-
目前, 光学测温技术在传感、治疗、诊断和成像等领域取得了重大突破. 但是, 基于传统热耦合能级荧光强度比测温的灵敏度较低, 限制了其进一步的发展. 本文基于基质与掺杂离子间不同的温度依赖行为, 提出了一种新型的具有高灵敏度的测温方案. 首先, 采用固相法成功合成了YVO4:Pr3+荧光粉. 然后, 采用X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜和荧光分光光度计对样品的结构与发光特性进行表征. XRD结果表明Pr3+成功掺入YVO4基质. SEM结果表明样品为长方体形状微米晶颗粒, 平均颗粒大小约为2.1 μm. 在320 nm激发下, YVO4:Pr3+主要呈现出在440 nm附近的蓝光发射和606 nm的红光发射, 发光峰不存在明显的重叠. 基于
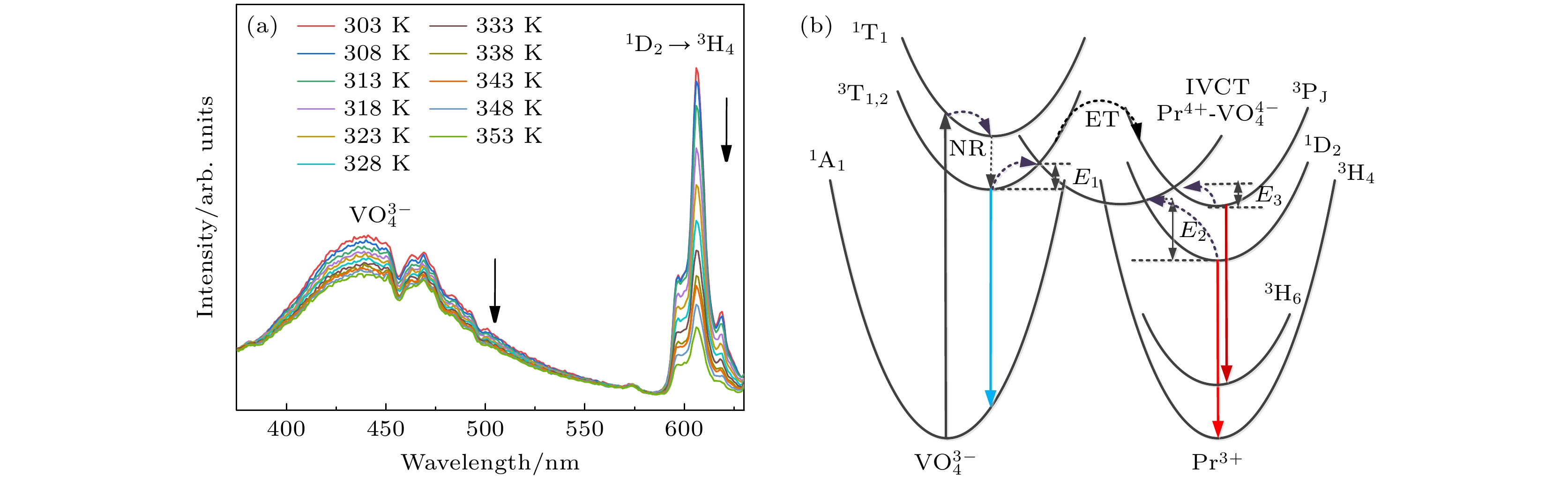
${\text{VO}}_4^{3 - } $ 与Pr3+的发光对温度的不同响应, 实现了新的荧光强度比测温方案. 测温范围为303—353 K, 最大绝对灵敏度和相对灵敏度分别为0.651 K–1和3.112×10–2 K–1@353 K, 远高于传统的热耦合能级测温方案. 这为设计具有优异温度灵敏度和信号可辨别性的自参考光学测温材料提供了一种有前景的途径.It is noteworthy that since 2010, the number of published and cited scientific papers on optical thermometry has increased exponentially. Optical thermometry technology is about to make a significant process in sensing, therapy, diagnosis, and imaging. The current research mainly focuses on optical thermometry that is developing towards high-sensitivity thermometry. In this work, a new thermometry strategy is proposed based on the different temperature-dependent behaviors between the host ions and the doped ions. Firstly, YVO4:xPr3+(x = 0%–1.5%) phosphors are successfully synthesized by the solid-state method. Then, the structure and luminescence properties of the samples are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and fluorescence spectrophotometer. The XRD results show that Pr3+ ions are successfully incorporated into the YVO4 host, and the sample has a tetragonal phase crystal structure with space group I41/amd. The SEM results show that the samples are rectangular-shaped micron particles with smooth surfaces, and the average grain size is about 2.1 μm. Under the excitation of 320 nm, the sample mainly exhibits broadband blue emission around 440 nm and red emission at 606 nm, which are attributed to the charge transfer transition of${\text{VO}}_4^{3 - }$ and the 1D2→3H4 transition of Pr3+, respectively. The relationship between the luminescence of the sample and the concentration of Pr3+ is studied. It is found that the optimal doping concentration of Pr3+ is 0.5%, and a higher doping concentration will cause concentration to be quenched. The reason for quenching concentration is the electric dipole-quadrupole interaction. The luminescence peak position of the temperature-dependent spectrum of YVO4:0.5%Pr3+ is consistent with that at room temperature. As the temperature increases, the total luminescence intensity gradually decreases, which is caused by thermal quenching, and the mechanism of thermal quenching is analyzed. Since the temperature-dependent behaviors of luminescence of${\text{VO}}_4^{3 - }$ and Pr3+ are significantly different from each other, a new fluorescence intensity ratio thermometry strategy is realized. Temperatures range is 303–353 K, and the maximum absolute sensitivity and relative sensitivity are 0.651 K–1 and 3.112×10–2 K–1 at 353 K, respectively, much higher than the traditional thermally coupled level thermometry strategy. In addition, there is no obvious overlap between the emission peaks of${\text{VO}}_4^{3 - }$ and Pr3+, which provides a good discrimination capability for signal detection. The above results show that this work provides a promising path for designing self-reference optical thermometry materials with excellent temperature sensitivity and signal discrimination.-
Keywords:
- luminescence properties /
- optical thermometry /
- fluorescence intensity ratio /
- temperature sensitivity
[1] Wang Y Z, Sun Y S, Xia Z G 2023 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kesarwani V, Rai V K 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 132 113102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shi X Y, Chen Y Q, Li G X, Qiang K R, Mao Q A, Pei L, Liu M J, Zhong J S 2023 Ceram. Int. 49 20839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kimura K, Morinaga Y, Imada H, Katayama I, Asakawa K, Yoshioka K, Kim Y, Takeda J 2021 ACS Photonics 8 982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y Q, Guo H J, Shi Q F, Qiao J W, Cui C E, Huang P, Wang L 2023 J. Alloys Compd. 965 171401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li L, Yang P X, Xia W D, Wang Y J, Ling F L, Cao Z M, Jiang S, Xiang G T, Zhou X J, Wang Y 2021 Ceram. Int. 47 769
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang C L, Jin Y H, Zhang R T, Yao Q, Hu Y H 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 894 162494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu W, Zhao L, Shang F K, Zheng L J, Zhang Z G 2022 J. Lumin. 249 119042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li Z J, Dong J N, Wang Q, Chen N Q, Cui W L, He Y B, Chen B L, Zhao D 2023 J. Lumin. 263 120070
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 吴晗, 陈浩然, 解小雨, 涂浪平, 李齐清, 孔祥贵, 常钰磊 2023 发光学报 44 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu H, Chen H R, Xie X Y, Xu L P, Li Q Q, Kong X G, Chang Y L 2023 Chin. J. Lumin. 44 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhou L, Du P, Li W, Luo L, Xing G 2020 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59 9989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Duan Y M, Sun Y L, Zhu H Y, Li Z H, Zhang L, Zhang G 2021 Opt. Laser Technol. 144 107429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王玉婷, 王妍, 曲征, 周少帅 2019 中国稀土学报 37 426
Wang Y T, Wang Y, Qu Z, Zhou S S 2019 J. Rare-Earths 37 426
[14] Zhou H T, Guo N, Liang Q M, Ding Y, Pan Y, Song Y Y, Ouyang R Z, Miao Y Q, Shao B Q 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 16651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kolesnikov I E, Mamonova D V, Kurochkin M A, Kolesnikov E Y, Lähderanta E 2021 ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4 1959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhou H, Gao W H, Cai P C, Zhang B Q, Li S 2020 Solid State Sci. 104 106283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tian X Y, Wen J, Wang S M, Hu J L, Li J, Peng H X 2016 Mater. Res. Bull. 77 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Blasse G 1968 Phys. Lett. A 28 444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Van Uitert L G 1967 J. Electrochem. Soc. 114 1048
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Boutinaud P, Pinel E, Oubaha M, Mahiou R, Cavalli E, Bettinelli M 2006 Opt. Mater. 28 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Struck C W, Fonger W H 1971 J. Appl. Phys. 42 4515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 吕兆承, 李营, 全桂英, 郑庆华, 周薇薇, 赵旺 2017 66 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü Z C, Li Y, Quan G Y, Zheng Q H, Zhou W W, Zhao W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 唐红霞, 王昌文, 宋美霖, 王春红, 于长兴 2023 中国稀土学报 1
Tang H X, Wang C W, Song M L, Wang C H, Yu C X 2023 J. Rare-Earths 1
[24] 缪菊红, 谢颖, 陈铭源, 李林珂, 韦松 2022 中国稀土学报 40 602
Liao J H, Xie Y, Chen M Y, Li L K, Wei S 2022 J. Rare-Earths 40 602
[25] 夏克尔阿·热帕提, 王林香, 李晴, 柏云凤, 买买提·穆妮热 2023 72 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Arepati X, Wang L X, Li Q, Bai Y F, Munire M 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 贾朝阳, 杨雪, 王志刚, 柴瑞鹏, 庞庆, 张翔宇, 高当丽 2023 72 224210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia C Y, Yang X, Wang Z G, Chai R P, Pang Q, Zhang X Y, Gao D L 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 224210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
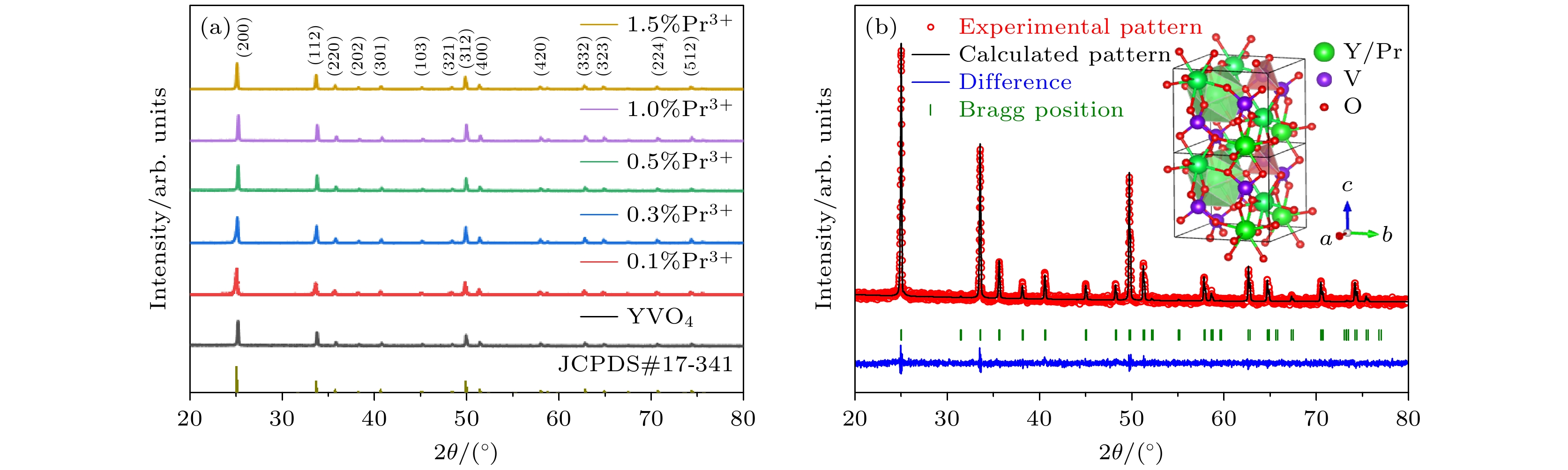
图 1 (a) YVO4:xPr3+ (x = 0%—1.5%)样品的XRD图谱及YVO4的标准卡片; (b) YVO4:0.5%Pr3+样品的XRD Rietveld精修图谱, 内插图为样品的晶体结构
Fig. 1. (a) XRD patterns of YVO4:xPr3+ (x = 0%–1.5%) samples, compared with the standard data of YVO4 reference pattern (JCPDS#17-341); (b) XRD Rietveld refinement pattern of YVO4:0.5%Pr3+ sample, the inset shows the crystal structure of the sample.
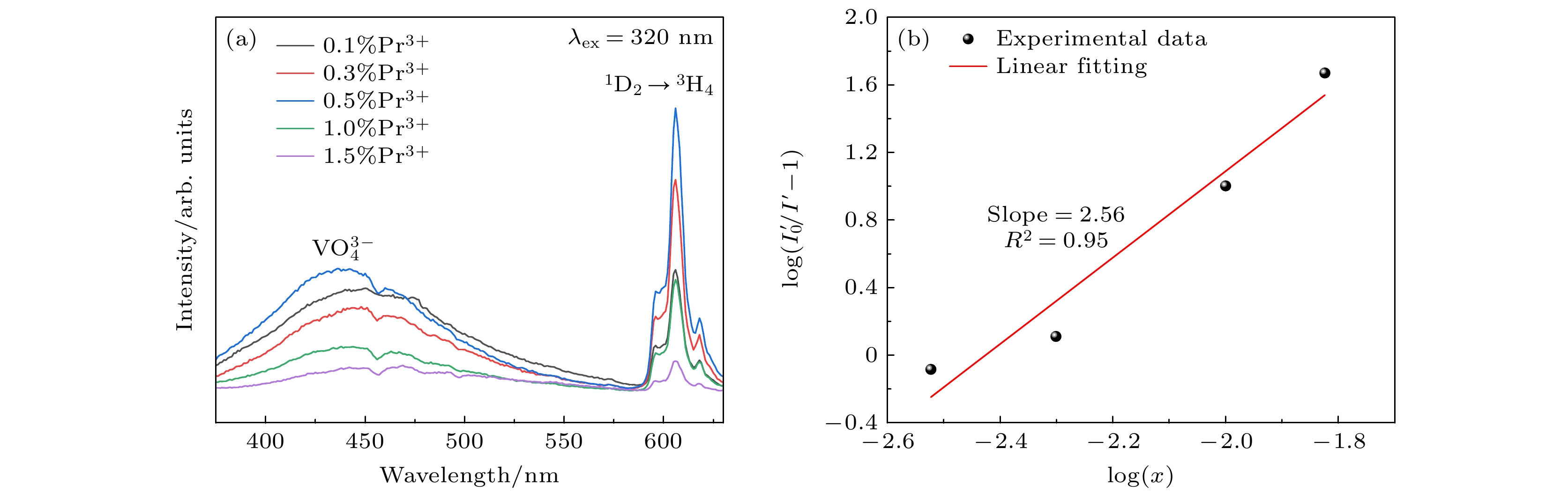
图 4 (a)不同掺杂浓度的YVO4:xPr3+(x = 0.1%—1.5%)在320 nm激发下的发射光谱; (b) $ \log \left( {{{I_0^\prime } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{I_0^\prime } {{I^\prime } - 1}}} \right. } {{I^\prime } - 1}}} \right) $对log(x)的线性拟合图(x≥0.3%)
Fig. 4. (a) Emission spectra of YVO4:xPr3+ (x = 0.1%–1.5%) with different doping concentrations under 320 nm excitation; (b) linear fit of $ \log \left( {{{I_0'} /{{I'} - 1}}} \right) $ to log(x) (x≥0.3%).
表 1 YVO4:0.5%Pr3+样品在XRD Rietveld精修后的相关参数
Table 1. Corresponding parameters of XRD Rietveld refinement for YVO4:0.5%Pr3+ sample.
相结构 空间群 晶胞参数 体积/Å3 质量因子 四方相 I41/amd a = b = 7.125 Å
c = 6.296 Å
α = β = γ = 90º319.63 Rp = 4.60
Rwp = 5.84
Re = 3.01
χ2 = 3.76表 2 基于FIR测温荧光粉的灵敏度
Table 2. Sensitivities of phosphors based on FIR thermometry.
Strategies Materials λex/nm Sa/K–1 Sr/(10–2 K–1) Temperature range/K Ref. TCLs YVO4:1%Er3+ 345 0.0102 1.070 303—573 [23] NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+/Tm3+ 980 0.2974 1.174 293—573 [24] Bi2WO6:Tm3+, Yb3+ 980 0.0025 0.144 298—573 [25] Li0.9K0.1NbO3:Pr3+, Er3+ 380 0.0054 1.120 297—443 [26] 808 0.0112 1.284 980 0.0083 1.106 Dual-mode SrMoO4:Pr3+ 449 0.0452 0.98 298—498 [6] GdVO4:0.5%Sm3+ 310 — 1.6 300—480 [13] YVO4:0.5%Pr3+ 320 0.6510 3.112 303—353 This work -
[1] Wang Y Z, Sun Y S, Xia Z G 2023 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kesarwani V, Rai V K 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 132 113102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shi X Y, Chen Y Q, Li G X, Qiang K R, Mao Q A, Pei L, Liu M J, Zhong J S 2023 Ceram. Int. 49 20839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kimura K, Morinaga Y, Imada H, Katayama I, Asakawa K, Yoshioka K, Kim Y, Takeda J 2021 ACS Photonics 8 982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y Q, Guo H J, Shi Q F, Qiao J W, Cui C E, Huang P, Wang L 2023 J. Alloys Compd. 965 171401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li L, Yang P X, Xia W D, Wang Y J, Ling F L, Cao Z M, Jiang S, Xiang G T, Zhou X J, Wang Y 2021 Ceram. Int. 47 769
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang C L, Jin Y H, Zhang R T, Yao Q, Hu Y H 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 894 162494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu W, Zhao L, Shang F K, Zheng L J, Zhang Z G 2022 J. Lumin. 249 119042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li Z J, Dong J N, Wang Q, Chen N Q, Cui W L, He Y B, Chen B L, Zhao D 2023 J. Lumin. 263 120070
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 吴晗, 陈浩然, 解小雨, 涂浪平, 李齐清, 孔祥贵, 常钰磊 2023 发光学报 44 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu H, Chen H R, Xie X Y, Xu L P, Li Q Q, Kong X G, Chang Y L 2023 Chin. J. Lumin. 44 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhou L, Du P, Li W, Luo L, Xing G 2020 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59 9989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Duan Y M, Sun Y L, Zhu H Y, Li Z H, Zhang L, Zhang G 2021 Opt. Laser Technol. 144 107429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王玉婷, 王妍, 曲征, 周少帅 2019 中国稀土学报 37 426
Wang Y T, Wang Y, Qu Z, Zhou S S 2019 J. Rare-Earths 37 426
[14] Zhou H T, Guo N, Liang Q M, Ding Y, Pan Y, Song Y Y, Ouyang R Z, Miao Y Q, Shao B Q 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 16651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kolesnikov I E, Mamonova D V, Kurochkin M A, Kolesnikov E Y, Lähderanta E 2021 ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4 1959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhou H, Gao W H, Cai P C, Zhang B Q, Li S 2020 Solid State Sci. 104 106283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tian X Y, Wen J, Wang S M, Hu J L, Li J, Peng H X 2016 Mater. Res. Bull. 77 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Blasse G 1968 Phys. Lett. A 28 444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Van Uitert L G 1967 J. Electrochem. Soc. 114 1048
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Boutinaud P, Pinel E, Oubaha M, Mahiou R, Cavalli E, Bettinelli M 2006 Opt. Mater. 28 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Struck C W, Fonger W H 1971 J. Appl. Phys. 42 4515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 吕兆承, 李营, 全桂英, 郑庆华, 周薇薇, 赵旺 2017 66 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü Z C, Li Y, Quan G Y, Zheng Q H, Zhou W W, Zhao W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 唐红霞, 王昌文, 宋美霖, 王春红, 于长兴 2023 中国稀土学报 1
Tang H X, Wang C W, Song M L, Wang C H, Yu C X 2023 J. Rare-Earths 1
[24] 缪菊红, 谢颖, 陈铭源, 李林珂, 韦松 2022 中国稀土学报 40 602
Liao J H, Xie Y, Chen M Y, Li L K, Wei S 2022 J. Rare-Earths 40 602
[25] 夏克尔阿·热帕提, 王林香, 李晴, 柏云凤, 买买提·穆妮热 2023 72 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Arepati X, Wang L X, Li Q, Bai Y F, Munire M 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 贾朝阳, 杨雪, 王志刚, 柴瑞鹏, 庞庆, 张翔宇, 高当丽 2023 72 224210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia C Y, Yang X, Wang Z G, Chai R P, Pang Q, Zhang X Y, Gao D L 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 224210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3140
- PDF下载量: 161
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: