-
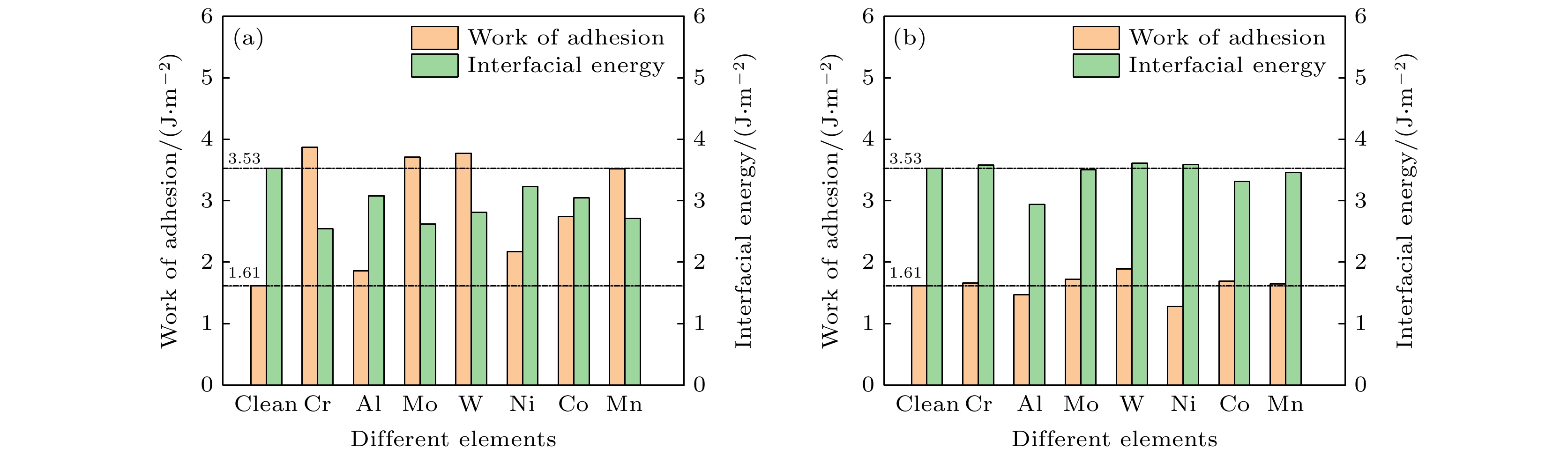
超高强度马氏体钢的力学性能强烈依赖于逆变奥氏体的形状、尺寸及含量. 通常, 提高逆变奥氏体含量, 有助于改善超高强度钢的塑韧性. 对含Cu马氏体淬火钢时效处理时, Cu粒子会在马氏体组织边界沉淀, 并作为质点促进逆变奥氏体形核. 为了探索不同合金元素对逆变奥氏体在Cu沉淀上异质形核的影响, 本文利用第一性原理方法研究了合金元素X (X = Cr, Al, Mo, W, Ni, Co, Mn)对Cu/γ-Fe界面性质的影响, 并分析了合金原子替换界面处Cu和Fe原子前后界面的黏附功、界面能和电子结构. 研究结果表明, 合金元素Cr, Mo, W, Mn替换Cu/γ-Fe界面处Cu原子时, Cu/γ-Fe界面处产生强烈的X—Fe共价键, 黏附功增大且界面能减小, 显著提高界面稳定性, 促进γ-Fe在Cu沉淀上异质形核. 而替换界面处Fe原子时, 界面稳定性变化很小, 掺杂原子与相邻的其他原子成键较弱.The mechanical properties of ultra-high strength martensite steel strongly depend on the shape, size and content of the reversed austenite. In general, the plasticity and toughness of the materials can be improved effectively by increasing the content of the reversed austenite. After aging treatment of Cu-bearing as-quenched steel with martensitic microstructure, Cu particles precipitate at the boundary of martensitic structure and act as heterogeneous nucleation sites to promote the nucleation of reversed austenite. In order to explore the effects of different alloying elements on heterogeneous nucleation of reversed austenite on Cu particles, the effects of X (X = Cr, Al, Mo, W, Ni, Co, Mn) on the interfacial properties of Cu/γ-Fe are studied via first-principles method. The adhesion work, interfacial energy and electronic structure of the interfaces before and after the replacement of Cu and Fe atoms at Cu/γ-Fe boundaries are calculated. The results show that when the alloying elements replace Cu atoms at the Cu/γ-Fe interface, strong X—Fe covalent bond forms at the Cu/γ-Fe interface, the adhesion work increases and the interfacial energy decreases, and thus improve the heterogeneous nucleation capability of reverted γ-Fe on Cu particles. When Fe atoms at the interface are replaced, the stability of the interface changes little, and the bonding between the doped atoms and the neighboring atoms is weak.
-
Keywords:
- first-principles /
- reversed austenite /
- heterogeneous nucleation /
- adhesion work
[1] Garrison W M 1990 JOM 42 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Skubisz P, Sinczak J 2018 Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 90 713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jia L J, Hui H B, Yu Q H, Song Y 2014 Adv. Mater. Res. 859 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mou B, Zhou W, Qiao Q, Feng P, Wu C 2021 Eng. Struct. 228 111483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Y, Sun J, Jiang T, Jiang T, Sun Y, Guo S, Liu Y 2018 Acta Mater. 158 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao L, Chen X, Wu T, Zhai Q 2020 Materials. 13 4340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhou J H, Shen Y F, Hong Y Y, Xue W Y, Misra R D K 2020 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 769 138471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Malakondaiah G, Srinivas M, Murthy J M, Rao P R 1994 Bull. Mater. Sci. 17 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ayer R, Machmeier P M 1993 Metall. Trans. A 24 1943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Viswanathan U K, Dey G K, Sethumadhavan V 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 398 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tomohiko H, Tomohiro K, Koh-ichi S 2010 Bull. Tsuy. Nat. Coll. Technol. 52 9
[12] He Y, Yang K, Qu W, Kong F, Su G 2002 Mater. Lett. 56 763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Machmeier P, Matuszewski T, Jones R, Ayer R 1997 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 6 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gruber M, Ressel G, F Méndez Martín, Ploberger S, Marsoner S, Ebner R 2016 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Govindaraj V, Hodgson P, Singh R P, Beladi H 2021 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 808 140909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang D, Yan J, Zuo X 2019 Mater. Charact. 155 109786
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B:Condens. Matter. 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bitter F, Kaufmann A R 1939 Phys. Rev. 56 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li Y, Gao Y, Xiao B, Min T, Fan Z, Ma S, Yi D 2011 Comput. Mater. Sci. 50 939
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu P, Han X, Sun D, Sun D, Chen Z, Wang Q 2018 Intermetallics 96 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lü Z, Xiao S, Xiao Z, Xiao S, Xiao Z, Qian L, Wang W, Zhou Y, Fu W 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 718 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang G, Liu Y, Hang Z, Xi N, Fu H, Chen H 2019 J. Rare Earths 37 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun M, Tang W, Ren Q, Wang S, Yu J, Du Y 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 356 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang J, Huang J, Fan D, Chen S, Zhao X 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 384 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhao X, Zhuo Y, Liu S, Zou Y, Zhao C, Wang C, Yang Q 2016 Surf. Coat. Technol. 305 200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhao X, Yuan X, Liu S, Zhao C, Wang C, Zhou Y, Yang Q 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 695 1753
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Christensen M, Dudiy S, Wahnstrm G 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 045408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Han Y F, Dai Y B, Wang J, Shu D, Sun B D 2011 Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 7831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lu S, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2010 Phys. Rev. B. 82 195103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yang J, Zhang P, Zhou Y, Guo J, Ren X, Yang Y, Yang Q 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 556 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Segall M D, Shah R, Pickard C J, Payne M C 1996 Phys. Rev. B:Condens. Matter. 54 16317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
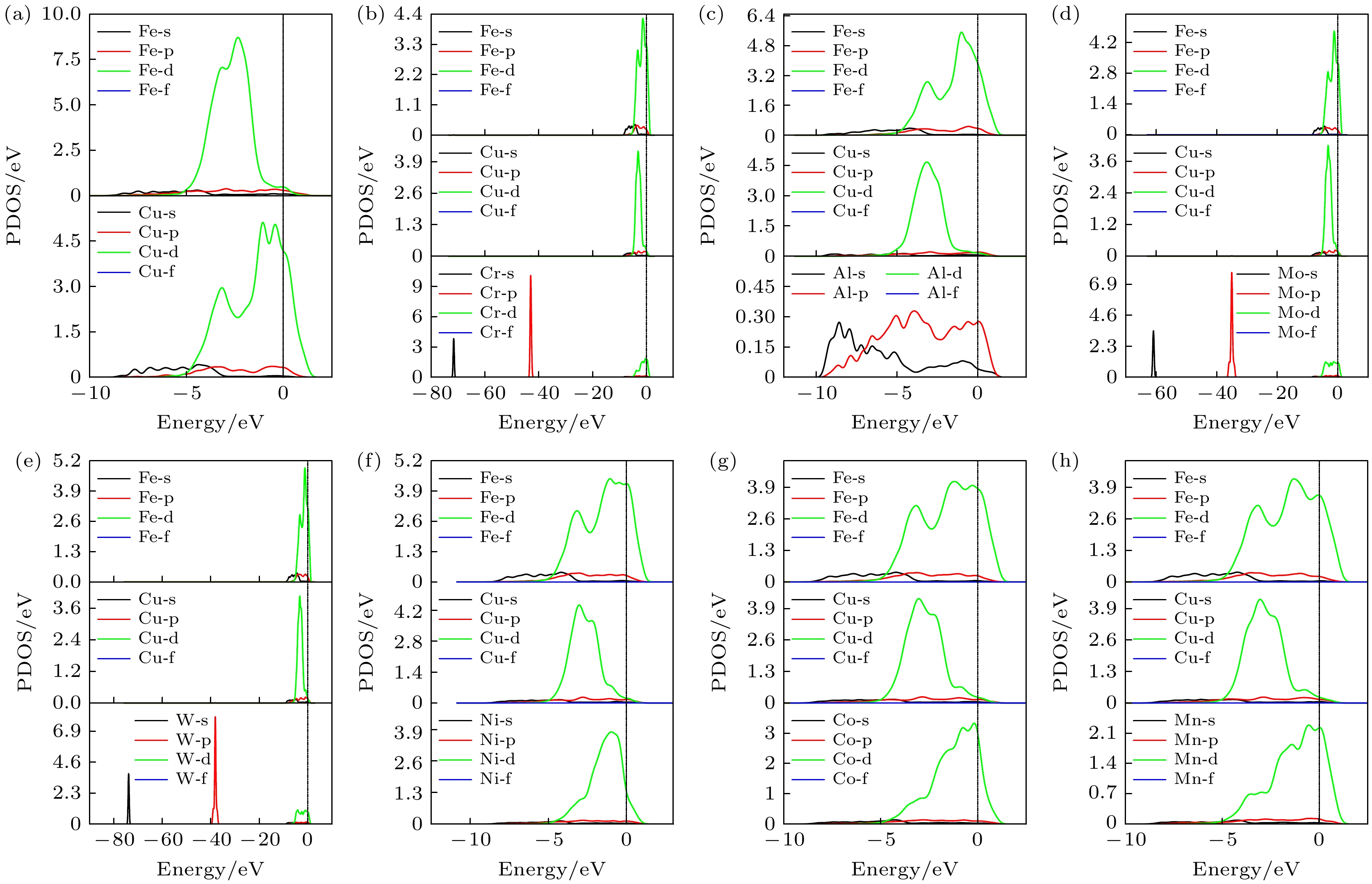
图 4 (a) 掺杂前界面的分波态密度; (b)—(h) Cr, Al, Mo, W, Ni, Co和Mn替换Cu原子后界面的分波态密度
Fig. 4. (a) Partial density of states on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) before doping; (b)–(h) partial density of states on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) after replacing Cu by Cr, Al, Mo, W, Ni, Co, and Mn, respectively.
图 5 (a)掺杂前界面的分波态密度; (b)—(h) Cr, Al, Mo, W, Ni, Co和Mn替换Fe原子后界面的分波态密度
Fig. 5. (a) Partial density of states on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) before doping; (b)–(h) partial density of states on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) after replacing Fe by by Cr, Al, Mo, W, Ni, Co, and Mn, respectively.
表 1 Cu(010)和γ-Fe(010)表面能收敛趋势
Table 1. Convergence of Cu(010) and γ-Fe(010) surface energy.
Number of pils N $ {E}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{f}}^{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{u}} $/(J·m–2) $ {E}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{f}}^{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}} $/(J·m–2) 5 1.41 3.79 7 1.44 3.75 9 1.43 3.76 11 1.44 3.75 表 2 合金元素X替换Cu前后界面布居分析
Table 2. Mulliken population analysis on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) before and after replacement of Cu by alloying element X
Atom Total electron/e Transfer charge/e Atom Total electron/e Transfer charge/e Cu 11.14 –0.14 Fe 7.90 0.10 Cr 13.76 0.24 Fe 7.97 0.03 Al 2.89 0.11 Fe 8.04 –0.04 Mo 13.73 0.27 Fe 8.03 –0.03 W 8.01 –0.01 Fe 13.92 0.08 Ni 9.83 0.17 Fe 7.98 0.02 Co 8.74 0.26 Fe 7.96 0.04 Mn 6.55 0.45 Fe 8.00 0 表 3 合金元素X替换Cu和Fe前后界面原子键长
Table 3. Bond length on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) before and after replacement of Cu or Fe by alloying element X
键 键长/Å 键 键长/Å Cu—Fe 2.42 Cu—Fe 2.42 Cr—Fe 2.06 Cr—Cu 2.48 Al—Fe 2.39 Al—Cu 2.53 Mo—Fe 2.23 Mo—Cu 2.57 W—Fe 2.28 W—Cu 2.57 Ni—Fe 2.31 Ni—Cu 2.48 Co—Fe 2.20 Co—Cu 2.41 Mn—Fe 2.13 Mn—Cu 2.47 表 4 合金元素X替换Fe前后界面布居分析
Table 4. Mulliken population analysis on the interface for Cu(010)/γ-Fe(010) before and after replacement of Fe by alloying element X atom.
Atom Total electron/e Transfer charge/e Atom Total electron/e Transfer charge/e Fe 7.90 0.10 Cu 11.14 –0.14 Cr 13.86 0.14 Cu 11.10 –0.10 Al 3.03 –0.03 Cu 11.11 –0.11 Mo 13.90 0.10 Cu 11.20 –0.20 W 14.09 –0.09 Cu 11.19 –0.19 Ni 11.04 –0.04 Cu 11.10 –0.10 Co 8.94 0.06 Cu 11.12 –0.12 Mn 6.67 0.33 Cu 11.18 –0.18 -
[1] Garrison W M 1990 JOM 42 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Skubisz P, Sinczak J 2018 Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 90 713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jia L J, Hui H B, Yu Q H, Song Y 2014 Adv. Mater. Res. 859 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mou B, Zhou W, Qiao Q, Feng P, Wu C 2021 Eng. Struct. 228 111483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Y, Sun J, Jiang T, Jiang T, Sun Y, Guo S, Liu Y 2018 Acta Mater. 158 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao L, Chen X, Wu T, Zhai Q 2020 Materials. 13 4340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhou J H, Shen Y F, Hong Y Y, Xue W Y, Misra R D K 2020 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 769 138471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Malakondaiah G, Srinivas M, Murthy J M, Rao P R 1994 Bull. Mater. Sci. 17 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ayer R, Machmeier P M 1993 Metall. Trans. A 24 1943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Viswanathan U K, Dey G K, Sethumadhavan V 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 398 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tomohiko H, Tomohiro K, Koh-ichi S 2010 Bull. Tsuy. Nat. Coll. Technol. 52 9
[12] He Y, Yang K, Qu W, Kong F, Su G 2002 Mater. Lett. 56 763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Machmeier P, Matuszewski T, Jones R, Ayer R 1997 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 6 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gruber M, Ressel G, F Méndez Martín, Ploberger S, Marsoner S, Ebner R 2016 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Govindaraj V, Hodgson P, Singh R P, Beladi H 2021 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 808 140909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang D, Yan J, Zuo X 2019 Mater. Charact. 155 109786
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B:Condens. Matter. 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bitter F, Kaufmann A R 1939 Phys. Rev. 56 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li Y, Gao Y, Xiao B, Min T, Fan Z, Ma S, Yi D 2011 Comput. Mater. Sci. 50 939
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu P, Han X, Sun D, Sun D, Chen Z, Wang Q 2018 Intermetallics 96 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lü Z, Xiao S, Xiao Z, Xiao S, Xiao Z, Qian L, Wang W, Zhou Y, Fu W 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 718 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang G, Liu Y, Hang Z, Xi N, Fu H, Chen H 2019 J. Rare Earths 37 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun M, Tang W, Ren Q, Wang S, Yu J, Du Y 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 356 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang J, Huang J, Fan D, Chen S, Zhao X 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 384 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhao X, Zhuo Y, Liu S, Zou Y, Zhao C, Wang C, Yang Q 2016 Surf. Coat. Technol. 305 200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhao X, Yuan X, Liu S, Zhao C, Wang C, Zhou Y, Yang Q 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 695 1753
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Christensen M, Dudiy S, Wahnstrm G 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 045408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Han Y F, Dai Y B, Wang J, Shu D, Sun B D 2011 Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 7831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lu S, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2010 Phys. Rev. B. 82 195103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yang J, Zhang P, Zhou Y, Guo J, Ren X, Yang Y, Yang Q 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 556 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Segall M D, Shah R, Pickard C J, Payne M C 1996 Phys. Rev. B:Condens. Matter. 54 16317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7663
- PDF下载量: 99
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: