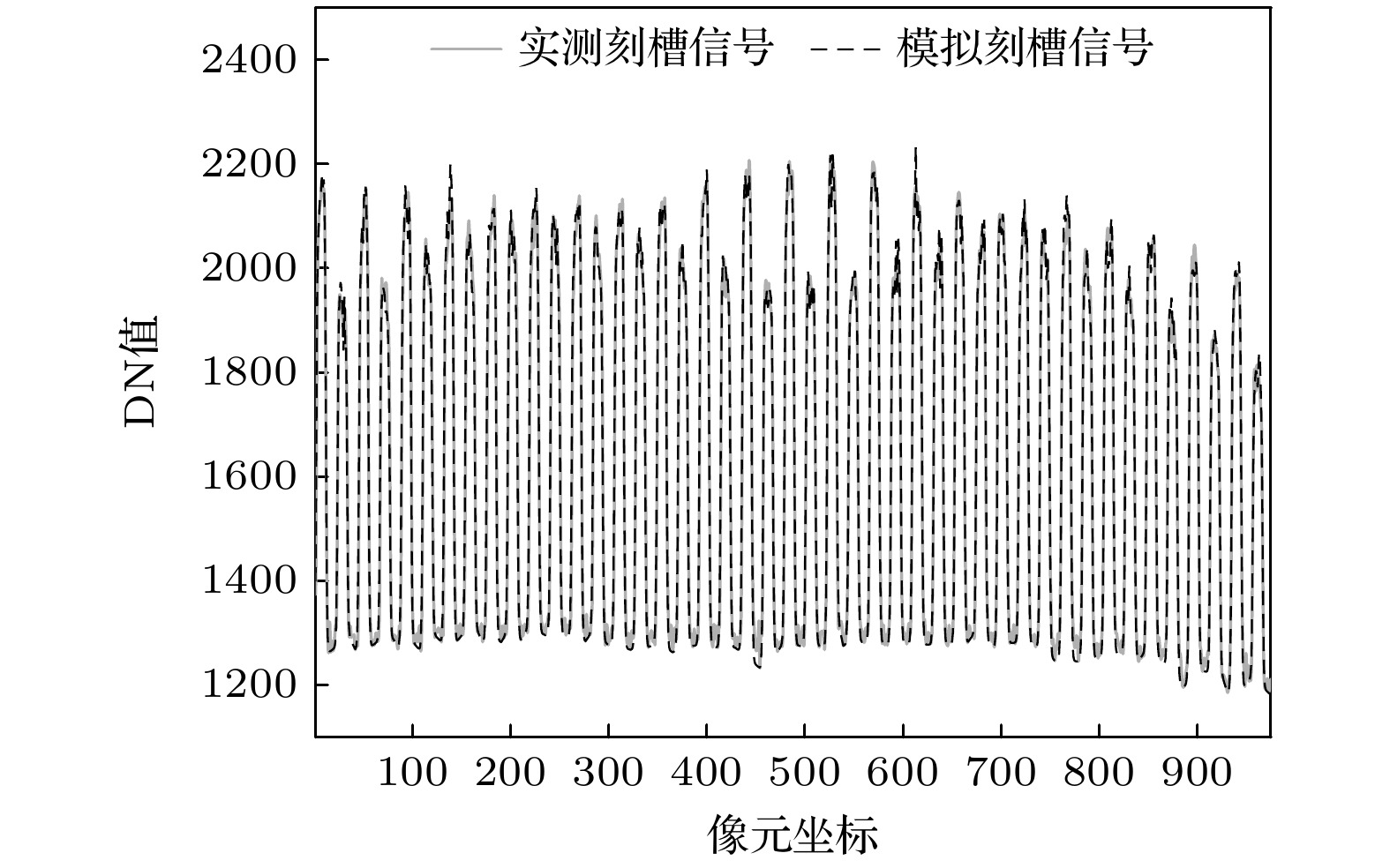
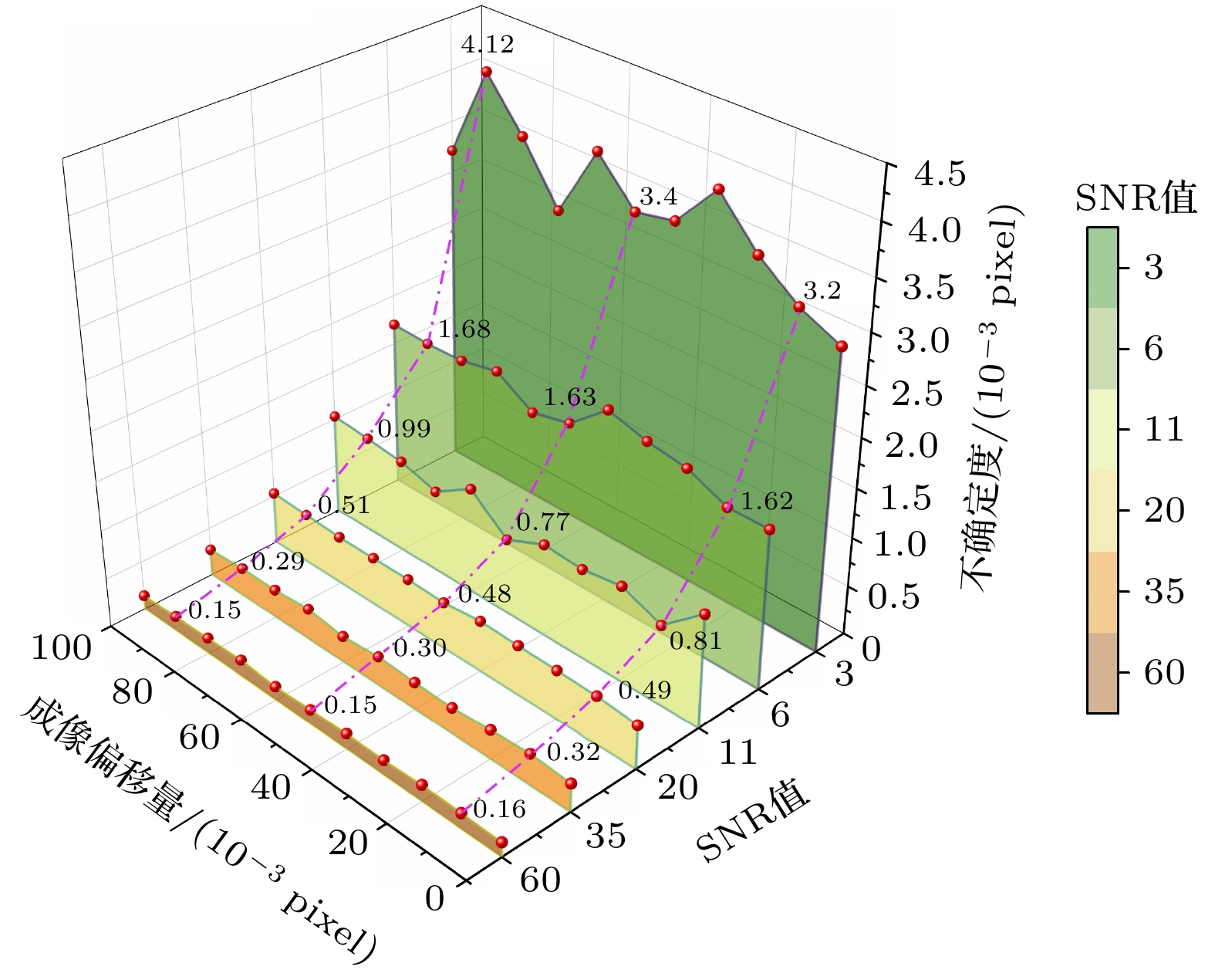
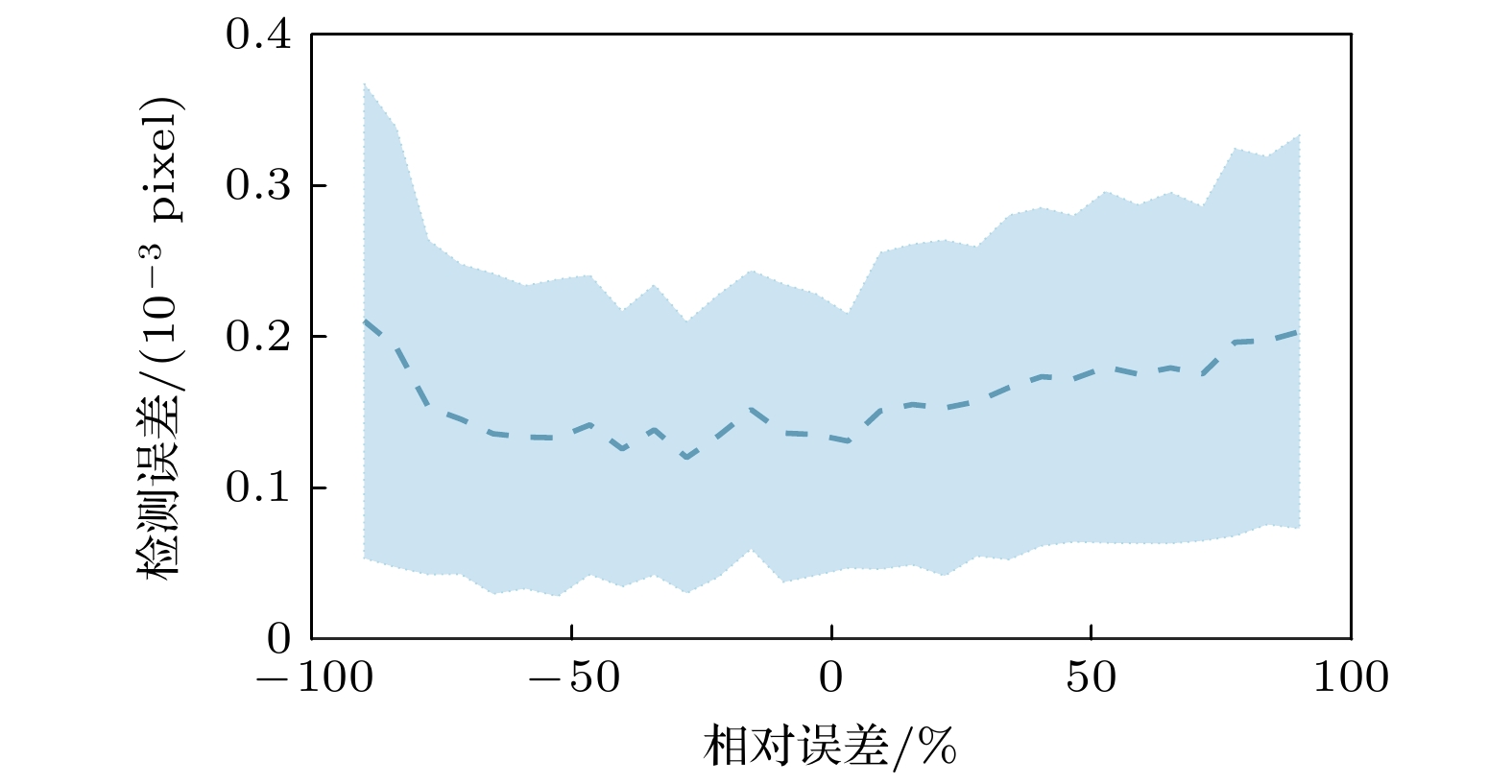
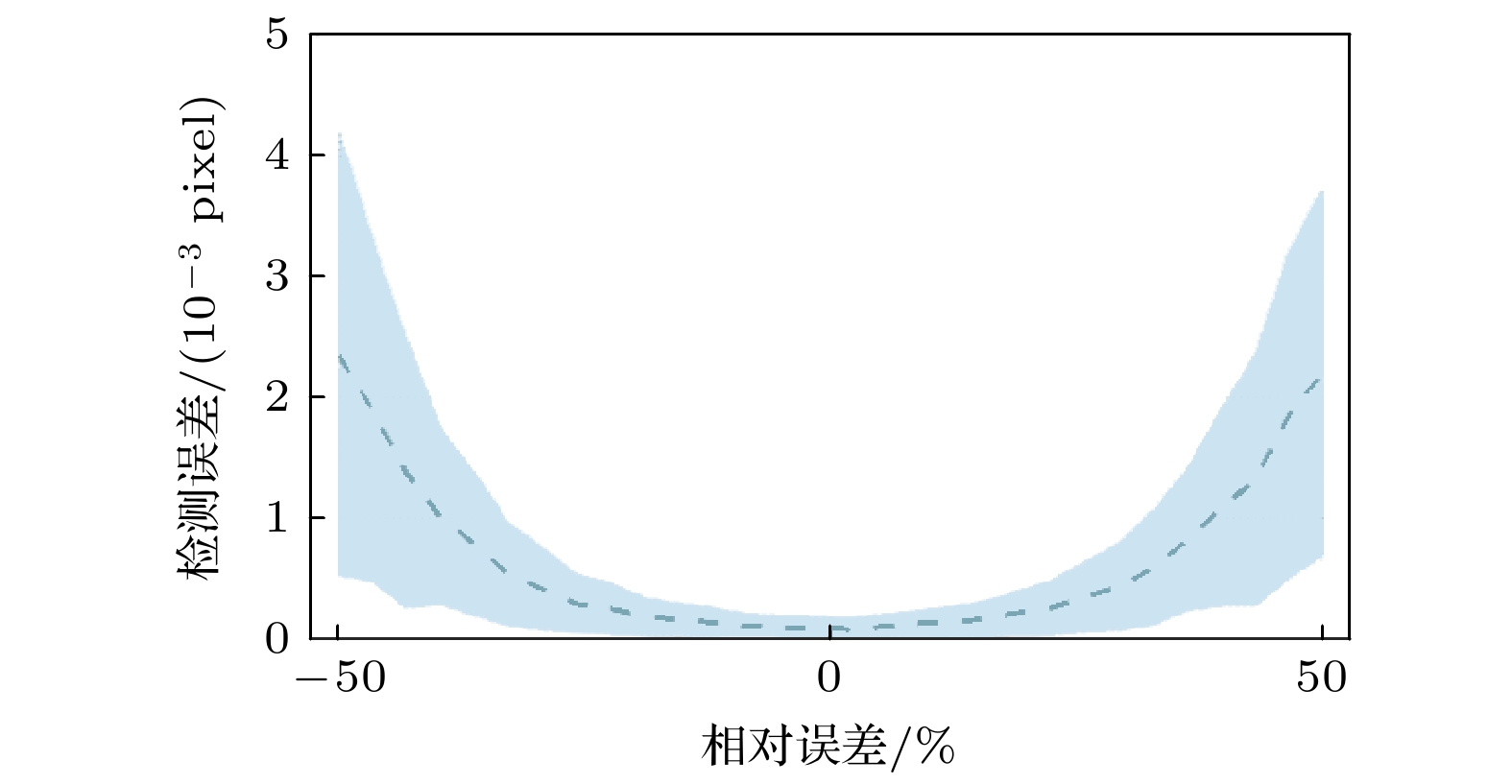
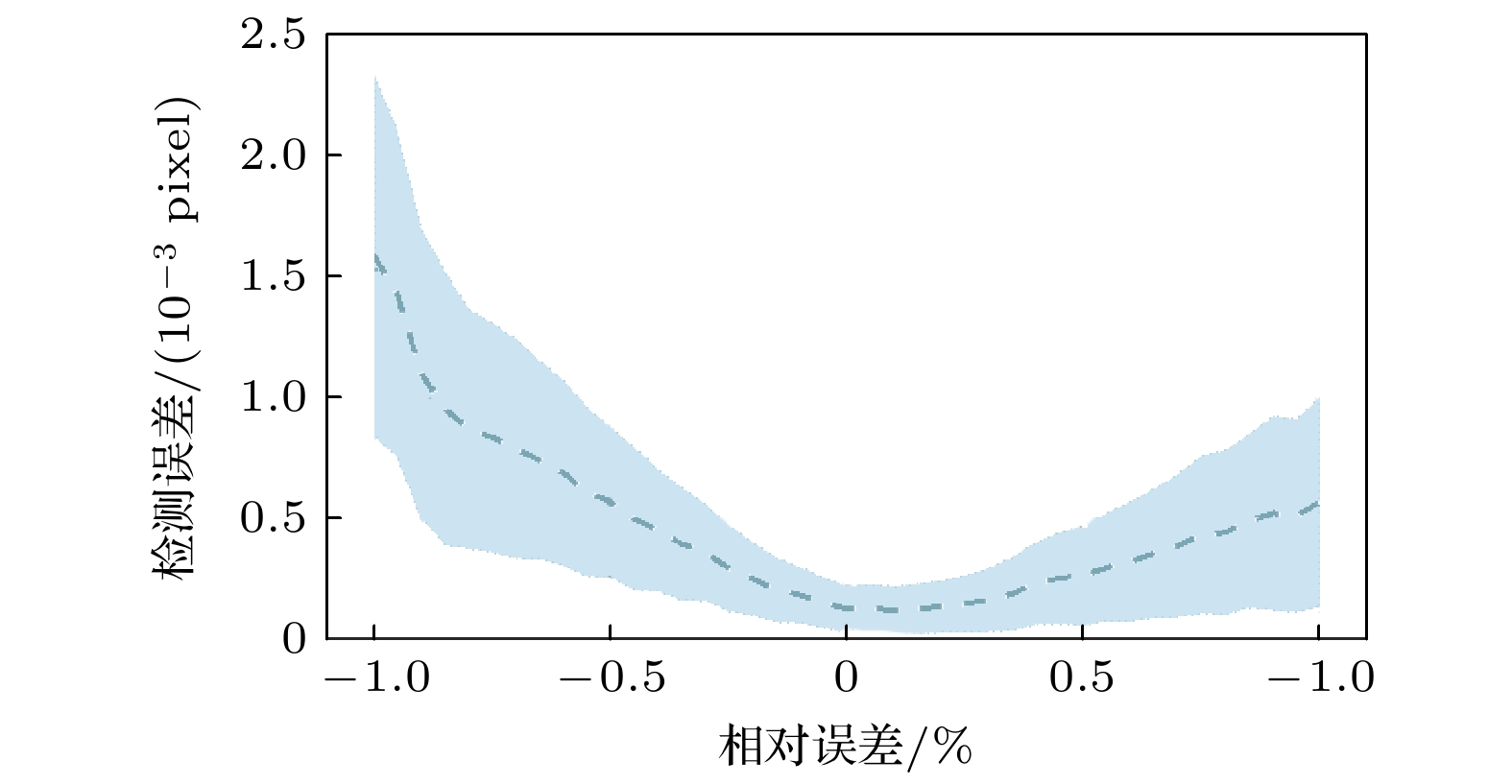
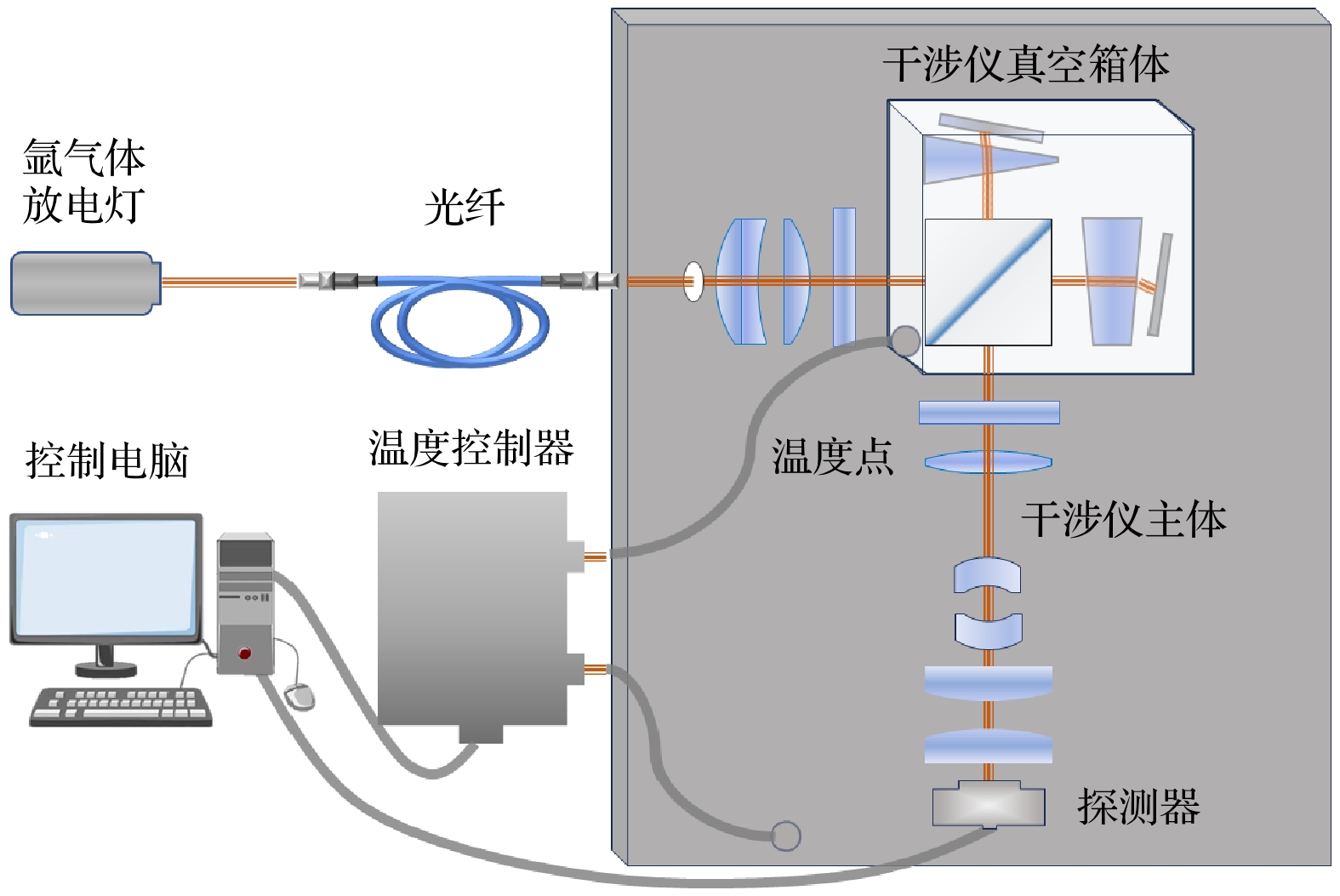
大气风场在全球气候研究和空间探测中具有重要作用, 多普勒差分干涉仪作为新型被动测风干涉仪, 其通过测量大气气辉谱线的多普勒频移引起的相位变化量来反演大气风速, 但环境温度波动会导致像面相对于干涉仪发生漂移, 从而影响风场测量结果. 本文提出一种在光栅上刻蚀周期性刻槽, 并对其成像图案进行建模与全局拟合以实现高精度成像漂移检测的方法. 对刻槽图像的信噪比及模型参数拟合误差对检测结果的影响进行仿真分析, 结果表明, 图像信噪比、刻槽数量拟合精度与刻槽宽度拟合精度是影响检测精度的关键因素, 而刻槽图像边缘的平滑度的拟合精度对检测结果影响较小. 在近红外多普勒差分干涉仪的热稳定实验中, 通过对实验所测数据人为施加漂移量, 并进行成像漂移监测, 结果表明该方法能够实现9.96 nm的检测精度. 此外, 经成像漂移校正后的干涉图相位的局部振荡显著减弱, 表明该方法能有效检测与校正成像漂移, 显著提升干涉图像相位稳定性, 为高精度风速测量提供了可靠保障.Accurate atmospheric wind field measurements are critical for understanding global climate dynamics and facilitating space exploration. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer (DASH) is used to measure atmospheric wind speed through detecting the phase changes in interferograms induced by Doppler shifts of airglow emission lines. However, environmental temperature fluctuations and mechanical vibrations often cause imaging plane to shift, thereby introducing phase deviations, and degrading the measurement accuracy. In this study, a novel method of monitoring global fitting-based imaging shift is proposed. By etching periodic notches on the diffraction grating surface, the method models and fits the notch patterns formed on the detector plane to achieve precise imaging shift detection and correction. The optimization of notch signal modeling significantly reduces the number of fitting parameters, thus improving computational efficiency and detection precision. Through extensive simulations, the influences of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and model parameter variation on detection accuracy are analyzed. The results indicate that when the SNR exceeds 11, the detection uncertainty is still below 6.5 nm. Sensitivity analysis reveals that the detection error stays within acceptable limits when the variations of notch number and notch width are controlled within 40% and 0.7%, respectively, while the influence of edge smoothness parameter of notch pattern is negligible. To validate the performance of the method, the thermal stability is tested by using a near-infrared DASH prototype. The experimental results demonstrate a strong correlation between interferogram phase shifts, imaging plane shifts, and environmental temperature variations. After applying the proposed correction method, local phase fluctuations in the interferogram are significantly reduced, thus the phase stability is improved. Further, artificially applied imaging shifts are accurately detected with errors consistently below 9.96 nm, thereby confirming the reliability and precision of this method. All in all, the proposed method effectively detects and corrects the imaging plane shifts caused by temperature variations, enhancing interferogram phase stability and ensuring high-precision wind speed measurements. This method provides a robust and computationally efficient solution for reducing imaging shifts in DASH systems, and has great potential applications in atmospheric wind field measurement and space-based observation.
-
Keywords:
- atmospheric wind field measurement /
- Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer /
- image plane shift /
- global fitting
[1] Shepherd G G 2015 Acta Astronaut. 115 206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dhadly M, Sassi F, Emmert J, Drob D, Conde M, Wu Q, Makela J, Budzien S Nicholas A 2023 Astron. Space Sci. 9 1050586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 唐远河, 崔进, 郜海阳, 屈欧阳, 段晓东, 李存霞, 刘丽娜 2017 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y H, Cui J, Gao H Y, Qu O Y, Duan X D, Li C X, Liu L N 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 冯玉涛, 傅頔, 赵增亮, 宗位国, 余涛, 盛峥, 朱亚军 2023 光学学报 43 0601011
Feng Y T, Fu D, Zhao Z L, Zong W G, Yu T, Sheng Z, Zhu Y J 2023 Acta Opt. Sin. 43 0601011
[5] Zhang S P, Thayer J P, Roble R G 2004 J. Atmos Sol-terr. Phys. 66 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Babcock D D, Stevens M H, Siskind D E 2006 Proc. SPIE 6303 63030T
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Englert C R, Babcock D D, Harlander J M 2006 Appl. Opt. 46 7297
[8] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Emmert J T, Babcock D D, Roesler F 2010 Opt. Express 18 26430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 肖旸, 冯玉涛, 文镇清 2022 光子学报 51 16
Xiao Y, Feng Y T, Wen Z Q 2022 Acta Photon. Sin. 51 16
[10] Harding B J, Chau J L, He M, Englert C R, Harlander J M, Marr K D, Makela J J, Clahsen M, Li G, Ratnam M V, Rao S V B, Wu Y J J, England S L, Immel T J 2021 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA028947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Brown C M, Makela J J, Marr K D, Immel T J In Fourier Transform Spectroscopy Lake Arrowhead, California, United States, March 1–4, 2015 pFM4A-1
[12] Stevens M H, Englert C R, Harlander J M, England S L, Marr K D, Brown C M, Immel T J 2018 Space Sci. Rev. 214 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Brown C M, Marr K D, Miller I J, Zastera V, Bach B W, Mende S B 2017 Space Sci. Rev. 212 601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Englert C R, Brown C M, Bach B, Bach E, Bach K, Harlander J M, Seely J F, Marr K D, Miller I 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 2090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Marr K D, Thayer A S, Englert C R, Harlander J M 2020 Opt. Eng. 59 013102
[16] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Marr K D, Harding B J, Makela J J, Fae T, Brown C M, Venkat Ratnam M, Vijaya Bhaskara Rao S , Immel T J 2023 Space Sci. Rev. 219 27
[17] 张亚飞, 冯玉涛, 傅頔, 畅晨光, 李娟, 白清兰, 胡炳樑 2022 71 084201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y F, Feng Y T, Fu D, Chang C G, Li J, Bai Q L, Hu B L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 084201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang Y F, Feng Y T, Fu D, Wang P C, Sun J, Bai Q L 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 104204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 傅頔, 畅晨光, 孙剑, 李娟, 武魁军, 冯玉涛, 刘学斌 2022 光学学报 42 18
Fu D, Chang C G, Sun J, Li J, Wu K J, Feng Y T, Liu X B 2022 Acta Opt. Sin. 42 18
[20] Wei D K, Zhu Y J, Liu J L, Gong Q C, Kaufmann M, Olschewski F, Knieling P, Xu J Y, Koppmann R, Riese M 2020 Opt Express 28 19887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
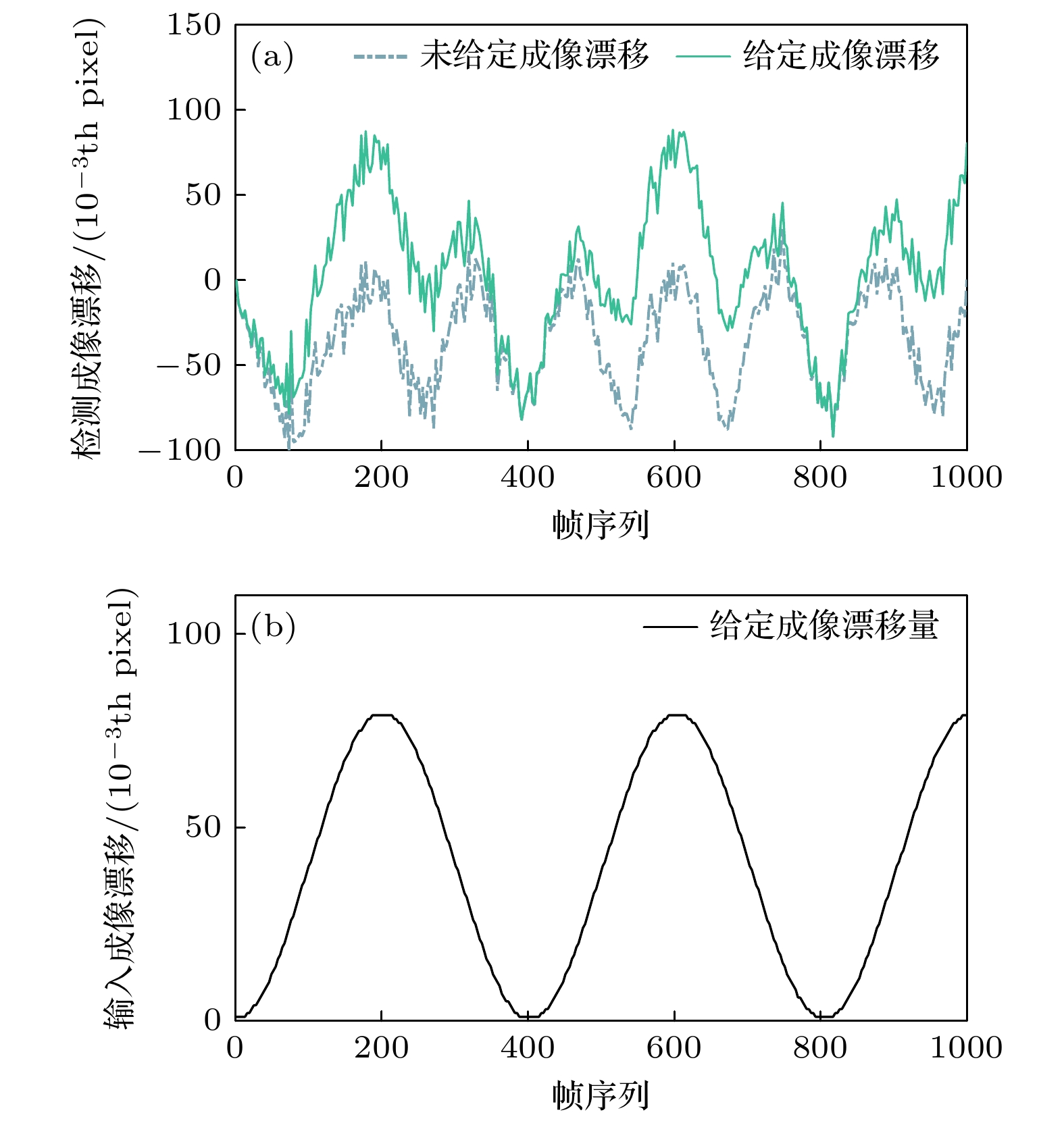
图 10 (a)实验中所测刻槽图像的成像漂移量(蓝色虚线), 对所测图像人为给定成像漂移量后对应的检测结果(绿色实线); (b)对实验中所测每一帧刻槽图像叠加固定的成像漂移量
Fig. 10. (a) The imaging shift of the notch image measured in the experiment (blue dashed line), and the corresponding detection result of the notch image measured in the experiment after artificially superimposing the imaging shift amount (green solid line); (b) the fixed imaging shift is superimposed on each frame of notch image measured in the experiment.
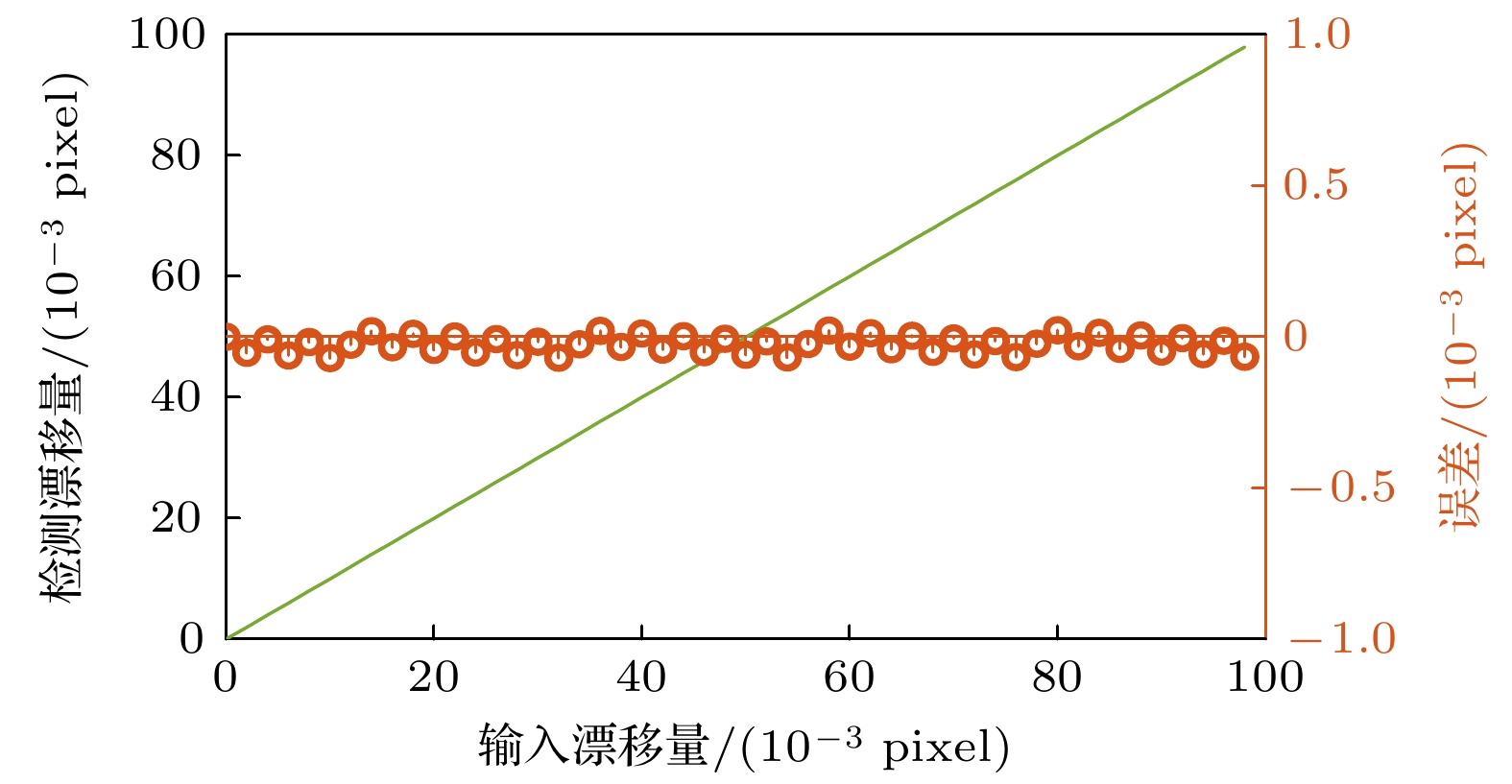
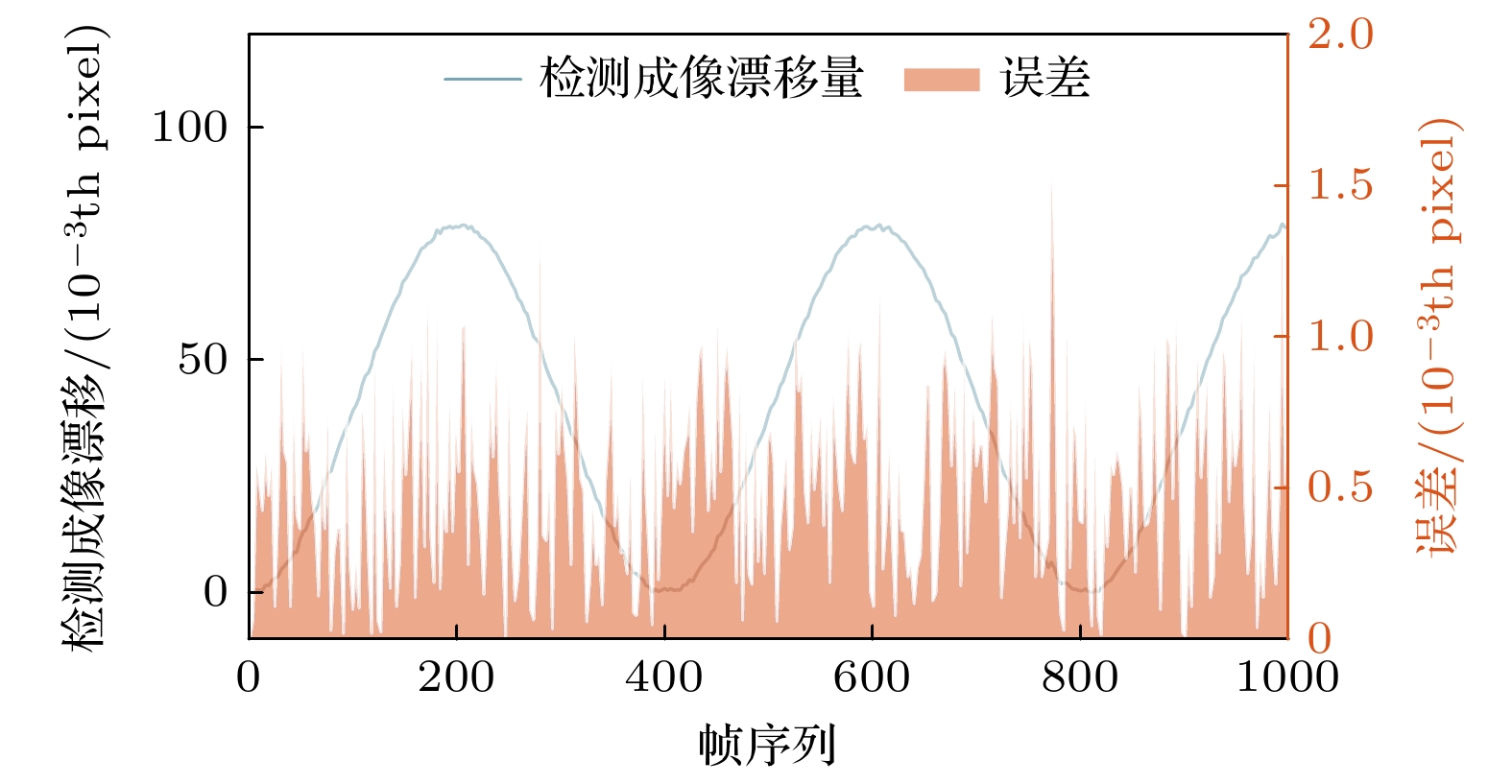
图 11 蓝线为图10(a)中两信号的差值, 即对人为给定漂移量的检测值, 红线为检测误差, 即检测成像漂移量与人为给定成像漂移量间的差值
Fig. 11. The blue line is the difference between the two signals in Fig.10 (a), that is, the measurement of the artificially given amount of shift. The red line is the measurement error, that is, the difference between the measured image shift and the input image shift.
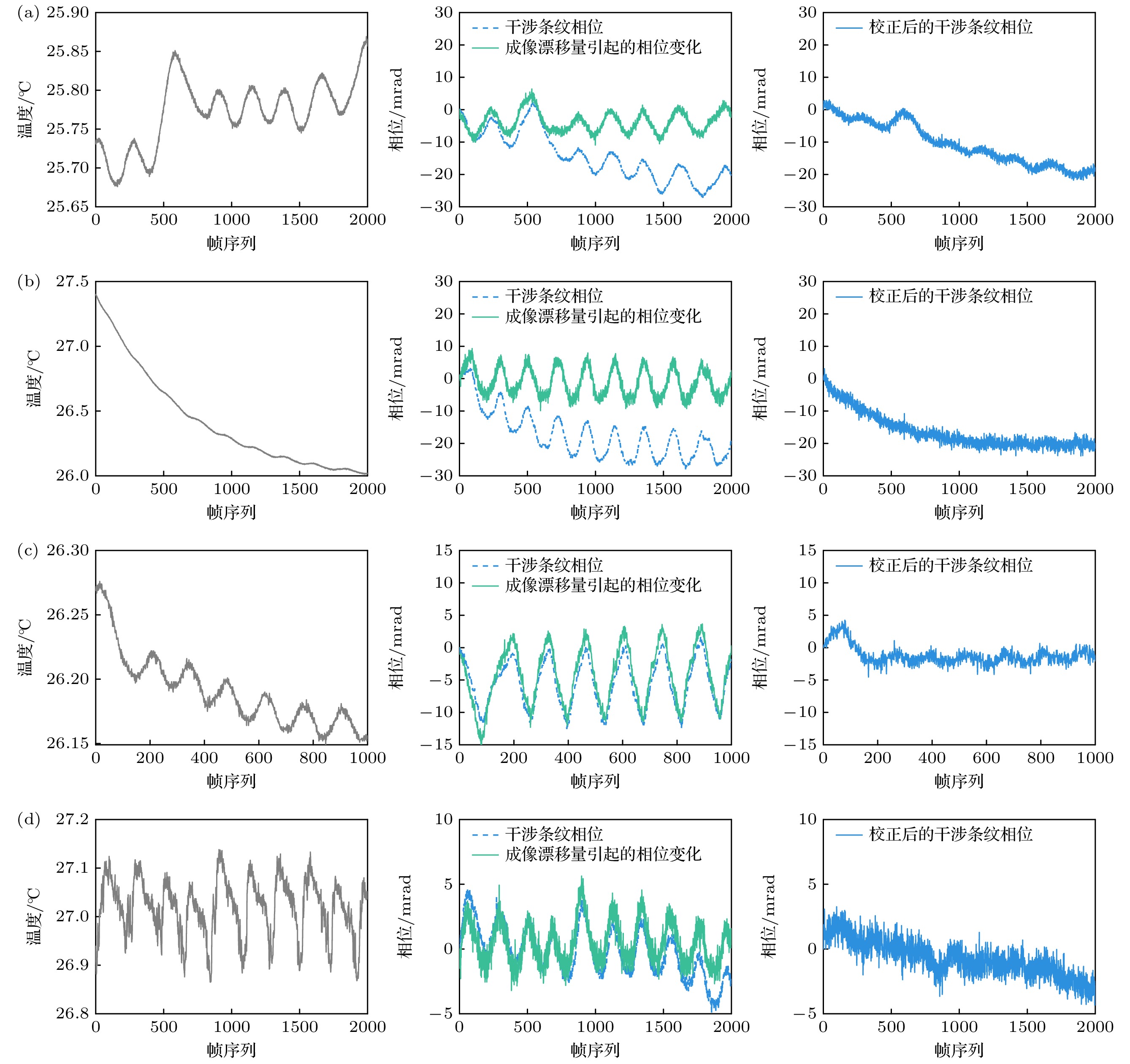
图 12 近红外多普勒差分干涉仪样机的连续热稳定性测试数据, 灰色线为温度数据, 蓝色虚线为干涉条纹相位, 绿色线为成像漂移引起的相位变化, 蓝色实线为成像漂移校正后的干涉条纹相位
Fig. 12. Thermal stability test data of the near infrared DASH prototype, the gray line is temperature data, the blue dashed line is fringe phase, the green line is phase change caused by imaging shift, and the blue solid line is fringe phase after imaging shift correction.
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters.
参数 数值 系统参数 波长/nm 867.16 光程差/mm 49.87 光栅参数 Littrow 波数/nm 868.24 光栅阶数 1 光栅闪耀角/(°) 10 光栅衍射效率 70% 探测器参数 像元数 2048×2048 量子效率 0.75 像元尺寸/μm 6.5 刻槽信号参数 刻槽数量 111.81 刻槽宽度/μm 59.52 -
[1] Shepherd G G 2015 Acta Astronaut. 115 206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dhadly M, Sassi F, Emmert J, Drob D, Conde M, Wu Q, Makela J, Budzien S Nicholas A 2023 Astron. Space Sci. 9 1050586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 唐远河, 崔进, 郜海阳, 屈欧阳, 段晓东, 李存霞, 刘丽娜 2017 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y H, Cui J, Gao H Y, Qu O Y, Duan X D, Li C X, Liu L N 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 冯玉涛, 傅頔, 赵增亮, 宗位国, 余涛, 盛峥, 朱亚军 2023 光学学报 43 0601011
Feng Y T, Fu D, Zhao Z L, Zong W G, Yu T, Sheng Z, Zhu Y J 2023 Acta Opt. Sin. 43 0601011
[5] Zhang S P, Thayer J P, Roble R G 2004 J. Atmos Sol-terr. Phys. 66 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Babcock D D, Stevens M H, Siskind D E 2006 Proc. SPIE 6303 63030T
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Englert C R, Babcock D D, Harlander J M 2006 Appl. Opt. 46 7297
[8] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Emmert J T, Babcock D D, Roesler F 2010 Opt. Express 18 26430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 肖旸, 冯玉涛, 文镇清 2022 光子学报 51 16
Xiao Y, Feng Y T, Wen Z Q 2022 Acta Photon. Sin. 51 16
[10] Harding B J, Chau J L, He M, Englert C R, Harlander J M, Marr K D, Makela J J, Clahsen M, Li G, Ratnam M V, Rao S V B, Wu Y J J, England S L, Immel T J 2021 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA028947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Brown C M, Makela J J, Marr K D, Immel T J In Fourier Transform Spectroscopy Lake Arrowhead, California, United States, March 1–4, 2015 pFM4A-1
[12] Stevens M H, Englert C R, Harlander J M, England S L, Marr K D, Brown C M, Immel T J 2018 Space Sci. Rev. 214 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Brown C M, Marr K D, Miller I J, Zastera V, Bach B W, Mende S B 2017 Space Sci. Rev. 212 601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Englert C R, Brown C M, Bach B, Bach E, Bach K, Harlander J M, Seely J F, Marr K D, Miller I 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 2090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Marr K D, Thayer A S, Englert C R, Harlander J M 2020 Opt. Eng. 59 013102
[16] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Marr K D, Harding B J, Makela J J, Fae T, Brown C M, Venkat Ratnam M, Vijaya Bhaskara Rao S , Immel T J 2023 Space Sci. Rev. 219 27
[17] 张亚飞, 冯玉涛, 傅頔, 畅晨光, 李娟, 白清兰, 胡炳樑 2022 71 084201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y F, Feng Y T, Fu D, Chang C G, Li J, Bai Q L, Hu B L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 084201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang Y F, Feng Y T, Fu D, Wang P C, Sun J, Bai Q L 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 104204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 傅頔, 畅晨光, 孙剑, 李娟, 武魁军, 冯玉涛, 刘学斌 2022 光学学报 42 18
Fu D, Chang C G, Sun J, Li J, Wu K J, Feng Y T, Liu X B 2022 Acta Opt. Sin. 42 18
[20] Wei D K, Zhu Y J, Liu J L, Gong Q C, Kaufmann M, Olschewski F, Knieling P, Xu J Y, Koppmann R, Riese M 2020 Opt Express 28 19887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3182
- PDF下载量: 63
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: