-
In this paper, a sound field model of elastically coupled normal mode suitable for complex eigenvalues is established. The normalization and coupling coefficient expression of elastic normal mode are given when the leaky mode is included. The coupling coefficients satisfy the conservation of sound energy flow. This model is used to analyze the coherent coupling characteristics of the normal mode of the sound field under the condition of the inclined elastic seabed. It is found that when the leaky mode is considered, the normal mode coupling will not only cause the amplitude of the normal mode to change, but also bring additional phase shift. The simulation calculation shows that under the condition of inclined elastic seabed, the acoustic propagation loss obtained by considering the effect of the additional phase shift of the leaky mode coupling is closer to the calculation result obtained by using the finite element commercial software, and that the mode coupling greatly enhances the amplitude of interface wave. In addition, this paper also analyzes the influence of changes in marine environmental parameters on sound transmission loss.
-
Keywords:
- elastic coupling mode model /
- leaky mode /
- phase shift
[1] Pekeris C L 1948 Mem. Geol. Soc. Amer. 27 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Press F, Ewing M 1950 Geophysics 15 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Porter M B, Reiss E L 1985 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 77 1760
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ainslie M A 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 954
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Schneiderwind J D, Collis J M, Simpson H J 2012 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 132 EL182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pierce A D 1965 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 37 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chwieroth F S, Nagl A, Uberall H, Zarur G L 1978 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 64 1105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Williams A O 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rutherford S R, Hawker K E 1981 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] McDaniel S T 1982 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72 916
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Evans R B 1983 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 74 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Porter M B, Jensen F B, Ferla C M 1991 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 89 1058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Abawi A T, Kuperman W A 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Knobles D P, Stotts S A, Koch R A 2003 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 莫亚枭, 朴胜春, 张海刚, 李丽 2016 声学学报 41 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mo Y X, Piao S C, Zhang H G, Li L 2016 Acta Acustica 41 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kennett B L N 1984 Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 79 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Odom R I 1986 Geophys J. R. Astron. Soc. 86 425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hall M 1986 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 79 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Maupin V 1988 Geophys. J. 93 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Collins M D 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 94 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Collins M D, Siegmann W L 1999 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 105 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jeroen T 1994 Geophys. J. Int. 117 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Abawi A T, Porter M B P 2008 https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a541636.pdf
[24] Odom R I, Park M, Mercer J A, Crosson R S, Paik P 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 2079
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Abawi A T, Porter M B 2007 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121 1374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Xie Z, Matzen Rene, Cristini P, Komatitsch D, Martin R 2016 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 140 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 骆文于, 于晓林, 张仁和 2016 声学学报 41 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo W Y, Yu X L, Zhang R H 2016 Acta Acustica 41 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 莫亚枭, 朴胜春, 张海刚, 李丽 2014 声学学报 39 428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mo Y X, Piao S C, Zhang H G, Li L 2014 Acta Acustica 39 428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chapman D M F, Ward P D, Ellis D D 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 85 648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] McCollom B A, Collis J M 2014 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 136 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang Z Y, Tindle C T 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Stickler D C 1975 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 57 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Westwood E K, Koch R A 1999 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106 2513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Westwood E K, Tindle C T, Chapman N R 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 3631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 杨士莪 1994 水声传播原理 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社) 第16页
Yang S E 1994 Principle of Underwater Acoustic Propagation (Harbin: Haerbin Engineering University Press) p16 (in Chinese)
-
图 3 是否考虑幅度相位处理的
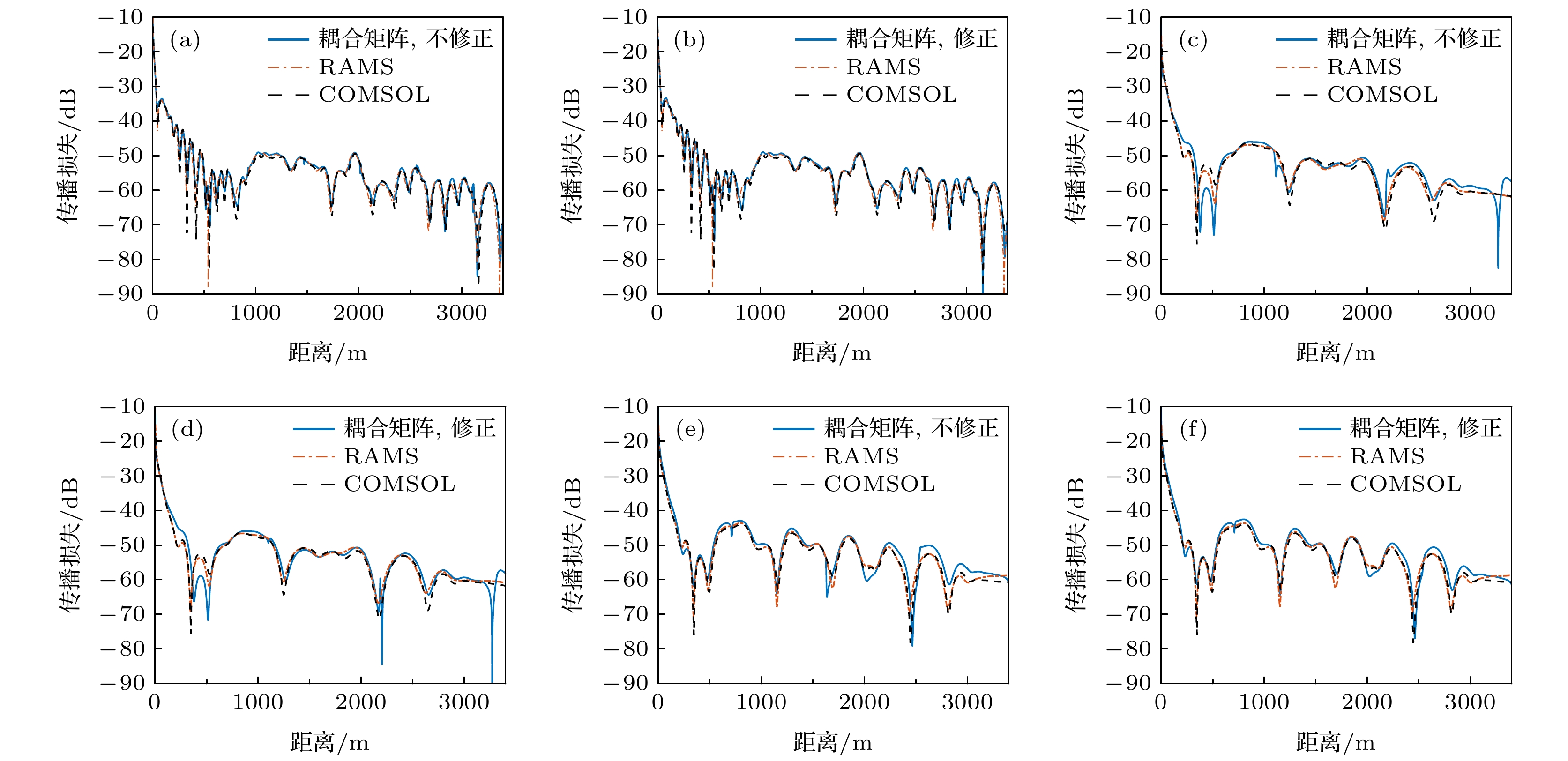
$\left\langle {{{\boldsymbol{u}}_m}, {{\boldsymbol{u}}_n}} \right\rangle$ 归一化时本文方法所得声压, 及其和RAMS以及COMSOL所得声压对比 (a) f = 50 Hz, 不考虑; (b) f = 50 Hz, 考虑; (c) f = 25 Hz时, 不考虑; (d) f = 25 Hz, 考虑; (e) f = 25 Hz, cs = 2000 m/s, 不考虑; (f) f = 25 Hz, cs = 2000 m/s, 考虑Fig. 3. Sound pressure obtained by the method in this paper when (a) f = 50 Hz, without, (b) f = 50 Hz, with, (c) f = 25 Hz, without, (d) f = 25 Hz, with, (e) f = 25 Hz, cs = 2000 m/s, without, (f) f = 25 Hz, cs = 2000 m/s, with considering the normalization of amplitude and phase processing, compared with the sound pressure obtained by RAMS and COMSOL.
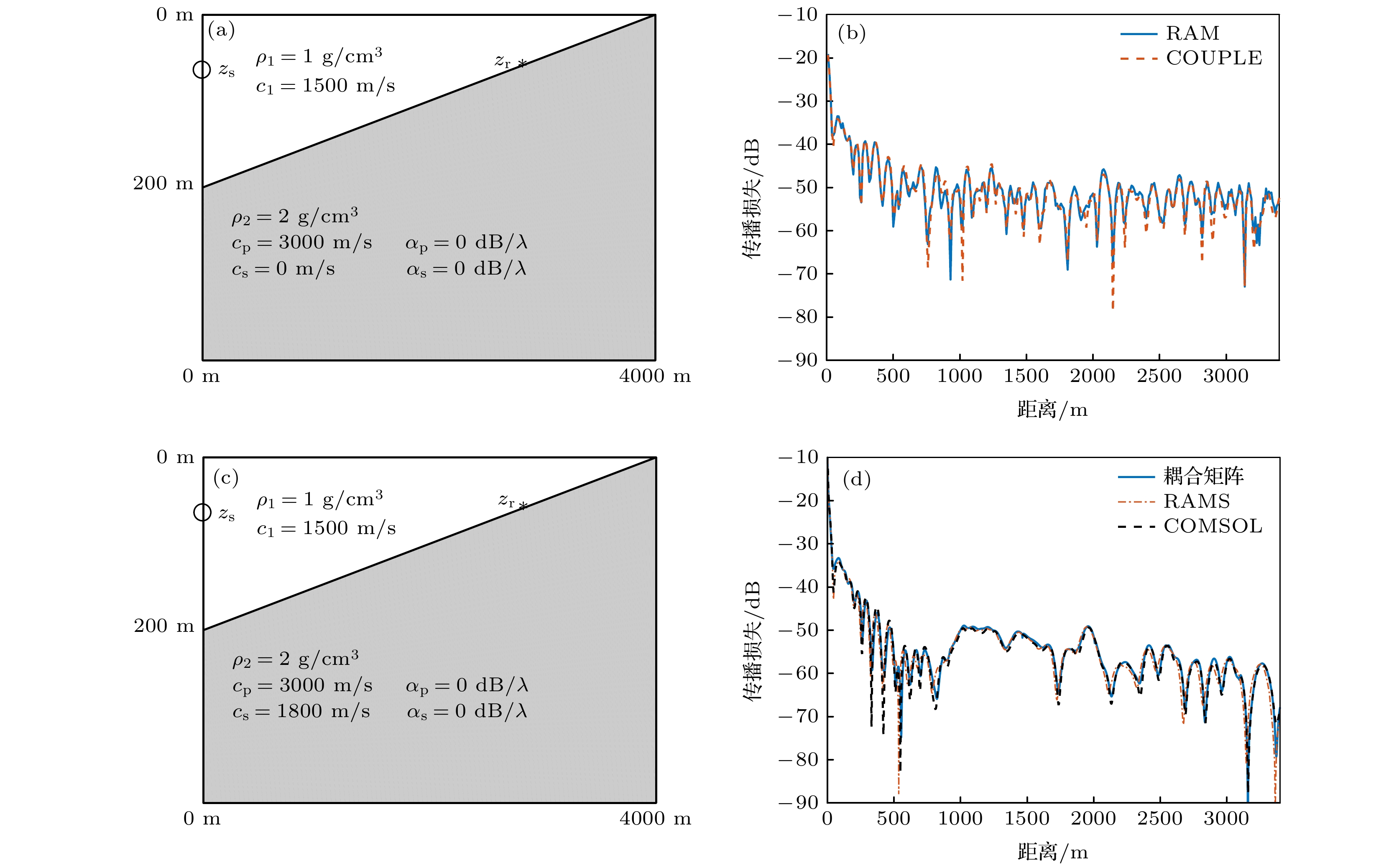
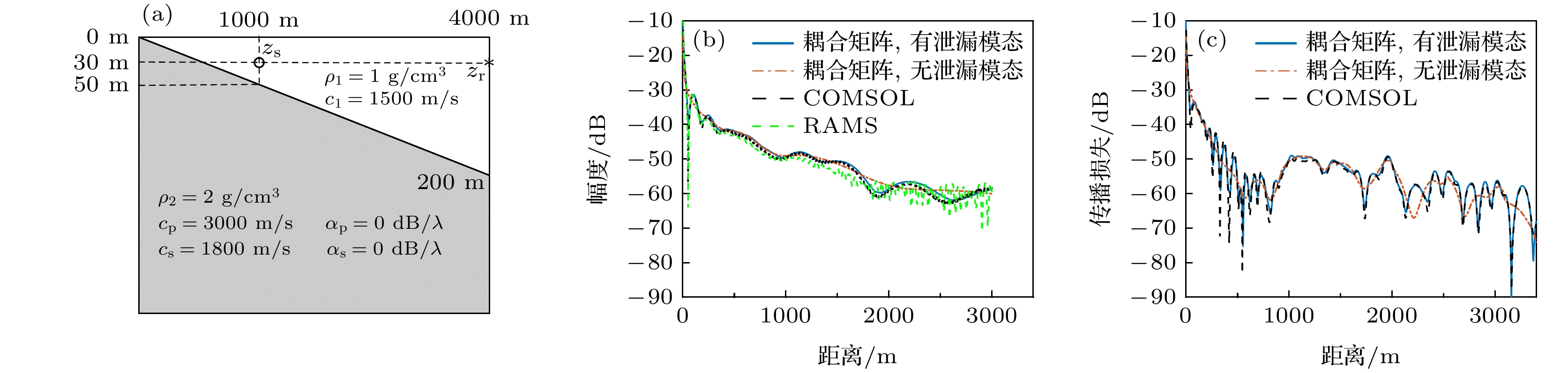
图 4 (a)不考虑和(b)考虑泄漏模态时的耦合矩阵法所得声压, 及其和RAMS, COMSOL程序所得声压的对比; (c) RAMS所得声压的FK变换结果
Fig. 4. Sound pressure obtained by the coupling matrix method when the leaky mode is (a) not considered or (b) considered, compared with the sound pressure obtained by the RAMS and COMSOL program; (c) the FK transformation result of the sound pressure obtained by RAMS.
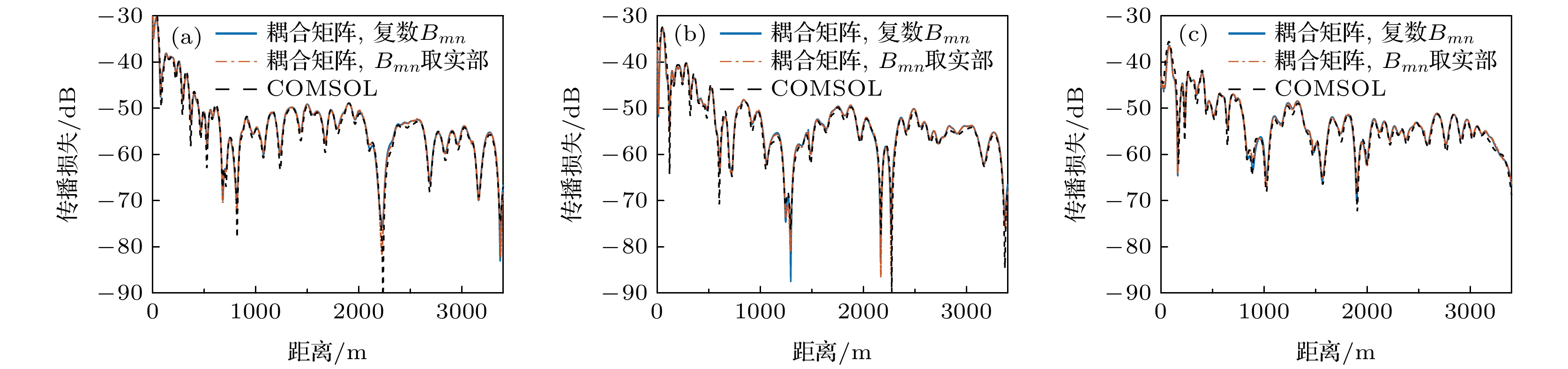
图 6 (a) zs = 50, (b) 70和(c) 100 m时, 不含波数差的耦合系数取实部和保持为复数时的声压对比
Fig. 6. Acoustic pressure when the real part of the coupling coefficient without wavenumber difference is taken when zs = (a) 50, (b) 70, (c) 100 m, compared with the sound pressure when the coupling coefficient is kept as a complex number.
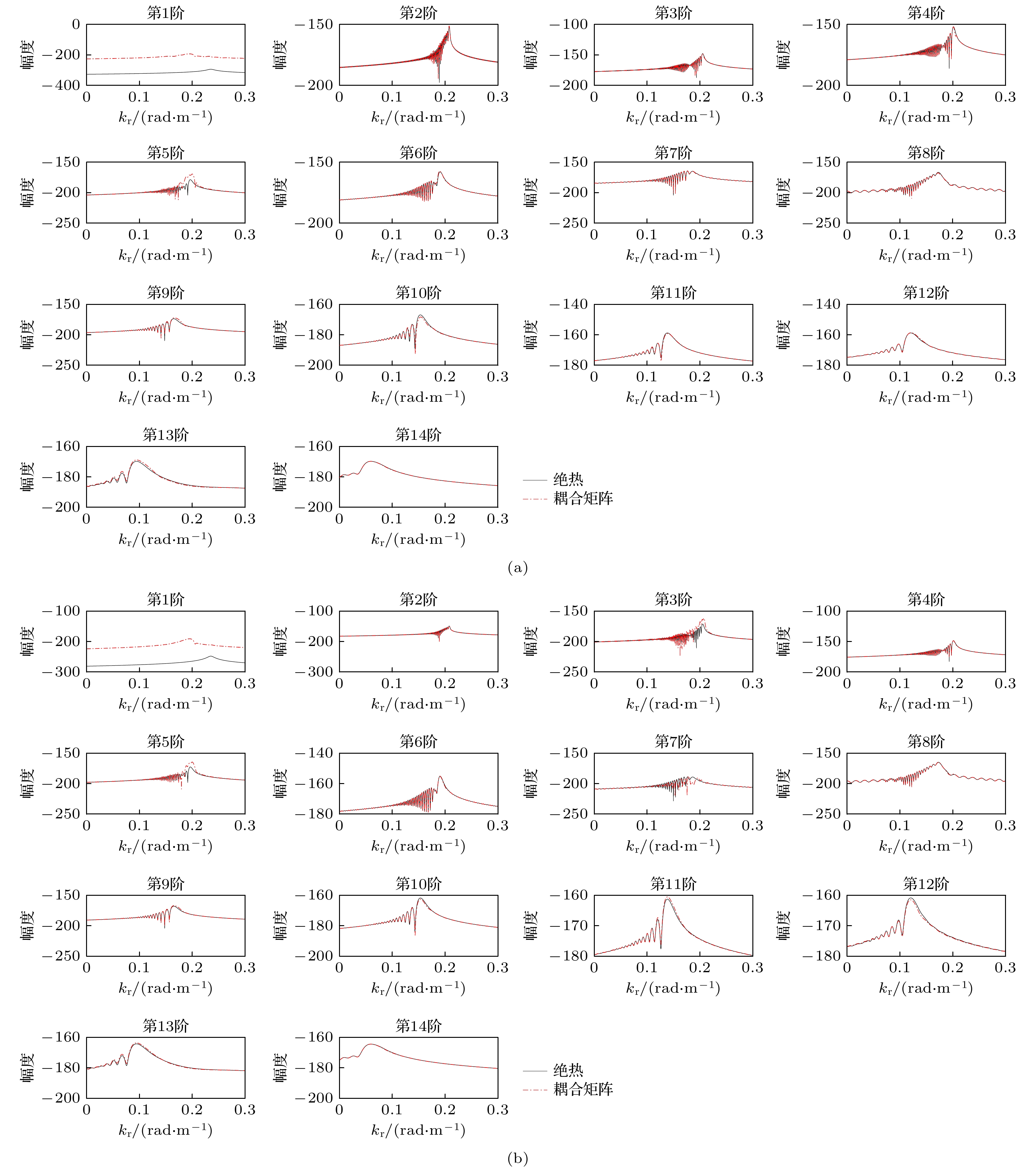
图 7 zs = 50 m, 各阶简正波的(a) |am|和(b) am的相位随距离的变化; (c) f = 50 Hz, 海洋环境如图2(c)时, 各阶简正波本征值的实部随距离的变化
Fig. 7. When zs = 50 m, (a) |am| and (b) the phases of am of each order of normal mode varying with distance. (c) When f = 50 Hz and the marine environment is shown in Fig. 2(c), the real part of the normal mode eigenvalues of each order varying with distance.
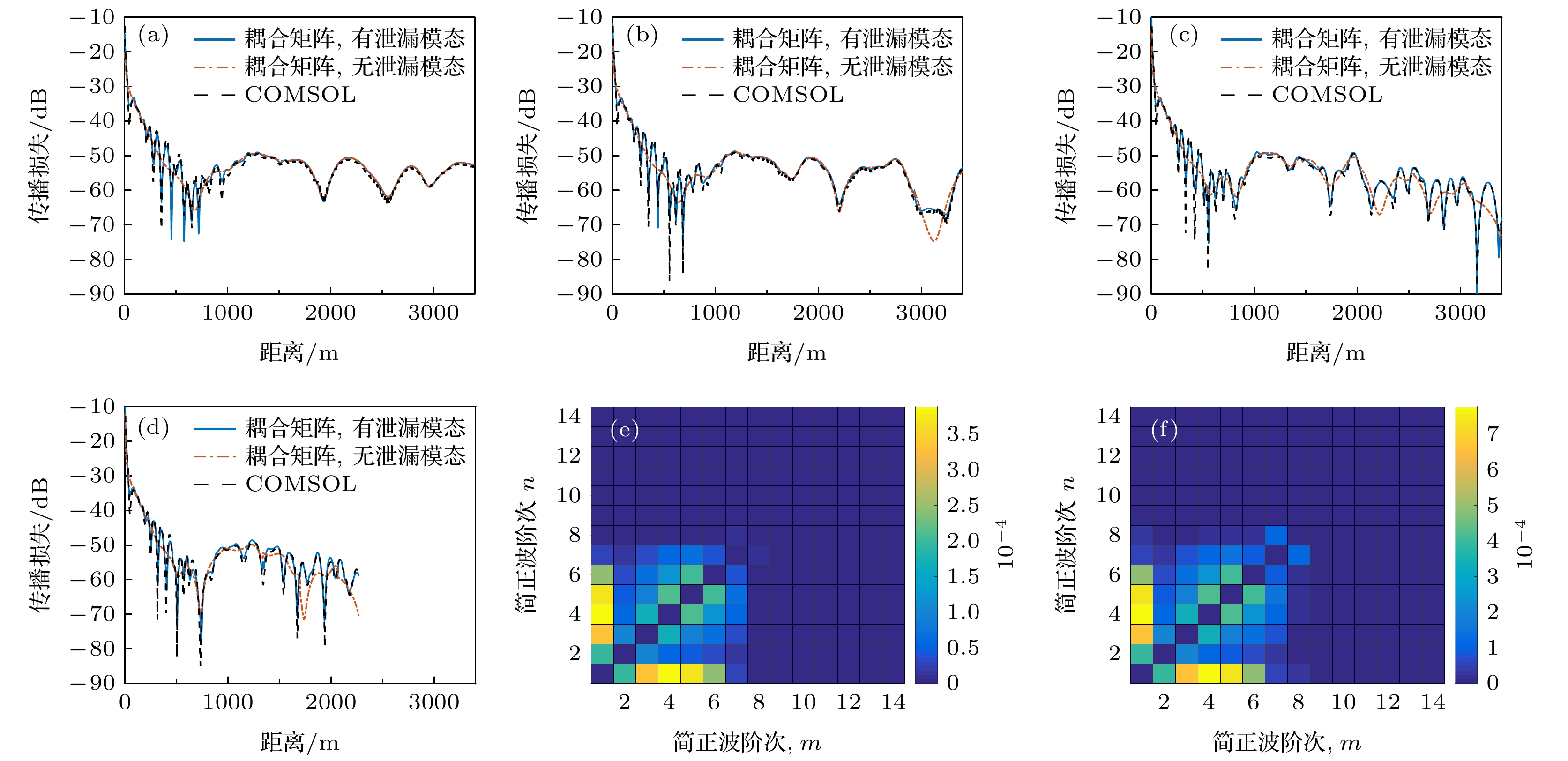
图 9 上坡弹性海底的坡度为(a) 0.0125, (b) 0.025, (c) 0.05和(d) 0.075时的水中声压; 考虑泄漏模态, 坡度为(e) 0.0125和(f) 0.025, x = 1 km时的|Bmn(x)|
Fig. 9. Sound pressure in water when the seabed slope is (a) 0.0125, (b) 0.025, (c) 0.05 and (d) 0.075 on the upslope elastic seabed. The |Bmn(x)| considering the leaky mode when x = 1 km when the slope is (e) 0.0125 and (f) 0.025.
图 11 cs = (a) 1800, (b) 1900, (c) 2000 m/s时的水中声压; (d) 考虑泄漏模态条件下, cs = 1800, 1900, 2000 m/s时采用耦合简正波法得到的声压对比
Fig. 11. Sound pressure in water when cs = (a) 1800, (b) 1900, (c) 2000 m/s; (d) sound pressure comparison obtained by mode coupling method while condidering leaky modes when cs = 1800, 1900, 2000 m/s.
图 12 cp = 1700 m/s, cs = (a) 600, (b) 700 和(c) 800 m/s时的水中声压; (d) cs = 600, 700, 800 m/s时, 考虑泄漏模态情况下, 采用耦合简正波方法所得声压对比; (e) cs = 600, 700, 800 m/s时第2阶简正波衰减系数随距离的变化
Fig. 12. Sound pressure in water when cs = (a) 600, (b) 700, (c) 800 m/s; (d) sound pressure obtained by mode coupling method considering leaky modes and when cs = 600, 700, 800 m/s; (e) the attenuation coefficient of the 2nd normal mode varying with range when cs = 600, 700, 800 m/s.
-
[1] Pekeris C L 1948 Mem. Geol. Soc. Amer. 27 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Press F, Ewing M 1950 Geophysics 15 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Porter M B, Reiss E L 1985 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 77 1760
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ainslie M A 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 954
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Schneiderwind J D, Collis J M, Simpson H J 2012 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 132 EL182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pierce A D 1965 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 37 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chwieroth F S, Nagl A, Uberall H, Zarur G L 1978 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 64 1105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Williams A O 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rutherford S R, Hawker K E 1981 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] McDaniel S T 1982 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72 916
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Evans R B 1983 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 74 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Porter M B, Jensen F B, Ferla C M 1991 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 89 1058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Abawi A T, Kuperman W A 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Knobles D P, Stotts S A, Koch R A 2003 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 莫亚枭, 朴胜春, 张海刚, 李丽 2016 声学学报 41 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mo Y X, Piao S C, Zhang H G, Li L 2016 Acta Acustica 41 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kennett B L N 1984 Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 79 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Odom R I 1986 Geophys J. R. Astron. Soc. 86 425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hall M 1986 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 79 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Maupin V 1988 Geophys. J. 93 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Collins M D 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 94 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Collins M D, Siegmann W L 1999 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 105 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jeroen T 1994 Geophys. J. Int. 117 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Abawi A T, Porter M B P 2008 https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a541636.pdf
[24] Odom R I, Park M, Mercer J A, Crosson R S, Paik P 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 2079
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Abawi A T, Porter M B 2007 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121 1374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Xie Z, Matzen Rene, Cristini P, Komatitsch D, Martin R 2016 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 140 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 骆文于, 于晓林, 张仁和 2016 声学学报 41 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo W Y, Yu X L, Zhang R H 2016 Acta Acustica 41 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 莫亚枭, 朴胜春, 张海刚, 李丽 2014 声学学报 39 428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mo Y X, Piao S C, Zhang H G, Li L 2014 Acta Acustica 39 428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chapman D M F, Ward P D, Ellis D D 1989 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 85 648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] McCollom B A, Collis J M 2014 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 136 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang Z Y, Tindle C T 1993 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Stickler D C 1975 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 57 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Westwood E K, Koch R A 1999 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106 2513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Westwood E K, Tindle C T, Chapman N R 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100 3631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 杨士莪 1994 水声传播原理 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社) 第16页
Yang S E 1994 Principle of Underwater Acoustic Propagation (Harbin: Haerbin Engineering University Press) p16 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 5827
- PDF下载量: 93
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: