-
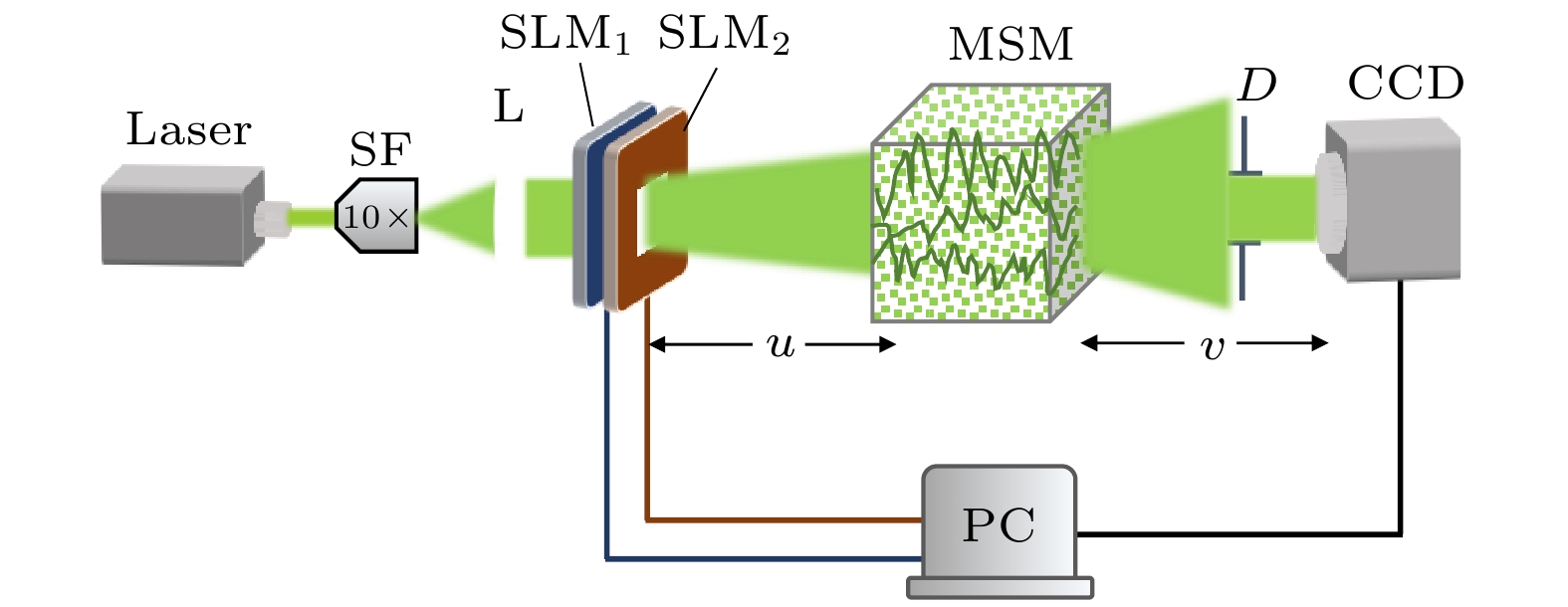
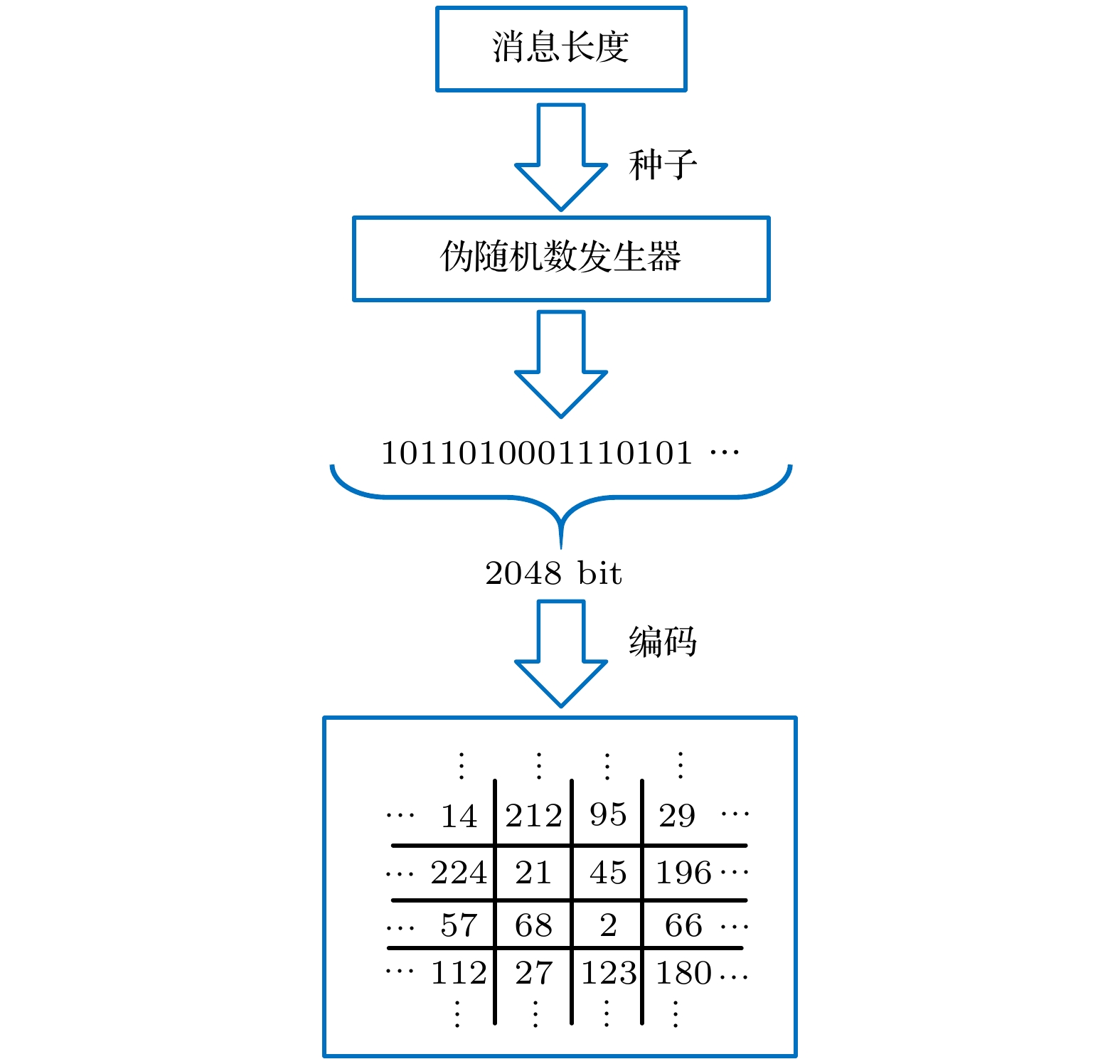
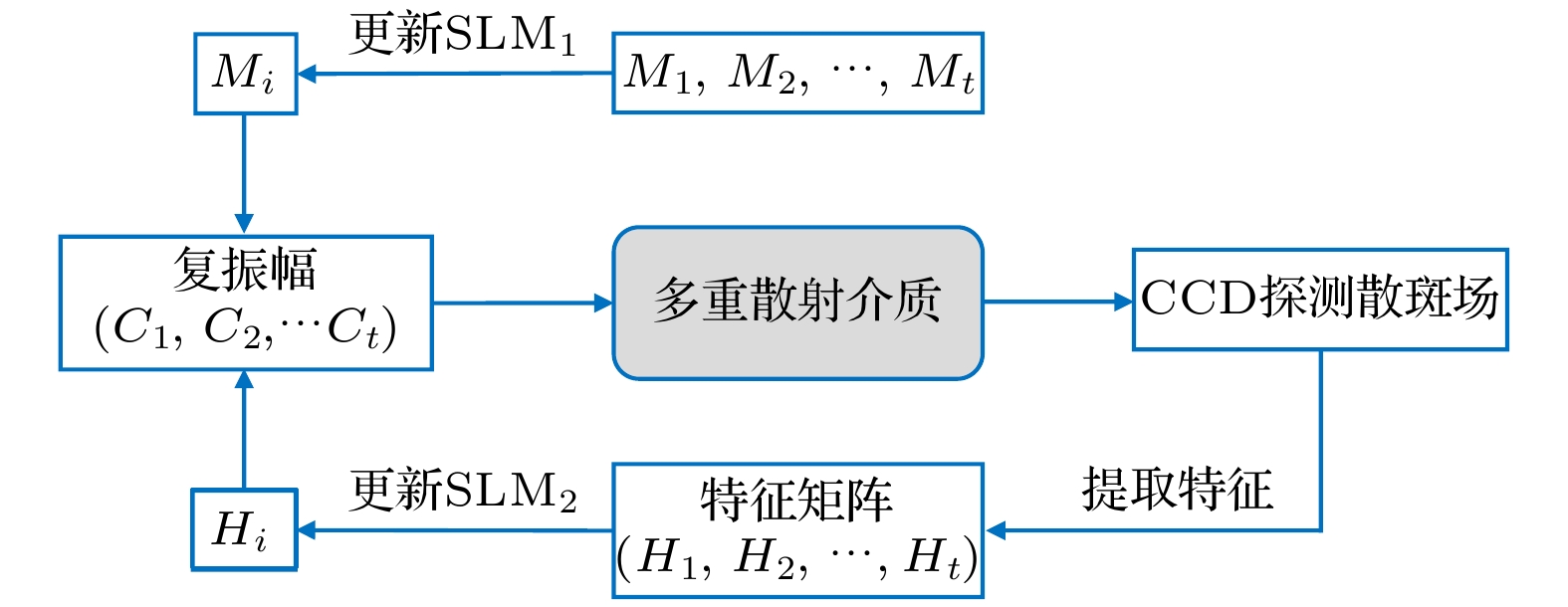
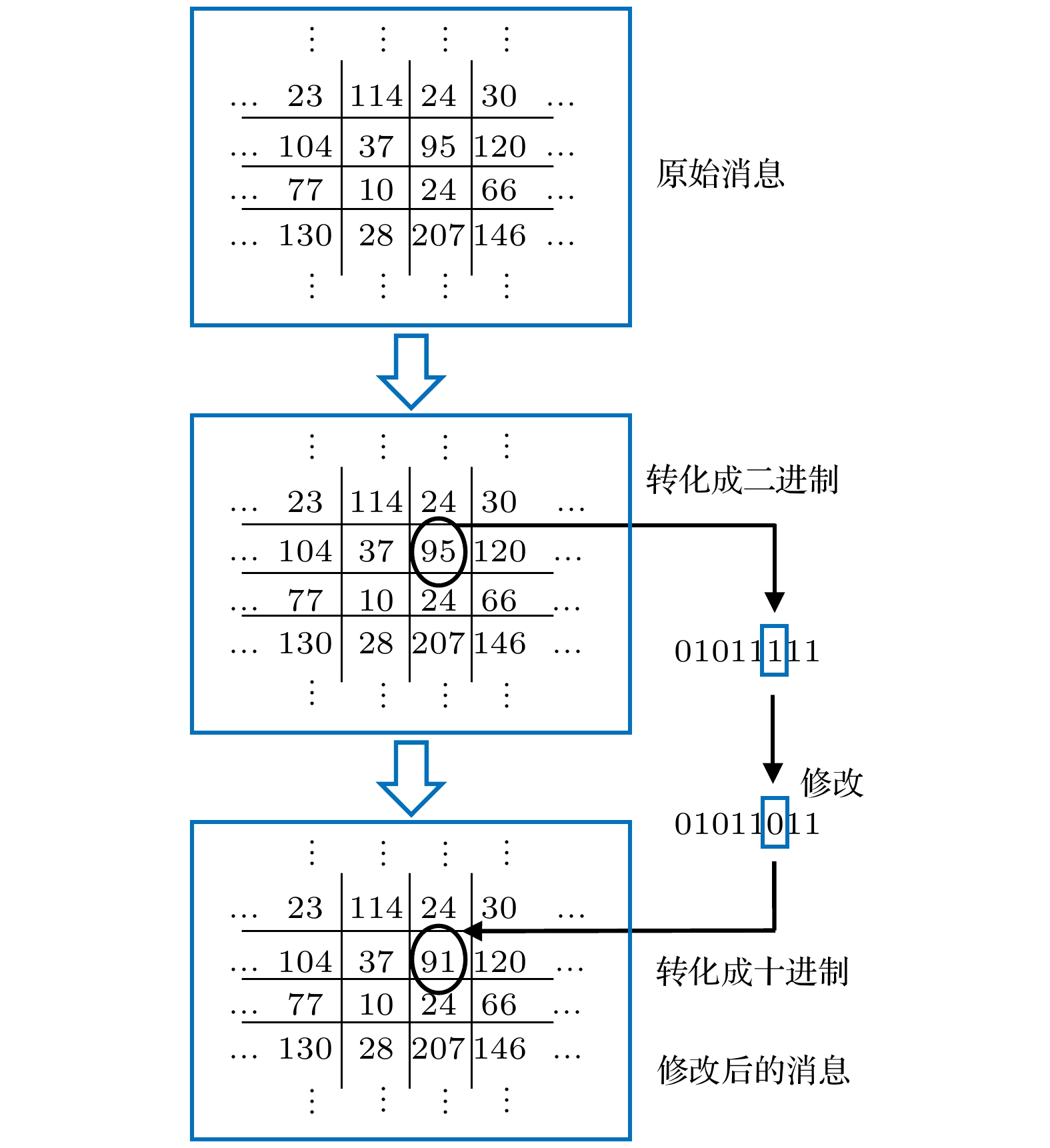
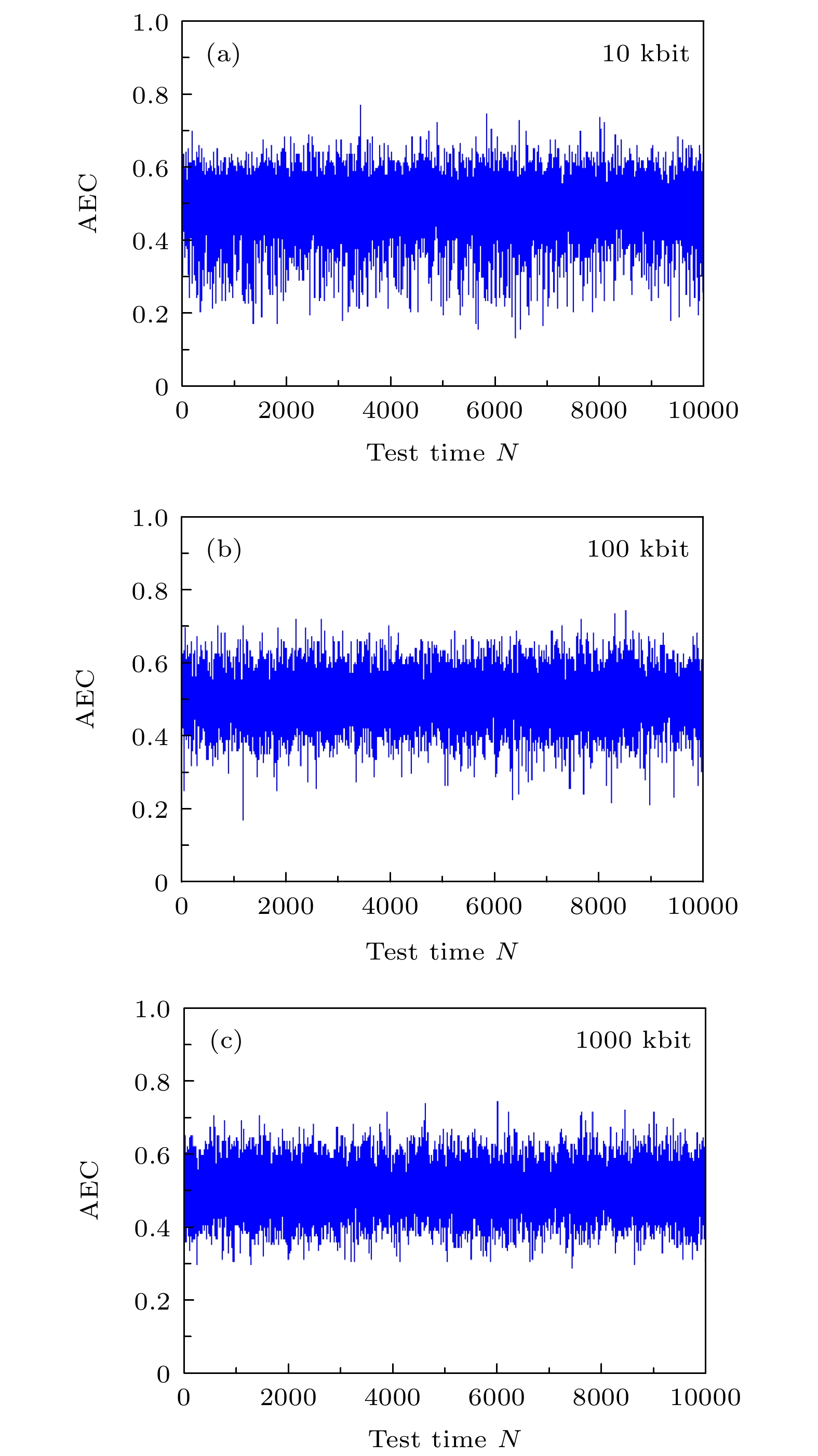
本文提出了一种基于光与多重散射介质相互作用的光学Hash函数构造方法. 该方法创新性地利用多重散射介质对相干调制光的天然随机散射作用, 实现了对调制光的“混淆”和“扩散”, 从而满足了Hash函数的核心功能要求: 高安全强度的单向编码/加密. 所设计的光电混合系统能有效地模拟Hash函数中的“压缩函数”, 结合具有特征提取功能的Sobel滤波器, 能实现将任意长度的输入数据压缩并加密为固定长度为256 bit的输出(即Hash值). 一系列仿真结果表明: 该方法所构造的光学Hash函数具有良好的“雪崩效应”和“抗碰撞性”, 其安全性能可比拟当前最为广泛使用的传统Hash函数(MD5和SHA-1).Hash functions, which can extract message digest from input messages as output, play an important role in digital signature and authentication. Meanwhile, Hash functions are essential in many cryptographic protocols and regimes. With the research becoming more and more in depth, a series of Hash functions is proposed, such as MD series and SHA series. At the same time, the security analysis and attacks against Hash functions are carried out. The security of Hash functions is threatened. In this case, how to improve the security of the Hash functions becomes the primary concern. In this paper, an optical Hash function based on the interaction between light and multiple scattering media is proposed. Unlike most of the traditional Hash functions which are based on mathematical transformations or complex logic operations, this method innovatively takes advantage of the natural random scattering effect of multiple scattering media on coherently modulated light, and realizes the “confusion” and “diffusion” of modulated light, which satisfies the core functional requirement of the Hash function: one-way encoding/encryption with strong security. The photoelectric hybrid system designed by this method can effectively simulate the "compression function" in the Hash function. Combined with the Sobel filter with feature extraction function, the input data of arbitrary length can be compressed and encrypted into the output with a fixed length of 256-bit (Hash value). The principle of the proposed optical Hash function can be described as follows. 1) Two 8-bit images with a size of 16×16 pixels are loaded in SLM1 (amplitude-only spatial modulator) and SLM2 (phase-only spatial modulator) respectively. 2) The coherent wavefront is modulated by SLM1 and SLM2, and then propagates on multiple scattering media. 3) A speckle pattern is recorded by CCD because of the confusion of multiple scattering media. 4) The features of the speckle pattern, which is extracted by Sobel filter, serve as the input of the next compression function. For the unpredicted and non-duplicated disorder multiple scattering media, it is tremendously difficult to determine the internal state of the multiple scattering media. Therefore, the proposed optical Hash function is considered to have a high security. A series of simulation results shows that the proposed optical Hash function has a good “avalanche effect” and “collision resistance”, and its security performance is comparable to that of the most widely used traditional Hash functions (MD5 and SHA-1).
-
Keywords:
- optical information security /
- optical Hash function /
- multiple scattering media /
- avalanche effect
[1] Schneier B, 1996 Government Information Quarterly 13 336
[2] Refregier P, Javidi B 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘福民, 翟宏琛, 杨晓苹 2003 52 2462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F M, Zhai H C, Yang X P 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Situ G H, Zhang J J 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Javidi B, Carnicer A, Yamaguchi M , Nomura T, Pérez-Cabré E 2016 J. Opt. 18 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Carnicer A, Montes-Usategui M, Arcos S, Juvells I 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 1644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Peng X, Zhang P, Wei H, Yu B 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 彭翔, 汤红乔, 田劲东 2007 56 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng X, Tang H Q, Tian J D 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cheng X C, Cai L Z, Wang Y R, Meng X F, Zhang H, Xu X F, Shen X X, Dong G Y 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 1575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liao M H, He W Q, Lu D J, Wu J C, Peng X 2017 Opt. Laser. Eng. 98 34
[11] Peng X, Wei H Z, Zhang P 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Qin W, Peng X 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cai J J, Shen X J, Lei M, Lin C, Dou S F 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Volodin B L, Kippelen B, Meerholz K, Javidi B, Peyghambarian N 1996 Nature 383 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X G, Chen W, Mei S T, Chen X D 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 15668
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 何江涛, 何文奇, 廖美华, 卢大江, 彭翔 2017 66 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He J T, He W Q, Liao M H, Lu D J, Peng X 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Rivest R L 1991 Lect. Notes. Comput. Sci. 537 303
[18] Rivest R L https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc1321 [2020-9-10]
[19] He W Q, Peng X, Qin W, Meng X F 2010 Opt. Commun. 283 2328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 何文奇, 彭翔, 祁永坤, 孟祥锋, 秦琬, 高志 2010 59 1762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He W Q, Peng X, Qi Y K, Meng X F, Qin W, Gao Z 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lai H, He W, Peng X 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 6213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Webster A F, Tavares S E 1986
Lect. Notes. Comput. Sci. 218 523 -
表 1 雪崩效应测试结果
Table 1. Results of testing avalanche effect.
10 kbit 100 kbit 1000 kbit 平均值 $ \overline{{\rm{AEC}}} $ 0.49 0.50 0.50 0.50 ${\Delta }{B} $ 0.0770 0.0647 0.0636 0.0684 表 2 与MD5和SHA-1算法的比较
Table 2. Comparison with MD5 and SHA-1.
本方案 MD5 SHA-1 $ \overline{{\rm{AEC}}} $ 0.50 0.50 0.50 ${\Delta }{B} $ 0.0684 0.0437 0.0392 -
[1] Schneier B, 1996 Government Information Quarterly 13 336
[2] Refregier P, Javidi B 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘福民, 翟宏琛, 杨晓苹 2003 52 2462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F M, Zhai H C, Yang X P 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Situ G H, Zhang J J 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Javidi B, Carnicer A, Yamaguchi M , Nomura T, Pérez-Cabré E 2016 J. Opt. 18 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Carnicer A, Montes-Usategui M, Arcos S, Juvells I 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 1644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Peng X, Zhang P, Wei H, Yu B 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 彭翔, 汤红乔, 田劲东 2007 56 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng X, Tang H Q, Tian J D 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cheng X C, Cai L Z, Wang Y R, Meng X F, Zhang H, Xu X F, Shen X X, Dong G Y 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 1575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liao M H, He W Q, Lu D J, Wu J C, Peng X 2017 Opt. Laser. Eng. 98 34
[11] Peng X, Wei H Z, Zhang P 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Qin W, Peng X 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cai J J, Shen X J, Lei M, Lin C, Dou S F 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Volodin B L, Kippelen B, Meerholz K, Javidi B, Peyghambarian N 1996 Nature 383 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X G, Chen W, Mei S T, Chen X D 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 15668
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 何江涛, 何文奇, 廖美华, 卢大江, 彭翔 2017 66 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He J T, He W Q, Liao M H, Lu D J, Peng X 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Rivest R L 1991 Lect. Notes. Comput. Sci. 537 303
[18] Rivest R L https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc1321 [2020-9-10]
[19] He W Q, Peng X, Qin W, Meng X F 2010 Opt. Commun. 283 2328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 何文奇, 彭翔, 祁永坤, 孟祥锋, 秦琬, 高志 2010 59 1762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He W Q, Peng X, Qi Y K, Meng X F, Qin W, Gao Z 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lai H, He W, Peng X 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 6213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Webster A F, Tavares S E 1986
Lect. Notes. Comput. Sci. 218 523
计量
- 文章访问数: 7053
- PDF下载量: 140
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: