-
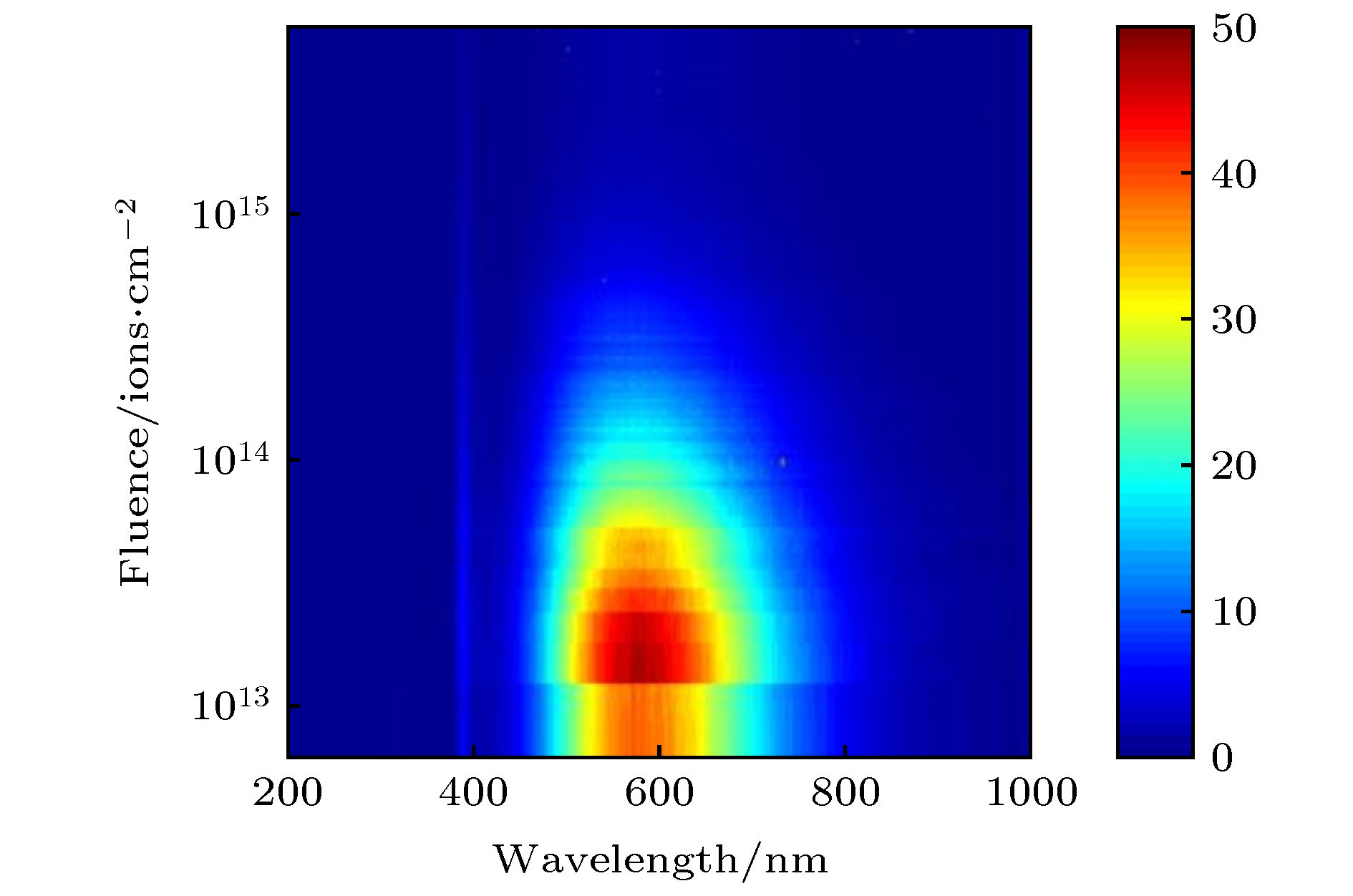
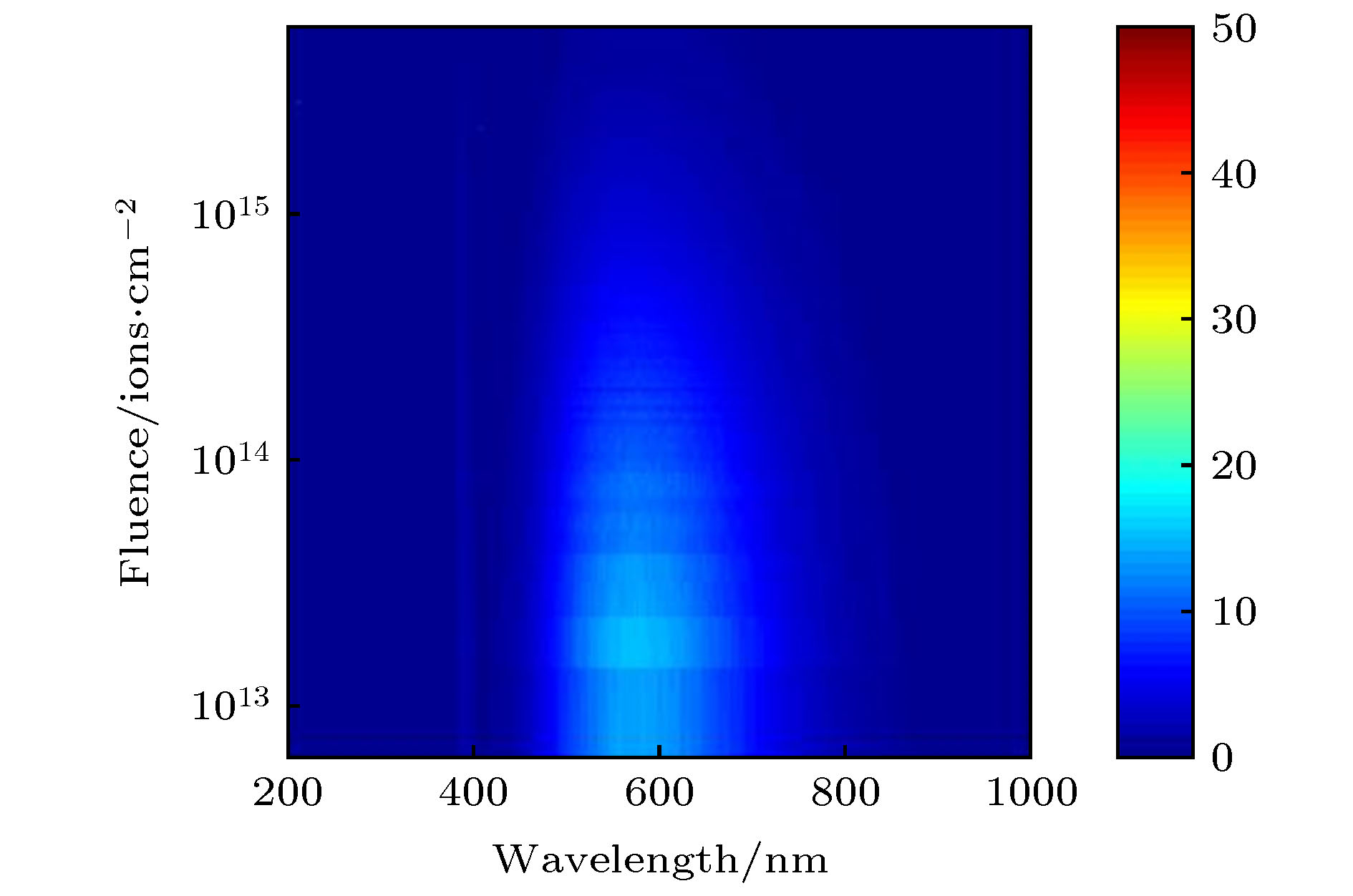
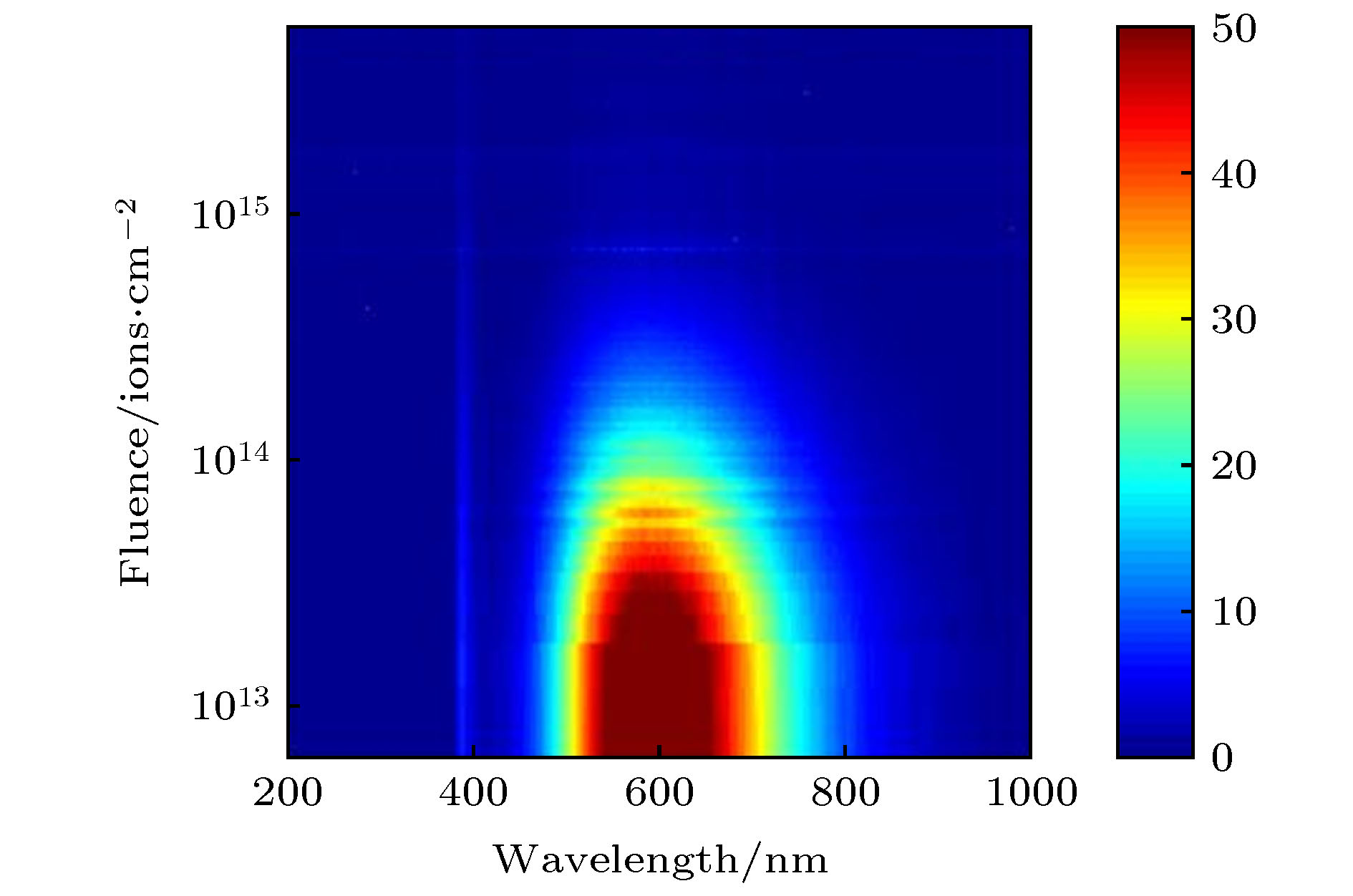
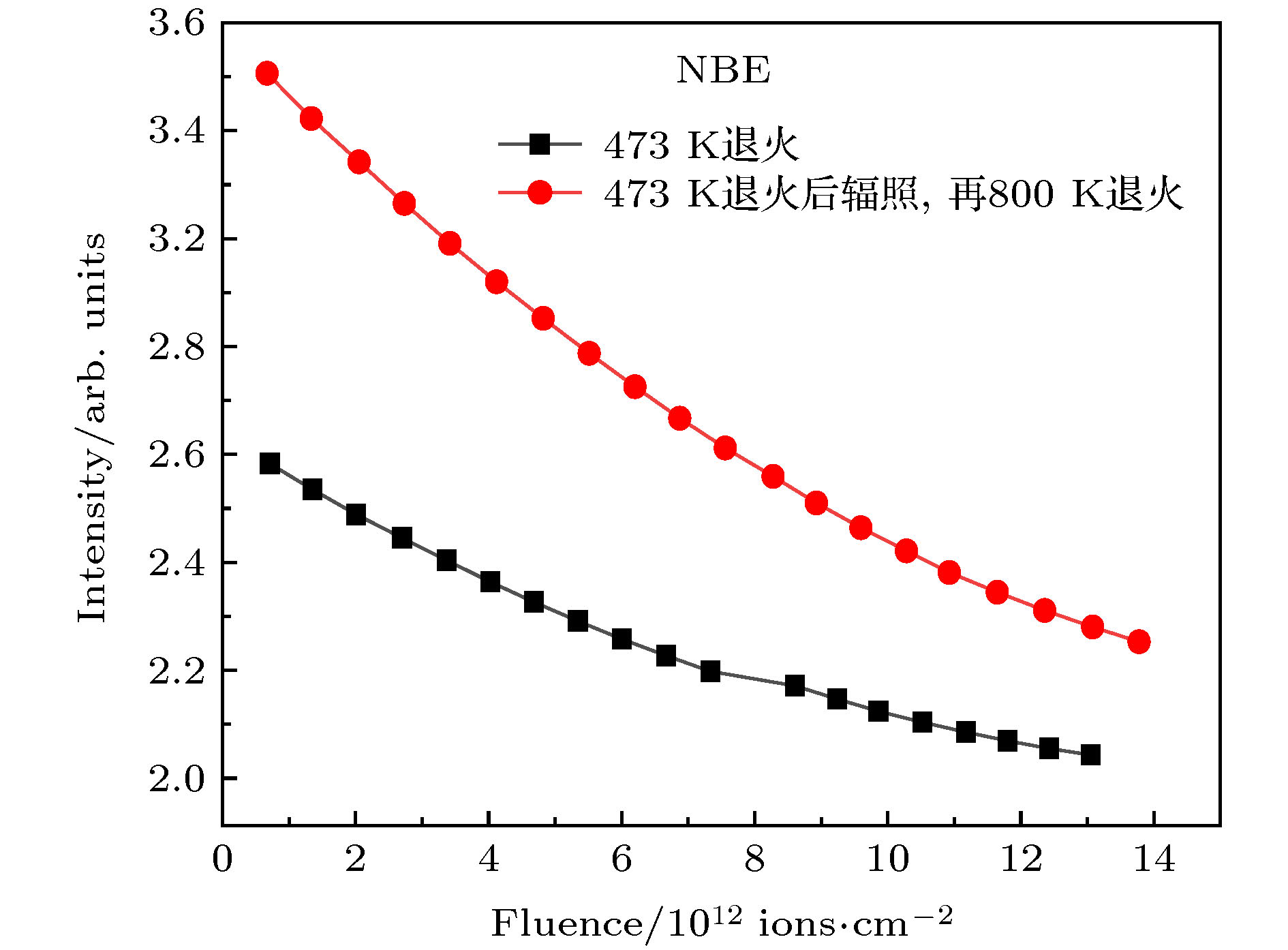
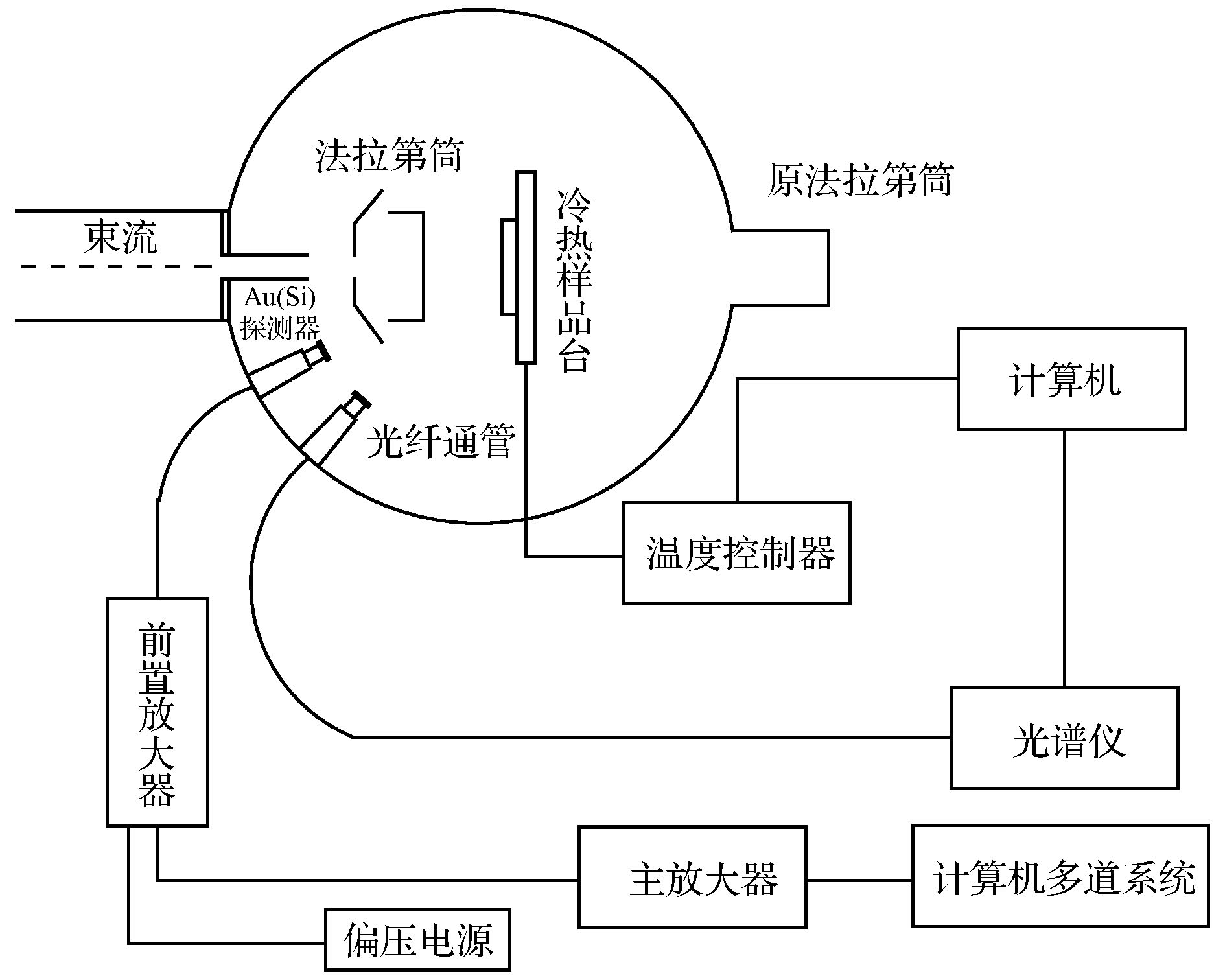
在北京师范大学GIC4117 2 × 1.7 MV串列加速器上, 利用离子激发发光(ions beam induced luminescence, IBIL)技术研究了2 MeV H+注入ZnO的缺陷变化及473和800 K退火处理对缺陷的恢复作用. 实验表明, 在2 MeV H+的辐照下, 晶体内部产生的点缺陷会快速移动、聚集成团簇, 从而抑制发光. 473 K退火后的受辐照ZnO晶体内仍存在着大量的缺陷和团簇, 而这些缺陷和团簇作为非辐射中心抑制着ZnO晶体的发光. 800 K的退火处理可以显著地分解辐照过程中形成的团簇, 也可以帮助点缺陷回到晶格位置, 从而减少晶体内部的不平衡缺陷, 提高晶体的结晶度, 使退火后的受辐照ZnO样品IBIL光强大幅度增强.
The optical and electrical properties of ZnO related on the type and the concentration of defects in ZnO crystal. Ion implantation and annealing can change the type and the concentration of defects in ZnO. To understand the variation of defects in ZnO during ion implantation and after different temperature annealing, in situ luminescence measurements of ZnO crystal samples were carried out by ion beam induced luminescence (IBIL) during ion implantation of 2 MeV H+ and then after annealing at 473 K and 800 K in vacuum on the GIC4117 tandem accelerator in Beijing Normal University. IBIL spectra of ZnO showtwo emission peaks: UV emission, which is called near band emission (NBE), and visible emission, which is called deep band emission (DBE).The high-intensity of DBE and weak NBE of IBIL spectra of ZnOmay be due to the NBE is intrinsic to ZnO samples and therefore is just visibly observed from samples that are virtually defect-free. With the ion implantation, the destruction of the crystal structure and the arising of a mass of defects, inducing the weak intensity NBE and intense DBE.In addition, the overall IBIL spectra of ZnOreveal decrease intensity with the ion fluence,which indicates that the concentration of luminescence centersdecreases duringion implantation.With the H+ fluence, the concentration of the point defects increases. The point defects migrate and subsequently agglomerate into larger defect clusters. These defect clusters serve as traps for catching electrons and holes, which result in the quenching of luminescence centres. Annealing can help todecompose the defect clusters and repair the defects of crystal. However, amounts of defects and clusters still remain in the irradiated sample annealed at 473 K in vacuum, which acted as nonradiative center and suppress the luminescence induced weak intensity of IBIL. Annealing the sample at 800 K in vacuum may facilitate the decomposition of defect clusters during ion irradiation to point defects and the point defect return to the lattice position that can reduce the nonequilibrium defects inside the crystal and improve the crystallinity of the crystal, which increase the intensity of its IBIL. -
Keywords:
- ions beam induced luminescence /
- annealing /
- ZnO
[1] Huddle J R, Grant P G, Ludington A R, Foster R L 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 261 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rodrigues J, Miranda S M C, Peres M, et al. 2013 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 306 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang X M, Lu M Y, Zhang Y, et al. 2009 Adv. Mater. 21 2767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li L, Yang H, ZhaoH, Yu J, Ma J, An L 2010 Appl. Phys. A-Mater. Sci. Process. 98 635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Epie E N, Chu W K 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 371 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 邢光建, 李钰梅, 江伟, 韩彬, 王怡, 武光明 2009 真空 46 41
Xing G J, Li Y M, Jiang W, Han B, Wang Y, Wu G M 2009 Vacuum 46 41
[7] Zhou Z, Kato K, Komaki T, Yoshino M, Morinaga M 2004 Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 29 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 潘峰, 丁斌峰, 法涛, 成枫锋, 周生强, 姚淑德 2011 60 108501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan F, Ding B F, Fa T, Cheng F F, Zhou S Q, Yao S D 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 108501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 李重阳, 邱诚, 柳丹, 叶霞, 王栋, 陈志权 2013 武汉大学学报(理学版) 04 96
Li C Y, Qu C, Liu D, Ye X, Wang D, Chen Z Q 2013 Journal of Wuhan University (Natural Science Edition) 04 96
[10] 徐自强, 邓宏, 谢娟, 李燕, 陈航, 祖小涛, 薛书文 2006 强激光与粒子束 18 169
Xu Z Q, Deng H, Xie J, Li Y, Chen H, Zu X T, Xue S W 2006 High Power Laser Part. Beams HPLPB 18 169
[11] 郭德双, 陈子男, 王登魁, 唐吉龙, 方铉, 房丹, 林逢源, 王新伟, 魏志鹏 2019 中国激光 46 0403002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo D S, Chen Z N, Wang D K, Tang J L, Fang X, Fang D, Lin F Y, Wang X W, Wei Z P 2019 Chin. J. Lasers 46 0403002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 朱影 2018 硕士学位论文 (杭州: 浙江大学)
Zhu Y 2018 M. S. Dissertation (Hangzhou: Zhejiang University) (in Chinese)
[13] 仇猛淋 2017 中国核学会 中国威海 2017 10月16日—18日 第6页
Qiu M L 2017 Proceedings of Chinese Nuclear Society Weihai, China, October 16–18, 2017 p6 (in Chinese)
[14] 仇猛淋, 王广甫, 褚莹洁, 郑力, 胥密, 殷鹏 2017 66 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiu M L, Wang GF, Chu YJ, Zheng L, Xu M, Yin P 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cui M, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Finch A, Townsend P D 2018 Luminescence 33 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Validzic I, Comor M, Ahrenkiel S P, Comor M I 2015 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46 3679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Trinh T A, Hong I S, Lee H R, Cho Y S 2009 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 267 3535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen Z Q, Sekiguchi T, Yuan X L, Maekawa M, KawasusoA 2004 J. Phys.Condens. Matter 16 S293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu Y, Xue X, Wu Y 2014 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 101 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gruzintsev A N, Yakimov E E 2005 Inorg. Mater. 41 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Huddle J R, Grant P G, Ludington A R, Foster R L 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 261 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rodrigues J, Miranda S M C, Peres M, et al. 2013 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 306 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang X M, Lu M Y, Zhang Y, et al. 2009 Adv. Mater. 21 2767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li L, Yang H, ZhaoH, Yu J, Ma J, An L 2010 Appl. Phys. A-Mater. Sci. Process. 98 635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Epie E N, Chu W K 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 371 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 邢光建, 李钰梅, 江伟, 韩彬, 王怡, 武光明 2009 真空 46 41
Xing G J, Li Y M, Jiang W, Han B, Wang Y, Wu G M 2009 Vacuum 46 41
[7] Zhou Z, Kato K, Komaki T, Yoshino M, Morinaga M 2004 Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 29 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 潘峰, 丁斌峰, 法涛, 成枫锋, 周生强, 姚淑德 2011 60 108501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan F, Ding B F, Fa T, Cheng F F, Zhou S Q, Yao S D 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 108501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 李重阳, 邱诚, 柳丹, 叶霞, 王栋, 陈志权 2013 武汉大学学报(理学版) 04 96
Li C Y, Qu C, Liu D, Ye X, Wang D, Chen Z Q 2013 Journal of Wuhan University (Natural Science Edition) 04 96
[10] 徐自强, 邓宏, 谢娟, 李燕, 陈航, 祖小涛, 薛书文 2006 强激光与粒子束 18 169
Xu Z Q, Deng H, Xie J, Li Y, Chen H, Zu X T, Xue S W 2006 High Power Laser Part. Beams HPLPB 18 169
[11] 郭德双, 陈子男, 王登魁, 唐吉龙, 方铉, 房丹, 林逢源, 王新伟, 魏志鹏 2019 中国激光 46 0403002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo D S, Chen Z N, Wang D K, Tang J L, Fang X, Fang D, Lin F Y, Wang X W, Wei Z P 2019 Chin. J. Lasers 46 0403002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 朱影 2018 硕士学位论文 (杭州: 浙江大学)
Zhu Y 2018 M. S. Dissertation (Hangzhou: Zhejiang University) (in Chinese)
[13] 仇猛淋 2017 中国核学会 中国威海 2017 10月16日—18日 第6页
Qiu M L 2017 Proceedings of Chinese Nuclear Society Weihai, China, October 16–18, 2017 p6 (in Chinese)
[14] 仇猛淋, 王广甫, 褚莹洁, 郑力, 胥密, 殷鹏 2017 66 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiu M L, Wang GF, Chu YJ, Zheng L, Xu M, Yin P 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cui M, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Finch A, Townsend P D 2018 Luminescence 33 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Validzic I, Comor M, Ahrenkiel S P, Comor M I 2015 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46 3679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Trinh T A, Hong I S, Lee H R, Cho Y S 2009 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 267 3535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen Z Q, Sekiguchi T, Yuan X L, Maekawa M, KawasusoA 2004 J. Phys.Condens. Matter 16 S293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu Y, Xue X, Wu Y 2014 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 101 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gruzintsev A N, Yakimov E E 2005 Inorg. Mater. 41 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9522
- PDF下载量: 138
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: