-
强激光诱导原子阈上电离中的低能结构(low-energy structure, LES)是当前强场领域的研究热点, 其背后的动力学过程引起了广泛讨论. 本文基于半经典模型、SCTS (semi-classical two-step)量子轨道模型和数值求解含时薛定谔方程(time-dependent Schrödinger equation, TDSE)方法, 研究了中红外激光场下Xe原子阈上电离中的LES随激光脉冲宽度的依赖. 发现LES随脉冲宽度的减小向更低能量方向移动. 分析表明: 长脉宽条件下, 能谱中的多峰结构(LESn)与电子前向散射的阶次n及电子初始横向动量密切相关, 而极低能结构(very-low-energy structure, VLES)主要由更高阶次前向散射的电子轨道贡献; 少周期脉冲条件下, LES峰值位置随载波包络相位(carrier-envelope phase, CEP)的移动可归因于激光场矢势和离子实库仑势的共同作用随CEP的变化, 其中库仑势导致的电子聚束效应是LES峰形成的主要原因.The low-energy structure (LES) of above-threshold ionization (ATI) of atoms subjected to an intense laser field is a hot topic in the strong-field atomic physics. The rich physical insights behind LES attract a lot of attention. Based on a semi-classical model, a semi-classical two-step (SCTS) quantum trajectory model and numerical solution of the time-dependent Schrödinger equation (TDSE), we study the pulse-duration dependence of LES for Xe atom subjected to a mid-infrared laser field. It is found that the energy of LES becomes lower for shorter pulse duration. Further analysis shows that in the case of multi-cycle laser field, the LESn structure is closely related to the number of times of forward scattering and the initial transverse momentum. In the case of few-cycle laser pulse, the carrier-envelope phase (CEP) dependence of the peak position of LES is mainly due to the CEP dependence of the influence of both vector-potential of the laser field and the Coulomb potential. In addition, the bunching effect of electrons, caused by Coulomb potential, is the main reason for the formation of LES.
[1] Keldysh L V 1965 Sov. Phys. JETP–USSR 20 1307
[2] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Schafer K J, Yang B, DiMauro L F, Kulander K C 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 1599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Agostini P, Fabre F, Mainfray G, Petite G, Rahman N K 1979 Phys. Rev. Lett. 42 1127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yergeau F, Petite G, Agostini P 1986 J. Phys. B 19 L663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Walker B, Sheehy B, DiMauro L F, Agostini P, Schafer K J, Kulander K C 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 1227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] L’Huillier A, Lompre L A, Mainfray G, Manus C 1983 Phys. Rev. A 27 2503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hao X L, Bai Y X, Li C, Zhang J Y, Li W D, Yang W F, Liu M Q, Chen J 2022 Commun. Phys. 5 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shore B W, Knight P L 1987 J. Phys. B 20 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] McPherson A, Gibson G, Jara H 1987 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 4 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nubbemeyer T, Gorling K, Saenz A, Eichmann U, Sandner W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 233001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Eichmann U, Nubbemeyer T, Rottke H, Sandner W 2009 Nature 461 1261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu M Q, Xu S P, Hu S L, Becker W, Quan W, Liu X J, Chen J 2021 Optica 8 765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Blaga C I, Catoire F, Colosimo P, Paulus G G, Muller H G, Agostini P, Dimauro L F 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Quan W, Lin Z Y, Wu M Y, et al. 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 093001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wu C Y, Yang D, Liu Y Q, et al. 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 043001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo L, Han S S, Liu X, Cheng Y, Xu Z Z, Fan J, Chen J, Chen S G, Becker W 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 013001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Y L, Xu S P, Chen Y J, et al. 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 063415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 全威, 肖智磊, 陈永菊, 许松坡, 赖炫扬, 华林强, 龚成, 陈京, 柳晓军 2017 中国科学: 物理 力学 天文学 47 033007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Quan W, Xiao Z L, Chen Y J, Xu S P, Lai X Y, Hua L Q, Gong C, Chen J, Liu X J 2017 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 47 033007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xia Q Z, Ye D F, Fu L B, Han X Y, Liu J 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 11473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Quan W, Hao X L, Chen Y J, et al. 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Moller M, Meyer F, Sayler A M, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 023412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu S P, Quan W, Chen Y J, Xiao Z L, Wang Y L, Kang H P, Hua L Q, Gong C, Lai X Y, Liu X J, Hao X L, Hu S L, Chen J 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 063405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wolter B, Lemell C, Baudisch M, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 063424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Liu C P, Hatsagortsyan K Z 2011 J. Phys. B 44 095402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Becker W, Goreslavski S P, Milošević D B, Paulus G G 2014 J. Phys. B 47 204022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Milošević D B 2016 J. Phys. B 49 175601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kästner A, Saalmann U, Rost J M 2012 J. Phys. B 45 074011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang K, Lai Y, Diesen E, et al. 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 021403
[30] Bambi H, Liu J, Chen S G 1997 Phys. Lett. A 236 533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Delone N B, Krainov V P 1991 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 8 1207
[32] Shvetsov-Shilovskia N I, Goreslavskia S P, Popruzhenkoa S V 2009 Laser Phys. 19 1550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Shvetsov-Shilovski N I, Lein M, Madsen L B, et al. 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 013415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Xiao Z L, Quan W, Yu S G, Lai X Y, Liu X J, Wei Z R, Chen J 2022 Opt. Express 30 14873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Hermann M R, Fleck, Jr J A 1988 Phys. Rev. A 38 6000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yu S G, Lai X Y, Wang Y L, Xu S P, Hua L Q, Quan W, Liu X J 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 023414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
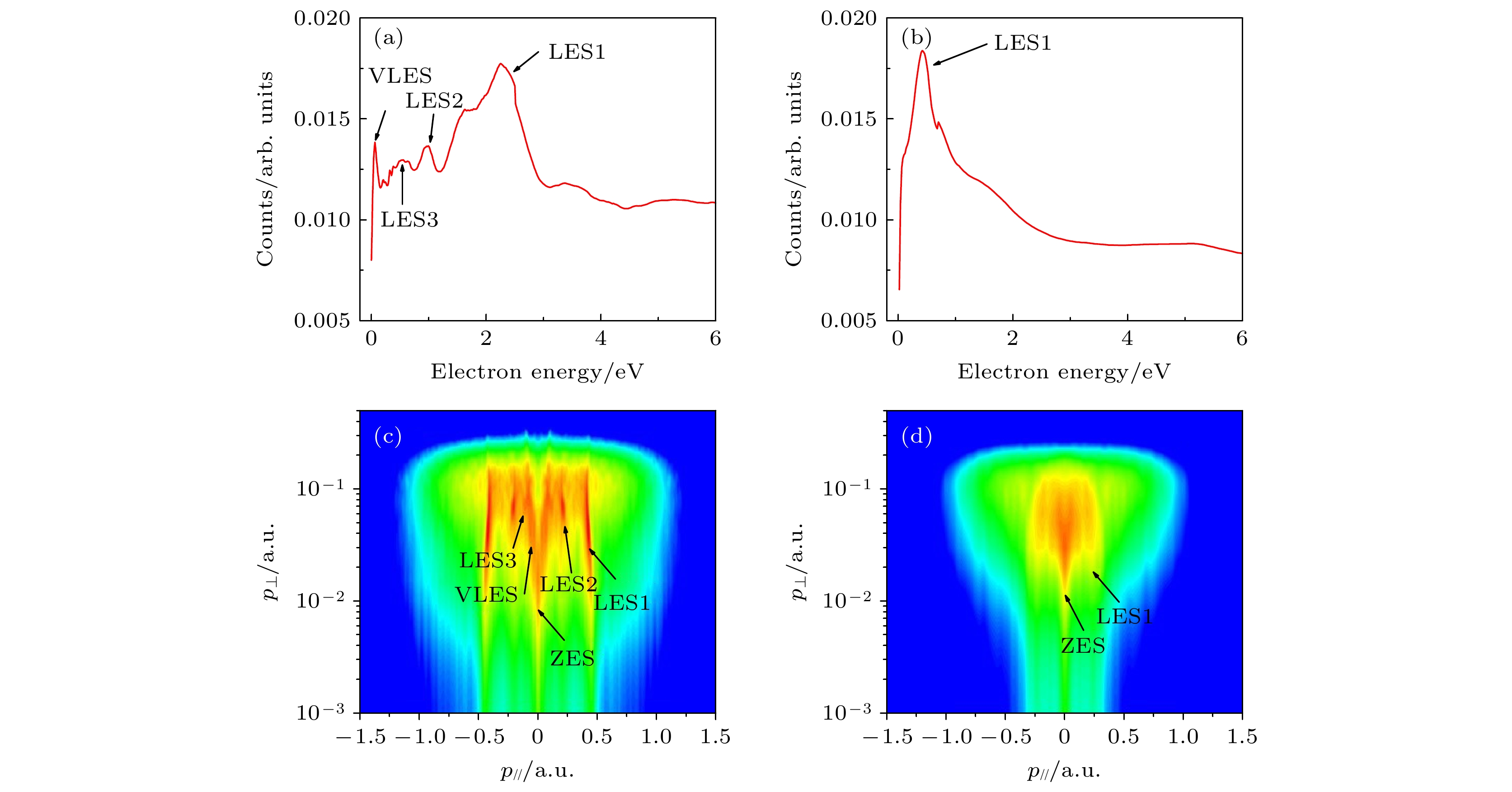
图 1 计算得到CEP平均后Xe原子在光强
$0.8 \times {10^{14}}$ W/cm2, 波长2000 nm线偏振激光场下的光电子能谱, 其中激光脉冲宽度分别为(a) 20T和(b)4T; (c),(d) 光电子二维动量分布(纵轴为对数坐标). 第一、二、三阶低能结构(即LES1, LES2, LES3)、极低低能结构(VLES)和零能结构(ZES)在图中都用箭头标出Fig. 1. The calculated CEP-averaged photoelectron energy structures (PES) of Xe atom with laser intensity of
$0.8 \times $ $ {10^{14}}$ W/cm2, wavelength of 2000 nm and the laser pulse durations of 20-cycles (a) and 4-cycles (b), respectively; (c),(d) the corresponding photoelectron momentum distributions with${p_ \bot }$ on logarithmic scales. The first-, second- and third-order LESs (LES1, LES2, LES3) and the very low energy structure (VLES) and zero energy structure (ZES) are indicated by arrows in all panels.图 2 使用SCTS量子轨道模型(a)和TDSE方法(b)计算得到Xe原子在不同脉宽线偏振激光场下的光电子能量谱; SCTS量子轨道模型(c)和TDSE方法(d)少周期激光场中二维光电子动量分布, 其中激光脉冲的CEP = 0
Fig. 2. The calculated PES of Xe atom under different laser pulse durations with SCTS model (a) and TDSE (b), respectively; (c), (d) the corresponding photoelectron momentum distributions under few-cycle laser fields with CEP = 0.
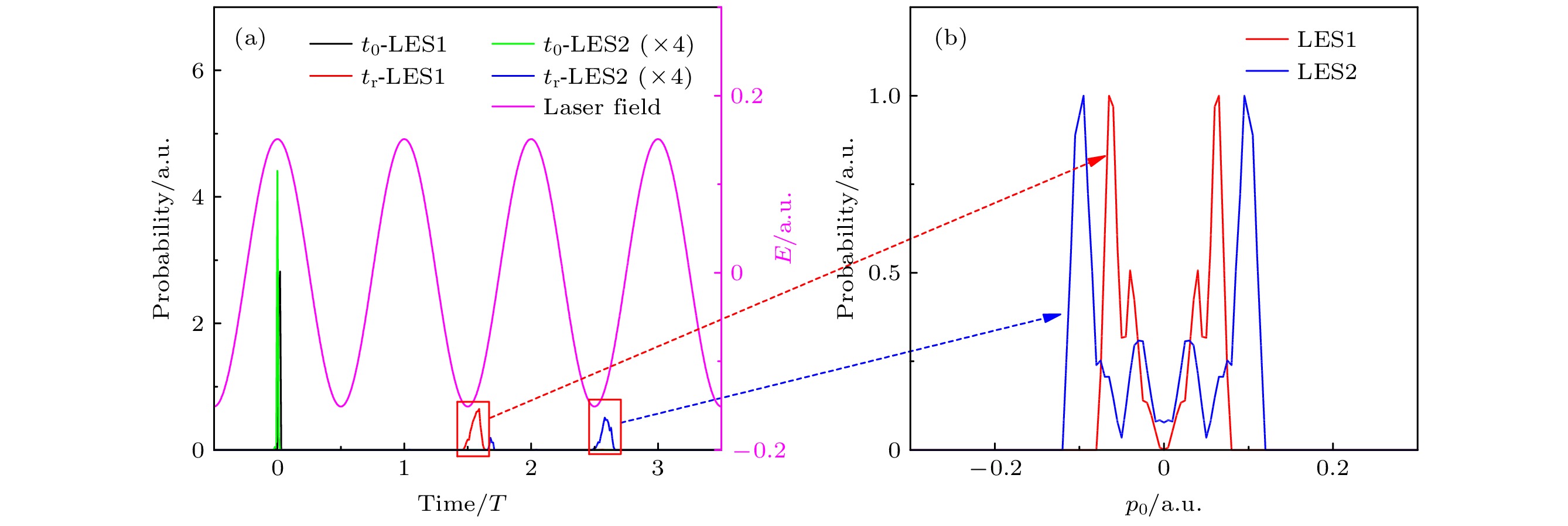
图 4 (a) 不同阶次LESn (n = 1, 2)对应电子电离时刻t0和最后一次发生前向散射时刻tr的概率分布, 紫色线为激光电场; (b) LES1第一次前向散射以及LES2第二次前向散射对应的电子初始横向动量分布
Fig. 4. (a) The distributions of tunneling instant t0 and last forward scattering instant tr for LES1 and LES2, respectively, the laser field is shown by the purple line; (b) the initial transverse momentum distributions of the first forward scattering photoelectron trajectory in LES1 and the second forward scattering photoelectron trajectory in LES2.
图 5 (a),(c) 长脉冲激光场下光电子能谱中LES1, LES2结构对应的典型轨道; (b),(d) LES1和LES2对应典型光电子轨道的横向动量、平行动量随时间的演化
Fig. 5. The typical orbitals corresponding to the LES1 (a) and LES2 (c) in the photoelectron spectra in multi-cycle laser field; the corresponding temporal evolution of transverse momentum (
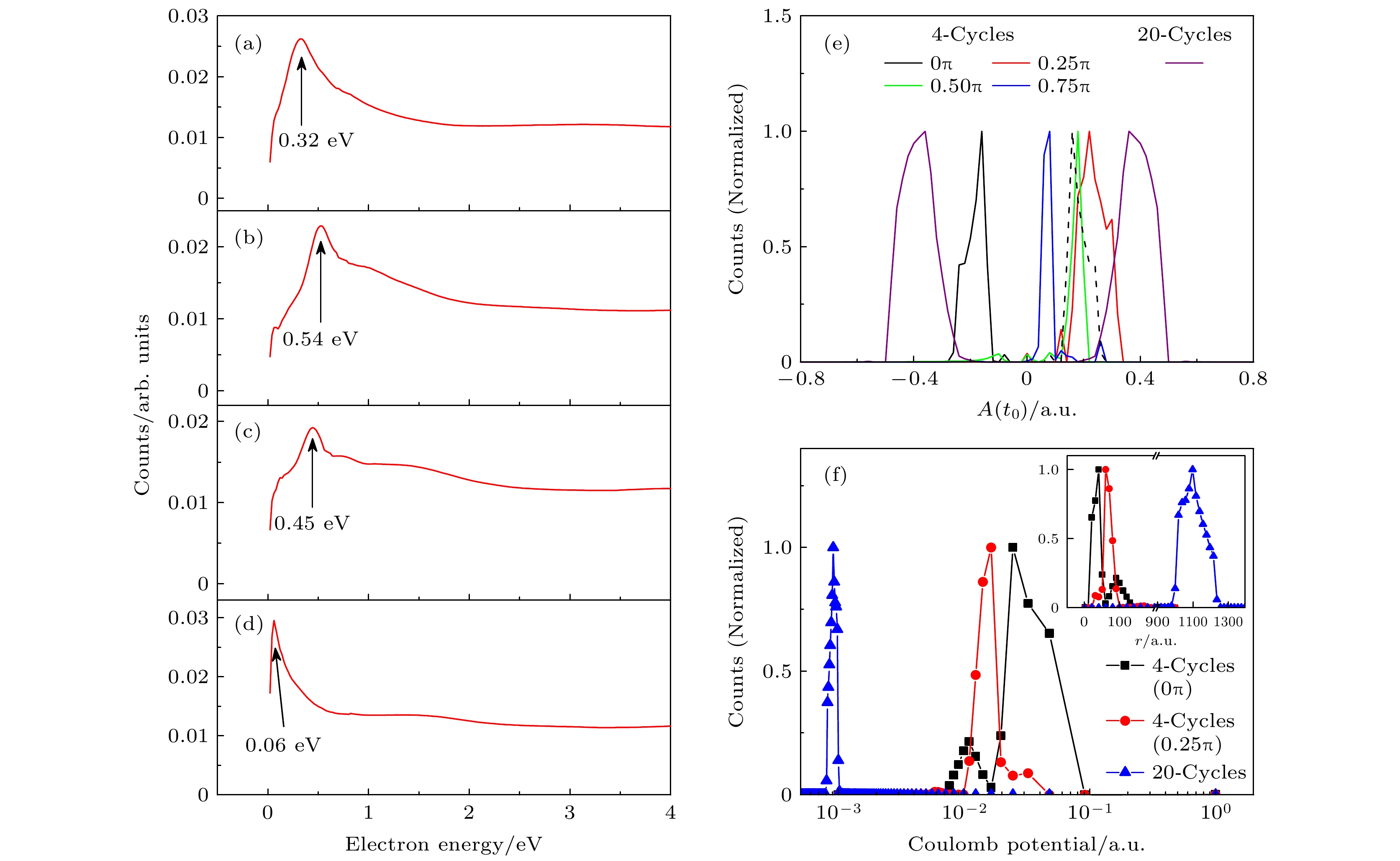
${p_ \bot }$ ) and parallel momentum (${p_{//}}$ ) of the two typical orbits of LES1 (b) and LES2 (d), respectively.图 6 (a)—(d) 少周期激光场下光电子能谱随CEP的依赖, 对应CEP从上至下分别为0πi, 0.25π, 0.5π, 0.75π; (e)少周期激光场中不同CEP条件下LES电子前向散射轨道电离时刻激光场矢势A(t0)分布和长脉宽激光场条件下LES1电子前向散射电离时刻激光场矢势A(t0)分布, 其中黑色虚线为0π时矢势在正方向的镜像; (f) 少周期和长脉宽激光场结束时刻电离产率关于库仑势大小的分布, 插图为电离产率关于电子与离子实距离的分布
Fig. 6. (a)–(d) The distributions of PES with different CEPs in few-cycle laser field, the corresponding CEPs are 0π, 0.25π, 0.5π, 0.75π from top to bottom; (e) the ionization yields with respect to the vector potential of rescattering photoelectron trajectories relevant to the LES at these CEPs in the case of the few-cycle laser pulse case and also the corresponding data of the photoelectron trajectories relevant to the LES1 in the multi-cycle pulse case; (f) the ionization yields with respect to the strength of the Coulomb potential when laser field ends, the inset shows the ionization yields with respect to the distance between the photoelectron and the core.
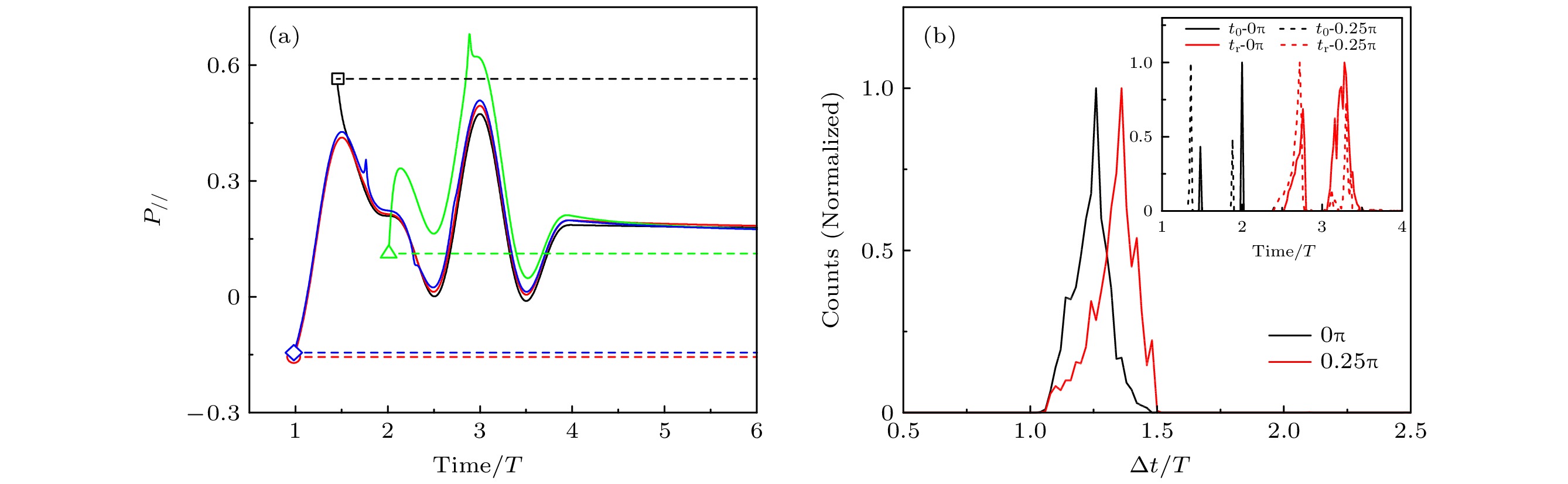
图 7 (a) 少周期CEP = 0时不同初始条件的4条轨道正则动量随时间的演化情况, 实线为考虑库仑势, 虚线为不考虑库仑势的情况; (b) 少周期CEP = 0和0.25π时电离概率关于前向散射电子的重散射时刻相较电离时刻延迟的分布, 插图为两CEP条件下电子电离时刻t0和散射时刻tr的概率分布
Fig. 7. (a) Temporal evolution of drift momenta of four trajectories with different initial conditions with (solid line) and without (dotted line) Coulomb potential with CEP = 0; (b) the distribution of the delay time between rescattering time (tr) and tunneling time (t0) in few-cycle laser fields with CEP = 0 and 0.25π. The inset shows the t0 and tr distributions for the two CEPs.
-
[1] Keldysh L V 1965 Sov. Phys. JETP–USSR 20 1307
[2] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Schafer K J, Yang B, DiMauro L F, Kulander K C 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 1599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Agostini P, Fabre F, Mainfray G, Petite G, Rahman N K 1979 Phys. Rev. Lett. 42 1127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yergeau F, Petite G, Agostini P 1986 J. Phys. B 19 L663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Walker B, Sheehy B, DiMauro L F, Agostini P, Schafer K J, Kulander K C 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 1227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] L’Huillier A, Lompre L A, Mainfray G, Manus C 1983 Phys. Rev. A 27 2503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hao X L, Bai Y X, Li C, Zhang J Y, Li W D, Yang W F, Liu M Q, Chen J 2022 Commun. Phys. 5 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shore B W, Knight P L 1987 J. Phys. B 20 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] McPherson A, Gibson G, Jara H 1987 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 4 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nubbemeyer T, Gorling K, Saenz A, Eichmann U, Sandner W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 233001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Eichmann U, Nubbemeyer T, Rottke H, Sandner W 2009 Nature 461 1261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu M Q, Xu S P, Hu S L, Becker W, Quan W, Liu X J, Chen J 2021 Optica 8 765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Blaga C I, Catoire F, Colosimo P, Paulus G G, Muller H G, Agostini P, Dimauro L F 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Quan W, Lin Z Y, Wu M Y, et al. 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 093001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wu C Y, Yang D, Liu Y Q, et al. 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 043001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo L, Han S S, Liu X, Cheng Y, Xu Z Z, Fan J, Chen J, Chen S G, Becker W 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 013001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Y L, Xu S P, Chen Y J, et al. 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 063415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 全威, 肖智磊, 陈永菊, 许松坡, 赖炫扬, 华林强, 龚成, 陈京, 柳晓军 2017 中国科学: 物理 力学 天文学 47 033007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Quan W, Xiao Z L, Chen Y J, Xu S P, Lai X Y, Hua L Q, Gong C, Chen J, Liu X J 2017 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 47 033007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xia Q Z, Ye D F, Fu L B, Han X Y, Liu J 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 11473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Quan W, Hao X L, Chen Y J, et al. 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Moller M, Meyer F, Sayler A M, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 023412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu S P, Quan W, Chen Y J, Xiao Z L, Wang Y L, Kang H P, Hua L Q, Gong C, Lai X Y, Liu X J, Hao X L, Hu S L, Chen J 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 063405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wolter B, Lemell C, Baudisch M, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 063424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Liu C P, Hatsagortsyan K Z 2011 J. Phys. B 44 095402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Becker W, Goreslavski S P, Milošević D B, Paulus G G 2014 J. Phys. B 47 204022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Milošević D B 2016 J. Phys. B 49 175601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kästner A, Saalmann U, Rost J M 2012 J. Phys. B 45 074011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang K, Lai Y, Diesen E, et al. 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 021403
[30] Bambi H, Liu J, Chen S G 1997 Phys. Lett. A 236 533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Delone N B, Krainov V P 1991 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 8 1207
[32] Shvetsov-Shilovskia N I, Goreslavskia S P, Popruzhenkoa S V 2009 Laser Phys. 19 1550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Shvetsov-Shilovski N I, Lein M, Madsen L B, et al. 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 013415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Xiao Z L, Quan W, Yu S G, Lai X Y, Liu X J, Wei Z R, Chen J 2022 Opt. Express 30 14873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Hermann M R, Fleck, Jr J A 1988 Phys. Rev. A 38 6000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yu S G, Lai X Y, Wang Y L, Xu S P, Hua L Q, Quan W, Liu X J 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 023414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7095
- PDF下载量: 114
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: