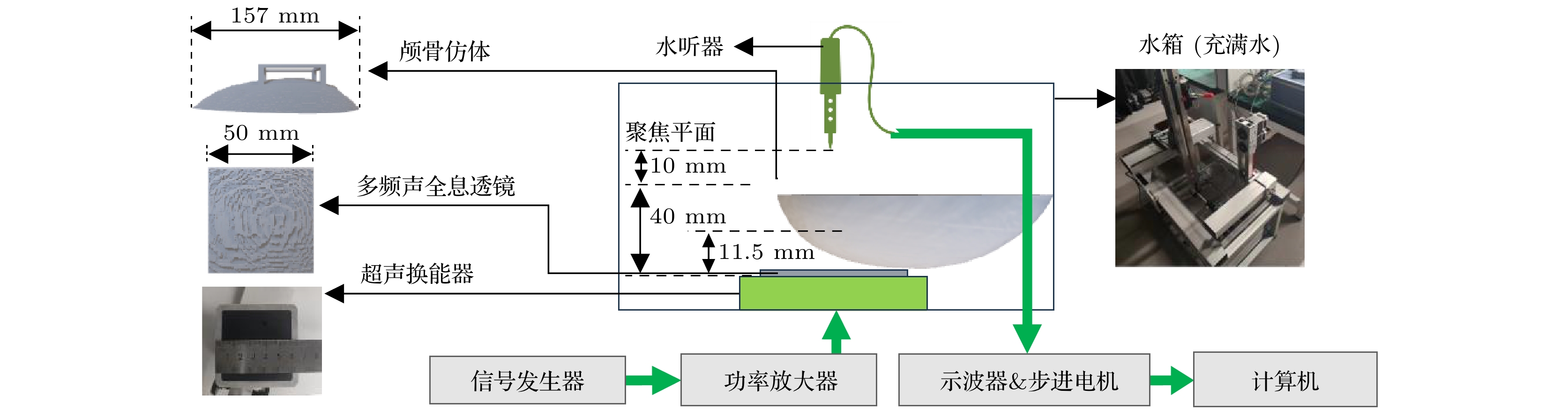
-
经颅聚焦超声是一种具有发展前景的技术, 具有无创、安全、穿透深度大等优点. 声全息透镜作为一种低成本且便捷的经颅聚焦方法, 具有较大的发展潜力. 然而, 基于单片声全息透镜通常只能实现单一经颅聚焦声场的重建, 在实际应用场景下缺乏应用灵活性. 针对该问题, 本文提出了一种用于经颅聚焦的多频声全息透镜的设计方法, 通过提取在不同频率下设计的聚焦到不同位置的两片声全息透镜中的有效信息, 并将其整合到一片声全息透镜中来实现, 生成的声全息透镜可以在不同频率的激发下聚焦到不同位置. 仿真和实验结果表明, 通过此方法设计的声全息透镜在不同频率的超声波激发下, 可以克服颅骨对超声波的散射效应, 在颅骨后方精确地形成高质量的声聚焦点.Transcranial focused ultrasound (tFUS) possesses significant advantages such as non-invasiveness and high tissue penetration depth, making it a promising tool in the field of brain science. Acoustic holographic lenses can manipulate the sound field through phase modulation, providing a low-cost and convenient approach for realizing transcranial focusing. Acoustic holographic lenses have been successfully utilized for achieving precise transcranial focusing in living mice to open the blood-brain barrier and for performing neural modulation, which shows considerable application potential. However, existing transcranial acoustic holographic lenses can only be driven by specific ultrasound frequencies and focused at predetermined positions, which limits their flexibility in complex applications. To address this issue, this study establishes a multi-frequency transcranial focusing method based on acoustic holographic lenses to enhance its adaptability in the field of tFUS. By integrating acoustic holographic lenses designed for different focal positions at various frequencies, we generate multi-frequency acoustic holographic lenses suitable for transcranial focusing and conduct experiments to evaluate their performance. In simulations, for single-focus tasks, the peak signal to noise ratio(PSNR) of the proposed method achieves 32.16 dB under 1 MHz ultrasound excitation, and 40.18 dB and 2 MHz ultrasound excitation, respectively; for multi-focus tasks, the PSNR values are 29.39 dB and 39.89 dB, respectively. In experiments, for single-focus tasks, the PSNR value of the proposed method is 27.48 dB under 1 MHz ultrasound excitation, and 32.33 dB under 2 MHz ultrasound excitation, respectively; for multi-focus tasks, the PSNR values are 23.30 dB and 32.17 dB, respectively. These results demonstrate that the multi-frequency transcranial acoustic holographic lens can effectively modulate the sound field under varying ultrasound frequencies and create high-quality focal points at different locations behind the skull, which significantly enhances the application flexibility of transcranial acoustic holographic lenses.
[1] Landhuis E 2017 Nature 551 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张玫玫, 吴意赟, 于洁, 屠娟, 章东 2023 72 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M M, Wu Y Y, Yu J, Tu J, Zhang D 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ballantine H, Bell E, Manlapaz J 1960 J. Neurosurg. 17 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Vykhodtseva N, Hynynen K, Damianou C 1995 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 21 969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Elias W J, Khaled M, Hilliard J D, Aubry J F, Frysinger R C, Sheehan J P, Wintermark M, Lopes M B 2013 J. Neurosurg. 119 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张芸芸, 李义方, 石勤振, 许乐修, 戴菲, 邢文宇, 他得安 2023 72 154303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y Y, Li Y F, Shi Q Z, Xu L X, Dai F, Xing W Y, Ta D A 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 154303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang Y, Wang C Z, Li Y C, Huang J Q, Cai F Y, Xiao Y, Ma T, Zheng H R 2019 IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 28 361
[8] Tufail Y, Yoshihiro A, Pati S, Li M M, Tyler W J 2011 Nat. Protoc. 6 1453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Melde K, Mark A G, Qiu T, Fischer P 2016 Nature 537 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Leith E N, Upatnieks J 1962 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 52 1123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 钟志, 赵婉婷, 单明广, 刘磊 2021 70 154202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong Z, Zhao W T, Shan M G, Liu L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 154202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Andrés D, Jiménez-Gambín S, Jiménez N, Camarena F 2020 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium Las Vegas, NV, USA, November 17, 2020 p1
[13] Jiménez-Gambín S, Jiménez N, Benlloch J M, Camarena F 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 014016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shah B R, Lehman V T, Kaufmann T J, Blezek D, Waugh J, Imphean D, Yu F F, Patel T R, Chitnis S, Dewey Jr R B 2020 Brain 143 2664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yin Y, Yan S, Huang J, Zhang B 2023 Sensors 23 9702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiménez-Gambín S, Jiménez N, Pouliopoulos A N, Benlloch J M, Konofagou E E, Camarena F 2021 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 69 1359
[17] Pouliopoulos A N, Wu S Y, Burgess M T, Karakatsani M E, Kamimura H A, Konofagou E E 2020 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 46 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tillander M, Hokland S, Koskela J, Dam H, Andersen N P, Pedersen M, Tanderup K, Ylihautala M, Köhler M 2016 Med. Phys. 43 1539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Treeby B E, Cox B T 2010 J. Biomed. Opt. 15 021314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Mast T D, Souriau L P, Liu D L, Tabei M, Nachman A I, Waag R C 2001 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 48 341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tabei M, Mast T D, Waag R C 2002 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 111 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kook G, Jo Y, Oh C, Liang X, Kim J, Lee S M, Kim S, Choi J W, Lee H J 2023 Microsyst. Nanoeng. 9 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Treeby B E, Cox B T 2010 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127 2741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Thomas J L, Fink M A 1996 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 43 1122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Aubry J F, Tanter M, Pernot M, Thomas J L, Fink M 2003 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Brown M D, Cox B T, Treeby B E 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 244101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] He J R, Wu J W, Zhu Y Y, Chen Y, Yuan M D, Zeng L M, Ji X R 2021 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 69 662
[28] Tanchenko A 2014 J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 25 874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bakaric M, Miloro P, Javaherian A, Cox B T, Treeby B E, Brown M D 2021 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 150 2798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
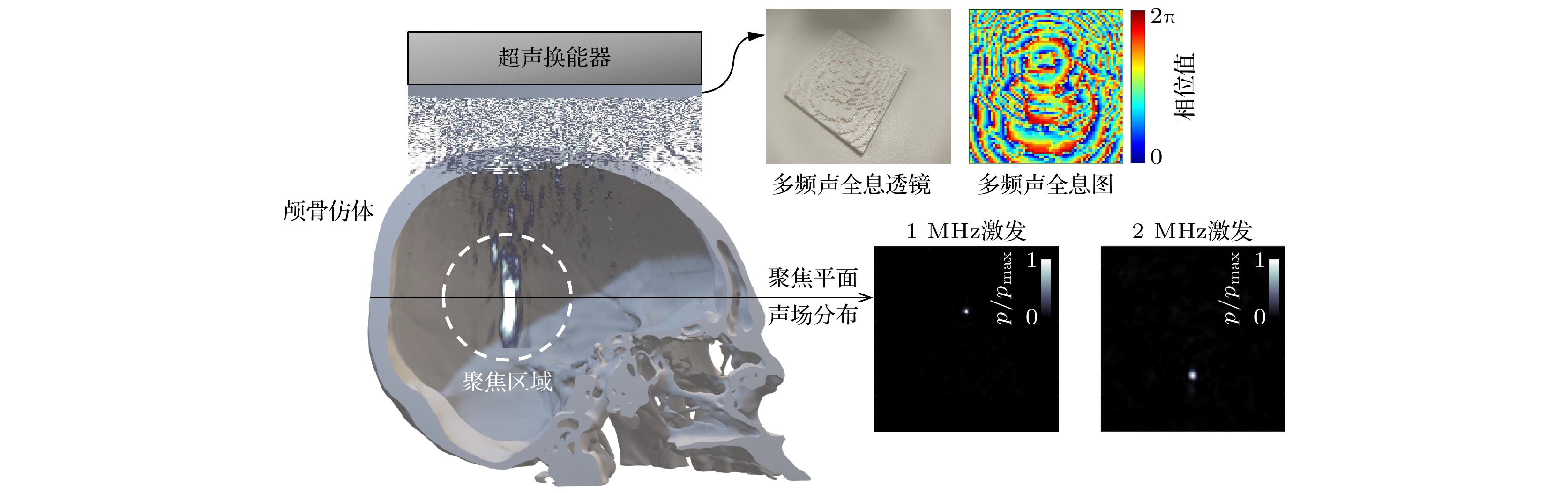
图 2 用于经颅聚焦的多频声全息透镜 (a)多频声全息透镜的3D视图; (b)多频声全息透镜俯视图; (c)多频声全息透镜的正视图
Fig. 2. Multi-frequency acoustic holographic lens for transcranial focusing: (a) 3D view of the multi-frequency acoustic holographic lens; (b) top view of the multi-frequency acoustic holographic lens; (c) front view of the multi-frequency acoustic holographic lens.
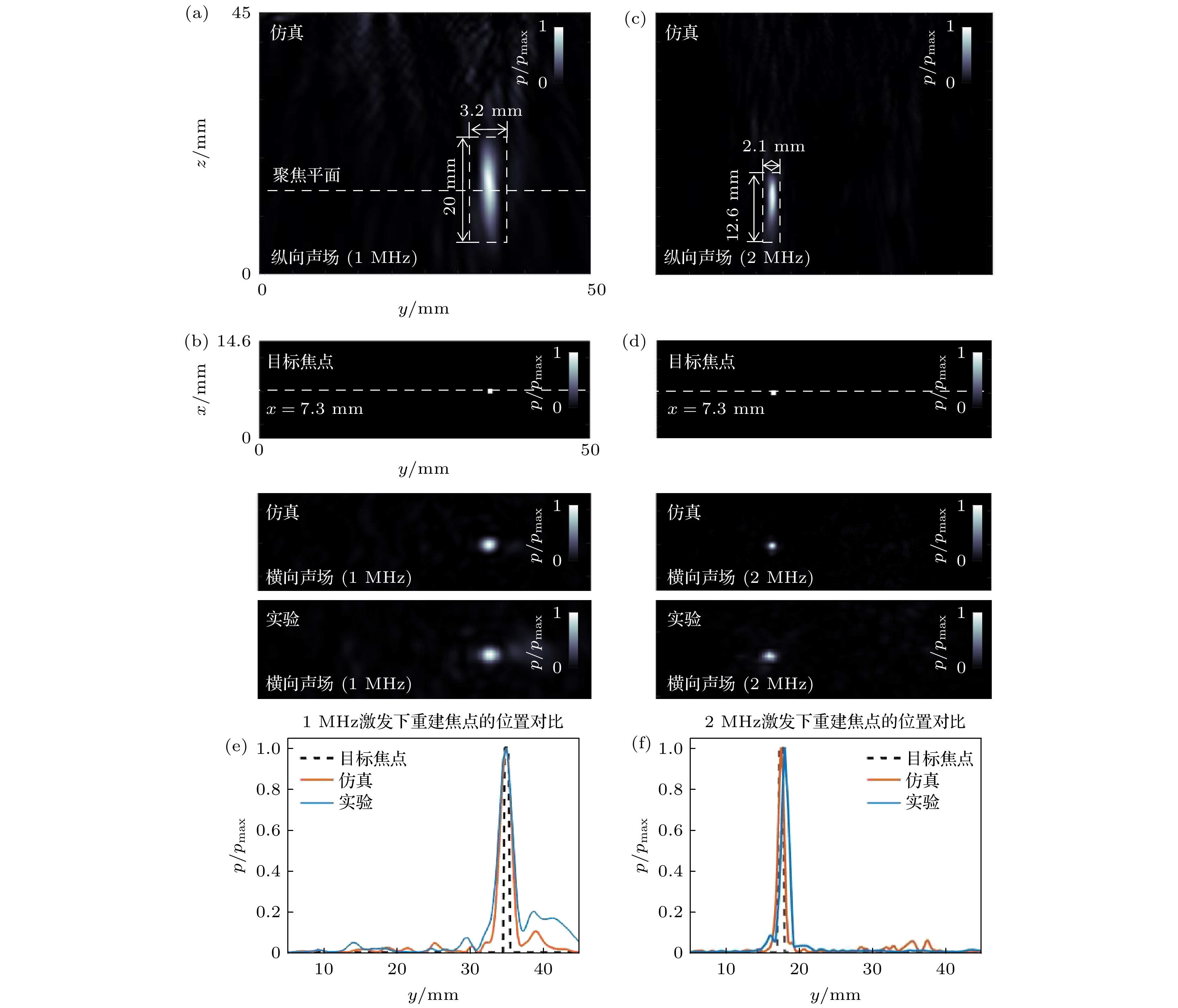
图 4 多频声全息透镜的仿真与实验结果 (a) 1 MHz仿真中, 焦点附近的纵向声场; (b)1 MHz激发下的仿真与实验重建的聚焦平面与目标焦点; (c) 2 MHz仿真中, 焦点附近的纵向声场; (d) 2 MHz激发下的仿真与实验重建的聚焦平面与目标焦点; (e) 1 MHz激发的情况下, 在仿真和实验中, 沿着x = 7.3 mm的虚线上的声压对比; (f) 2 MHz激发的情况下, 在仿真和实验中, 沿着x = 7.3 mm的虚线上的声压对比
Fig. 4. Simulation and experimental results of multi-frequency acoustic holographic lenses: (a) Longitudinal acoustic field near the focal point in 1 MHz simulation; (b) focusing plane and target foci reconstructed by simulation and experiment under 1 MHz excitation; (c) longitudinal acoustic field near the focal point in 2 MHz simulation; (d) focusing plane versus target foci reconstructed from simulation and experiment under 2 MHz excitation; (e) sound pressure comparison along the dashed line at x = 7.3 mm in simulation and experiment for the case of 1 MHz excitation; (f) sound pressure comparison along the dashed line at x = 7.3 mm in simulation and experiment for the case of 2 MHz excitation.
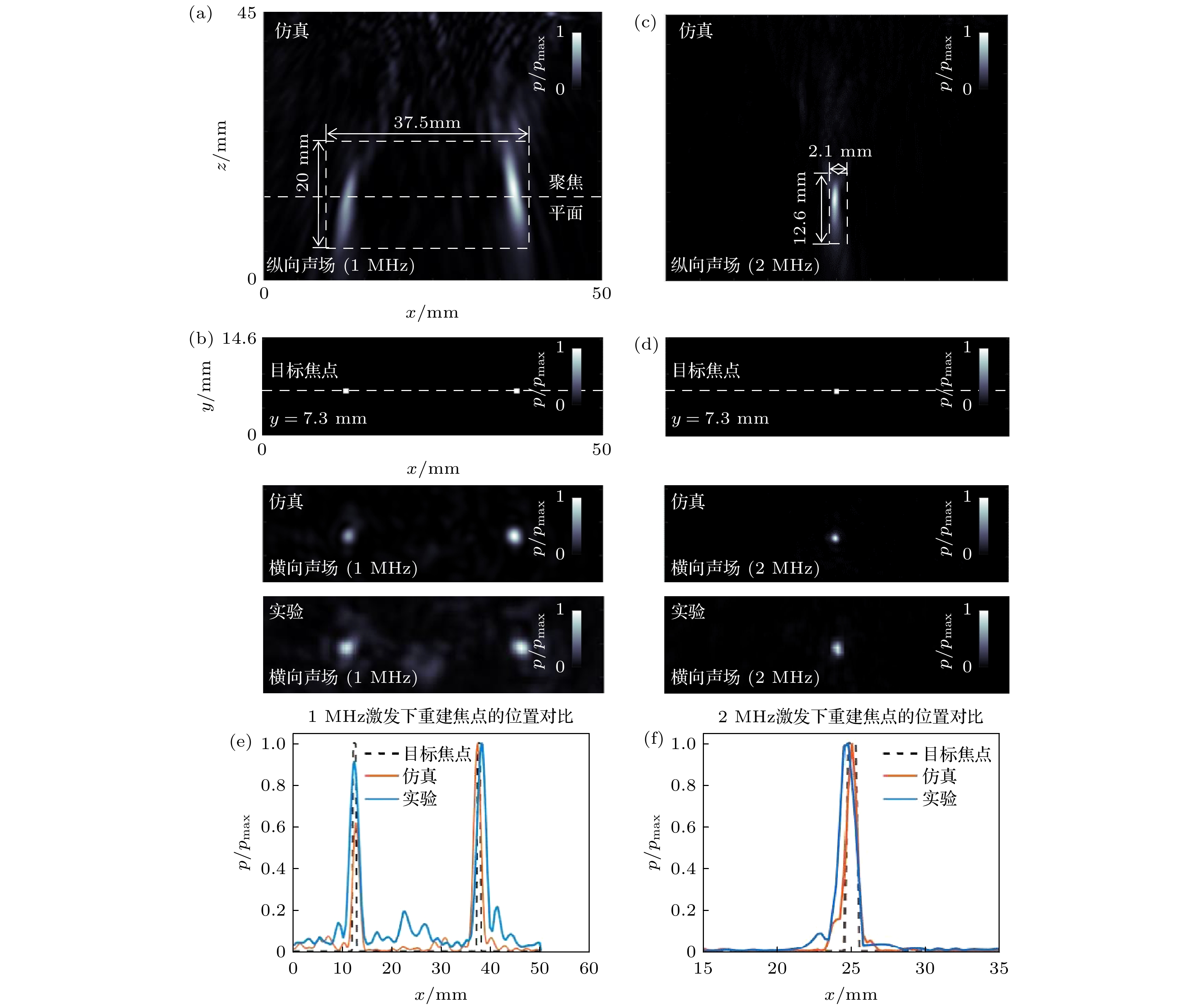
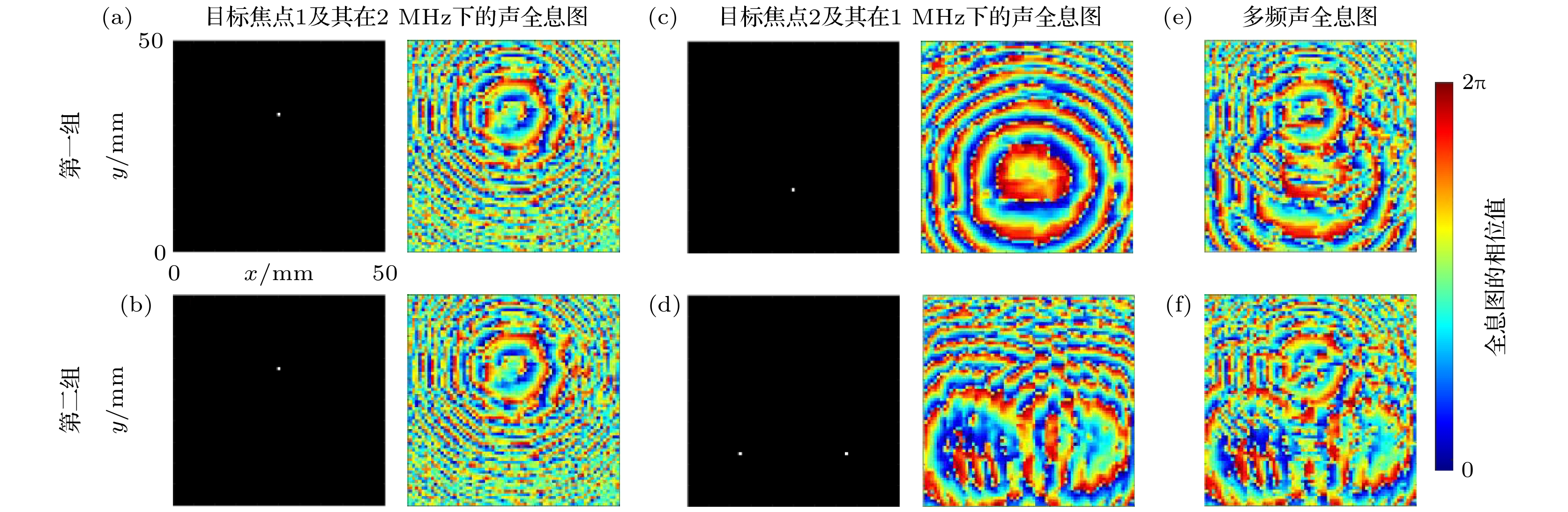
图 5 多频声全息透镜在多焦点情况下的仿真与实验结果 (a) 1 MHz仿真中, 焦点附近的纵向声场; (b)1 MHz激发下的仿真与实验重建的聚焦平面与目标焦点; (c)在2 MHz仿真中, 焦点附近的纵向声场; (d) 2 MHz激发下的仿真与实验重建的聚焦平面与目标焦点; (e)1 MHz激发的情况下, 在仿真和实验中, 沿着y = 7.3 mm的虚线上的声压对比; (f)2 MHz激发的情况下, 在仿真和实验中, 沿着y = 7.3 mm的虚线上的声压对比
Fig. 5. Simulation and experimental results of multi-frequency acoustic holographic lenses in the case of multiple focal points: (a) Longitudinal acoustic field near the focal point in the 1 MHz simulation; (b) focused plane and target foci reconstructed by simulation and experiment for the 1 MHz excitation; (c) longitudinal acoustic field near the focal point in the 2 MHz simulation; (d) focused plane and target foci reconstructed by simulation and experiment for the 2 MHz excitation; (e) sound pressure comparison in the 1 MHz excitation case in the simulation and experiment along the y = 7.3 mm dashed line; (f) sound pressure comparison along the dashed line at y = 7.3 mm in simulation and experiment for the case of 2 MHz excitation.
表 1 聚焦平面的声场与目标图像之间的PSNR
Table 1. PSNR between the sound field at the focal plane and the target image
频率/MHz PSNR(仿真) PSNR(实验) 1 32.16 27.48 2 40.18 32.33 表 2 聚焦平面的声场与目标图像之间的PSNR
Table 2. PSNR between the sound field at the focal plane and the target image.
频率/MHz PSNR(仿真) PSNR(实验) 1 29.39 23.30 2 39.89 32.17 -
[1] Landhuis E 2017 Nature 551 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张玫玫, 吴意赟, 于洁, 屠娟, 章东 2023 72 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M M, Wu Y Y, Yu J, Tu J, Zhang D 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ballantine H, Bell E, Manlapaz J 1960 J. Neurosurg. 17 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Vykhodtseva N, Hynynen K, Damianou C 1995 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 21 969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Elias W J, Khaled M, Hilliard J D, Aubry J F, Frysinger R C, Sheehan J P, Wintermark M, Lopes M B 2013 J. Neurosurg. 119 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张芸芸, 李义方, 石勤振, 许乐修, 戴菲, 邢文宇, 他得安 2023 72 154303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y Y, Li Y F, Shi Q Z, Xu L X, Dai F, Xing W Y, Ta D A 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 154303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang Y, Wang C Z, Li Y C, Huang J Q, Cai F Y, Xiao Y, Ma T, Zheng H R 2019 IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 28 361
[8] Tufail Y, Yoshihiro A, Pati S, Li M M, Tyler W J 2011 Nat. Protoc. 6 1453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Melde K, Mark A G, Qiu T, Fischer P 2016 Nature 537 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Leith E N, Upatnieks J 1962 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 52 1123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 钟志, 赵婉婷, 单明广, 刘磊 2021 70 154202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong Z, Zhao W T, Shan M G, Liu L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 154202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Andrés D, Jiménez-Gambín S, Jiménez N, Camarena F 2020 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium Las Vegas, NV, USA, November 17, 2020 p1
[13] Jiménez-Gambín S, Jiménez N, Benlloch J M, Camarena F 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 014016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shah B R, Lehman V T, Kaufmann T J, Blezek D, Waugh J, Imphean D, Yu F F, Patel T R, Chitnis S, Dewey Jr R B 2020 Brain 143 2664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yin Y, Yan S, Huang J, Zhang B 2023 Sensors 23 9702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiménez-Gambín S, Jiménez N, Pouliopoulos A N, Benlloch J M, Konofagou E E, Camarena F 2021 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 69 1359
[17] Pouliopoulos A N, Wu S Y, Burgess M T, Karakatsani M E, Kamimura H A, Konofagou E E 2020 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 46 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tillander M, Hokland S, Koskela J, Dam H, Andersen N P, Pedersen M, Tanderup K, Ylihautala M, Köhler M 2016 Med. Phys. 43 1539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Treeby B E, Cox B T 2010 J. Biomed. Opt. 15 021314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Mast T D, Souriau L P, Liu D L, Tabei M, Nachman A I, Waag R C 2001 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 48 341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tabei M, Mast T D, Waag R C 2002 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 111 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kook G, Jo Y, Oh C, Liang X, Kim J, Lee S M, Kim S, Choi J W, Lee H J 2023 Microsyst. Nanoeng. 9 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Treeby B E, Cox B T 2010 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127 2741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Thomas J L, Fink M A 1996 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 43 1122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Aubry J F, Tanter M, Pernot M, Thomas J L, Fink M 2003 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Brown M D, Cox B T, Treeby B E 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 244101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] He J R, Wu J W, Zhu Y Y, Chen Y, Yuan M D, Zeng L M, Ji X R 2021 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 69 662
[28] Tanchenko A 2014 J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 25 874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bakaric M, Miloro P, Javaherian A, Cox B T, Treeby B E, Brown M D 2021 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 150 2798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3208
- PDF下载量: 101
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: