-
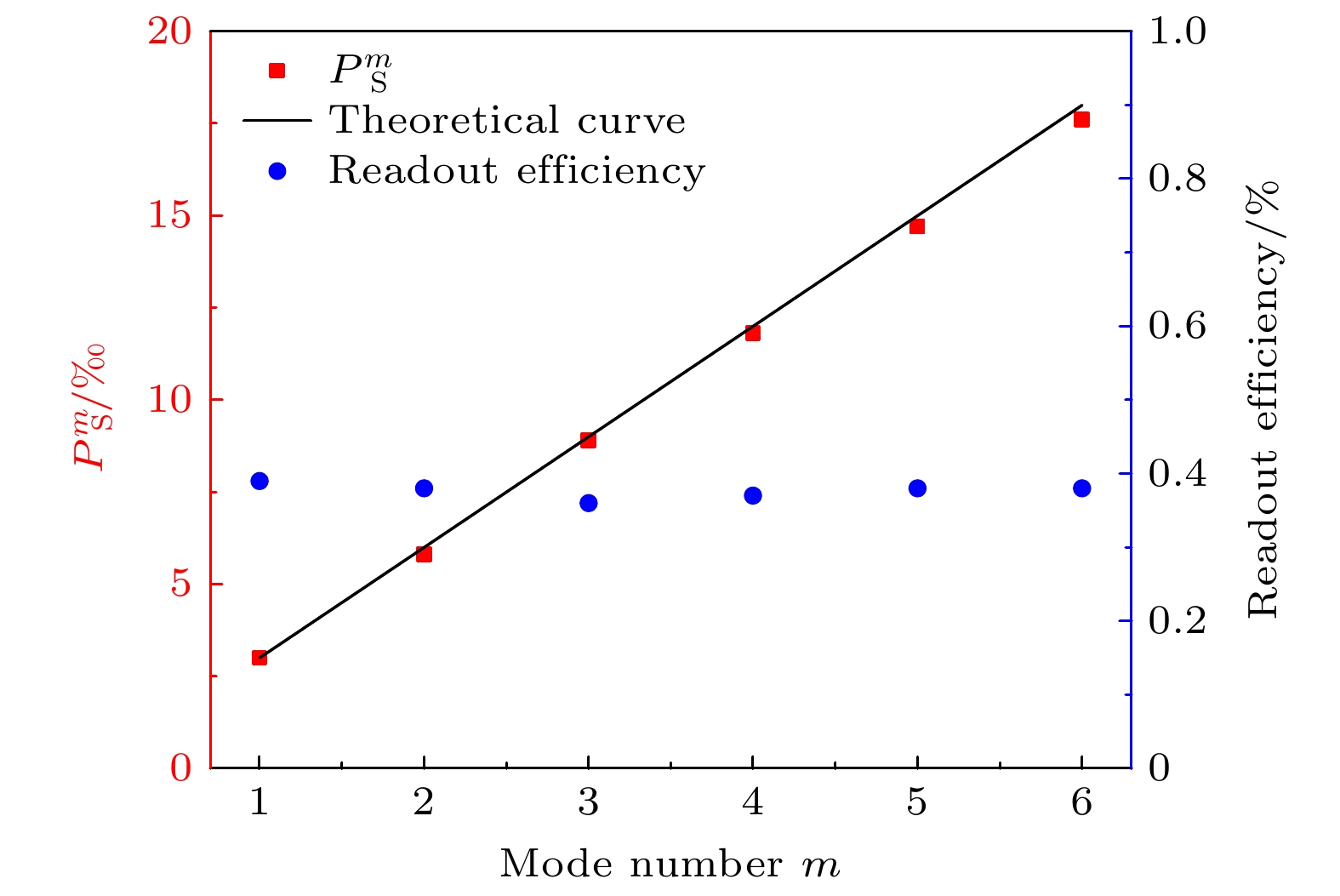
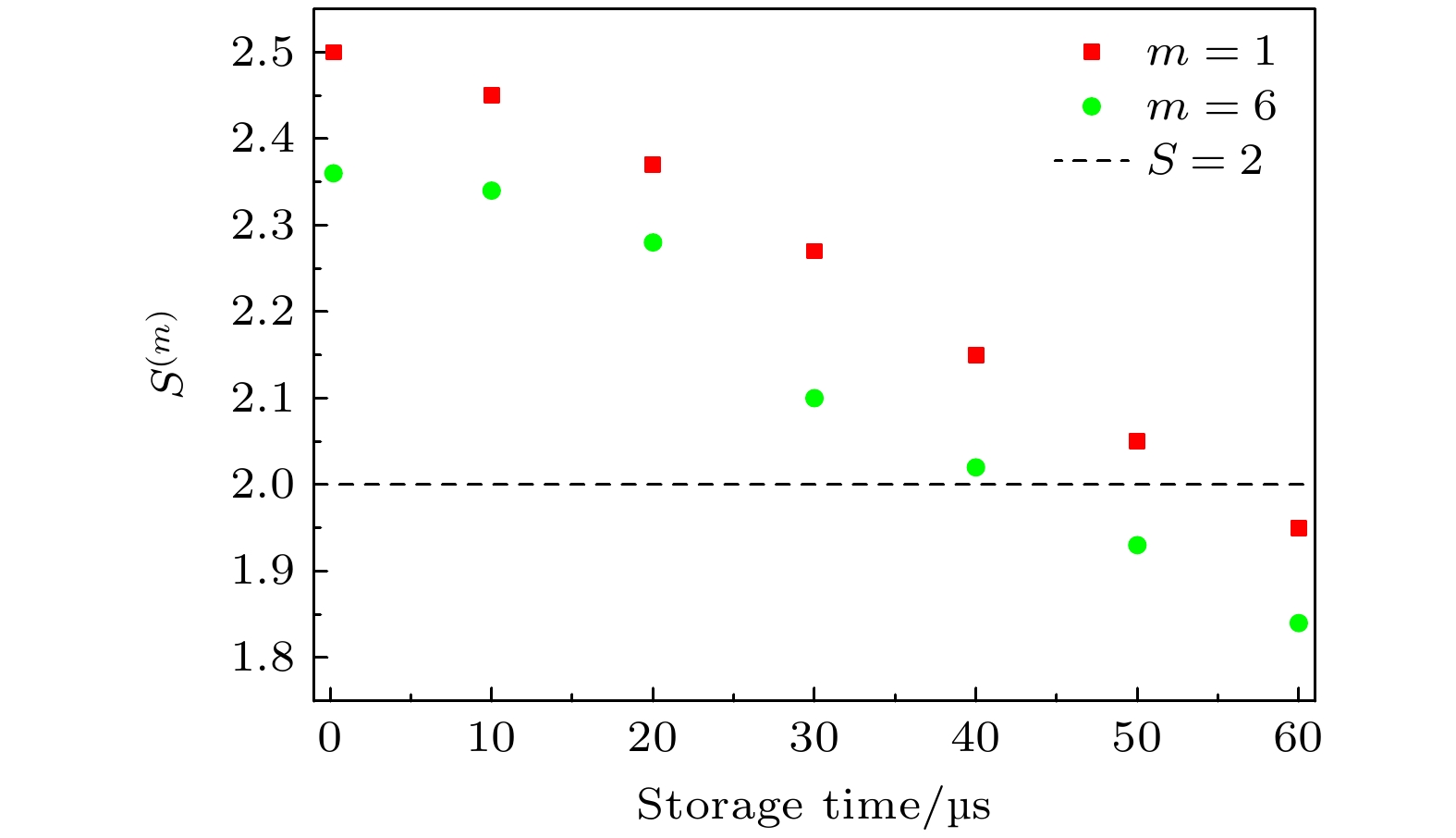
Quantum interfaces that generate entanglement or correlations between a photon and an atomic memory are fundamental building blocks in quantum repeater research. Temporal, spatial, and spectral multiplexed atom–photon entanglement interfaces in cold atomic systems based on spontaneous Raman scattering processes, present an effective technical approach to realizing quantum repeaters. Compared with the other schemes, temporal-multiplexing schemes are particularly attractive since they repeatedly use the same physical process. In these schemes, readout efficiency plays a crucial role. Theoretical models indicate that even if the readout efficiency is increased by 1%, the probability of long-distance entanglement distribution will be increased by 7%–18%. However, current implementation of temporal-multimode quantum memory often suffers low readout efficiency unless an optical cavity or an atomic ensemble with a large optical-depth is adopted. In this study, we solve this challenge by using the expandable pulsed light fabricating technology and carefully selecting energy level transitions, so as to develop an efficient temporal-multiplexed quantum source. Our approach involves applying a train of write laser pulses to an atomic ensemble from different directions, thereby creating spin-wave memories and Stokes-photon emissions. We design an expandable pulsed light fabrication device based on the principle of optical path reversibility, allowing a writing laser beam to pass through an acousto-optic modulator (AOM) network in two different directions. This setup enables precise control over the directions of the write pulse train through real-time manipulation of the field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and the diffraction order of the AOMs. In our experiment, we prepare six pairs of modes. After detecting Stokes photons during the experimental cycle, the FPGA outputs a feedforward signal after a specified storage time, triggering the application of a corresponding reading pulse from the read AOM network to the atomic ensemble, thereby generating an anti-Stokes photon. To enhance readout efficiency, we optimize the energy level structure of the read pulse transitions, $ \left| {{{b}} \to {{{e}}_2}} \right\rangle $ to$ \left| {{{b}} \to {{{e}}_1}} \right\rangle $ ; specifically, we adjust the transition frequencies of the read pulses by comparing with those used in current temporal-multimode quantum memory schemes. Theoretical calculations show that when the frequencies of the read pulses are tuned to the transitions$ \left| {{{b}} \to {{{e}}_1}} \right\rangle $ and$ \left| {{{b}} \to {{{e}}_2}} \right\rangle $ , the readout efficiencies are about 33% and 15%, suggesting that the chosen energy level transitions can double the readout efficiency.Experimental results indicate a readout efficiency of 38% for the multiplexed source and the Bell parameter of 2.35. Additionally, our device has a 5.83-fold higher probability of successfully generating entanglement than a single channel entanglement source. Our method is cost-effective, easy to operate, and highly applicable. For instance, based on our findings, the readout efficiency can be further improved through cavity-enhanced atom–photon coupling, and entanglement fidelity can be increased by suppressing noise in temporal-multimode memory schemes. This work provides a solid foundation and effective methods for realizing the high-efficiency temporal-multimode quantum memory and developing the large-scale quantum networks. -
Keywords:
- high efficiency /
- temporal-multimode memories /
- energy level transition selection /
- pulsed light fabrication technology
[1] Kimble H J 2008 Nature 453 1023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Simon C 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 678
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sangouard N, Simon C, Minář J, Zbinden H, de Riedmatten H, Gisin N 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 050301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Duan L M, Lukin M D, Cirac J I, Zoller P 2001 Nature 414 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 廖骎, 柳海杰, 王铮, 朱凌瑾 2023 72 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao Q, Liu H J, Wang Z, Zhu L J 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zheng Q L, Liu J C, Wu C, Xue S C, Zhu P Y, Wang Y, Yu X Y, Yu M M, Deng M T, Wu J J, Xu P 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 024206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sun Y, Sun C W, Zhou W, Yang R, Duan J C, Gong Y X, Xu P, Zhu S N 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 080308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Abruzzo S, Kampermann H, Bruß D 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 012301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Inagaki T, Matsuda N, Tadanaga O, Asobe M, Takesue H 2013 Opt. Express 21 23241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ding D S, Zhang W, Zhou Z Y, Shi S, Shi B S, Guo G C 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu Y L, Tian L, Xu Z X, Ge W, Chen L R, Li S J, Peng K C 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 052327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wen Y F, Zhou P, Xu Z, Yuan L, Zhang H, Wang S, Wang H 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 012342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu H L, Wang M J, Jiao H L, Lu J J, Fan W X, Li S J, Wang H 2023 Opt. Express 31 7200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li Y, Wen Y F, Wang M J, Liu C, Liu H L, Li S J, Wang H 2022 Phy. Rev. A 106 022610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pu Y F, Jiang N, Chang W, Yang H X, Li C, Duan L M 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 15359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tian L, Xu Z X, Chen L R, Ge W, Yuan H X, Wen Y F, Wang H 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 130505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lipka M, Mazelanik M, Leszczyński A, Wasilewski W, Parniak M 2021 Commun. Phys. 4 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Krovi H, Guha S, Dutton Z, Slater J A, Simon C, Tittel W 2016 Appl. Phys. B. 52 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Saglamyurek E, Puigibert M G, Zhou Q, Giner L, Marsili F, Verma V B, Nam S W, Oesterling L, Nippa D, Oblak D, Tittel W 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Albrecht B, Farrera P, Heinze G, Cristiani M, de Riedmatten H 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 160501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Farrera P, Heinze G, de Riedmatten H 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 100501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Heller L, Farrera P, Heinze G, de Riedmatten H 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 210504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sangouard N, Simon C, de Riedmatten H, Gisin N 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jiang L, Taylor J M, Lukin M D 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 012301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 温亚飞, 田剑锋, 王志强, 庄园园 2023 72 060301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen Y F, Tian J F, Wang Z Q, Zhuang Y Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 060301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yang S J, Wang X J, Li J, Rui J, Bao X H, Pan J W 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 210501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bao X H, Reingruber A, Dietrich P, Rui J, Dück A, Strassel T, Li L, Liu N L, Zhao B, Pan J W 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Simon C, de Riedmatten H, Afzelius M 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 010304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Cho Y W, Campbell G T, Everett J L, Bernu J, Higginbottom D B, Cao M T, Geng J, Robins N P, Lam P K, Buchler B C 2016 Optica 3 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhao B, Chen Y A, Bao X H, Strassel T, Chuu C S, Jin X M, Schmiedmayer J, Yuan Z S, Chen S, Pan J W 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 周湃, 温亚飞, 袁亮, 李雅, 李淑静, 王海 2020 量子光学学报 26 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou P, Wen Y F, Yuan L, Li Y, Li S J, Wang H 2020 Acta Sin. Quan. Opt. 26 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
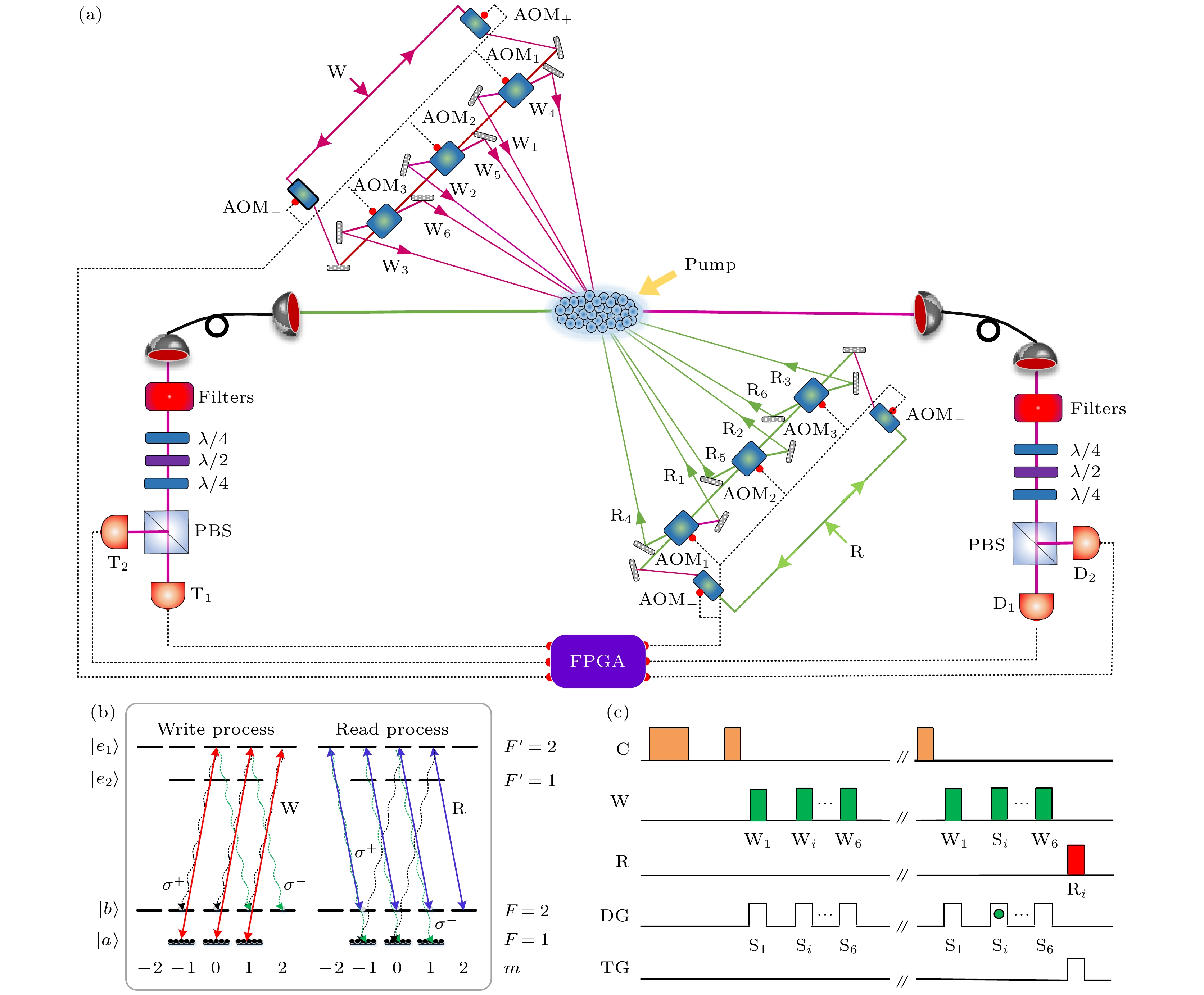
图 1 (a) 实验装置图, 其中Wi (Ri)为第i路写(读)光, Filters为滤波器, D (T)为单光子探测器, PBS为偏振分束棱镜, AOM为声光调制器; (b) 原子能级图, 其中$ {\sigma ^ + } $($ {\sigma ^ - } $)为不同偏振的出射光子(右旋或左旋); (c) 实验时序图, 其中W, C, R为写光、清洁光(泵浦光)、读光; DG, TG为单光子探测器门开关
Fig. 1. (a) Experimental setup; Wi (Ri), the i-th write (read) pulses; Filters, F-P etalons; D (T), single photon detector; PBS, polarization beam splitter; AOM, acousto-optic modulator; (b) relevant atomic levels; $ {\sigma ^ + } $($ {\sigma ^ - } $), right (left) polarization of emitted photon; (c) time sequence of the experimental trials; W, C, R, write, cleaning, and read pulses; DG (TG), timeline of the D (T) detector gate.
表 1 单路纠缠源读出效率
Table 1. Readout efficiency of single channel entangled source.
第 i 路 1 2 3 4 5 6 恢复效率$ {\gamma _{{i}}} $/% 0.39 0.36 0.35 0.38 0.38 0.36 表 2 单路纠缠源Bell参数测量
Table 2. Measurement of Bell parameters for single channel entanglement source.
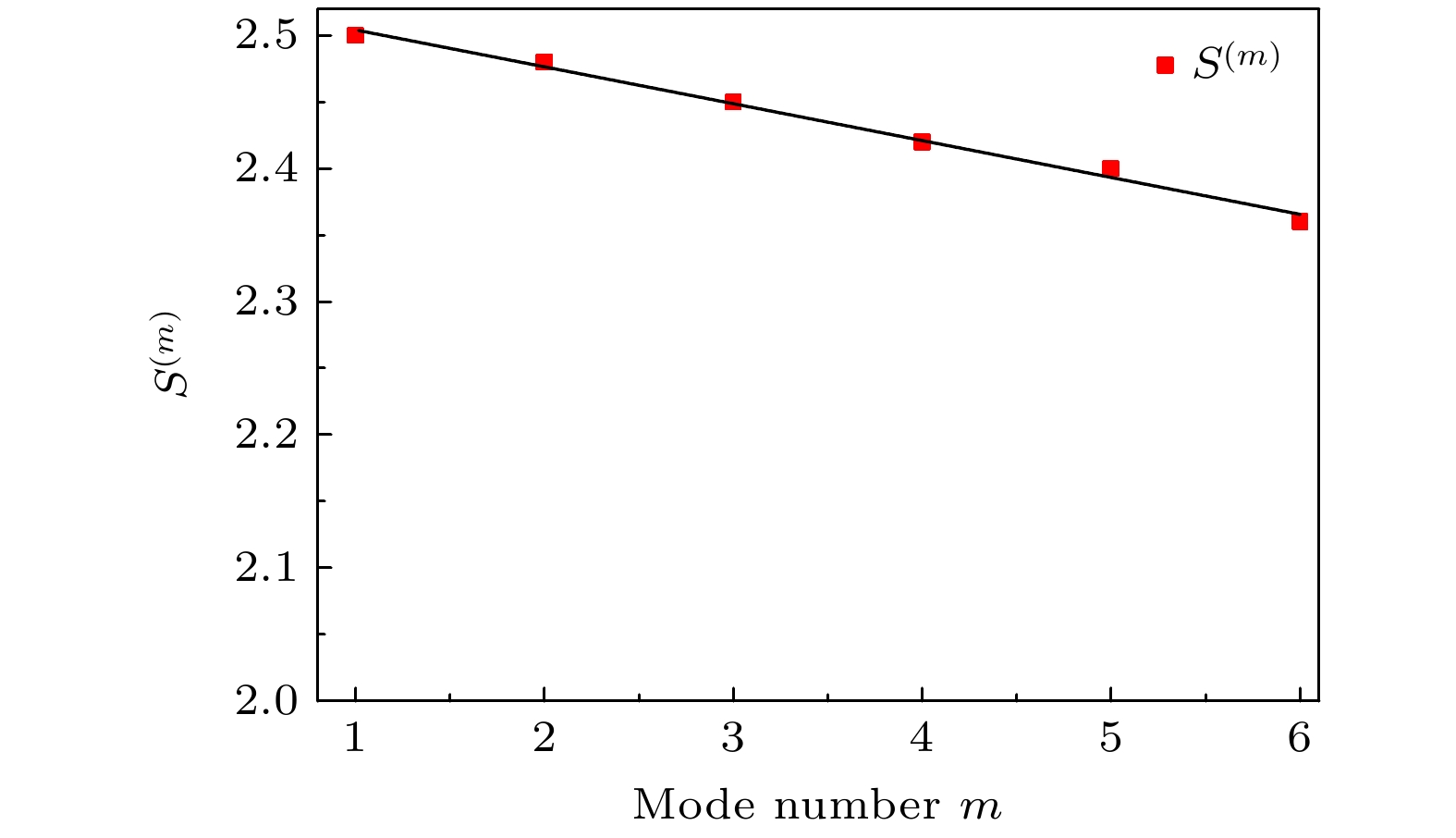
第i 路 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bell参数S 2.50 2.47 2.48 2.51 2.47 2.46 -
[1] Kimble H J 2008 Nature 453 1023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Simon C 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 678
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sangouard N, Simon C, Minář J, Zbinden H, de Riedmatten H, Gisin N 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 050301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Duan L M, Lukin M D, Cirac J I, Zoller P 2001 Nature 414 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 廖骎, 柳海杰, 王铮, 朱凌瑾 2023 72 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao Q, Liu H J, Wang Z, Zhu L J 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zheng Q L, Liu J C, Wu C, Xue S C, Zhu P Y, Wang Y, Yu X Y, Yu M M, Deng M T, Wu J J, Xu P 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 024206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sun Y, Sun C W, Zhou W, Yang R, Duan J C, Gong Y X, Xu P, Zhu S N 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 080308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Abruzzo S, Kampermann H, Bruß D 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 012301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Inagaki T, Matsuda N, Tadanaga O, Asobe M, Takesue H 2013 Opt. Express 21 23241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ding D S, Zhang W, Zhou Z Y, Shi S, Shi B S, Guo G C 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu Y L, Tian L, Xu Z X, Ge W, Chen L R, Li S J, Peng K C 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 052327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wen Y F, Zhou P, Xu Z, Yuan L, Zhang H, Wang S, Wang H 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 012342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu H L, Wang M J, Jiao H L, Lu J J, Fan W X, Li S J, Wang H 2023 Opt. Express 31 7200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li Y, Wen Y F, Wang M J, Liu C, Liu H L, Li S J, Wang H 2022 Phy. Rev. A 106 022610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pu Y F, Jiang N, Chang W, Yang H X, Li C, Duan L M 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 15359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tian L, Xu Z X, Chen L R, Ge W, Yuan H X, Wen Y F, Wang H 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 130505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lipka M, Mazelanik M, Leszczyński A, Wasilewski W, Parniak M 2021 Commun. Phys. 4 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Krovi H, Guha S, Dutton Z, Slater J A, Simon C, Tittel W 2016 Appl. Phys. B. 52 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Saglamyurek E, Puigibert M G, Zhou Q, Giner L, Marsili F, Verma V B, Nam S W, Oesterling L, Nippa D, Oblak D, Tittel W 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Albrecht B, Farrera P, Heinze G, Cristiani M, de Riedmatten H 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 160501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Farrera P, Heinze G, de Riedmatten H 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 100501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Heller L, Farrera P, Heinze G, de Riedmatten H 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 210504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sangouard N, Simon C, de Riedmatten H, Gisin N 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jiang L, Taylor J M, Lukin M D 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 012301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 温亚飞, 田剑锋, 王志强, 庄园园 2023 72 060301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen Y F, Tian J F, Wang Z Q, Zhuang Y Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 060301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yang S J, Wang X J, Li J, Rui J, Bao X H, Pan J W 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 210501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bao X H, Reingruber A, Dietrich P, Rui J, Dück A, Strassel T, Li L, Liu N L, Zhao B, Pan J W 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Simon C, de Riedmatten H, Afzelius M 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 010304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Cho Y W, Campbell G T, Everett J L, Bernu J, Higginbottom D B, Cao M T, Geng J, Robins N P, Lam P K, Buchler B C 2016 Optica 3 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhao B, Chen Y A, Bao X H, Strassel T, Chuu C S, Jin X M, Schmiedmayer J, Yuan Z S, Chen S, Pan J W 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 周湃, 温亚飞, 袁亮, 李雅, 李淑静, 王海 2020 量子光学学报 26 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou P, Wen Y F, Yuan L, Li Y, Li S J, Wang H 2020 Acta Sin. Quan. Opt. 26 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3239
- PDF下载量: 83
- 被引次数: 0















 下载:
下载: