-
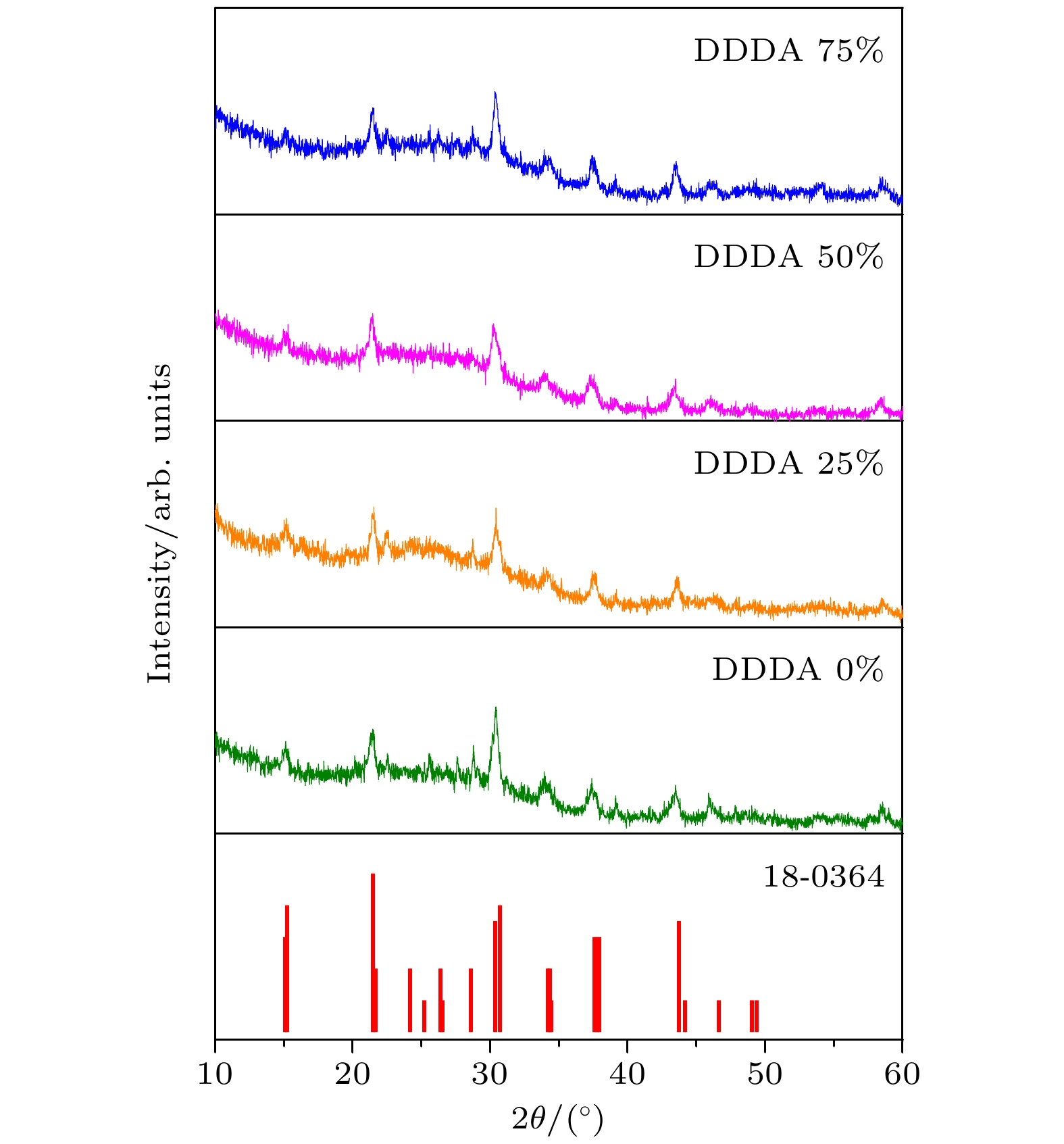
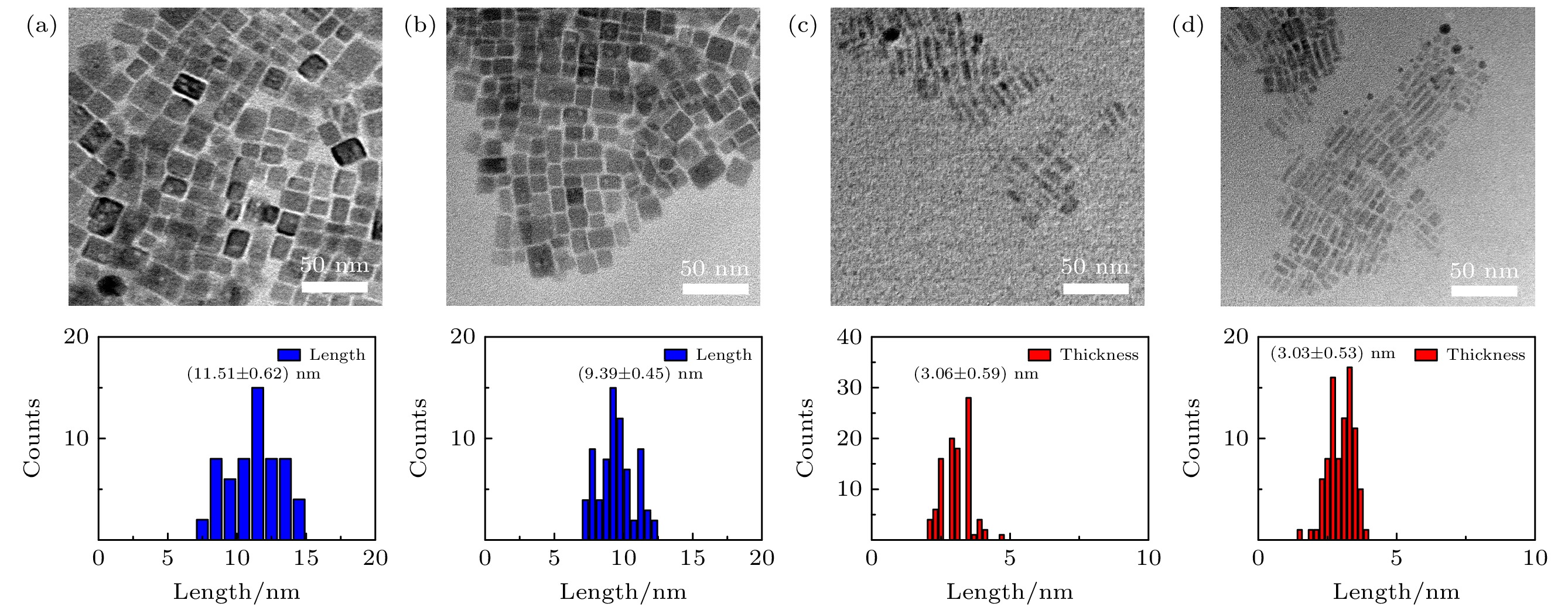
通过添加不同比例的十二烷二酸(DDDA)配体, 在室温下采用配体辅助再沉淀法制备CsPbBr3钙钛矿纳米晶. 利用X射线衍射仪、透射电子显微镜、紫外分光光度计、荧光光谱仪等对纳米晶的相结构、微结构和光学性质进行了表征. 结果显示: 所有纳米晶产物均为立方相结构; 而纳米晶形貌会随着DDDA浓度的增加从纳米立方块逐渐转变为厚度均一的纳米片, 同时光致发光光谱从绿光区移至蓝光区. 结合实验室搭建的具有超高时间分辨率(约100 ms)的原位光致发光装置, 实时监测了不同形貌纳米晶在形成过程中光致发光光谱的演变. 结果表明: 未使用DDDA时前驱体经历了快速成核和尺寸分布聚焦生长后生成纳米立方块; DDDA的出现促进了纳米晶在形成早期生成各向异性的纳米片, 然而随着反应时间的延长, 具有不对称结构的纳米片会通过溶解-再结晶方式转变为热力学稳定的纳米立方块. 本工作对形貌可控的钙钛矿纳米晶的精准合成具有一定参考价值.Cesium-lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbX3 (X = Br, Cl, I) PNCs) have become ideal luminescent materials for wide color gamut display devices, white LED lighting and high-efficiency solar cells, due to adjustable energy band gap, high fluorescence quantum yield, narrow fluorescence emission peak, and ultra-high defect tolerance. The preparation of CsPbX3 PNCs with controllable size and morphology is a prerequisite for obtaining efficient and stable photovoltaic/photovoltaic devices. In this report, the CsPbBr3 PNCs with different shapes are prepared by adding different concentrations of dodecanedioic acid (DDDA) ligands at room temperature through using ligand-assisted reprecipitation method. Utilizing the X-ray diffractometer, transmission electron microscopy, ultraviolet spectrophotometer, fluorescence spectrometers (PL), the phase structure, microstructure and optical properties of the nanocrystals are investigated. The results show that the presence of DDDA ligands have no influence on the phase structure of nanocrystal products, they all present a cubic phase structure. Surprisingly, the morphology of the nanocrystals gradually transforms from nanocubes into nanoplatelets with ~5 layers in thickness as the concentration of DDDA increases. In addition, the PL spectrum shows a significant blue shift from 509 nm to 478 nm. By using the in-situ homemade PL device with ultra-high time resolution (~100 ms), the real-time monitoring PL spectra of nanocrystals in the formation process are measured. The results demonstrate that nanocrystals undergo rapid nucleation and focusing of size distribution growth to generate nanocubes in the absence of DDDA ligand. When the DDDA ligand is present, nanocrystals are mainly nanoplatelets in the early growth stage due to the decelerated reaction. As the reaction proceeds, nanocubes can emerge and grow gradually while the nanoplatelets disappear when the concentrations of DDDA ligands are 25% and 50%. As the concentration is further increased to 75%, almost nanoplatelets could be formed after the nucleation stage and growth stage. Unexpectedly, preformed nanoplatelets are unstable for the prolonged reaction time as a result of the high surface energy, and they will eventually transform into isotropic nanocubes through dissolution-recrystallization pathway, indicating that the process in the later stage is controlled mainly by thermodynamics. Our findings offer an efficient strategy to synthesize the perovskite nanocrystals with controllable size and morphology.
-
Keywords:
- perovskite nanocrystals /
- shape transformation /
- in-situ photoluminescence /
- growth kinetics
[1] Shamsi J, Urban A S, Imran M, De Trizio L, Manna L 2019 Chem. Rev. 119 3296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Akkerman Q A, D’Innocenzo V, Accornero S, Scarpellini A, Petrozza A, Prato M, Manna L 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 10276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kovalenko M V, Protesescu L, Bodnarchuk M I 2017 Science 358 745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schmidt L, Pertegás A, Gonzalez-Carrero S, et al. 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Travis W, Glover E N K, Bronstein H, Scanlon D O, Palgrave R G 2016 Chem. Sci. 7 4548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shi Z F, Li S, Li Y, et al. 2018 ACS Nano 12 1462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 林月明, 巨博, 李燕, 陈雪莲 2021 70 128803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin M Y, Ju B, Li Y, Chen X L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 128803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu L M, Yuan S C, Zeng H B, Song J Z 2019 Mater. Today Nano 6 100036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, et al. 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li X M, Wu Y, Zhang S L, Cai B, Gu Y, Song J Z, Zeng H B 2016 Adv. Funct. Mater. 26 2435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] De Roo J, Ibáñez M, Geiregat P, et al. 2016 ACS Nano 10 2071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhu F, Men L, Guo Y J, et al. 2015 ACS Nano 9 2948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Nedelcu G, Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, Grotevent M J, Kovalenko M V 2015 Nano Lett. 15 5635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sun S B, Yuan D, Xu Y, Wang A F, Deng Z T 2016 ACS Nano 10 3648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pan A Z, He B, Fan X Y, Liu Z K, Urban J J, Alivisatos A P, He L, Liu Y 2016 ACS Nano 10 7943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shamsi J, Dang Z Y, Bianchini P, et al. 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 7240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bekenstein Y, Koscher B A, Eaton S W, Yang P D, Alivisatos A P 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 16008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Akkerman Q A, Motti S G, Kandada A R S, et al. 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 1010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen X L, Wei M, Jiang S, Förster S 2019 Langmuir 35 12130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen X L, Wang J G, Pan R J, Roth S, Förster S 2021 J. Phys. Chem. C 125 1087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ng C K, Wang C, Jasieniak J J 2019 Langmuir 35 11609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao J Y, Cao S N, Li Z, Ma N 2018 Chem. Mater. 30 6737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sichert J A, Tong Y, Mutz N, et al. 2015 Nano Lett. 15 6521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang Y, Li X M, Sreejith S, Cao F, Wang Z, Stuparu M C, Zeng H B, Sun H D 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 10637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang H, Li Y X, Tong Y, et al. 2019 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 58 16558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Peng X G, Wickham J, Alivisatos A P 1998 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 5343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Qu L H, Yu W W, Peng X G 2004 Nano Lett. 4 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Koolyk M, Amgar D, Aharon S, Etgar L 2016 Nanoscale 8 6403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Burlakov V M, Hassan Y, Danaie M, Snaith H J, Goriely A 2020 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 6535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ng C K, Deng H, Li H C, Yin W P, Alan T, Jasieniak J J 2021 J. Mater. Chem. C 9 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Peng L C, Dutta A, Xie R G, Yang W S, Pradhan N 2018 ACS Energy Lett. 3 2014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
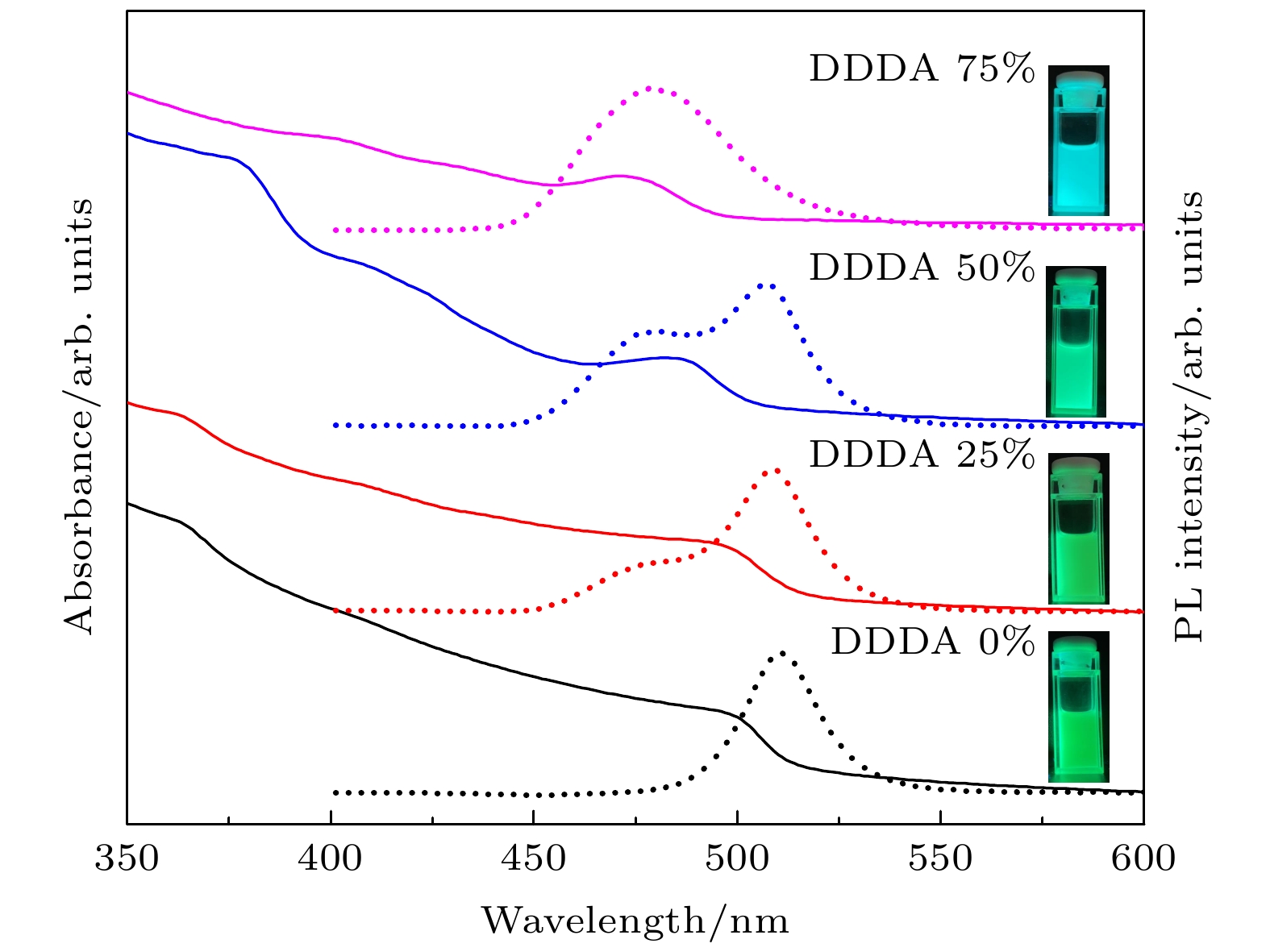
图 4 不同DDDA比例下所得CsPbBr3 PNCs的吸收光谱(实线)和荧光光谱(虚线)(插图为365 nm紫外光照射下的纳米晶溶液照片)
Fig. 4. Absorption spectra (solid curves) and fluorescence spectra (dotted curves) of CsPbBr3 PNCs synthesized with varying DDDA loadings (Inserts are the photographs of PNCs solutions under 365 nm ultraviolet light illumination)
图 6 不同DDDA比例下CsPbBr3 PNCs的PL峰位、FWHM和峰强随反应时间的变化 (a), (d), (g), (j) 峰位; (b), (e), (h), (k) FWHM; (c), (f), (i), (l) 峰强
Fig. 6. Changes in PL peak position, FWHM, peak intensity of CsPbBr3 PNCs synthesized with varying DDDA loadings as a function of reaction time: (a), (d), (g), (j) Peak position; (b), (e), (h), (k) FWHM; (c), (f), (i), (l) peak intensity.
-
[1] Shamsi J, Urban A S, Imran M, De Trizio L, Manna L 2019 Chem. Rev. 119 3296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Akkerman Q A, D’Innocenzo V, Accornero S, Scarpellini A, Petrozza A, Prato M, Manna L 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 10276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kovalenko M V, Protesescu L, Bodnarchuk M I 2017 Science 358 745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schmidt L, Pertegás A, Gonzalez-Carrero S, et al. 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Travis W, Glover E N K, Bronstein H, Scanlon D O, Palgrave R G 2016 Chem. Sci. 7 4548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shi Z F, Li S, Li Y, et al. 2018 ACS Nano 12 1462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 林月明, 巨博, 李燕, 陈雪莲 2021 70 128803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin M Y, Ju B, Li Y, Chen X L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 128803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu L M, Yuan S C, Zeng H B, Song J Z 2019 Mater. Today Nano 6 100036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, et al. 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li X M, Wu Y, Zhang S L, Cai B, Gu Y, Song J Z, Zeng H B 2016 Adv. Funct. Mater. 26 2435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] De Roo J, Ibáñez M, Geiregat P, et al. 2016 ACS Nano 10 2071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhu F, Men L, Guo Y J, et al. 2015 ACS Nano 9 2948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Nedelcu G, Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, Grotevent M J, Kovalenko M V 2015 Nano Lett. 15 5635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sun S B, Yuan D, Xu Y, Wang A F, Deng Z T 2016 ACS Nano 10 3648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pan A Z, He B, Fan X Y, Liu Z K, Urban J J, Alivisatos A P, He L, Liu Y 2016 ACS Nano 10 7943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shamsi J, Dang Z Y, Bianchini P, et al. 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 7240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bekenstein Y, Koscher B A, Eaton S W, Yang P D, Alivisatos A P 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 16008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Akkerman Q A, Motti S G, Kandada A R S, et al. 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 1010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen X L, Wei M, Jiang S, Förster S 2019 Langmuir 35 12130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen X L, Wang J G, Pan R J, Roth S, Förster S 2021 J. Phys. Chem. C 125 1087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ng C K, Wang C, Jasieniak J J 2019 Langmuir 35 11609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao J Y, Cao S N, Li Z, Ma N 2018 Chem. Mater. 30 6737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sichert J A, Tong Y, Mutz N, et al. 2015 Nano Lett. 15 6521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang Y, Li X M, Sreejith S, Cao F, Wang Z, Stuparu M C, Zeng H B, Sun H D 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 10637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang H, Li Y X, Tong Y, et al. 2019 Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 58 16558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Peng X G, Wickham J, Alivisatos A P 1998 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 5343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Qu L H, Yu W W, Peng X G 2004 Nano Lett. 4 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Koolyk M, Amgar D, Aharon S, Etgar L 2016 Nanoscale 8 6403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Burlakov V M, Hassan Y, Danaie M, Snaith H J, Goriely A 2020 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 6535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ng C K, Deng H, Li H C, Yin W P, Alan T, Jasieniak J J 2021 J. Mater. Chem. C 9 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Peng L C, Dutta A, Xie R G, Yang W S, Pradhan N 2018 ACS Energy Lett. 3 2014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 14446
- PDF下载量: 313
- 被引次数: 0
















 下载:
下载: