-
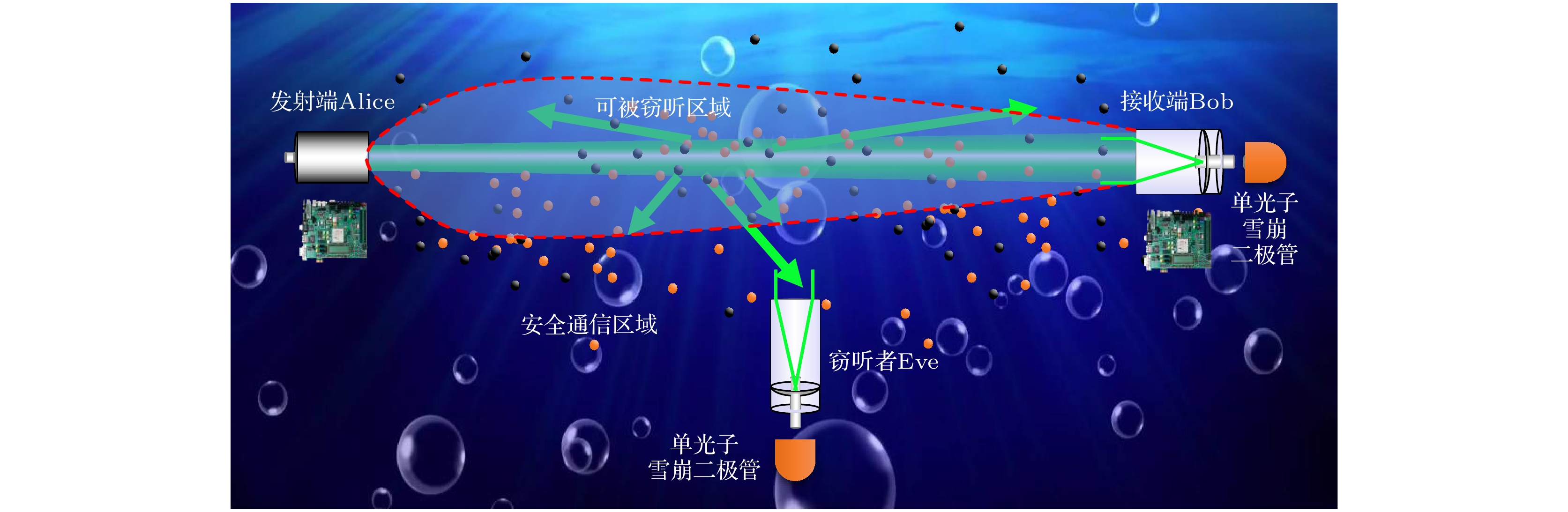
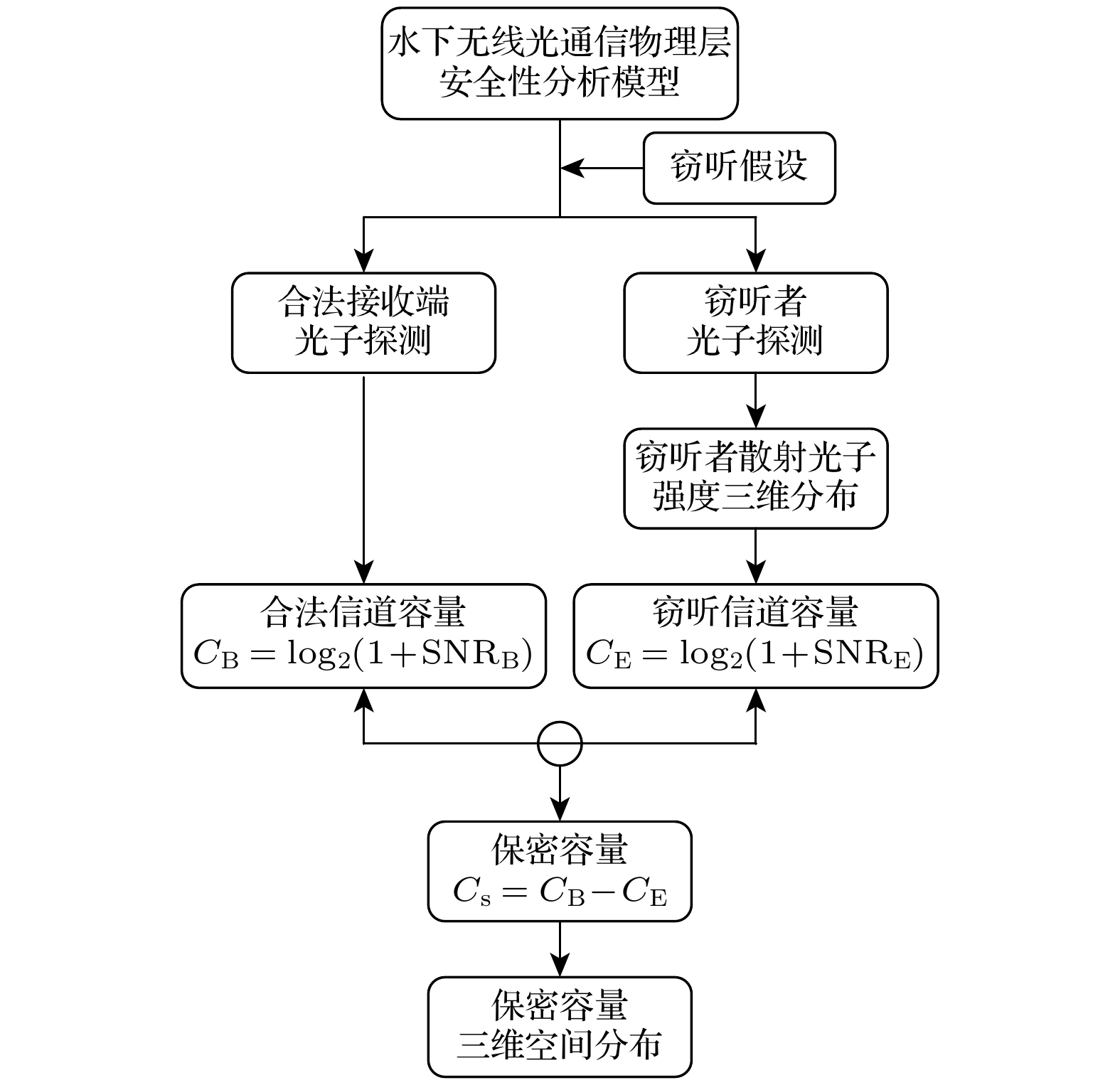
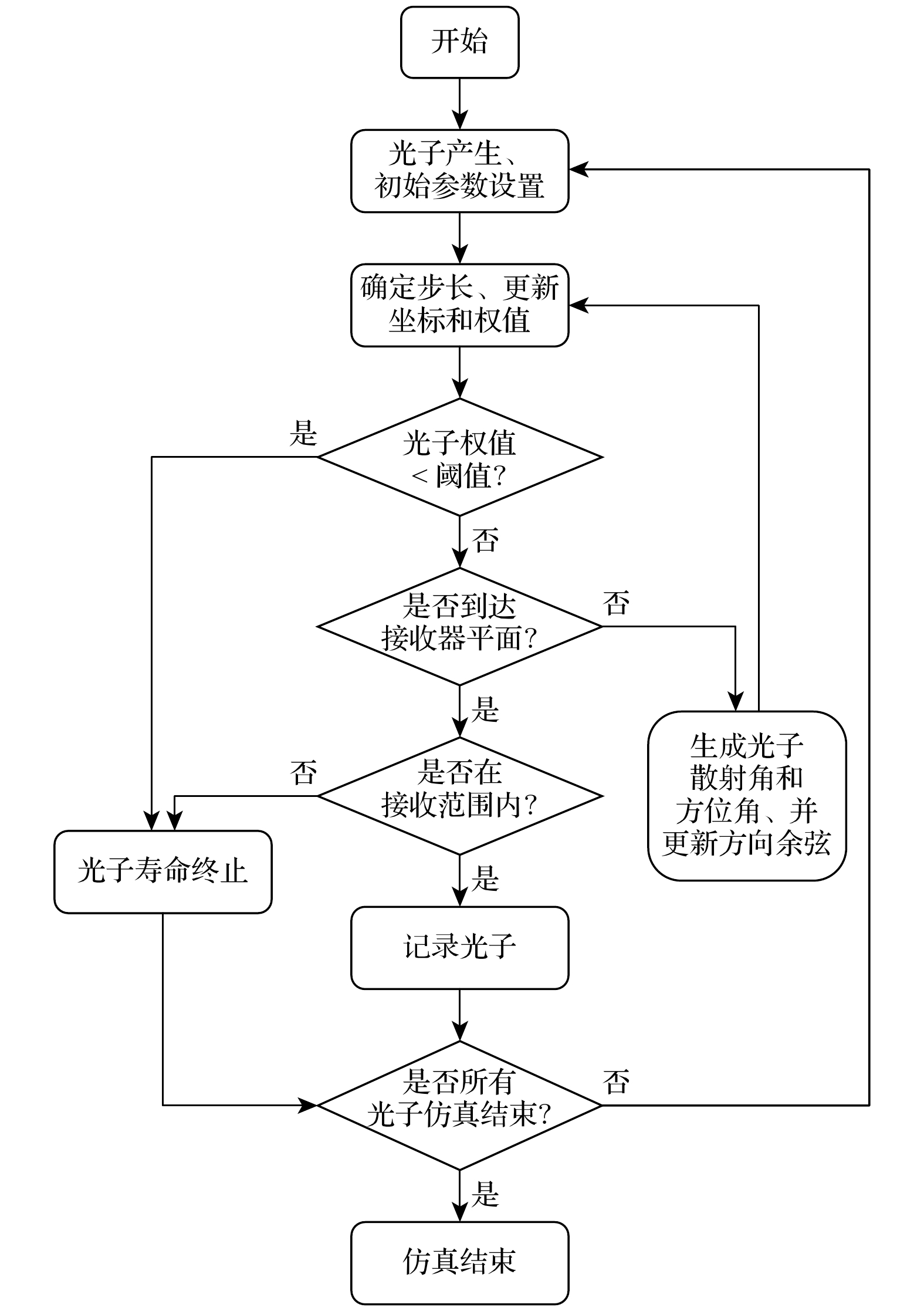
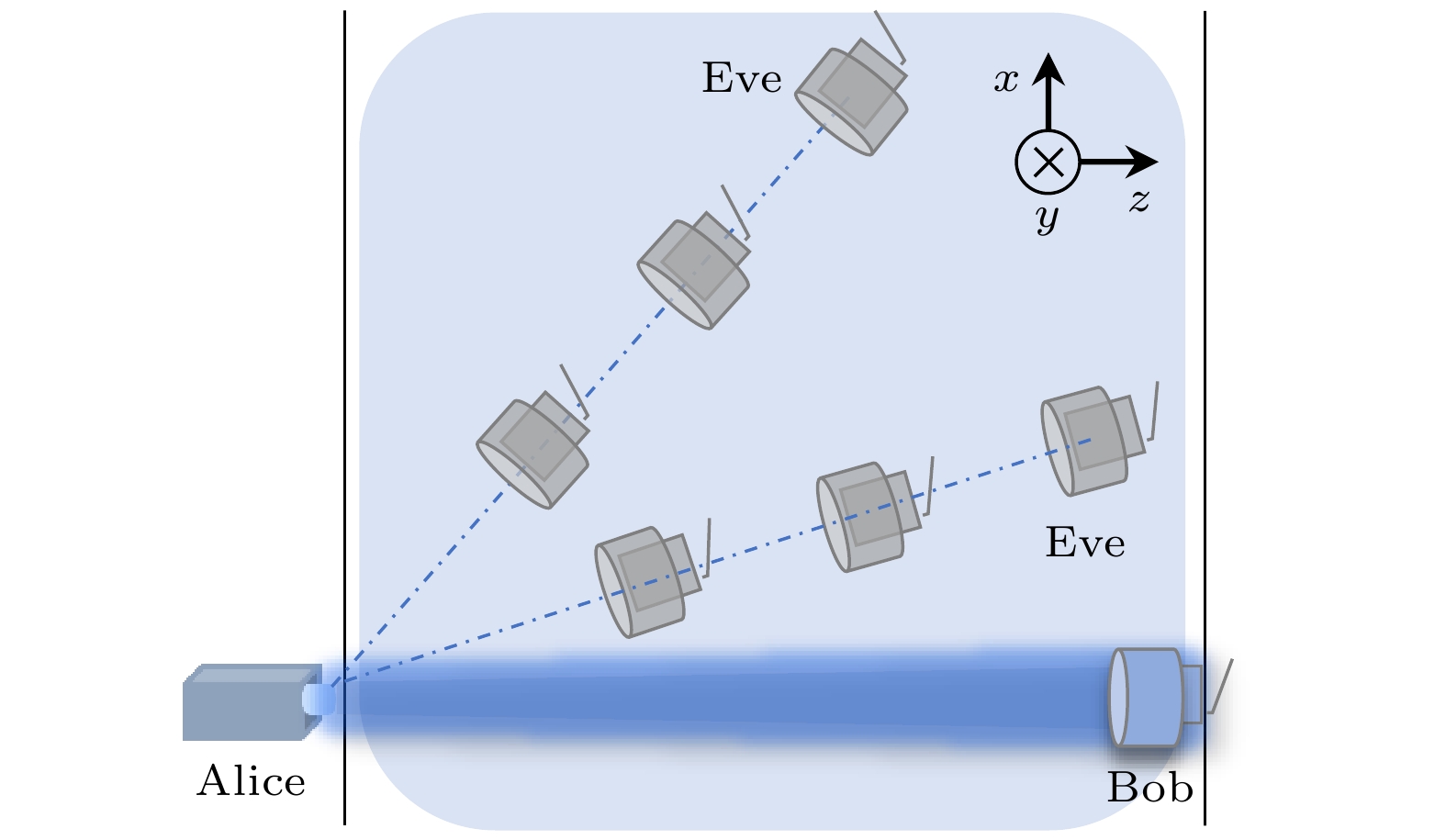
水下无线光通信(UWOC)具有定向传输的特点, 相较于声呐、无线电等广播式传输模式具有更高的安全性. 然而, 由于海水散射效应部分光子在传输过程中会被散射出预设路径, 从而造成信息泄漏风险. 本文基于搭线窃听信道模型提出一种UWOC物理层安全性分析模型以评估信息泄漏风险. 该模型通过计算UWOC系统中合法信道与窃听信道的容量差值, 来评估通信系统的安全性. 具体而言, 该模型首先基于蒙特卡罗模拟与实验测量方法分析信道中散射光子的三维分布, 然后从信息论角度分析合法通信双方信道容量以及窃听信道容量, 最终获得安全保密容量的三维空间分布, 从而评估散射光子所造成的信息泄漏风险与系统的通信安全性. 本文应用该模型对清澈海水环境下的UWOC系统的安全性进行了分析, 研究发现传输路径附近一定范围内系统的保密容量为零, 证明散射光子会造成信息泄漏. 本研究成果为UWOC系统定量安全分析提供了解决策略, 能够为UWOC系统和编解码方案设计提供有力支撑.Underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) possesses significant advantages, such as high bandwidth, low latency, and low power consumption, making it a key technology for building information networks in marine environments. However, due to the scattering effect of seawater, some photons carrying information inevitably scatter out of their predetermined paths, leading to the possibility for information leakage. Therefore, we propose a physical-layer security analysis model for UWOC systems based on the wiretap channel model. The model evaluates the security of the communication system by calculating the capacity difference between the legitimate channel and the eavesdropping channel in the UWOC system. Specifically, the model first constructs the three-dimensional intensity distribution of scattered photons in the underwater channel via Monte Carlo simulations and experimental measurements. Then, it calculates the capacities of both the legitimate and eavesdropping channels based on the decoding results. Finally, the three-dimensional distribution of secrecy capacity is derived to assess the security of the communication system. In this work this model is used to analyze the security of the UWOC system in clear seawater environments. The results show that the secrecy capacity of the system is zero within a certain range near the transmission path, demonstrating that scattered photons can cause information leakage. We recommend that, in practical applications, monitoring the non-signal transmission area near the transmitter is essential to ensure communication security. This research provides a solution for analyzing the quantitative security of UWOC, which can strongly support the design of UWOC systems and encoding/decoding schemes.
-
Keywords:
- underwater wireless optical communication /
- physical-layer security /
- scattered photons /
- Monte Carlo /
- secrecy capacity
[1] Qi Z R, Zhao X Y, Pompili D 2023 IEEE Trans. Commun. 71 7163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Naik R P, Salman M, Bolboli J, Shetty C S, Chung W Y 2024 IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 73 8420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Esmaiel H, Sun H X 2024 Sensors 24 7075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 郑晓桐, 郭立新, 程明建, 李江挺 2018 67 214206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng X T, Guo L X, Cheng M J, Li J T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 214206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Abd El-Mottaleb S A, Singh M, Armghan A, Atieh A, Aly M H 2025 Opt. Commun. 574 131204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang L, Wang Z M, Wei Z X, Chen C, Wei G D, Fu H Y, Dong Y H 2020 Opt. Express 28 31796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan Z Q, Hu C Q, Li Z M, Li Z Y, Hang Z, Xian M J 2021 Photonics Res. 9 2360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fei C, Wang Y, Du J, Chen R L, Lv N F, Zhang G W, Tian J H, Hong X J, He S L 2022 Opt. Express 30 2326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Nath N, Chouhan S 2024 IEEE Internet Things J. 11 39721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li S, Wang P, Li G, Zhang X, Li H, Zhou B, Yang T 2023 Opt. Express 31 34729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kong M W, Wang J L, Chen Y F, Ali T, Sarwar R, Qiu Y, Wang S L, Han J, Xu J 2017 Opt. Express 25 21509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fu X Q, Li H W, Shi J H, Li T, Bao W S 2025 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 68 210314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z F, Kong X H, Zhang J, Shao L D, Zhang D J, Liu J, Wang X, Zhu W R, Qiu C W 2022 Laser Photon. Rev. 16 2200113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang H M, Zhang X, Jiang J C 2019 IEEE Wirel. Commun. 26 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wyner A D 1975 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 54 1355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Guan K, Cho J, Winzer P J 2018 Opt. Commun. 408 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Shannon C E, Weaver W 1949 The Mathematical Theory of Information (Urbana: University of Illinois Press) p145
[18] Williamson C A, Hollins R C 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 9951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang J L, Kou L L, Yang Y, He F T, Duan Z L 2020 Opt. Commun. 475 126214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ramley I, Alzayed H M, Al-Hadeethi Y, Chen M G, Barasheed A Z 2024 Mathematics 12 3904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wen H, Yin H X, Ji X Y, Huang A 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 6883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gabriel C, Khalighi M A, Bourennane S, Léon P, Rigaud V 2013 J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 5 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hollins R C, Williamson C A 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 6218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu J Y, Yu B, Jing M Y, Xiao L T, Jia S T, Qin G Q, Long G L 2016 Light Sci. Appl. 5 e16144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hu J Y, Jing M Y, Zhang G F, Qin C B, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2018 Opt. Express 26 20835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hoang T M, Vahid A, Tuan H D, Hanzo L 2024 IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 26 1830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Illi E, Qaraqe M, Althunibat S, Alhasanat A, Alsafasfeh M, de Ree M, Mantas G, Rodriguez J, Aman W, Al-Kuwari S 2024 IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 26 347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 韩彦睿, 李伟, 臧延华, 杨昌钢, 陈瑞云, 张国峰, 秦成兵, 胡建勇, 肖连团 2023 72 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han Y R, Li W, Zang Y H, Yang C G, Chen R Y, Zhang G F, Qin C B, Hu J Y, Xiao L T 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Rioul O, Magossi J C 2014 Entropy 16 4892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Solonenko M G, Mobley C D 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 5392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu X Y, Yang S H, Gao Y Z, Li J, Li C F, Xu Z, Fan C Y 2024 Opt. Commun. 569 130747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
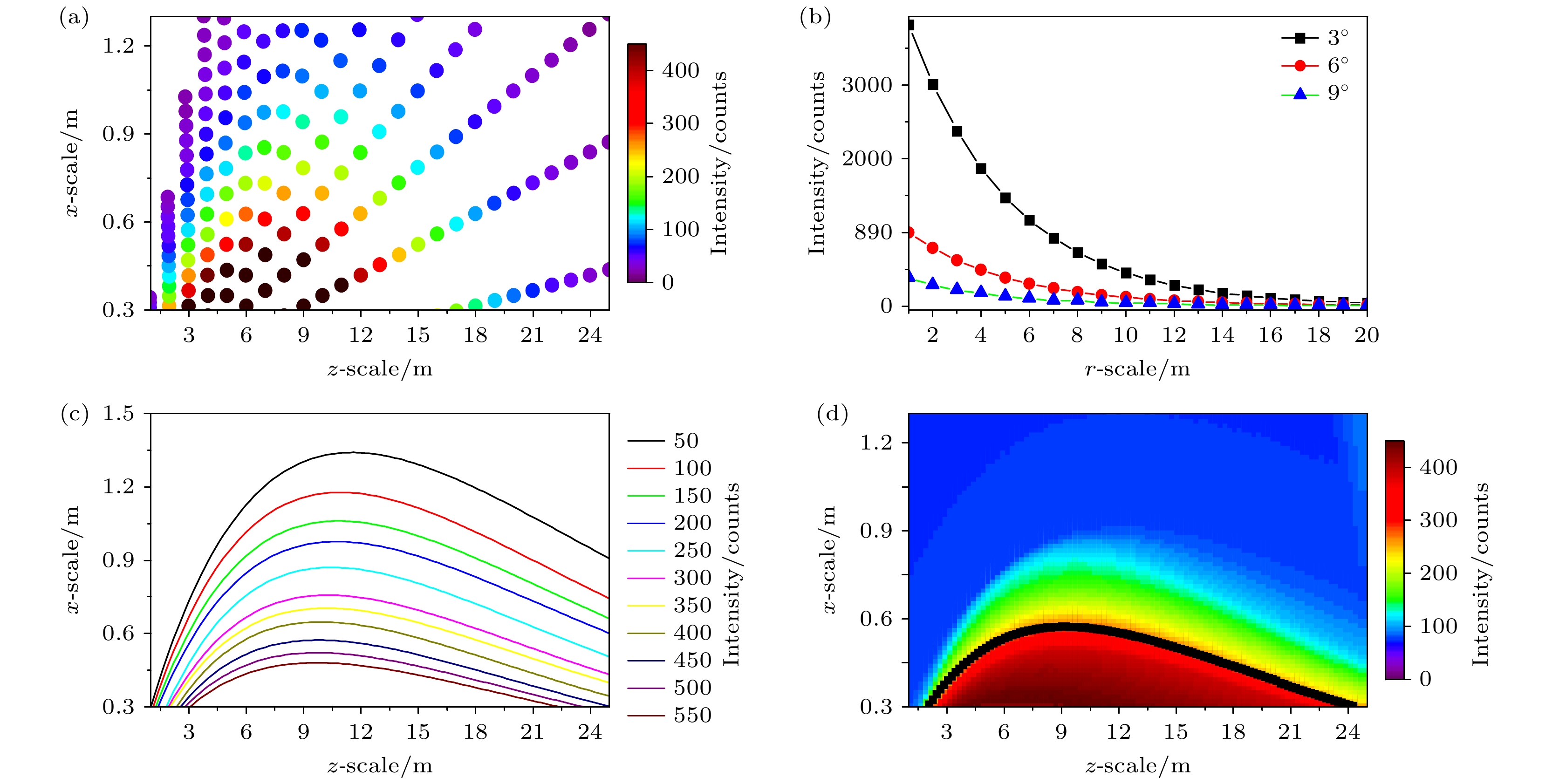
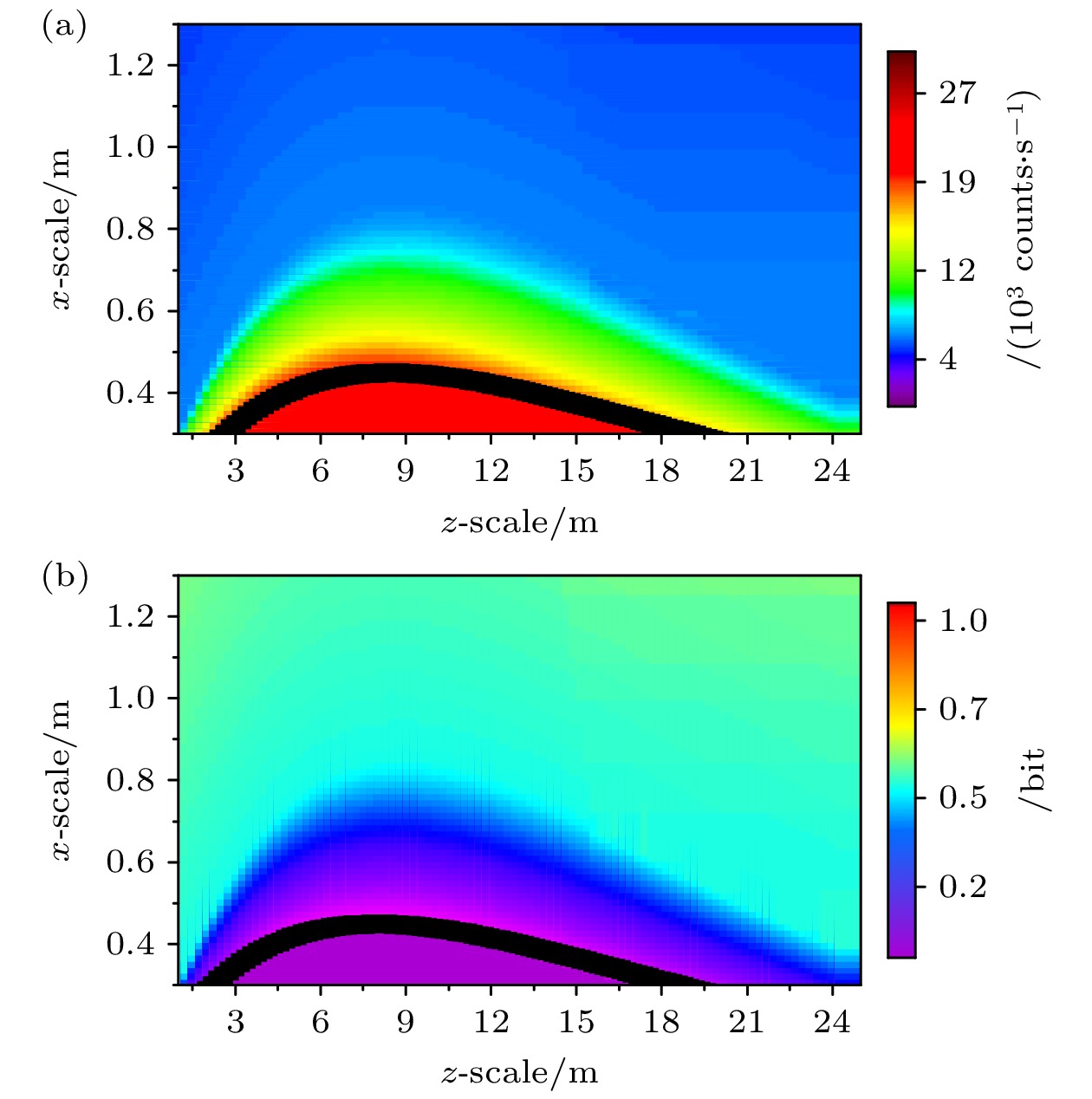
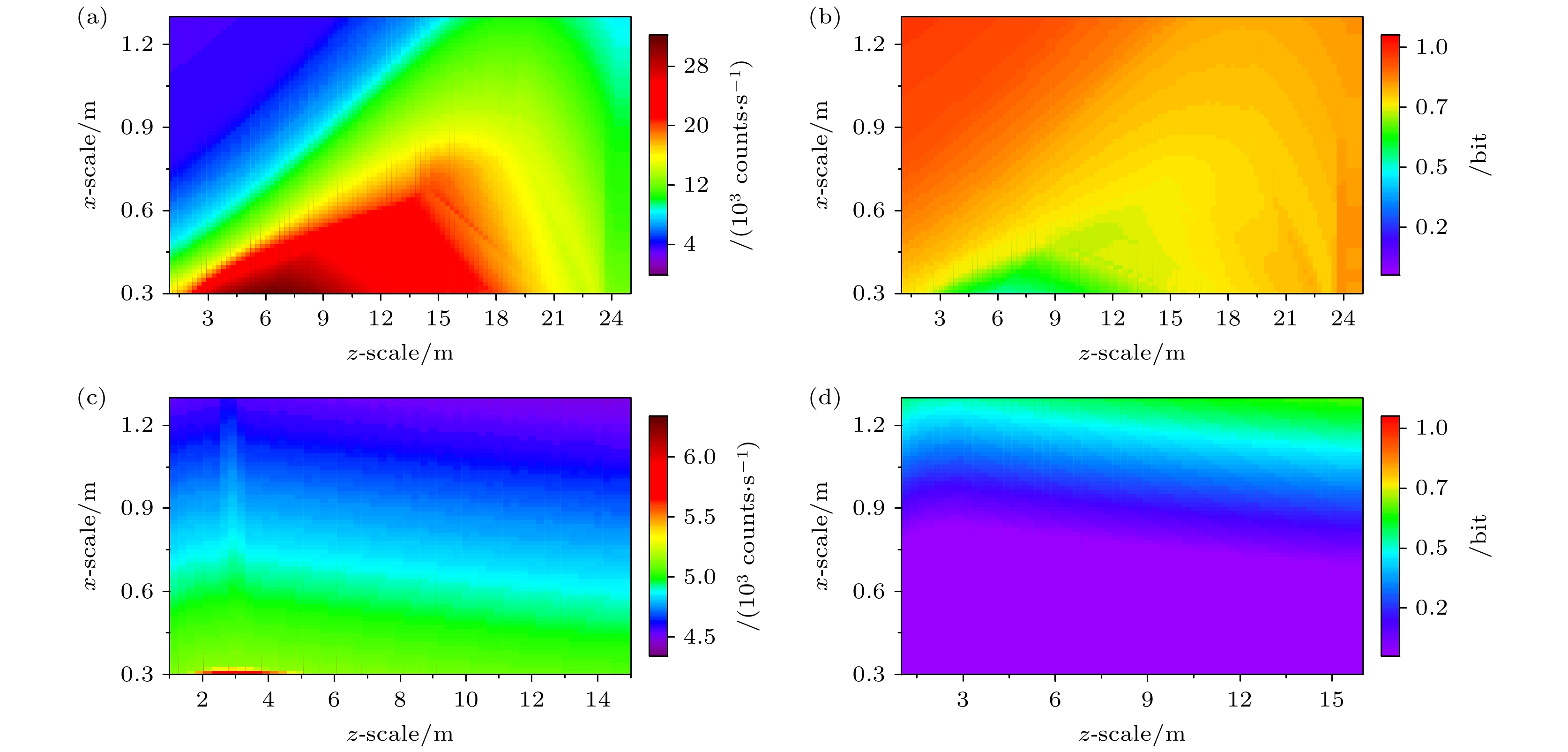
图 6 远洋清澈海水环境下窃听者散射光子强度的模拟仿真 (a) 散射光子的三维散点分布图; (b) 3°, 6°, 9°径向下散射光子强度的衰减曲线, 其可通过单指数衰减函数拟合; (c) 散射光子等光强曲线, 其可通过双指数函数拟合; (d) 散射光子强度三维空间分布图, 由于光子分布沿光束传输方向具有轴对称性, 图中以二维剖面图的形式展示光子的三维分布
Fig. 6. Simulation of scattered photon intensity in clear seawater: (a) Scatter plot of scattered photon intensity; (b) intensity decay curves of scattered photon at radial angles of 3°, 6°, and 9°, which can be fitted by single exponential decay function; (c) contours of scattered photon intensity, which can be fitted by double exponential function; (d) intensity distribution map of scattered photons by simulation, the three-dimensional spatial distribution of scattered photon intensity is represented in the form of a two-dimensional profile due to the axial symmetry of photon distribution along the beam propagation direction.
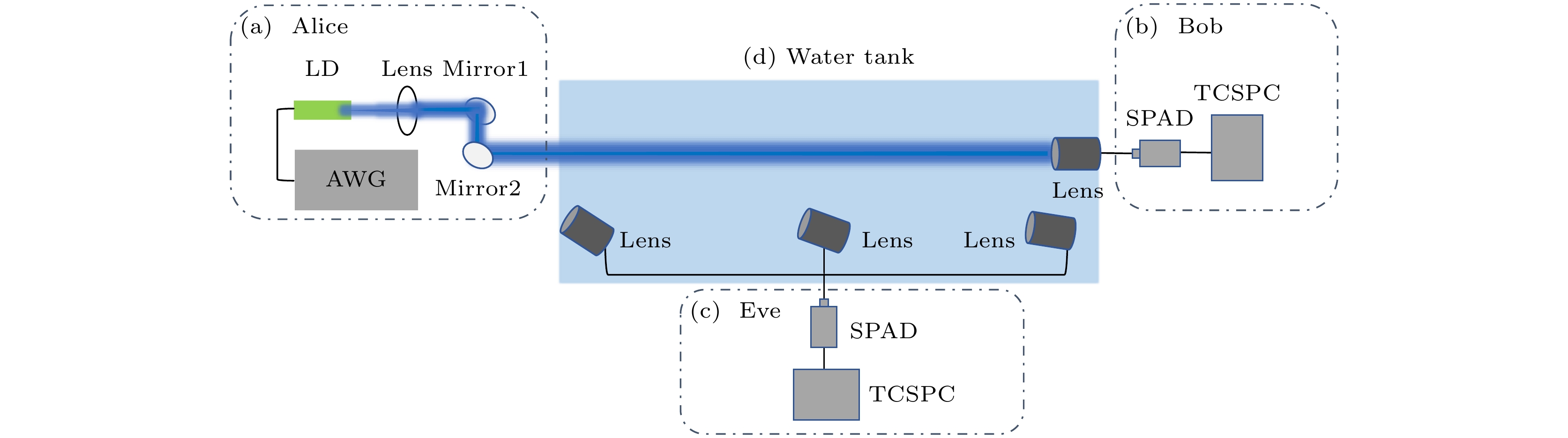
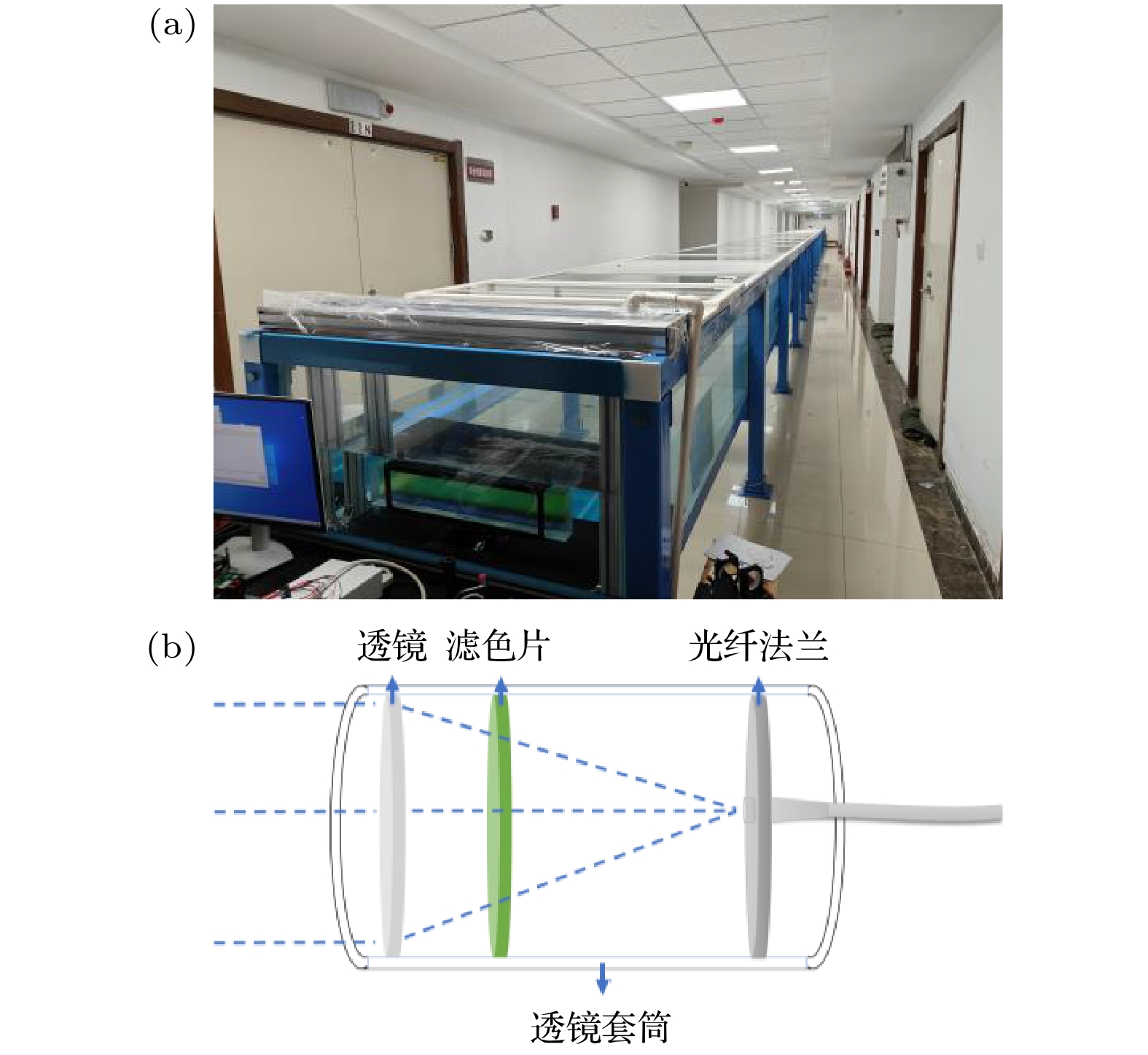
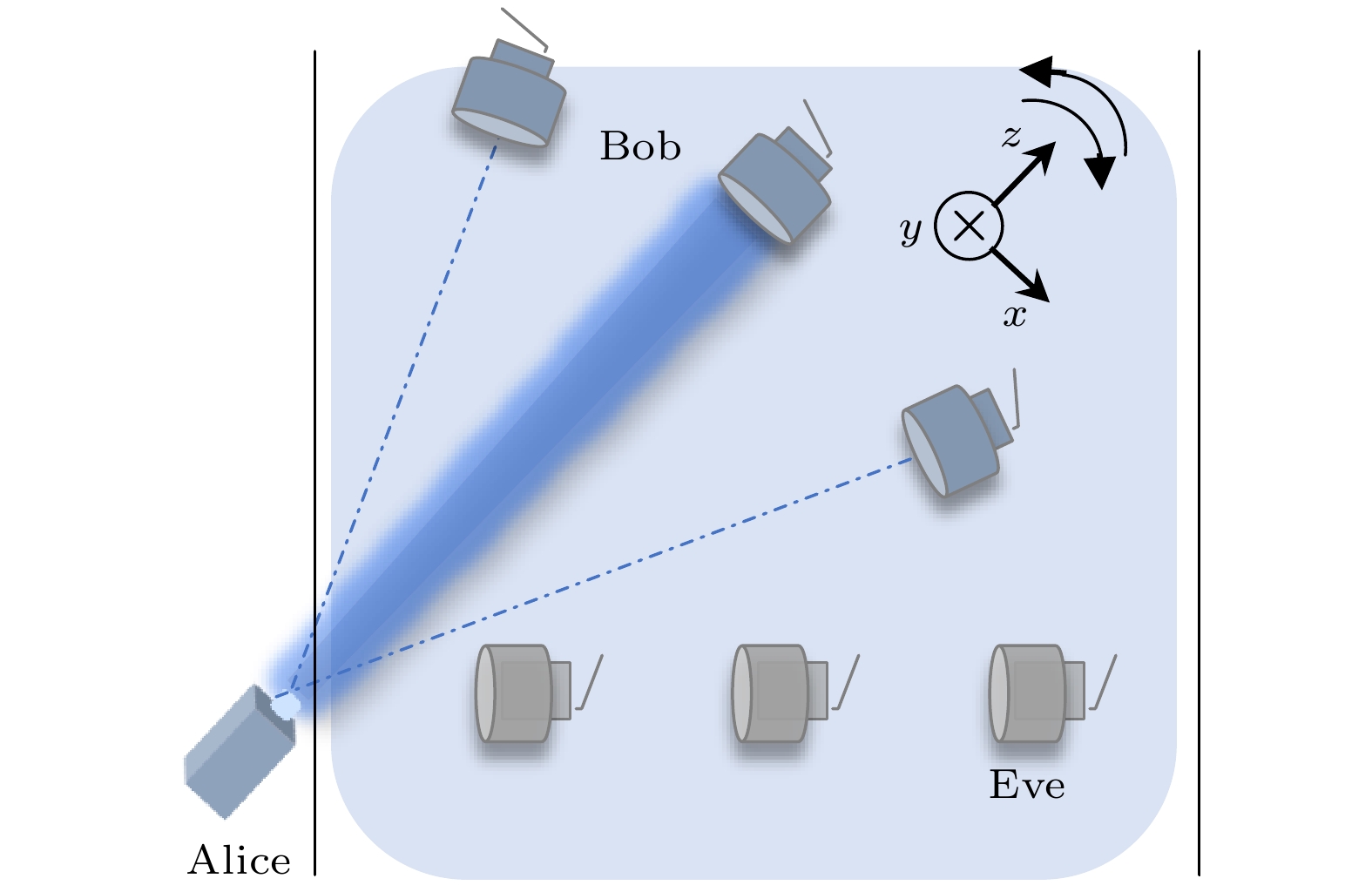
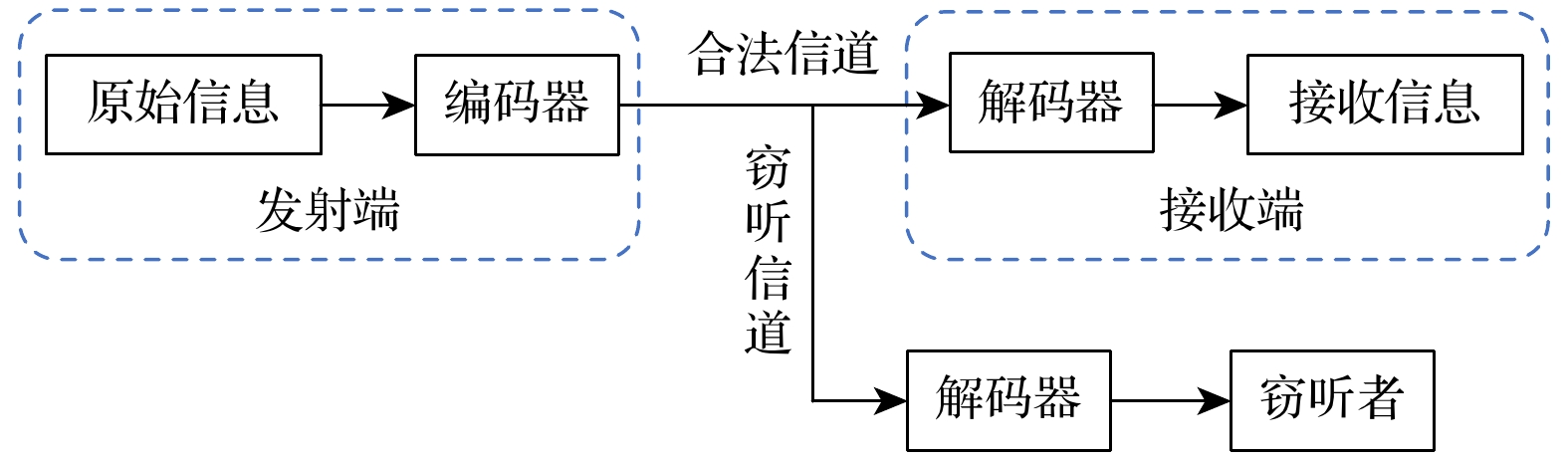
图 7 UWOC系统装置示意图 (a) 发射端模块; (b) 接收端模块; (c) 窃听者模块; (d) 水下光程池; LD为激光二极管, AWG为任意波形发生器, SPAD为单光子雪崩二极管, TCSPC为时间相关单光子计数采集卡
Fig. 7. UWOC system: (a) Transmitter; (b) receiver; (c) eavesdropper; (d) water tank. LD represents laser diode, AWG represents arbitrary waveform generator, SPAD represents single-photon avalanche diode, TCSPC represents time-correlated single photon counting.
表 1 蒙特卡罗仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters for the Monte Carlo simulation.
参数 数值 参数 数值 光子数 107 接收孔径/mm 50 光斑直径/mm 25 接收器视场角/(°) 4 光束发散角/rad 10–4 光子阈值 10–5 吸收系数a/m–1 0.065 散射系数b/m–1 0.195 -
[1] Qi Z R, Zhao X Y, Pompili D 2023 IEEE Trans. Commun. 71 7163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Naik R P, Salman M, Bolboli J, Shetty C S, Chung W Y 2024 IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 73 8420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Esmaiel H, Sun H X 2024 Sensors 24 7075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 郑晓桐, 郭立新, 程明建, 李江挺 2018 67 214206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng X T, Guo L X, Cheng M J, Li J T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 214206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Abd El-Mottaleb S A, Singh M, Armghan A, Atieh A, Aly M H 2025 Opt. Commun. 574 131204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang L, Wang Z M, Wei Z X, Chen C, Wei G D, Fu H Y, Dong Y H 2020 Opt. Express 28 31796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan Z Q, Hu C Q, Li Z M, Li Z Y, Hang Z, Xian M J 2021 Photonics Res. 9 2360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fei C, Wang Y, Du J, Chen R L, Lv N F, Zhang G W, Tian J H, Hong X J, He S L 2022 Opt. Express 30 2326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Nath N, Chouhan S 2024 IEEE Internet Things J. 11 39721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li S, Wang P, Li G, Zhang X, Li H, Zhou B, Yang T 2023 Opt. Express 31 34729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kong M W, Wang J L, Chen Y F, Ali T, Sarwar R, Qiu Y, Wang S L, Han J, Xu J 2017 Opt. Express 25 21509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fu X Q, Li H W, Shi J H, Li T, Bao W S 2025 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 68 210314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z F, Kong X H, Zhang J, Shao L D, Zhang D J, Liu J, Wang X, Zhu W R, Qiu C W 2022 Laser Photon. Rev. 16 2200113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang H M, Zhang X, Jiang J C 2019 IEEE Wirel. Commun. 26 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wyner A D 1975 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 54 1355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Guan K, Cho J, Winzer P J 2018 Opt. Commun. 408 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Shannon C E, Weaver W 1949 The Mathematical Theory of Information (Urbana: University of Illinois Press) p145
[18] Williamson C A, Hollins R C 2022 Appl. Opt. 61 9951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang J L, Kou L L, Yang Y, He F T, Duan Z L 2020 Opt. Commun. 475 126214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ramley I, Alzayed H M, Al-Hadeethi Y, Chen M G, Barasheed A Z 2024 Mathematics 12 3904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wen H, Yin H X, Ji X Y, Huang A 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 6883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gabriel C, Khalighi M A, Bourennane S, Léon P, Rigaud V 2013 J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 5 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hollins R C, Williamson C A 2023 Appl. Opt. 62 6218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu J Y, Yu B, Jing M Y, Xiao L T, Jia S T, Qin G Q, Long G L 2016 Light Sci. Appl. 5 e16144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hu J Y, Jing M Y, Zhang G F, Qin C B, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2018 Opt. Express 26 20835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hoang T M, Vahid A, Tuan H D, Hanzo L 2024 IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 26 1830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Illi E, Qaraqe M, Althunibat S, Alhasanat A, Alsafasfeh M, de Ree M, Mantas G, Rodriguez J, Aman W, Al-Kuwari S 2024 IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 26 347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 韩彦睿, 李伟, 臧延华, 杨昌钢, 陈瑞云, 张国峰, 秦成兵, 胡建勇, 肖连团 2023 72 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han Y R, Li W, Zang Y H, Yang C G, Chen R Y, Zhang G F, Qin C B, Hu J Y, Xiao L T 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 160301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Rioul O, Magossi J C 2014 Entropy 16 4892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Solonenko M G, Mobley C D 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 5392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu X Y, Yang S H, Gao Y Z, Li J, Li C F, Xu Z, Fan C Y 2024 Opt. Commun. 569 130747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1587
- PDF下载量: 92
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: