-
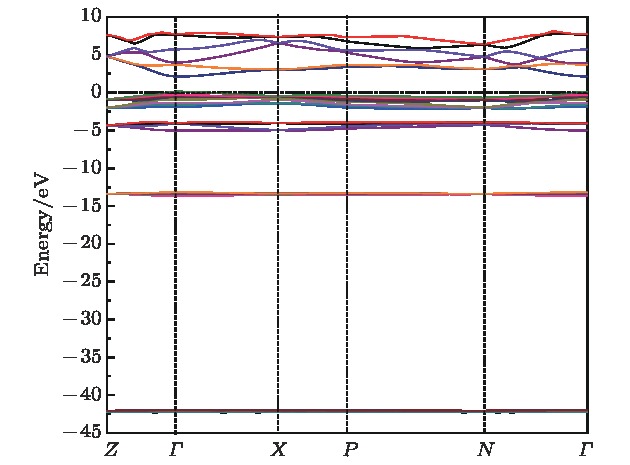
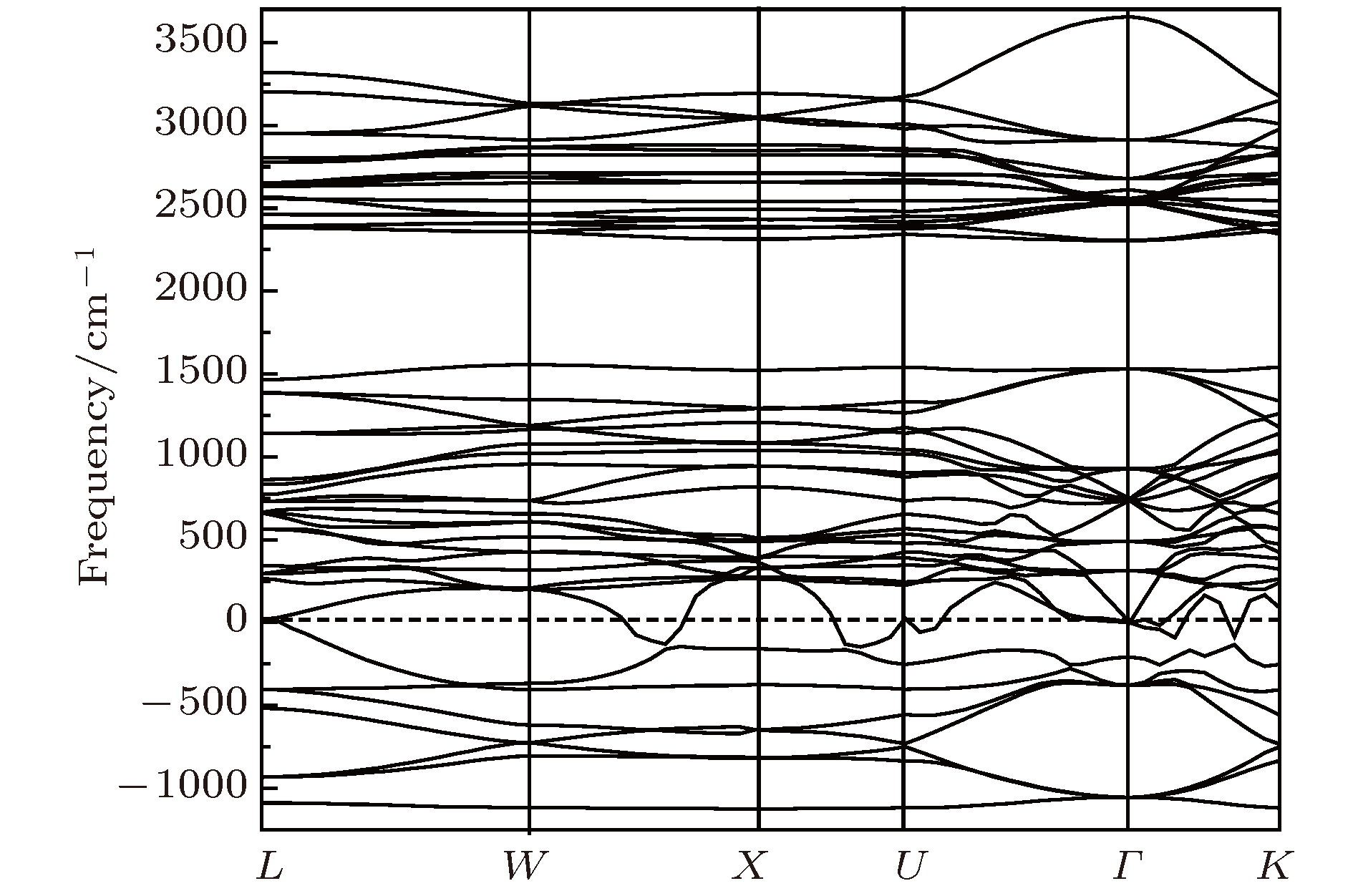
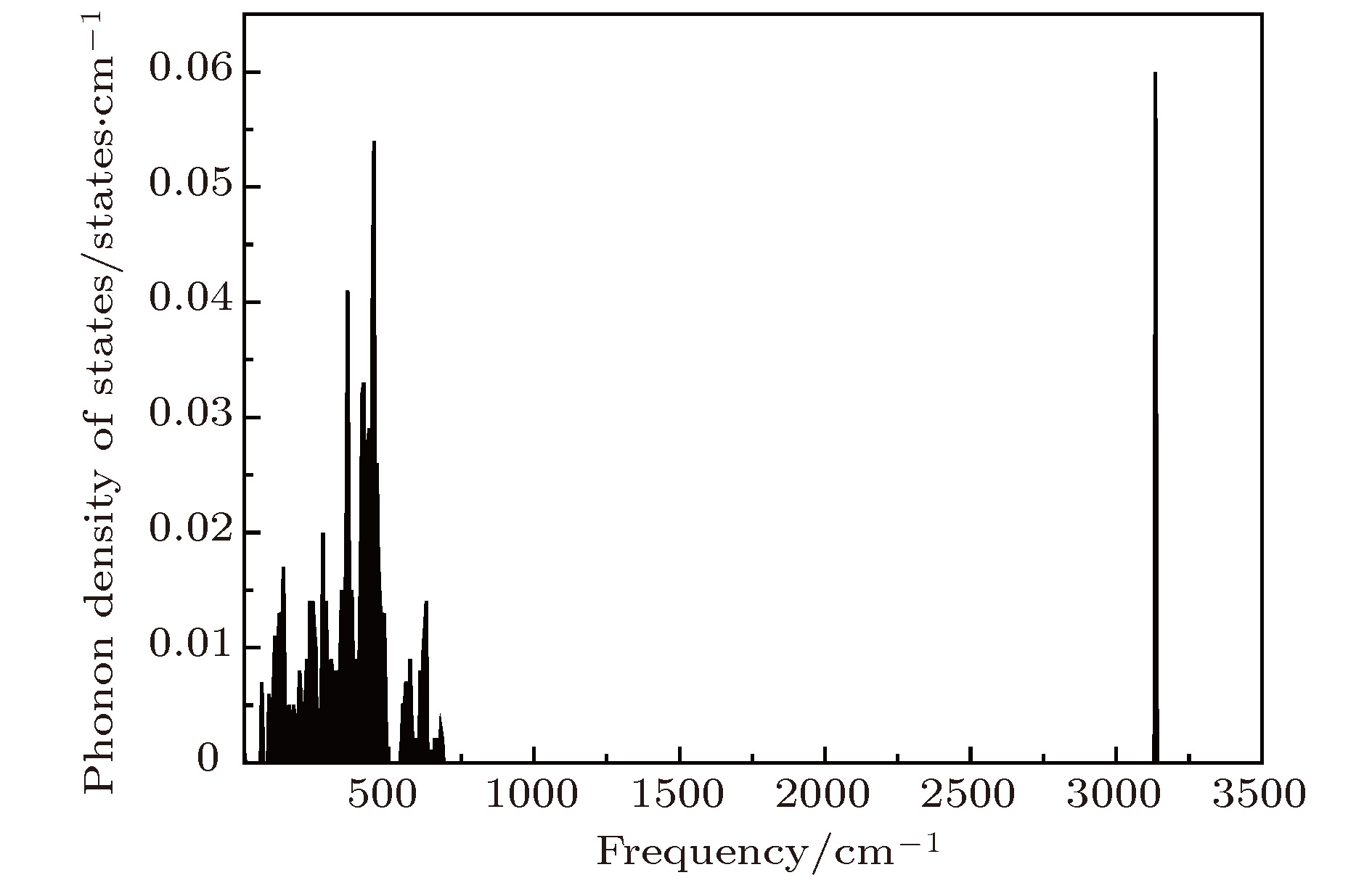
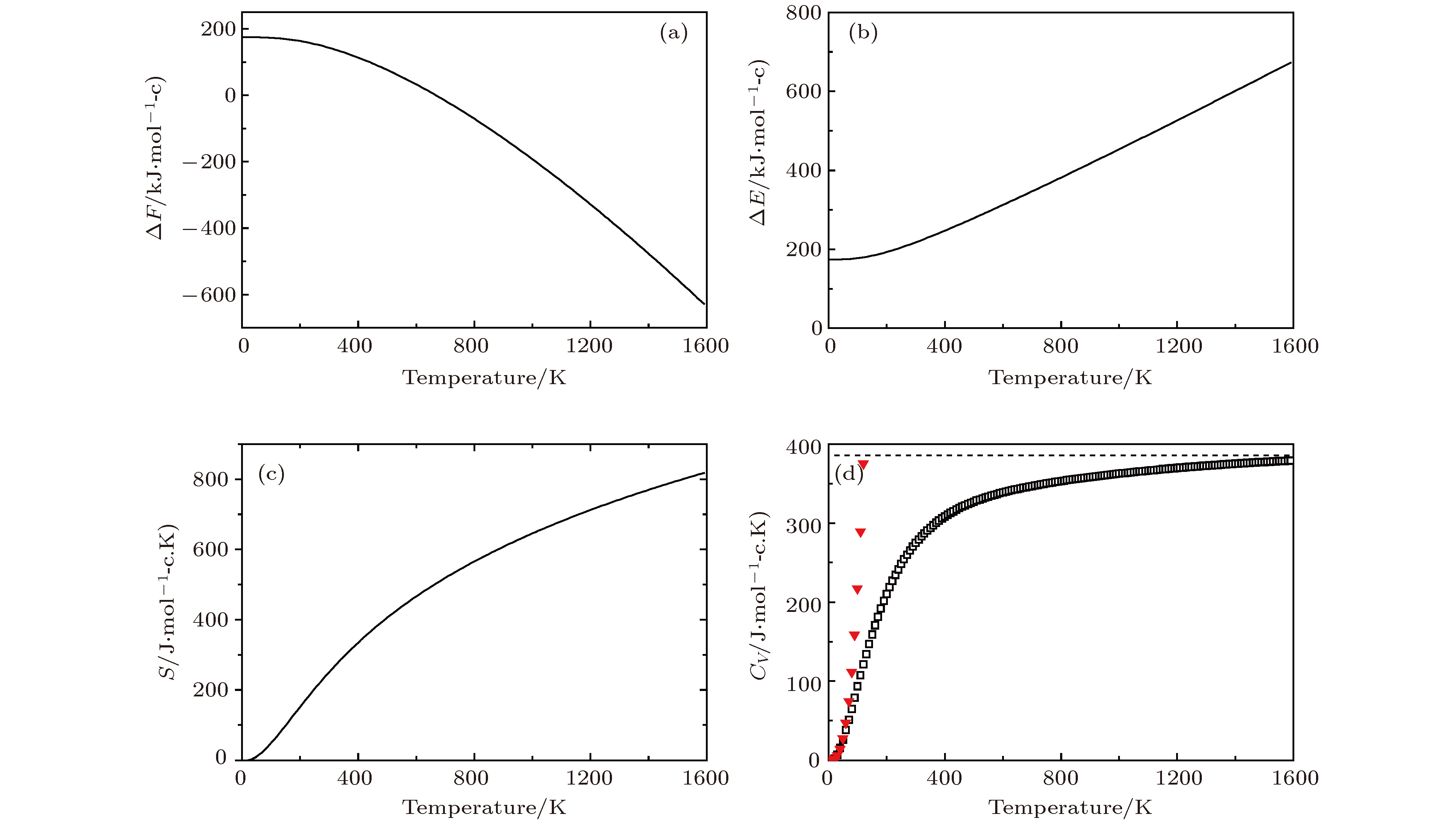
采用第一性原理的赝势平面波方法系统地研究了Li2NH的电子结构、晶格动力学和热力学性质. 计算得到的晶格常数与先前的理论和实验结果符合得很好. 运用线性响应理论计算了整个布里渊区高对称方向上的声子色散曲线和相应的声子态密度, 发现Li2NH(Pnma)声子色散曲线没有虚频, 动力学性能相对最稳定, 计算结果和先前实验及理论数据符合得很好. 最后, 利用得到的声子态密度进一步预测了Li2NH的热力学性质, 包括晶格振动对Helmholtz自由能、内能、熵和热容的贡献, 计算结果在一定程度上可为Li-N-H储氢体系的应用提供理论指导.
One of the key issues for scale applications of hydrogen energy is the availability of safe, efficient and ecnomicical hydrogen storage technologies. In the past few years, light metal hydrides have attracted considerable attention due to their high hydrogen capacity. With a hydrogen capacity up to ~6.5 wt%, Li2NH is regarded as one of the most promising hydrogen storage materials. Although the hydrogen physical and thermodynamic properties of Li2NH have been studied, the electronic structure, phonon vibration mode and thermodynamic properties of Li2NH have not yet been resolved. In this paper, by using the first principles based on the density functional theory (DFT), we investigate the electronic structure, lattice dynamical and thermodynamic properties of Li2NH in detail. Firstly, the structure of Li2NH is optimized and the lattice parameters and total energy of the crystals are calculated. As shown by the calculation results, the lattice parameters are in good agreement with previous theoretical and experimental results. Our lowest-energy structure of Li2NH has orthorhombic Pnma symmetry at T=0 K for all of the proposed structures. Secondly, the electronic band-structure studies reveal that Li2NH has a small band gap of about 2.0 eV. The analysis of total and partial density of states of Li2NH show that the bonding between the N and H has a covalent character. Thirdly, the lattice dynamical properties of Li2NH are investgated at the corresponding equilibrium states. These results show that only the phonon dispersion curves of Li2NH (Pnma) without negative frequencies are calculated along the high-symmetry points. The optical modes of phonon frequencies at Γ point are assigned as Raman and Infrared-active modes. Based on the calculated phonon density of states, the thermodynamic properties are computed, such as the Helmholtz free energy, internal energy, entropy and the constant-volume specific heat versus temperature. The calculation results may explore the applications in areas of hydrogen storage for Li-N-H, which is of great importance forusing hydrogen in the future. [1] Chen P, Xiong Z, Luo J, Lin J, Tan K L 2002 Nature 420 302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ohoyama K, Nakamori Y, Orimo S, Yamada K 2005 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 74 483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Noritake T, Nozaki H, Aoki M, Towata S, Kitahara G, Nakamori Y, Orimo S 2005 J. Alloys Compd. 393 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Herbst J F, Hector Jr L G 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 125120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Balogh M P, Jones C Y, Herbst J F, Hector Jr. L G, Kundrat M 2006 J. Alloys Compd. 420 326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mueller T, Ceder G 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 134104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kojima Y, Kawai Y 2005 J. Alloys Compd. 395 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Magyari-Köpe B, Ozoliņš V, Wolverton C 2006 Phys. Rev. B 73 220101(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Song Y, Guo Z X 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 195120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hector Jr L G, Herbst J F 2008 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20 064229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang J, Lamsal J, Cai Q, Yelon W B, James W J 2008 MRS Proceedings 1098 1098 1098−HH03-06
[12] Miceli G, Cucinotta C, Bernasconi M, Parrinello M 2010 J. Phys. Chem. C 114 15174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Miceli G, Ceriotti M, Angioletti-Uberti S, Bernasconi M, Parrinello M 2011 J. Phys. Chem. C 115 7076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wolverton C, Siegel J D, Akbarazadeh R A, Ozolis V 2008 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20 064228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈玉红, 吕晓霞, 杜瑞, 董肖, 张材荣, 康龙, 罗永春 2013 稀有金属材料与工程 4 2
Chen Y H, Lv X X, Du R, Dong X, Zhang C R, Kang L, Luo Y C 2013 Rare Metal Materials and Engineering 4 2
[16] Rajeswarapalanichamy R, Santhosh M, Sudhapriyanga G, Kanagaprabha S, Iyakutti K 2015 Acta Metall. Sinica 28 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Crivello J C, Gupta M, Černý R, Latroche M, Chandra D 2010 Phys. Rev. B 81 104113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Q, ChenY G, Zheng X, Niu G, Wu C L, Tao M D T 2009 Physica B 404 3431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] The ABINIT code is a common project of the Université Catholique de Louvain, and other contributors (URL http://www.abinit.org)
[20] Troullier N, Martins J L 1991 Phys. Rev. B 43 1993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Baroni S, Giannozzi P, Testa A 1987 Phys. Rev. Lett. 58 1861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Baroni S, de Gironcoli S, Dal Corso A, Giannozzi P 2001 Rev. Mod. Phys. 73 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lee C, Gonze X 1995 Phys. Rev. B 51 8610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li W 2011 Ph. D. Dissertation (Zhejiang: Zhejiang University)
[26] Aulbur W G, Jonsson L, Wilkins J W 2000 Solid States Phys. 54 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Stampfl C, Van de Walle C G 1999 Phys. Rev. B 5 9
[28] Gupta M, Gupta R P 2007 J. Alloys Compd. 319 446
[29] Yao J H 2007 Ph. D. Dissertation (London: University of London) 0-239
[30] 陈玉红2008 博士学位论文(兰州: 兰州理工大学)
Chen Y H 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation(Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology)(in Chinese)
[31] Born M, Huang K 1954 Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices (Oxford:Oxford University Press) p121
[32] Maradudin A A, Montroll E W, Weiss C H, Ipatova I P 1971 Theory of Lattice Dynamics in the Harmonic Approximation (2nd Ed.) (New York: Academic Press)
-
图 8 Li2NH的热力学性质 (a)晶格振动对自由能的贡献ΔF; (b)内能ΔE随温度的变化; (c)熵S随温度的变化; (d)热容Cv随温度的变化 (▼表示Debye的T3定律)
Fig. 8. Thermodynamic properties for Li2NH: (a) The phonon contribution to the free energies ΔF of Li2NH; (b)the internal energies ΔE verus temperature; (c)the entropy S verus temperature; (d) the constant-volume specific heats Cv verus temperature(▼ meansT3 law of Debye)
表 1 Li2NH晶体结构参数
Table 1. Lattice parameters of Li2NH.
Space group Lattice parameter/Å Etot/eV Present Experimental Other Calculated Present $F\bar 43m$ a = 5.6249 a = 5.0769[2] a = 5.159[17],5.223[17],5.074[17],5.649[16],5.1076[18],5.2968[9] –1920.4448 $Pnma$ a = 7.781
b = 3.623
c = 4.902a = 7.733[8],7.704[16],7.742[17],7.753[17],7.775[17]
b = 3.60[8],3.75[16],3.604[17],3.609[17],3.618[17]
c = 4.872[8],5.074[16],4.883[17],4.890[17],4.881[17]–2702.3588 $Fm\bar 3m$ a = 5.0696 a = 5.0742[3] a = 5.047[3],5.045[16] –1913.6655 表 2 Li2NH(
$Pnma$ )在布里渊区中心Γ点的光学模声子频率(单位:cm–1)Table 2. Phonon frequencies (unit:cm–1) at the Γ point of Li2NH.
B2u B1u B3g B2g B3u Au B1g Ag 123.6 137.9 160 161.5 168 198.5 222 223.5 310 195.8 380 232.0 289 243.0 359 287 408 318 432 300 350.5 446 435 335 644 450 660 350.5 385 625 654 380 550 412 620 542 630 580 668 598 3122 640 3123 3132 3134 表 3 Li2NH的热力学函数
Table 3. Thermodynamic functions for Li2NH.
Temprature/K S/J·(mol-c·K)–1 CV/J·(mol-c·K)–1 ΔH(H–H298)/KJ·mol–1 298 248.9 273.8 0 300 250.2 274.9 2.9 500 405.4 327.1 55.1 700 519.0 347.0 75.0 900 607.7 358.5 86.5 1100 680.5 366.6 94.2 1300 742.3 372.8 100.8 1500 796.0 377.5 105.5 -
[1] Chen P, Xiong Z, Luo J, Lin J, Tan K L 2002 Nature 420 302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ohoyama K, Nakamori Y, Orimo S, Yamada K 2005 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 74 483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Noritake T, Nozaki H, Aoki M, Towata S, Kitahara G, Nakamori Y, Orimo S 2005 J. Alloys Compd. 393 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Herbst J F, Hector Jr L G 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 125120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Balogh M P, Jones C Y, Herbst J F, Hector Jr. L G, Kundrat M 2006 J. Alloys Compd. 420 326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mueller T, Ceder G 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 134104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kojima Y, Kawai Y 2005 J. Alloys Compd. 395 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Magyari-Köpe B, Ozoliņš V, Wolverton C 2006 Phys. Rev. B 73 220101(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Song Y, Guo Z X 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 195120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hector Jr L G, Herbst J F 2008 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20 064229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang J, Lamsal J, Cai Q, Yelon W B, James W J 2008 MRS Proceedings 1098 1098 1098−HH03-06
[12] Miceli G, Cucinotta C, Bernasconi M, Parrinello M 2010 J. Phys. Chem. C 114 15174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Miceli G, Ceriotti M, Angioletti-Uberti S, Bernasconi M, Parrinello M 2011 J. Phys. Chem. C 115 7076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wolverton C, Siegel J D, Akbarazadeh R A, Ozolis V 2008 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20 064228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈玉红, 吕晓霞, 杜瑞, 董肖, 张材荣, 康龙, 罗永春 2013 稀有金属材料与工程 4 2
Chen Y H, Lv X X, Du R, Dong X, Zhang C R, Kang L, Luo Y C 2013 Rare Metal Materials and Engineering 4 2
[16] Rajeswarapalanichamy R, Santhosh M, Sudhapriyanga G, Kanagaprabha S, Iyakutti K 2015 Acta Metall. Sinica 28 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Crivello J C, Gupta M, Černý R, Latroche M, Chandra D 2010 Phys. Rev. B 81 104113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Q, ChenY G, Zheng X, Niu G, Wu C L, Tao M D T 2009 Physica B 404 3431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] The ABINIT code is a common project of the Université Catholique de Louvain, and other contributors (URL http://www.abinit.org)
[20] Troullier N, Martins J L 1991 Phys. Rev. B 43 1993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Baroni S, Giannozzi P, Testa A 1987 Phys. Rev. Lett. 58 1861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Baroni S, de Gironcoli S, Dal Corso A, Giannozzi P 2001 Rev. Mod. Phys. 73 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lee C, Gonze X 1995 Phys. Rev. B 51 8610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li W 2011 Ph. D. Dissertation (Zhejiang: Zhejiang University)
[26] Aulbur W G, Jonsson L, Wilkins J W 2000 Solid States Phys. 54 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Stampfl C, Van de Walle C G 1999 Phys. Rev. B 5 9
[28] Gupta M, Gupta R P 2007 J. Alloys Compd. 319 446
[29] Yao J H 2007 Ph. D. Dissertation (London: University of London) 0-239
[30] 陈玉红2008 博士学位论文(兰州: 兰州理工大学)
Chen Y H 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation(Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology)(in Chinese)
[31] Born M, Huang K 1954 Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices (Oxford:Oxford University Press) p121
[32] Maradudin A A, Montroll E W, Weiss C H, Ipatova I P 1971 Theory of Lattice Dynamics in the Harmonic Approximation (2nd Ed.) (New York: Academic Press)
计量
- 文章访问数: 11400
- PDF下载量: 123
- 被引次数: 0




















 下载:
下载: