-
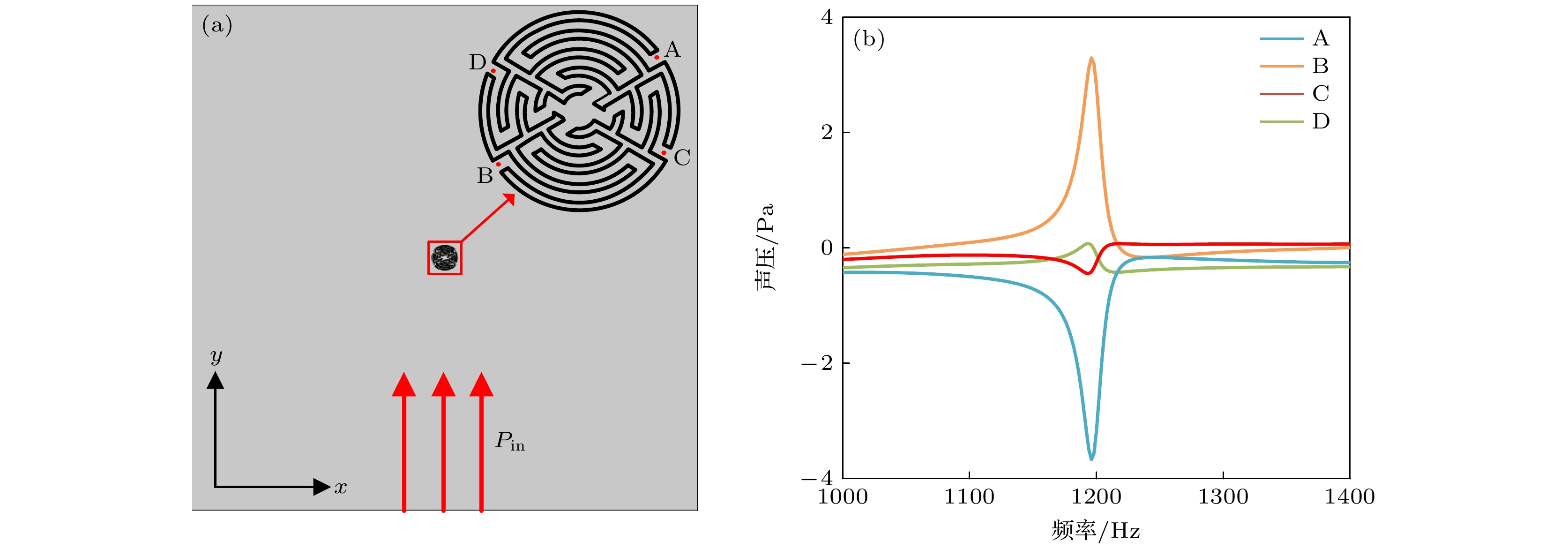
构造了一种圆柱形四通道非均匀迷宫结构, 利用该结构设计的圆环型超构材料能够实现动态可调的定向声辐射. 所构造的圆柱形非均匀迷宫结构具有偶极子共振特性, 在偶极子共振频率附近, 声波能够从两个占比较大的扇形通道开口向外辐射, 此时的圆柱形非均匀迷宫结构可近似地看作一个偶极子源. 当圆柱形非均匀迷宫结构围绕圆心进行旋转时, 所形成的偶极子源的位置和向外辐射声波的方向也随之发生改变. 将点声源放置在由18个非均匀迷宫结构组成的圆环型超构材料的中心, 调节圆柱形非均匀迷宫结构的旋转角度, 使各微结构处于导通或截止状态, 从而控制点声源在各个方向上的传播特性, 实现具有动态可调特性的定向声辐射. 此外, 研究了圆柱形非均匀迷宫结构旋转角度对透射声波的影响, 探究了微结构的开关效应, 为构造简易的声定向辐射设备提供了新思路.In this work, a cylindrical four-channel non-uniform labyrinth structure is constructed. The ring shaped metamaterial designed by using the rotational anisotropy of the structure can control sound wave and achieve dynamically adjustable directional sound radiation. The cylindrical non-uniform labyrinth structure comprised of four channels has dipole resonance characteristic. At the dipole resonance frequency, sound waves can radiate from the openings of two sector channels that occupy a large proportion. At this time, the cylindrical non-uniform labyrinth structure can be approximately regarded as a dipole sound source. For the cylindrical uniform labyrinth structure, the sound transmission property will not change as it rotates around its center. However, when the cylindrical non-uniform labyrinth structure rotates around its own center, the position of the dipole sound source and the direction of the radiated sound wave also change. Placing a point sound source in the center of the circular metamaterial composed of 18 non-uniform labyrinth structures, and adjusting the rotation angle of the circular non-uniform labyrinth structure so that each structure lies in the conductive or cut-off state, the propagation of the point sound source in all directions can be controlled. The propagation characteristics of these structures are utilized to achieve dynamically adjustable directional sound radiation. In addition, the influence of the rotation angle of the cylindrical non-uniform labyrinth structure on the transmitted sound wave is studied, and the switching effect of the non-uniform cylindrical labyrinth structure in the constructed sound source system is explored, which provides a new idea for constructing simple directional radiation acoustic equipment.
-
Keywords:
- non-uniform labyrinth structure /
- dipole resonance /
- rotational adjustability /
- directional acoustic radiation
[1] Zhao X, Liu G, Zhang C, Xia D, Lu Z 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 074101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Liang Z, Willatzen M, Li J, et al. 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 田源, 葛浩, 卢明辉, 陈延峰 2019 68 194301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian Y, Ge H, Lu M H, Chen Y F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 194301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gu Z M, Liang B, Li Y, Zou X Y, Yin L L, Cheng J C 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 074502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Long H Y, Gao S X, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 033507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 胥强荣, 朱洋, 林康, 沈承, 卢天健 2022 71 214301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Q R, Zhu Y, Lin K, Shen C, Lu T J 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 214301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Polychronopoulos S, Memoli G 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 4254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Walker E L, Jin Y Q, Reyes D, Neogi A 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 5967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang Z, Mei J, Yang M, et al. 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 204301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ma G, Sheng P 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1501595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tan Y, Liang B, Cheng J C 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 034303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Song K, Kim J, Hur S, et al. 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 32300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Esfahlani H, Karkar S, Lissek H, Mosig J R 2016 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 139 3259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Qian J, Sun H, Yuan S, Liu X 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 013506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tang S, Han J N, Wen T D 2018 AIP Adv. 8 085312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Z W, Tian Y, Wang Y H, Gao S X, Cheng Y, Liu X J, Christensen J 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1803229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Craig S R, Wang B H, Su X S, Banerjee D, Welch P J, Yip M C, Hu Y H, Shi C Z 2022 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 151 1722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bai L, Song G Y, Jiang W X, Cheng Q, Cui T J 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 115 231902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dai H Q, Xia B Z, Yu D J 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 065103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen Z Y, Wang X Y, Lim C W 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 185112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jiang X, Zhang L K, Liang B, Zou X Y, Cheng J 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 093506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen X, Cai L, Wen J H 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 057803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ju F F, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 11113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li W P, Liu F M, Mei L R, Ke M Z, Liu Z Y 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 061904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 蔡成欣, 陈韶赓, 王学梅, 梁俊燕, 王兆宏 2020 69 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai C X, Chen S G, Wang X M, Liang J Y, Wang Z H 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang Z W, Cheng Y, Liu X J, Christensen J 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 224104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lu G X, Ding E L, Wang Y Y, Peng X Y, Cui J, Liu X Z, Liu X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 123507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y, Liang B, Zou X Y, Cheng J C 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 063509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang J, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 233502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu C, Long H Y, Zhou C, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 1519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhou C, Yuan B, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 063501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhang J, Rui W, Ma C R, et al. 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 3670
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
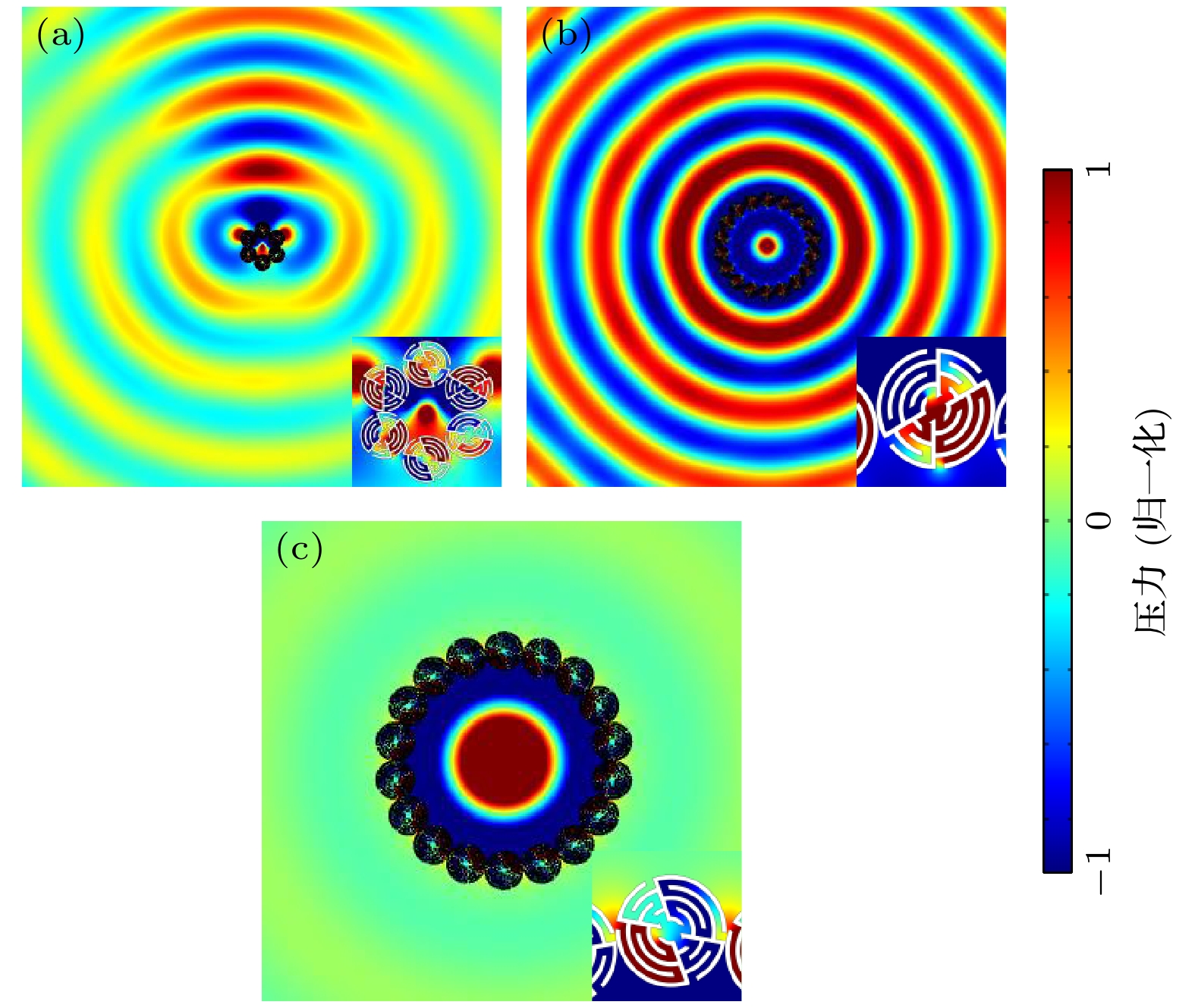
图 4 平面波作用下的非均匀迷宫结构的散射声场图 (a)原始微结构; (b)结构旋转60°; (c)结构旋转70°; (d)结构旋转140°, 图4(a)—(d)中的右下角插图为结构特写; (e)实心刚性圆; (f)微结构逆时针旋转不同角度情况下的声辐射图
Fig. 4. Scattering sound field diagram of non-uniform labyrinth structure under the plane wave: (a) Original microstructure; (b) the structure rotates by 60°; (c) the structure rotates by 70°; (d) the structure rotates by 140°, and the insets at the lower right corner of Figure 4(a)-(d) are the clear views of structure; (e) solid rigid circle; (f) acoustic radiation patterns of microstructures under different counterclockwise rotation angles.
图 5 (a)由18个非均匀迷宫结构构成的圆环型超构材料; (b)圆环型超构材料中求取微结构中心到点声源的距离D的具体示意图; (c)单个微结构处于打开状态时的声压场分布图; (d)两个指定的微结构同时处于打开状态时的声压场分布图
Fig. 5. (a) Toroidal metamaterial constructed with 18 non-uniform labyrinth structures; (b) the specific schematic diagram of the distance D from the center of the microstructure to the point sound source in the ring type metamaterial; (c) sound pressure field distribution diagram when a single microstructure is in the open state; (d) sound pressure field distribution diagram when two designated microstructures are in the open state at the same time.
图 6 (a)由6个微结构构成的圆环型超构材料实现的声定向辐射; (b)圆环型超构材料的18个微结构全部处于打开状态时的声压场分布图; (c)圆环型超构材料的18个微结构全部处于关闭状态时的声压场分布图
Fig. 6. (a) Acoustic directional radiation realized by toroidal metamaterials composed of 6 microstructures; (b) sound pressure field distribution diagram when all the 18 microstructures of the toroidal metamaterial are in the open state; (c) sound pressure field distribution diagram when all the 18 microstructures of the toroidal metamaterial are in the closed state.
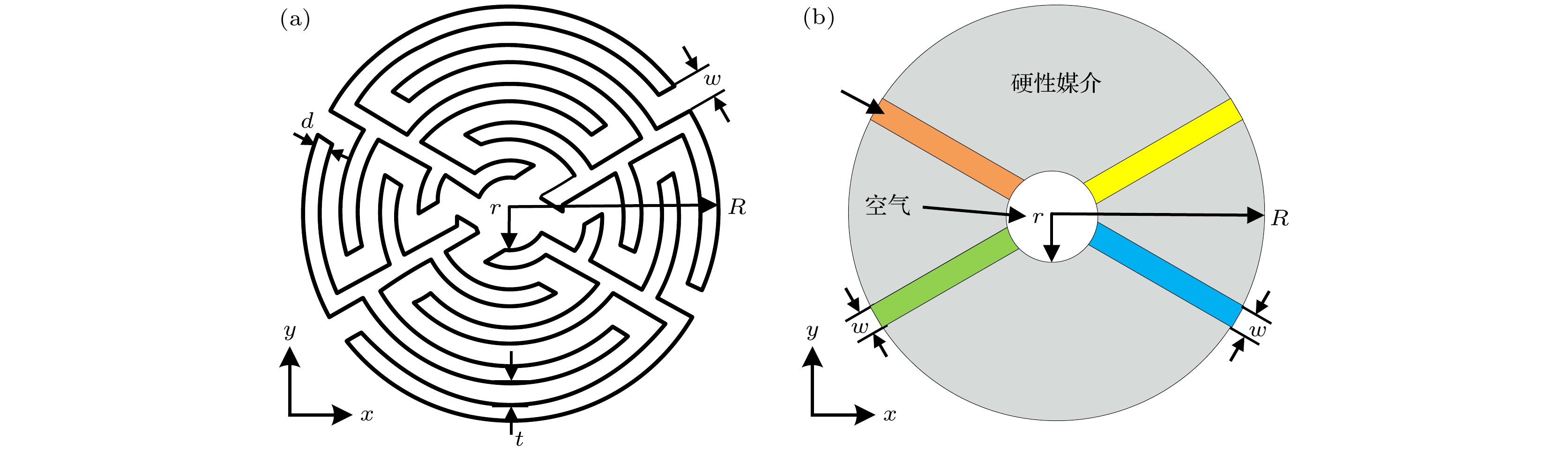
表 1 圆柱形非均匀迷宫结构的结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of cylindrical non-uniform labyrinth structure.
参数类型 数值/cm 通道口宽度w 0.42 壁厚d 0.25 通道宽度t 0.306 外圆半径R 3 内圆半径r 0.526 -
[1] Zhao X, Liu G, Zhang C, Xia D, Lu Z 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 074101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Liang Z, Willatzen M, Li J, et al. 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 田源, 葛浩, 卢明辉, 陈延峰 2019 68 194301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian Y, Ge H, Lu M H, Chen Y F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 194301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gu Z M, Liang B, Li Y, Zou X Y, Yin L L, Cheng J C 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 074502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Long H Y, Gao S X, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 033507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 胥强荣, 朱洋, 林康, 沈承, 卢天健 2022 71 214301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Q R, Zhu Y, Lin K, Shen C, Lu T J 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 214301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Polychronopoulos S, Memoli G 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 4254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Walker E L, Jin Y Q, Reyes D, Neogi A 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 5967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang Z, Mei J, Yang M, et al. 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 204301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ma G, Sheng P 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1501595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tan Y, Liang B, Cheng J C 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 034303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Song K, Kim J, Hur S, et al. 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 32300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Esfahlani H, Karkar S, Lissek H, Mosig J R 2016 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 139 3259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Qian J, Sun H, Yuan S, Liu X 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 013506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tang S, Han J N, Wen T D 2018 AIP Adv. 8 085312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Z W, Tian Y, Wang Y H, Gao S X, Cheng Y, Liu X J, Christensen J 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1803229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Craig S R, Wang B H, Su X S, Banerjee D, Welch P J, Yip M C, Hu Y H, Shi C Z 2022 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 151 1722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bai L, Song G Y, Jiang W X, Cheng Q, Cui T J 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 115 231902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dai H Q, Xia B Z, Yu D J 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 065103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen Z Y, Wang X Y, Lim C W 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 185112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jiang X, Zhang L K, Liang B, Zou X Y, Cheng J 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 093506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen X, Cai L, Wen J H 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 057803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ju F F, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 11113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li W P, Liu F M, Mei L R, Ke M Z, Liu Z Y 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 061904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 蔡成欣, 陈韶赓, 王学梅, 梁俊燕, 王兆宏 2020 69 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai C X, Chen S G, Wang X M, Liang J Y, Wang Z H 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang Z W, Cheng Y, Liu X J, Christensen J 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 224104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lu G X, Ding E L, Wang Y Y, Peng X Y, Cui J, Liu X Z, Liu X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 123507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y, Liang B, Zou X Y, Cheng J C 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 063509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang J, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 233502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu C, Long H Y, Zhou C, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 1519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhou C, Yuan B, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 063501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhang J, Rui W, Ma C R, et al. 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 3670
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5944
- PDF下载量: 80
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: