-
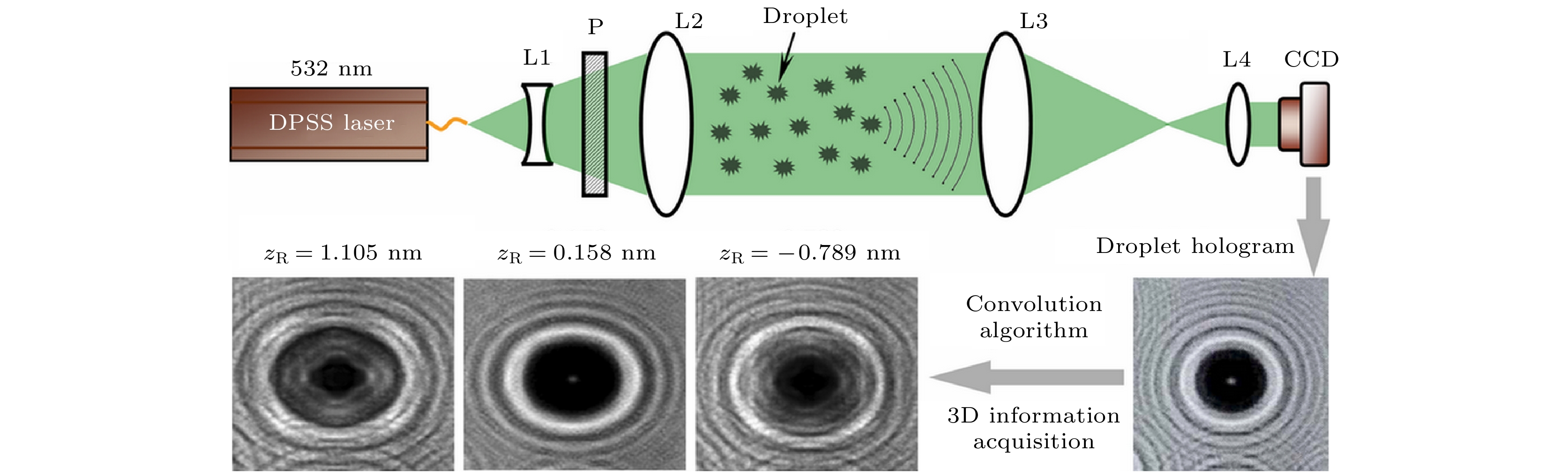
云微物理参数对气候变化、天气预测、人工影响天气、飞行安全等领域具有重要的影响. 目前, 基于光散射、碰撞和成像理论的云微物理参数测量方法存在反演过程需要对云滴谱和粒子特性进行假设、撞击过程会破坏粒子特征、无法获得云粒子三维特征等瓶颈问题. 本文提出了基于干涉理论, 结合光信息处理、景深压缩与融合全息图的灰度梯度方差技术的同轴数字全息干涉术测量方法, 可为云滴谱、云粒子直径、数浓度精细同步探测提供z轴定位精度为0.01 mm、系统分辨率为2 μm的技术手段. 实验中, 以超声波雾化器产生的中值直径为3.9 μm的液滴粒子作为液相云粒子的模拟, 测量结果与实际相符. 该方法可为研究云中液态水含量, 及夹卷、凝结、碰撞和时空演化规律提供有效的支持, 对粒子的动力学研究具有借鉴意义, 并为我国陆基及机载测云应用提供了一套可行的系统解决方案.Investigation of cloud microphysical is of great significance in deepening the understanding of the radiation energy budget, water cycle process, and precipitation mechanism, and improving the scientificity and effectiveness of artificial precipitation. Especially under the action of turbulence, in addition to shear and inertia, the turbulence in the cloud will accelerate the collision of cloud droplets through vortex superposition. The above process will further complicate the cloud microphysical characters. At present, the methods of measuring cloud microphysical parameters based on light scattering, collision and imaging theories encounter bottlenecks: the inversion process needs to make the assumptions about cloud droplet spectrum and particle characteristics, the impact process will destroy particle characteristics, and the three-dimensional characteristics of cloud particles cannot be obtained. Because of its many advantages, such as fast, real-time, non-destructive, non-invasive, high-resolution, full-field optical measurement, etc., in-line digital holographic interferometry is considered as a new potential tool for the dynamical measurement of cloud microphysical property. In particular, the mutual interference between the particle image and twin image is small under far-field recording conditions. In this paper, the measurement method of the on-line digital holographic interferometry based on interference theory, combining optical information processing, depth of field compression, and gray gradient variance technology of fusion holograms, is investigated. This method, with a z-axis position accuracy of 0.01 mm and system resolution of 2 μm, is employed for simultaneously and finely detecting the cloud droplet spectrum, cloud particle diameter, and number concentration. In the experiment, the liquid droplet with a median diameter of 3.9 μm, produced by the ultrasonic atomizer, is used as an example of the cloud particle. The measurement results are consistent with realistic scenario. By using a high speed charge coupled device or complementary metal oxide semiconductor camera, this method can solve the technical bottleneck of three-dimensional fine characteristics of cloud particle in airborne measurement by using cloud droplet spectrometer. It can provide effective support for the research of liquid water in the cloud, entrainment, condensation, collision, and temporal and spatial evolution laws. In addition, it has reference significance for the study of particle dynamics. Simultaneously, this method provides a feasible solution for the measurement of cloud in land-based and airborne platforms.
-
Keywords:
- cloud microphysics /
- cloud droplet spectrum /
- particle diameter /
- number concentration /
- digital holographic interferometry
[1] Li J, Jian B, Huang J, Hu Y, Zhao C, Kawamoto K, Liao S, Wu M 2018 Remote. Sens. Environ. 213 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li J, Lv Q, Zhang M, Wang T, Kawamoto K, Chen S, Zhang B 2017 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 17 1847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lu C, Liu Y, Seong S Y, Chen J, Zhu L, Gao S, Yin Y, Jia X, Wang Y 2020 J. Geophys Res. 125 031868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gao S, Lu C, Liu Y, Mei F, Wang J, Zhu L, Yan S 2020 Geophys. Res. Lett. 47 086970
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 宋跃辉, 周煜东, 王玉峰, 李仕春, 高飞, 李博, 华灯鑫 2018 67 249201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Y H, Zhou Y D, Wang Y F, Li S C, Gao F, Li B, Hua D X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 249201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李书磊, 刘磊, 高太长, 胡帅, 黄威 2017 66 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S L, Liu L, Gao T C, Hu S, Huang W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 黄敏松, 雷恒池 2018 67 249202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang M S, Lei H C 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 249202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jiang F, Zhang Y, Bu L, Chu C 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 9777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Stephens G L, Kummerow C D 2007 J. Atmos. Sci. 64 3742
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黄亦鹏, 李万彪, 赵玉春, 白兰强 2019 地球科学进展 34 1273
Huang Y P, Li W B, Zhao Y C, Bai L Q 2019 Advan. Earth Sci. 34 1273
[11] Smith H R, Ulanowski Z, Kaye P H 2019 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 12 6579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fujiwara M, Sugidachi T, Arai T 2016 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 9 5911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kuhn T, Heymsfield A J 2016 Pure Appl. Geophys. 173 3065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Miloshevich L M, Heymsfield A J 1997 J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 14 753
[15] Waugh S M, Ziegler C L, MacGorman D R 2015 J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 32 1562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Suzuki K, Shimizu K, Ohigashi T 2012 Sola 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李大山 2002 人工影响天气现状与展望 (北京: 气象出版社) 第441页
Li D S 2002 Current Situation and Prospect of Weather Modification (Beijing: China Meteorological Press) p441 (in Chinese)
[18] Di J, Li Y, Xie M, Zhang J, Ma C, Xi T, Li E, Zhao J 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 7287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 吴羽峰, 吴佳琛, 郝然, 金尚忠, 曹良才 2020 应用光学 41 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Wu J C, Hao R, Jin S Z, Cao L C 2020 J. Appl. Opt. 41 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张益溢, 吴佳琛, 郝然, 金尚忠, 曹良才 2020 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y Y, Wu J C, Hao R, Jin S L, Cao L C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xi T, Di J, Li Y, Dai S, Ma C, Zhao J 2018 Opt. Express 26 28497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Beals M J, Fugal J P, Sh aw, R A, L u, J, Spuler S M, Stith J L 2015 Science 350 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Peter A, Olaf S, Martin S, Evelyn H, Stefan B, Ottmar M, Ulrike L 2009 Appl. Opt. 48 5811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Fugal J P, Shaw R A 2009 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yao L, Chen J, Sojka P E, Wu X C, Cen K 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
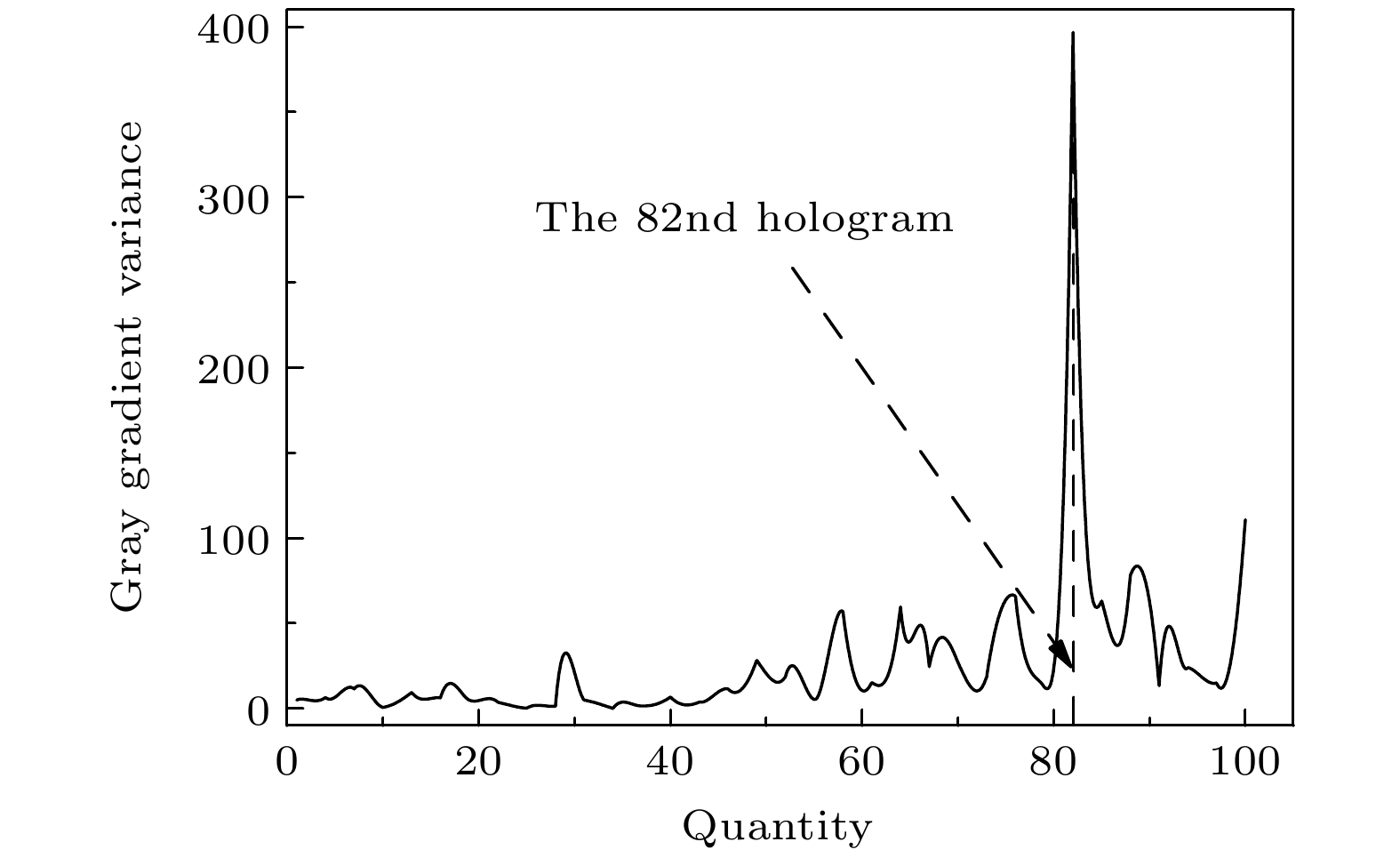
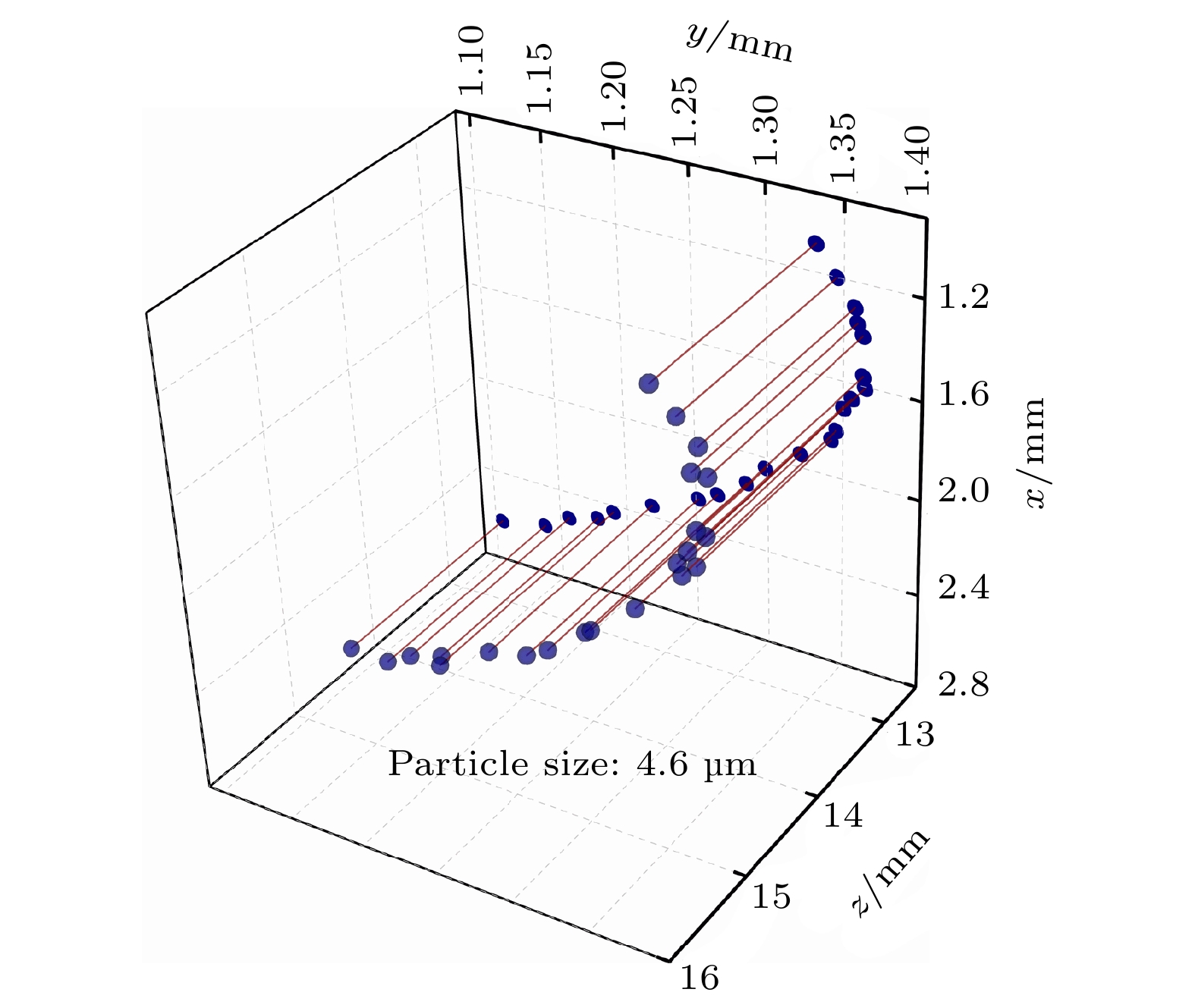
图 7 中值直径3.9 μm的液滴粒子测量结果 (a) 粒子分布; (b) 粒子谱; (c) z轴60—100 mm数浓度; (d) z轴0—60 mm粒子谱
Fig. 7. Measurement results of droplet particles with the median diameter of 3.9 μm: (a) Particles distribution; (b) particles spectrum; (c) number concentration from 60 mm to 100 mm at z axis; (d) number concentration from 0 mm to 60 mm at z axis
-
[1] Li J, Jian B, Huang J, Hu Y, Zhao C, Kawamoto K, Liao S, Wu M 2018 Remote. Sens. Environ. 213 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li J, Lv Q, Zhang M, Wang T, Kawamoto K, Chen S, Zhang B 2017 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 17 1847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lu C, Liu Y, Seong S Y, Chen J, Zhu L, Gao S, Yin Y, Jia X, Wang Y 2020 J. Geophys Res. 125 031868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gao S, Lu C, Liu Y, Mei F, Wang J, Zhu L, Yan S 2020 Geophys. Res. Lett. 47 086970
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 宋跃辉, 周煜东, 王玉峰, 李仕春, 高飞, 李博, 华灯鑫 2018 67 249201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Y H, Zhou Y D, Wang Y F, Li S C, Gao F, Li B, Hua D X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 249201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李书磊, 刘磊, 高太长, 胡帅, 黄威 2017 66 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S L, Liu L, Gao T C, Hu S, Huang W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 黄敏松, 雷恒池 2018 67 249202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang M S, Lei H C 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 249202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jiang F, Zhang Y, Bu L, Chu C 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 9777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Stephens G L, Kummerow C D 2007 J. Atmos. Sci. 64 3742
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黄亦鹏, 李万彪, 赵玉春, 白兰强 2019 地球科学进展 34 1273
Huang Y P, Li W B, Zhao Y C, Bai L Q 2019 Advan. Earth Sci. 34 1273
[11] Smith H R, Ulanowski Z, Kaye P H 2019 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 12 6579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fujiwara M, Sugidachi T, Arai T 2016 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 9 5911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kuhn T, Heymsfield A J 2016 Pure Appl. Geophys. 173 3065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Miloshevich L M, Heymsfield A J 1997 J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 14 753
[15] Waugh S M, Ziegler C L, MacGorman D R 2015 J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 32 1562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Suzuki K, Shimizu K, Ohigashi T 2012 Sola 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李大山 2002 人工影响天气现状与展望 (北京: 气象出版社) 第441页
Li D S 2002 Current Situation and Prospect of Weather Modification (Beijing: China Meteorological Press) p441 (in Chinese)
[18] Di J, Li Y, Xie M, Zhang J, Ma C, Xi T, Li E, Zhao J 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 7287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 吴羽峰, 吴佳琛, 郝然, 金尚忠, 曹良才 2020 应用光学 41 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Wu J C, Hao R, Jin S Z, Cao L C 2020 J. Appl. Opt. 41 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张益溢, 吴佳琛, 郝然, 金尚忠, 曹良才 2020 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y Y, Wu J C, Hao R, Jin S L, Cao L C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xi T, Di J, Li Y, Dai S, Ma C, Zhao J 2018 Opt. Express 26 28497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Beals M J, Fugal J P, Sh aw, R A, L u, J, Spuler S M, Stith J L 2015 Science 350 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Peter A, Olaf S, Martin S, Evelyn H, Stefan B, Ottmar M, Ulrike L 2009 Appl. Opt. 48 5811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Fugal J P, Shaw R A 2009 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yao L, Chen J, Sojka P E, Wu X C, Cen K 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7006
- PDF下载量: 74
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: