-
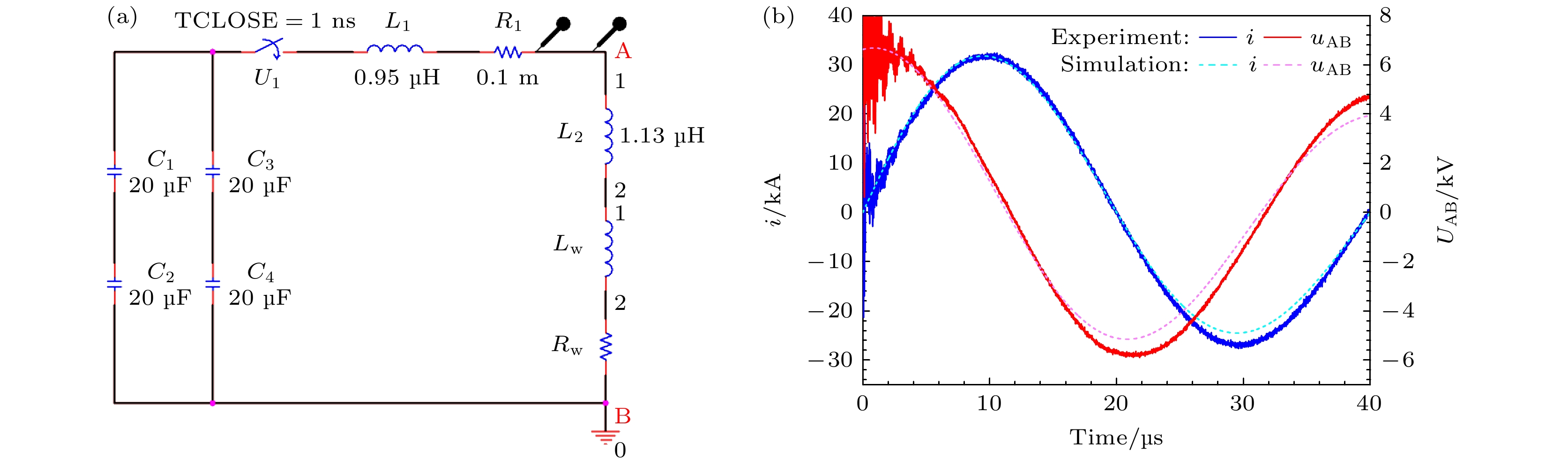
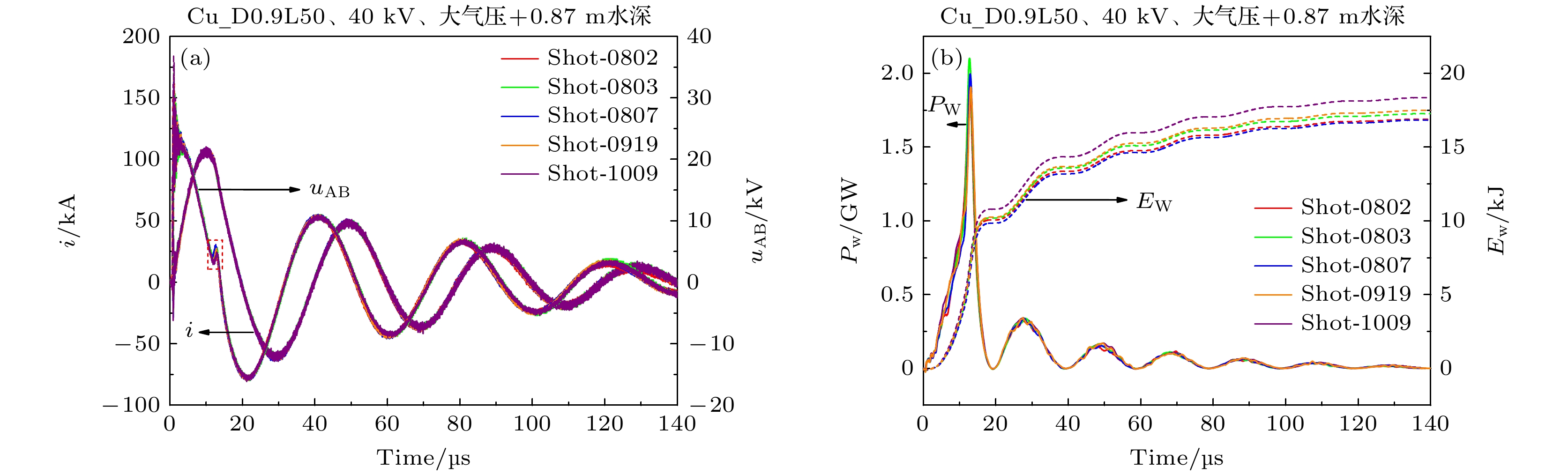
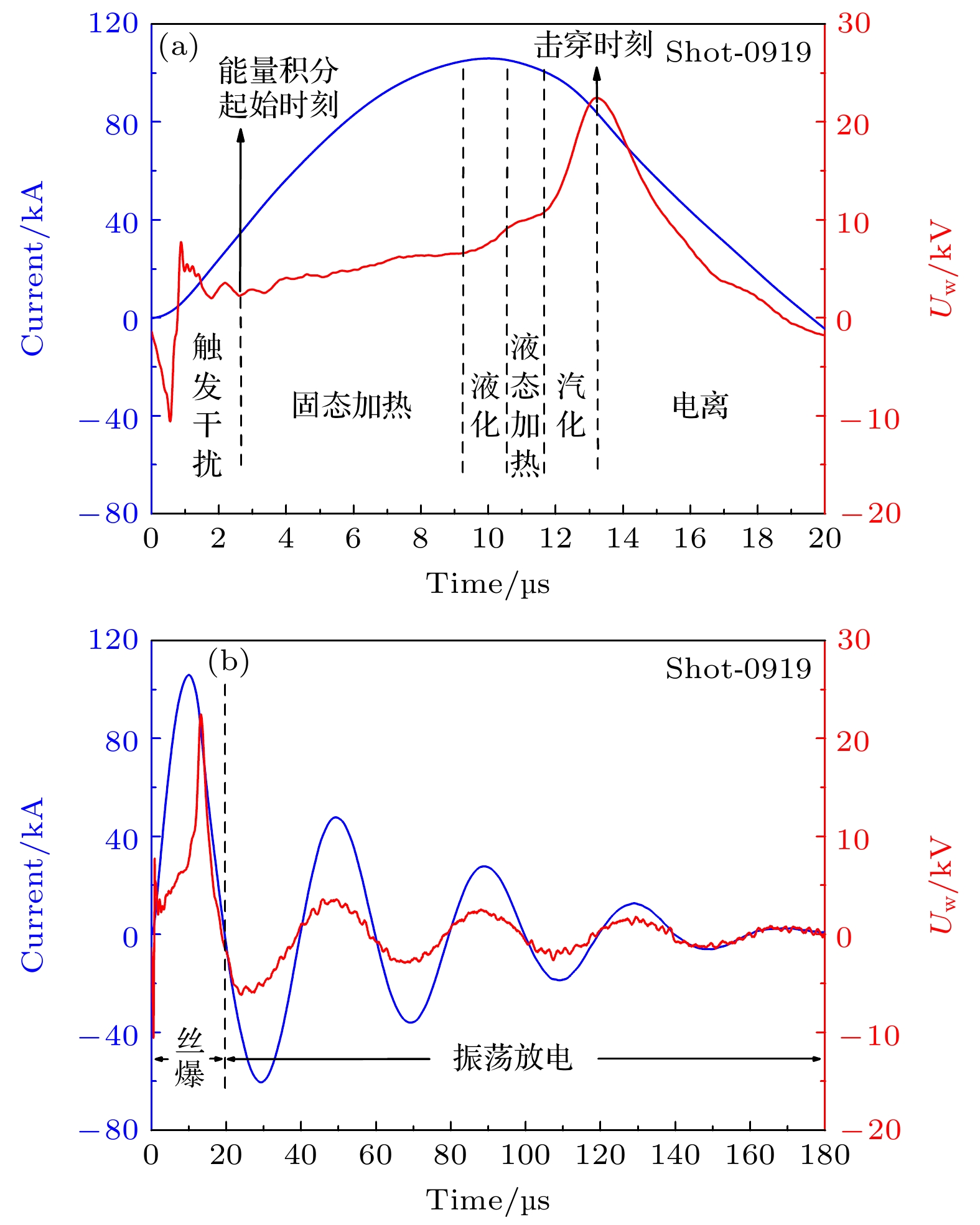
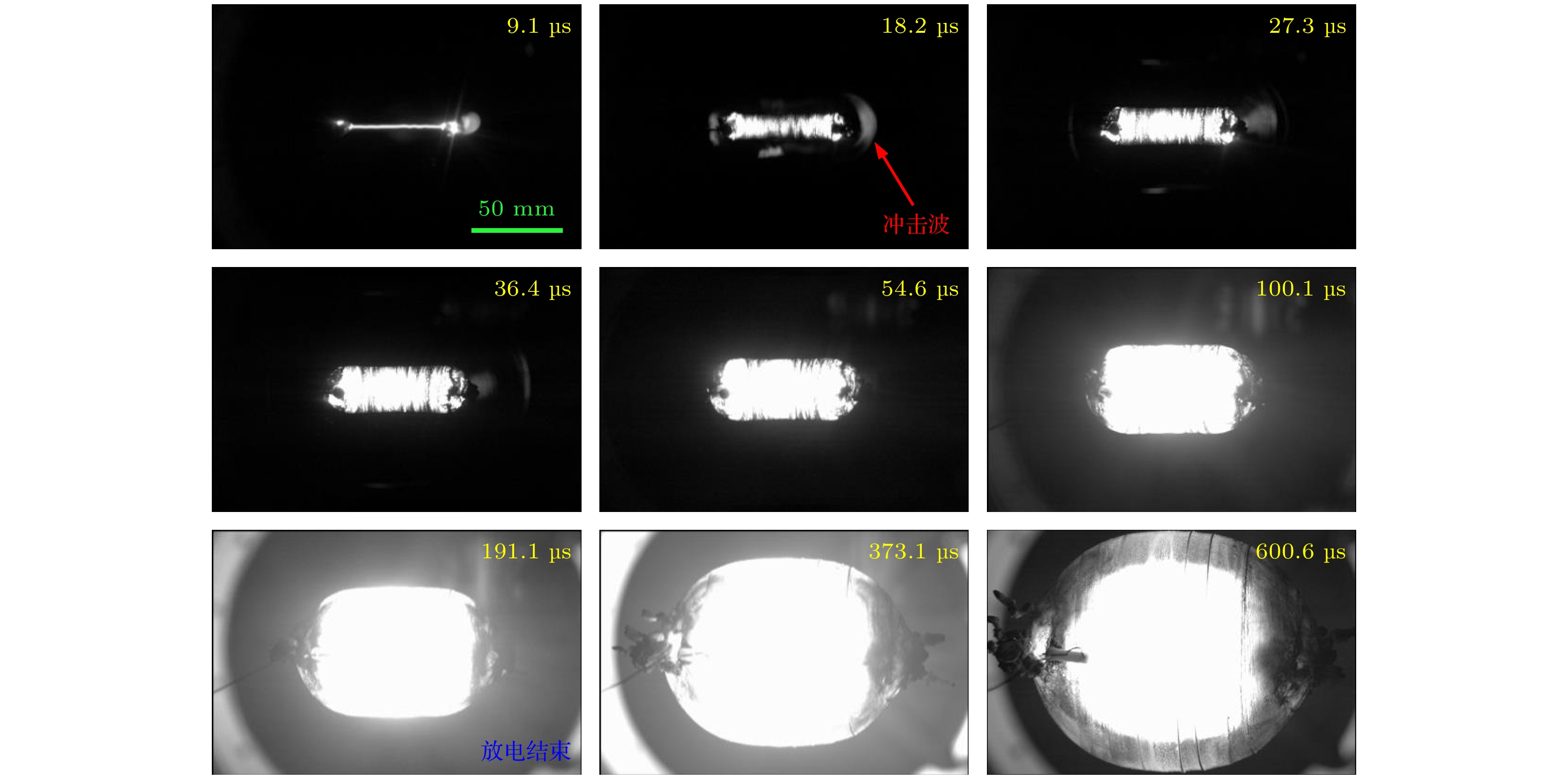
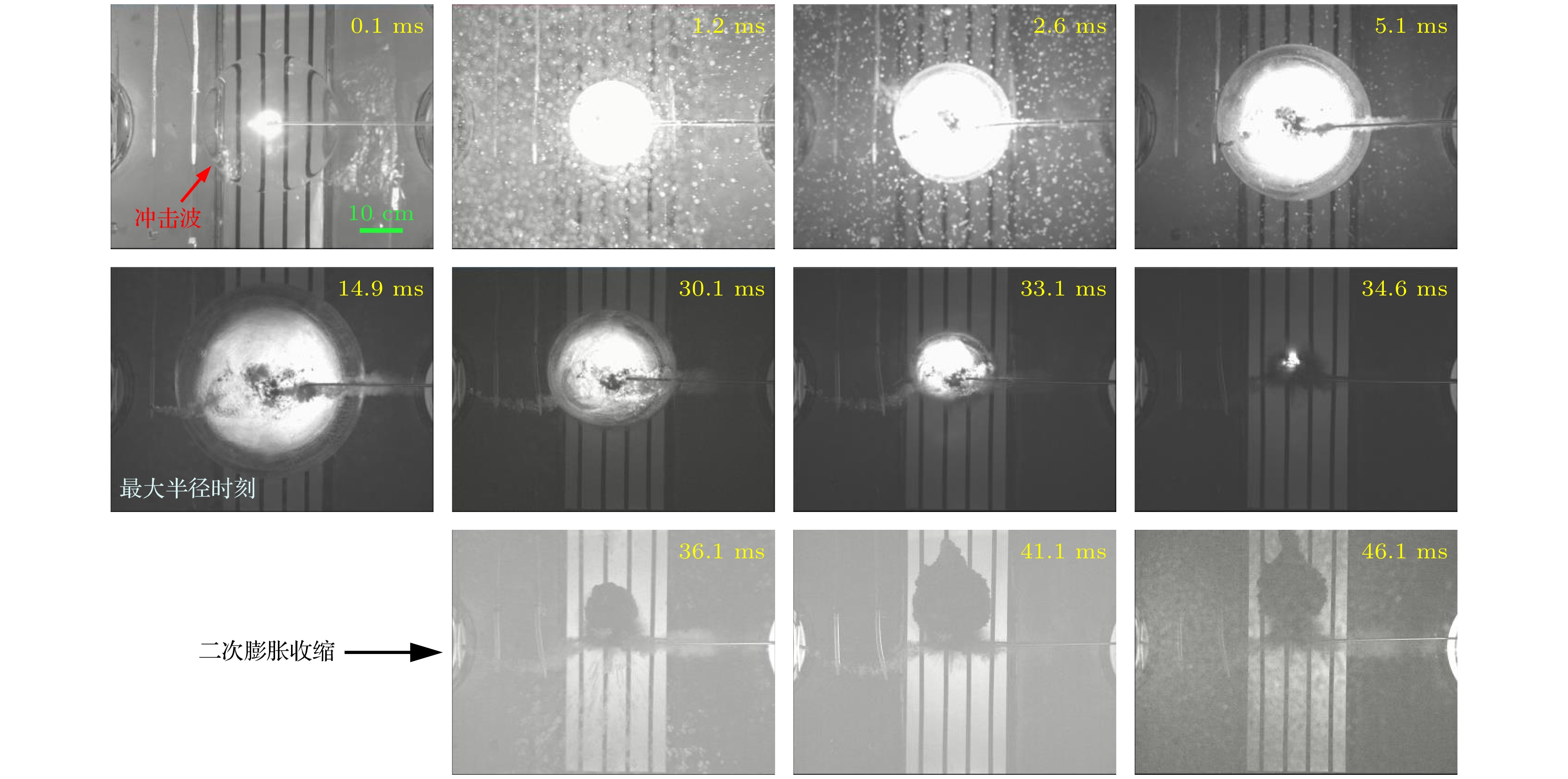
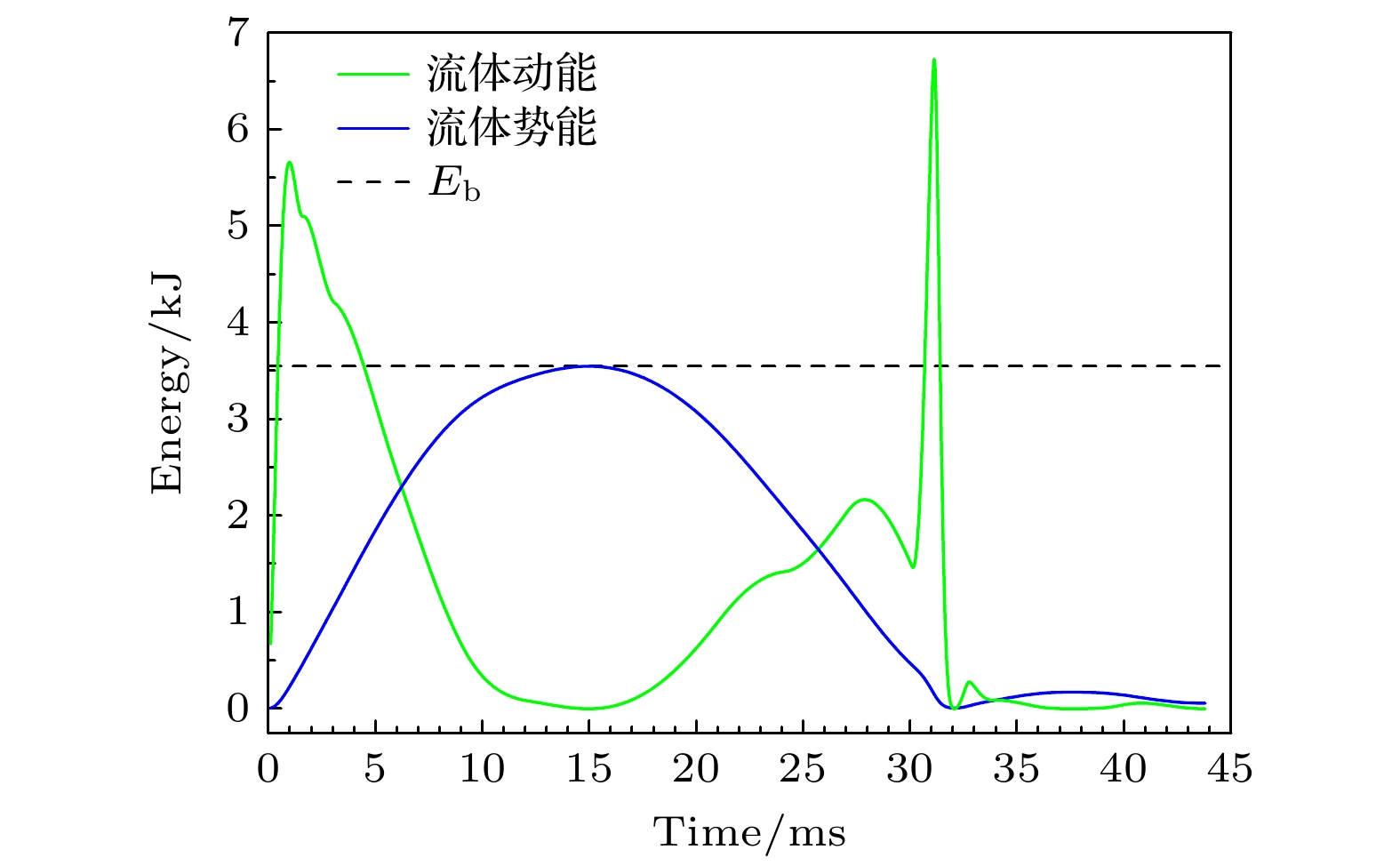
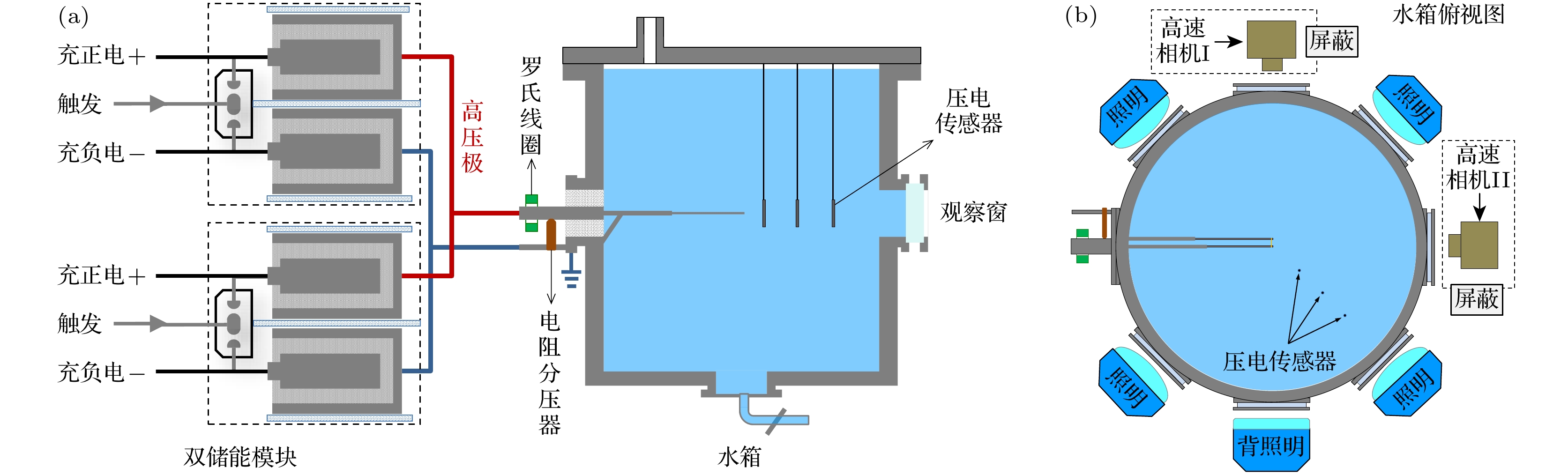
水下爆炸气泡脉动产生的压力波及滞后流可以对舰船的整体结构产生破坏作用. 本文介绍了采用电爆炸丝的技术途径开展水下爆炸气泡的初步实验研究工作, 重点聚焦于气泡的宏观物理特征、运动规律、以及与传统化爆气泡的差异. 实验装置主要由2个并联的储能放电模块和爆炸水箱组成. 每个模块由2台20 μF的电容器以及位于电容器之间的气体放电开关串联构成. 负载采用了1根直径0.9 mm、长度50 mm的纯铜丝. 实验结果显示, 铜丝被电离后形成等离子体的最高能量密度与TNT相当; 等离子体在膨胀过程中汽化周围的水介质并逐渐演变为气泡; 气泡的总脉动次数不超过4次, 内部的主要成分应该为铜蒸气和水蒸气, 并在能量耗尽后直接溃灭于水中. 通过实验数据与现有理论运动模型的比较发现, 气泡在膨胀阶段汽化水介质导致一定的内能损耗, 使得其运动轨迹的模拟结果与实验数据具有一定差异.Low-frequency hysteresis flow and pulsating pressure caused by underwater explosion bubbles can cause overall damage to ships. The hydrodynamic and energy conversion of bubbles are very important in studying underwater explosion bubbles. At present the study of bubble dynamics is based on ideal gas hypothesis, which does not involve heat exchange and is only suitable for bubbles of chemical detonating, but not for bubbles at higher temperatures. The evolution of underwater explosion bubbles is studied experimentally by underwater exploding wire. There is obvious heat exchange during the evolution of bubbles, which is different from bubble behavior in chemical detonating underwater. This study focuses on pulsating behavior and energy characteristic of bubbles, and the difference from chemical detonating as well. The experimental facility is mainly composed of two parallel energy storage-discharge modules and a water tank. Each module is composed of two 20 μF capacitors connected and a gas switch connected in series with these two capacitors. A copper wire with a diameter of 0.9 mm and a length of 50 mm is used as a load. The experimental results show that the deposited energy density generated by electric explosion is almost equal to that of TNT. The wire plasma expansion produces an initial bubble with temperature of radially spatial distribution. The total pulsation frequency of bubble will not exceed 4 times. After energy exhaustion, bubbles collapse directly into water because the main component is condensable gas. The comparison of the experimental data with the existing theoretical models shows that the vaporization of water in bubble expansion stage leads to certain energy loss, which makes difference in motion trajectory of bubbles between the simulation and the experiment. This study provides ideas and data support for the dynamical study of high temperature bubbles in underwater explosion.
-
Keywords:
- underwater explosion /
- bubbles /
- underwater electrical explosion /
- bubble pulsation
[1] Rayleigh L 1917 Philos. Mag. 34 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cole R H 1948 Underwater Explosion (Princeton: Princeton University Press
[3] Plesset M 1949 J. Appl. Mech. 16 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gilmore F 1952 The Growth and Collapse of a Spherical Bubble in a Viscous Compressible Liquid (Pasadena: Hydrodynamics Laboratory California Institute of Technology) Tech. Report No. 26-4
[5] Keller J B, Miksis M 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Prosperetti A, Lezzi A 1986 J. Fluid Mech. 168 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lezzi A, Prosperetti A 1987 J. Fluid Mech. 185 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Best J 1991 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wollongong: University of Wollongong
[9] Geers T L, Hunter K S 2002 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 111 1584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 姚熊亮, 汪玉, 张阿漫 2012 水下爆炸气泡动力学 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社)
Yao X L, Wang Y, Zhang A M 2012 Bubble Dynamics of Underwater Explosion (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press
[11] 张阿漫, 姚熊亮 2008 57 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang A M, Yao X L 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张阿漫, 姚熊亮, 李佳 2008 57 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang A M, Yao X L, Li J 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张阿漫, 王超, 王诗平, 程晓达 2012 61 084701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang A M, Wang C, Wang S P, Cheng X D 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 084701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 叶曦, 姚熊亮, 张阿漫, 庞福振 2013 62 114702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ye X, Yao X L, Zhang A M, Pang F Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 114702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李帅, 孙龙泉, 张阿漫 2014 63 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S, Sun L Q, Zhang A M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang A M, Li S M, Cui P 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 033323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张阿漫, 明付仁, 刘云龙, 李帅, 王诗平 2023 中国舰船研究 18 139
Zhang A M, Ming F R, Liu Y L, Li S, Wang S P 2023 Chin. J. Ship Res. 18 139
[18] 段超伟, 宋浦, 胡宏伟, 杨青, 冯海云 2022 爆破 39 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan W C, Song P, Hu H W, Yang Q, Feng H Y 2022 Blasting 39 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Thomsen J M, Ruhl S F 1980 Mitigation of Explosion Bubble Pulsation Caused by the Deep Underwater Detonation of a Tapered Charge (Washington, D. C.: Director Defense Nuclear Agency) Phys. Int. Co. AD-A107804
[20] Kriebel A R, Bechtel J S 1970 Hydro dynamic Data From Exploding Wires (Washington, D.C.: Office of Naval Research Department of the Navy) URS Res. Co. AD-706074
[21] Buntzen R R 1962 The Use of Exploding Wires in the Study of Small-Scale Underwater Explosions (New York: Plenum Press) USRDL Tech. Report No. 195
[22] Hege J S 1963 Hydra Program Determination of the Total Thermal Radiant Energy Emitted by an Underwater Exploding Wire (San Francisco: U.S. Naval Radiological Defense Laboratory) Def. Doc. Center AD-401342
[23] Zhou Q, Zhang Q G, Zhang J, Zhao J P, Ren B Z, Pang L 2011 Plasma Sci. Tech. 11 661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 韩若愚, 吴佳玮, 周海滨, 邱爱慈 2017 电工技术学报 32 257
Han R Y, Wu J W, Zhou H B, Qiu A C 2017 Trans. Chin. Eeletrotech. Soc. 32 257
[25] 吴坚, 阴国锋, 范云飞, 李兴文, 邱爱慈 2018 高电压技术 44 4003
Wu J, Yin G F, Fan Y F, Li X W, Qiu A C 2018 High Voltage Eng. 44 4003
[26] 钱盾, 刘志刚, 邹晓兵, 王新新 2021 高电压技术 47 815
Qian D, Liu Z G, Zou X B, Wang X X 2021 High Voltage Eng. 47 815
[27] Antonov O, Gilburd L, Efimov S, Bazalitski G, Gurovich V T, Krasik Y E 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 102702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lauterborn W, Bolle H 1975 J. Fluid Mech. 72 391
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 宗思光, 王江安, 刘涛, 郭广立 2011 爆炸与冲击 31 0641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zong S G, Wang J A, Liu T, Guo G L 2011 Explosion and Shock Waves 31 0641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Jia Z W, Li D, Tian Y, Pan H P, Zhong Q, Yao Z F, Lu Y, Guo J J, Zheng R E 2023 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 206 106713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 梁川, 章林文, 李欣 2004 强激光与粒子束 16 787
Liang C, Zhang L W, Li X 2004 High Power Laser Part. Beams 16 787
[32] Oreshkin V I, Chaikovsky S A, Ratakhin N A, Grinenko A, Krasik Y E 2007 Phys. Plasmas 14 102703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhang A M, Wang S P, Huang C, Wang B 2013 Eur. J. Mech. B. Fluids 42 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kolacek K, Prukner V, Schmidt J, Frolovo O, Straus J 2010 Laser Part. Beams 28 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang Q X 2013 Phys. Fluids 25 072104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
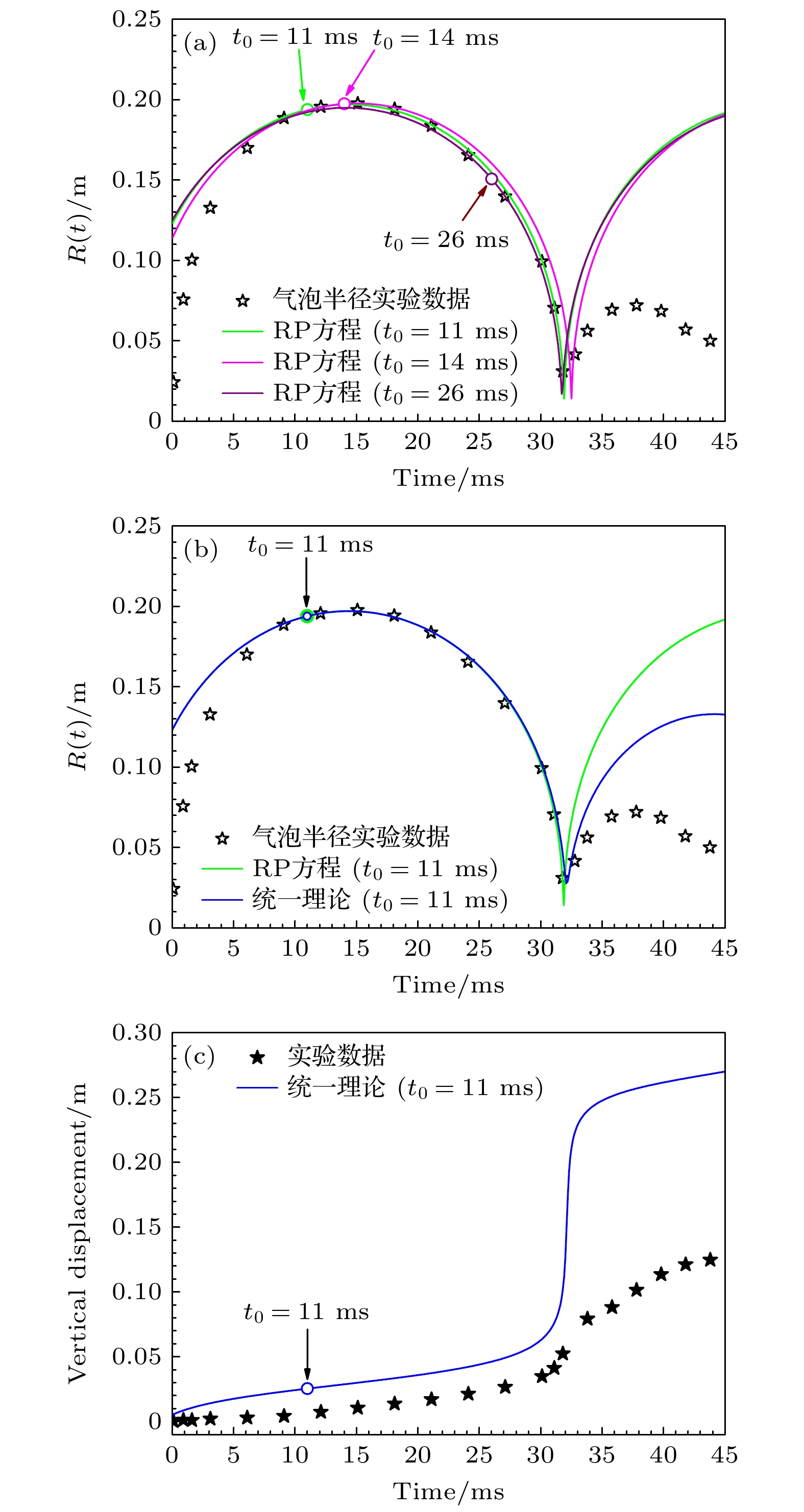
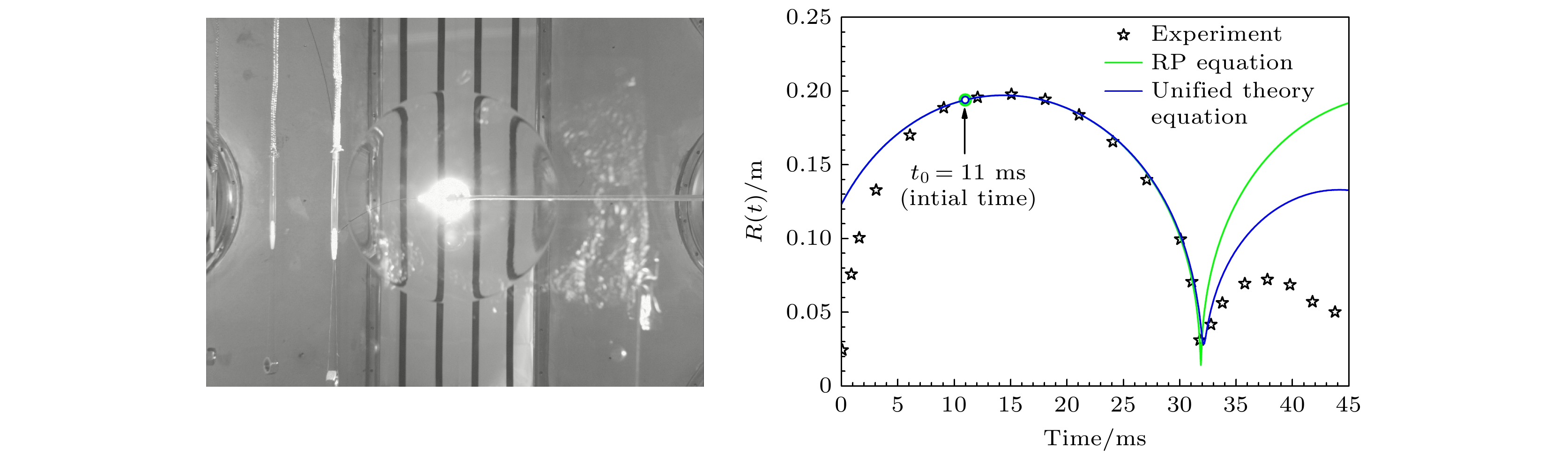
图 10 (a) RP理论模型在不同初始条件下的气泡膨胀轨迹模拟比较; (b)二种理论模型对气泡膨胀轨迹的模拟及与实验比较; (c)气泡质心垂直位移的实验与模拟结果比较
Fig. 10. Experimental data and simulation results of (a) bubble expansion trajectory in different initial conditions of the RP theoretical model, (b) bubble expansion trajectory by two theoretical models and (c) vertical migration of bubble centroid.
-
[1] Rayleigh L 1917 Philos. Mag. 34 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cole R H 1948 Underwater Explosion (Princeton: Princeton University Press
[3] Plesset M 1949 J. Appl. Mech. 16 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gilmore F 1952 The Growth and Collapse of a Spherical Bubble in a Viscous Compressible Liquid (Pasadena: Hydrodynamics Laboratory California Institute of Technology) Tech. Report No. 26-4
[5] Keller J B, Miksis M 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Prosperetti A, Lezzi A 1986 J. Fluid Mech. 168 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lezzi A, Prosperetti A 1987 J. Fluid Mech. 185 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Best J 1991 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wollongong: University of Wollongong
[9] Geers T L, Hunter K S 2002 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 111 1584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 姚熊亮, 汪玉, 张阿漫 2012 水下爆炸气泡动力学 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社)
Yao X L, Wang Y, Zhang A M 2012 Bubble Dynamics of Underwater Explosion (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press
[11] 张阿漫, 姚熊亮 2008 57 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang A M, Yao X L 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张阿漫, 姚熊亮, 李佳 2008 57 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang A M, Yao X L, Li J 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张阿漫, 王超, 王诗平, 程晓达 2012 61 084701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang A M, Wang C, Wang S P, Cheng X D 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 084701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 叶曦, 姚熊亮, 张阿漫, 庞福振 2013 62 114702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ye X, Yao X L, Zhang A M, Pang F Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 114702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李帅, 孙龙泉, 张阿漫 2014 63 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S, Sun L Q, Zhang A M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang A M, Li S M, Cui P 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 033323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张阿漫, 明付仁, 刘云龙, 李帅, 王诗平 2023 中国舰船研究 18 139
Zhang A M, Ming F R, Liu Y L, Li S, Wang S P 2023 Chin. J. Ship Res. 18 139
[18] 段超伟, 宋浦, 胡宏伟, 杨青, 冯海云 2022 爆破 39 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan W C, Song P, Hu H W, Yang Q, Feng H Y 2022 Blasting 39 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Thomsen J M, Ruhl S F 1980 Mitigation of Explosion Bubble Pulsation Caused by the Deep Underwater Detonation of a Tapered Charge (Washington, D. C.: Director Defense Nuclear Agency) Phys. Int. Co. AD-A107804
[20] Kriebel A R, Bechtel J S 1970 Hydro dynamic Data From Exploding Wires (Washington, D.C.: Office of Naval Research Department of the Navy) URS Res. Co. AD-706074
[21] Buntzen R R 1962 The Use of Exploding Wires in the Study of Small-Scale Underwater Explosions (New York: Plenum Press) USRDL Tech. Report No. 195
[22] Hege J S 1963 Hydra Program Determination of the Total Thermal Radiant Energy Emitted by an Underwater Exploding Wire (San Francisco: U.S. Naval Radiological Defense Laboratory) Def. Doc. Center AD-401342
[23] Zhou Q, Zhang Q G, Zhang J, Zhao J P, Ren B Z, Pang L 2011 Plasma Sci. Tech. 11 661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 韩若愚, 吴佳玮, 周海滨, 邱爱慈 2017 电工技术学报 32 257
Han R Y, Wu J W, Zhou H B, Qiu A C 2017 Trans. Chin. Eeletrotech. Soc. 32 257
[25] 吴坚, 阴国锋, 范云飞, 李兴文, 邱爱慈 2018 高电压技术 44 4003
Wu J, Yin G F, Fan Y F, Li X W, Qiu A C 2018 High Voltage Eng. 44 4003
[26] 钱盾, 刘志刚, 邹晓兵, 王新新 2021 高电压技术 47 815
Qian D, Liu Z G, Zou X B, Wang X X 2021 High Voltage Eng. 47 815
[27] Antonov O, Gilburd L, Efimov S, Bazalitski G, Gurovich V T, Krasik Y E 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 102702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lauterborn W, Bolle H 1975 J. Fluid Mech. 72 391
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 宗思光, 王江安, 刘涛, 郭广立 2011 爆炸与冲击 31 0641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zong S G, Wang J A, Liu T, Guo G L 2011 Explosion and Shock Waves 31 0641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Jia Z W, Li D, Tian Y, Pan H P, Zhong Q, Yao Z F, Lu Y, Guo J J, Zheng R E 2023 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 206 106713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 梁川, 章林文, 李欣 2004 强激光与粒子束 16 787
Liang C, Zhang L W, Li X 2004 High Power Laser Part. Beams 16 787
[32] Oreshkin V I, Chaikovsky S A, Ratakhin N A, Grinenko A, Krasik Y E 2007 Phys. Plasmas 14 102703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhang A M, Wang S P, Huang C, Wang B 2013 Eur. J. Mech. B. Fluids 42 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kolacek K, Prukner V, Schmidt J, Frolovo O, Straus J 2010 Laser Part. Beams 28 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang Q X 2013 Phys. Fluids 25 072104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4453
- PDF下载量: 628
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: