-
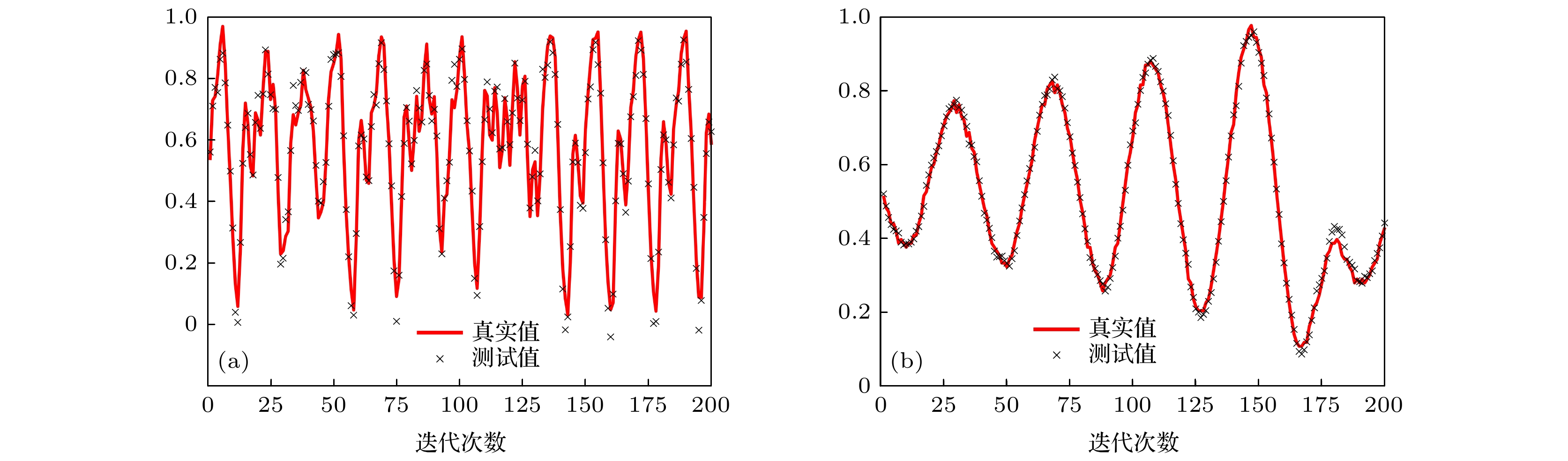
混沌时间序列能够较好反映真实环境的非线性和非平稳性特性, 然而具有二阶统计特性的核自适应滤波器(kernel adaptive filter, KAF)在处理含噪声和异常值的混沌时间序列时, 其预测性能显著下降. 为提高核自适应滤波器的鲁棒性, 本文提出了一种用于测量非线性相似度的柯西核损失(Cauchy kernel loss, CKL), 并采用半平方(half-quadratic, HQ)方法保证了CKL的全局凸性. 为改善随机梯度下降法收敛速度较慢且容易陷入局部最优的不足, 采用共轭梯度(conjugate gradient, CG)方法优化CKL. 进一步, 为解决核矩阵网络增长的问题, 采取Nyström稀疏策略近似核矩阵, 并利用概率密度秩量化(probability density rank-based quantization, PRQ)提高逼近精度. 基于此, 本文提出了一种新的基于Nyström和PRQ的柯西核共轭梯度(Nyström Cauchy kernel conjugate gradient with PRQ, NCKCG-PRQ)算法有效实现了混沌时间序列的预测. 基于合成和真实两类混沌时间序列验证了所提NCKCG-PRQ算法在稳态性能, 鲁棒性和计算存储复杂度上的优势.Chaotic time series can well reflect the nonlinearity and non-stationarity of real environment changes. The traditional kernel adaptive filter (KAF) with second-order statistical characteristics suffers performance degeneration dramatically for predicting chaotic time series containing noises and outliers. In order to improve the robustness of adaptive filters in the presence of impulsive noise, a nonlinear similarity measure named Cauchy kernel loss (CKL) is proposed, and the global convexity of CKL is guaranteed by the half-quadratic (HQ) method. To improve the convergence rate of stochastic gradient descent and avoid a local optimum simultaneously, the conjugate gradient (CG) method is used to optimize CKL. Furthermore, to address the issue of kernel matrix network growth, the Nyström sparse strategy is adopted to approximate the kernel matrix and then the probability density rank-based quantization (PRQ) is used to improve the approximation accuracy. To this end, a novel Nyström Cauchy kernel conjugate gradient with PRQ (NCKCG-PRQ) algorithm is proposed for the prediction of chaotic time series in this paper. Simulations on prediction of synthetic and real-world chaotic time series validate the advantages of the proposed algorithm in terms of filtering accuracy, robustness, and computational storage complexity.
-
Keywords:
- prediction of chaotic time series /
- kernel adaptive filtering /
- Cauchy kernel loss /
- Nyström method
[1] 林毅, 刘文波, 沈骞 2018 67 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin Y, Liu W B, Shen Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王梦蛟, 吴中堂, 冯久超 2015 64 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M J, Wu Z T, Feng J C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 唐舟进, 任峰, 彭涛, 王文博 2014 63 050505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Z J, Ren F, Peng T, Wang W B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 050505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 梅英, 谭冠政, 刘振焘, 武鹤 2018 67 080502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mei Y, Tan G Z, Liu Z T, Wu H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 080502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王新迎, 韩敏, 王亚楠 2013 62 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Y, Han M, Wang Y N 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王世元, 史春芬, 钱国兵, 王万里 2018 67 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S Y, Shi C F, Qian G B, Wang W L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Peng L B, Li X F, Bi D J, Xie Y L 2018 Signal Process. Lett. 25 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 赵永平, 张丽艳, 李德才, 王立峰, 蒋洪章 2013 62 120511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Y P, Zhang L Y, Li D C, Wang L F, Jiang H Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 120511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张家树, 党建亮, 李恒超 2007 56 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J S, Dang J L, Li H C 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张洪宾, 孙小端, 贺玉龙 2014 63 040505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H B, Sun X D, He Y L 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 040505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 唐舟进, 彭涛, 王文博 2014 63 130504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Z J, Peng T, Wang W B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 130504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 火元莲, 王丹凤, 龙小强, 连培君, 齐永锋 2021 70 158401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huo Y L, Wang D F, Long X Q, Lian P J, Qi Y F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 158401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 火元莲, 王丹凤, 龙小强, 连培君, 齐永锋 2021 70 028401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huo Y L, Wang D F, Long X Q, Lian P J, Qi Y F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 028401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu Z, Shi J, Xie Z, Ma W 2015 Signal Process. 117 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu W F, Pokharel P P, Príncipe J C 2008 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56 543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R 2004 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52 2275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen B D, Príncipe J C 2012 Signal Process. Lett. 19 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li C G, Shen P C, Liu Y, Zhang Z Y 2013 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61 4011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen B D, Xing L, Zhao H Q, Zheng N N, Príncipe J C 2016 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64 3376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li X L, Lu Q M, Dong Y S, Tao D C 2019 Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30 2067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shi W, Xiong K, Wang S Y 2019 IEEE Access. 7 120548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lei Y W, Hu T, Li G Y, Tang K 2020 Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31 4394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang M, Wang X J, Chen X M, Zhang A X 2018 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66 4377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xiong K, Herbert H C, Wang S Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Cybern. 51 5497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen B D, Zhao S L, Zhu P P, Príncipe J C 2013 Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 24 1484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang T, Wang S Y, Huang X W, Jia L 2020 Signal Process. Lett. 27 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang T, He F L, Zheng Z, Wang S Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 67 2772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] He F L, Xiong K, Wang S Y 2020 IEEE Access. 8 18716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang T, Wang S Y 2020 Signal Process. Lett. 27 1535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qi L T, Shen M L, Wang D L, Wang S Y 2021 Signal Process. Lett. 28 1011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang H N, Yang B, Wang L, Wang S Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 69 1859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Xiong K, Wang S Y 2019 Signal Process. Lett. 26 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Qin Z D, Chen B D, GU Y T, Zheng N N, Príncipe J C 2020 IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31 3100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zheng Y F, Wang S Y, Feng J C, Tse C K 2016 Digit. Signal Process. 48 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Weng B W, Barner K E 2005 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53 2588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang X W, Wang S Y, Xiong K 2019 Symmetry 11 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
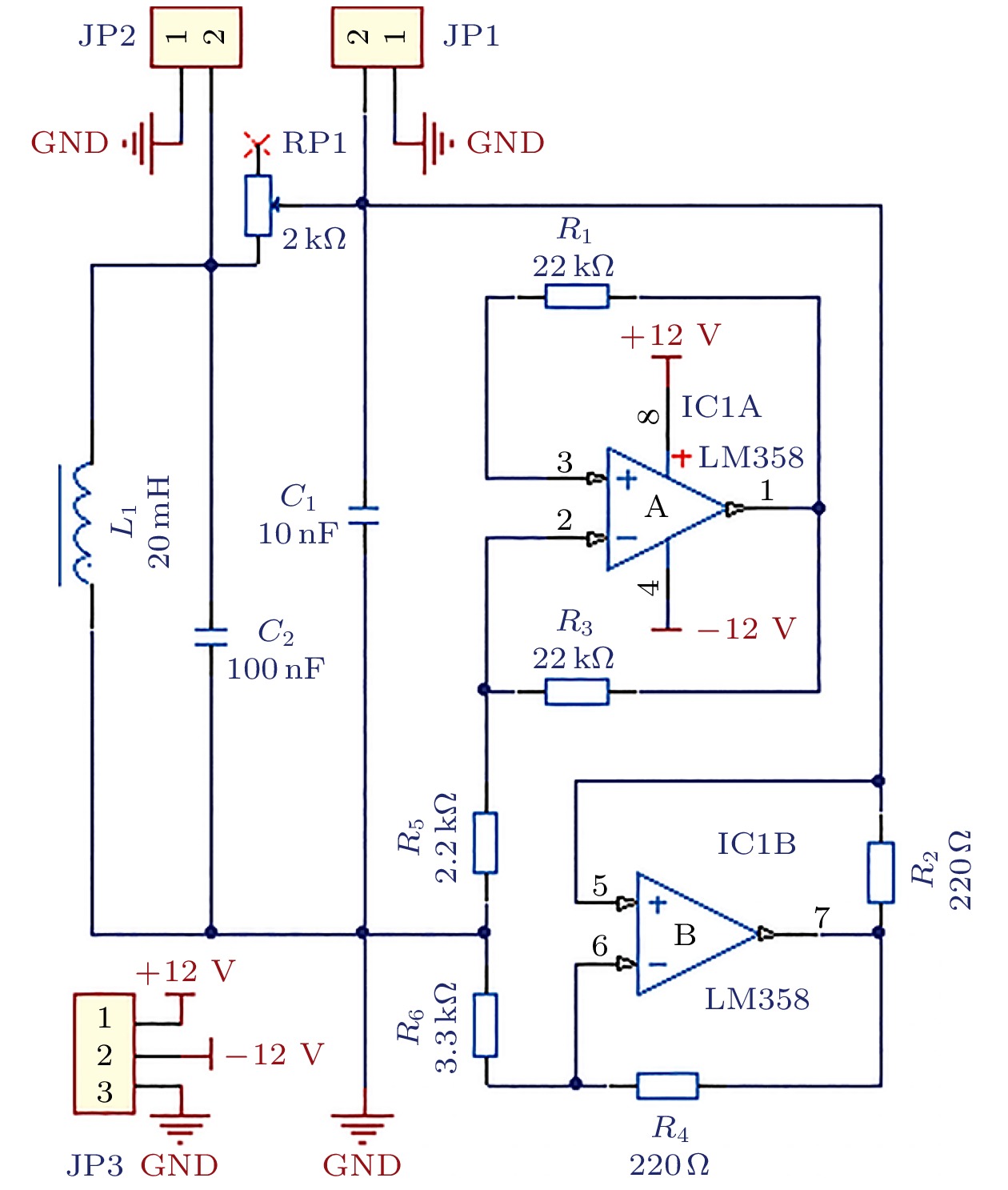
表 1 NCKCG-PRQ算法
Table 1. NCKCG-PRQ algorithm.
输入: 输入输出对$\left\{ { {{\boldsymbol{u}}_k}, {d_k} } \right\}, k{\text{ = } }1, 2, \cdot \cdot \cdot$ 初始化参数: $ {\boldsymbol{\hat u}}(i) $为PRQ采样后样本点; $ {\boldsymbol{\varLambda }} $和W分别为有关$ {\boldsymbol{\hat U}} $核矩阵的特征值降序排列的对角矩阵和对应特征向量构成列正交矩阵; ${ {\boldsymbol{K} }_c}(1) = [\kappa ({\boldsymbol{u} }(1), {\boldsymbol{\hat u} }(1)), \cdots , \kappa ({\boldsymbol{u} }(1), {\boldsymbol{\hat u} }(m))]$为初始核向量; 映射输入$ {{\boldsymbol{z}}_1} = {{\boldsymbol{\varLambda }}^{ - 1/2}}{{\boldsymbol{W}}^{\text{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{K}}_c}{(1)^{\text{T}}} $; 权重$ {\boldsymbol{\varOmega }}_1^z = 0 $; 加权函数$ {\zeta _1} = {\exp}( - {s_1})/\left\{ {{\delta ^2}\left[ {{\eta ^{ - 1}} + {s_1}{\exp}( - {s_1})} \right]} \right\} $; 期望$ {d_1}{\text{ = }}{({{\boldsymbol{\varOmega }}_1}^z)^{\text{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{z}}_1} $; 相关矩阵$ R_1^z = {\zeta _1}{{\boldsymbol{z}}_1}{\boldsymbol{z}}_1^{\rm T} $; 互相关向量${\boldsymbol{c}}_1^z={\zeta _1}{d_1}{{\bf{z}}_1}$; 冗余向量${\boldsymbol{r}}_1^z ={\boldsymbol{ c}}_1^z - {\boldsymbol{R}}_1^z{\boldsymbol{\varOmega } }_1^z$; 方向向量${\boldsymbol{p}}_1^z = {\boldsymbol{r}}_1^z$, 遗忘因子$ \lambda {\text{ = }}0.999 $
循环$ \left( {k{\text{ = 2}}, 3, \cdot \cdot \cdot } \right) $:1.输入核向量${ {\boldsymbol{K} }_c}(i) = [\kappa ({\boldsymbol{u} }(i), {\boldsymbol{\hat u} }(1)), \cdots , \kappa ({\boldsymbol{u} }(i), {\boldsymbol{\hat u} }(m)]$;
2.映射输入${\boldsymbol{z} }( \cdot ) = { {\boldsymbol{\varLambda } }^{ - 1/2} }{ {\boldsymbol{W} }^{\text{T} } }{[\kappa ( \cdot , {\boldsymbol{\hat u} }(1)), \cdots , \kappa ( \cdot , {\boldsymbol{\hat u} }(m))]^{\text{T} } }$;
3.误差更新$ {e_{k + 1}} = {d_{k + 1}} - {\left( {{\boldsymbol{\varOmega }}_k^z} \right)^{\text{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{z}}_{k + 1}} $, 加权函数$ {\zeta _k} = {\exp}( - {s_k})/\left\{ {{\delta ^2}\left[ {{\eta ^{ - 1}} + {s_k}{\exp}( - {s_k})} \right]} \right\} $
4.自相关矩阵更新${\boldsymbol{R}}_{k + 1}^z = \lambda {\boldsymbol{R}}_k^z + {\zeta _{k + 1} }{ {\boldsymbol{z} }_{k + 1} }{\boldsymbol{z} }_{k + 1}^{\rm T}$, 计算步长${\alpha _k} = \frac{ { { {\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^z} \right)}^{\text{T} } }{\boldsymbol{r}}_k^z} }{ { { {\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^z} \right)}^{\text{T} } }{\boldsymbol{R}}_{k + 1}^z{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^z} }$;
5.权重更新${\boldsymbol{\varOmega } }_{k + 1}^z = {\boldsymbol{\varOmega } }_k^z + {\alpha _k}{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^z$, 残差向量更新${\boldsymbol{r}}_{k + 1}^z = \lambda {\boldsymbol{r}}_k^z - {\alpha _k}{\boldsymbol{R}}_{k + 1}^z{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^z + {\zeta _{k + 1} }{{\bf{z}}_{k + 1} }{{\boldsymbol{e}}_{k + 1} }$;
6.计算步长 ${\beta _k} = \frac{ { { {\left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_{k + 1}^z} \right)}^{\text{T} } }\left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_{k + 1}^z - {\boldsymbol{r}}_k^z} \right)} }{ { { {\left( {{\boldsymbol{r}}_k^z} \right)}^{\text{T} } }{\boldsymbol{r}}_k^z} }$, 共轭方向更新${\boldsymbol{p}}_{k + 1}^z = {\boldsymbol{r}}_{k + 1}^z + {\beta _k}r_k^z$
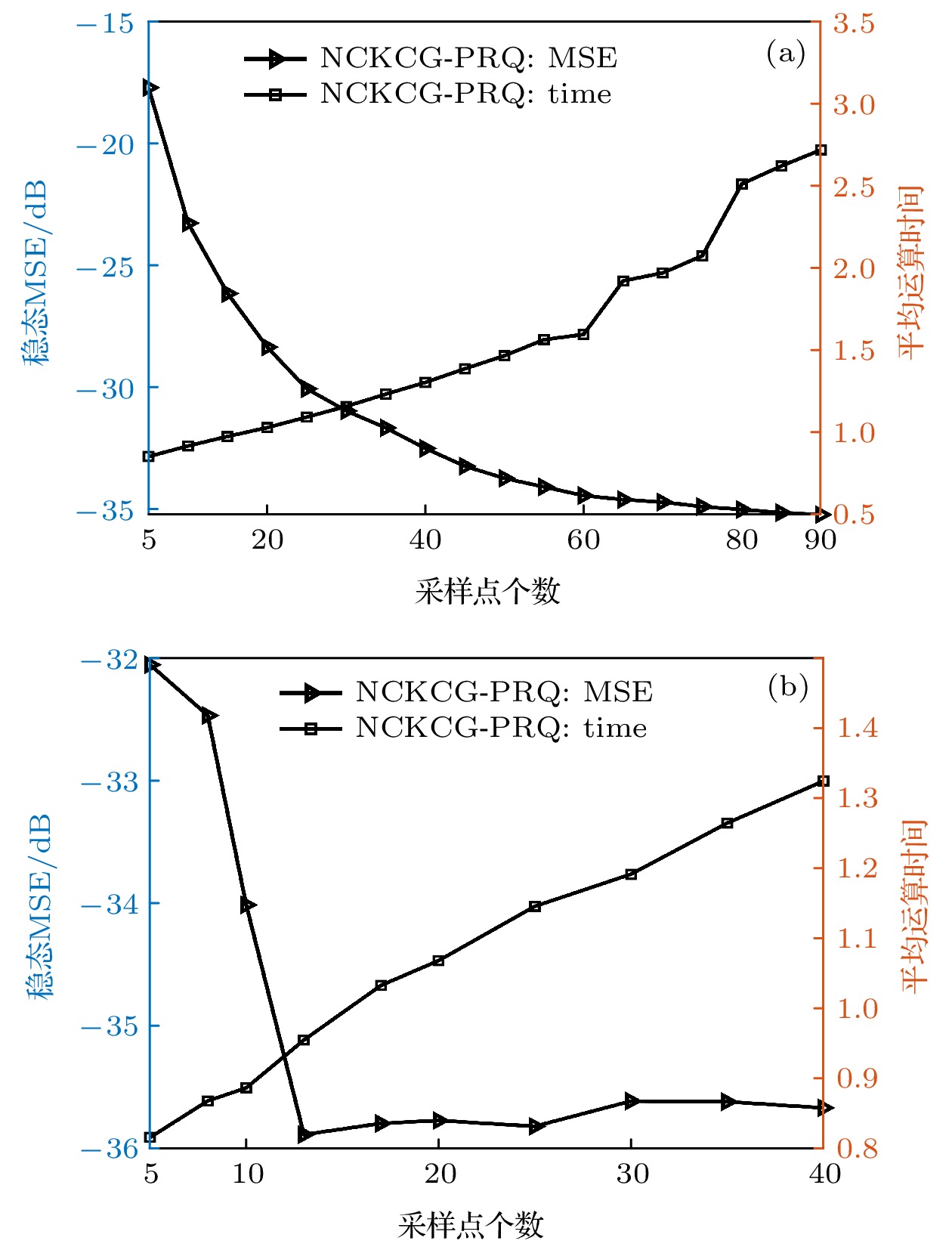
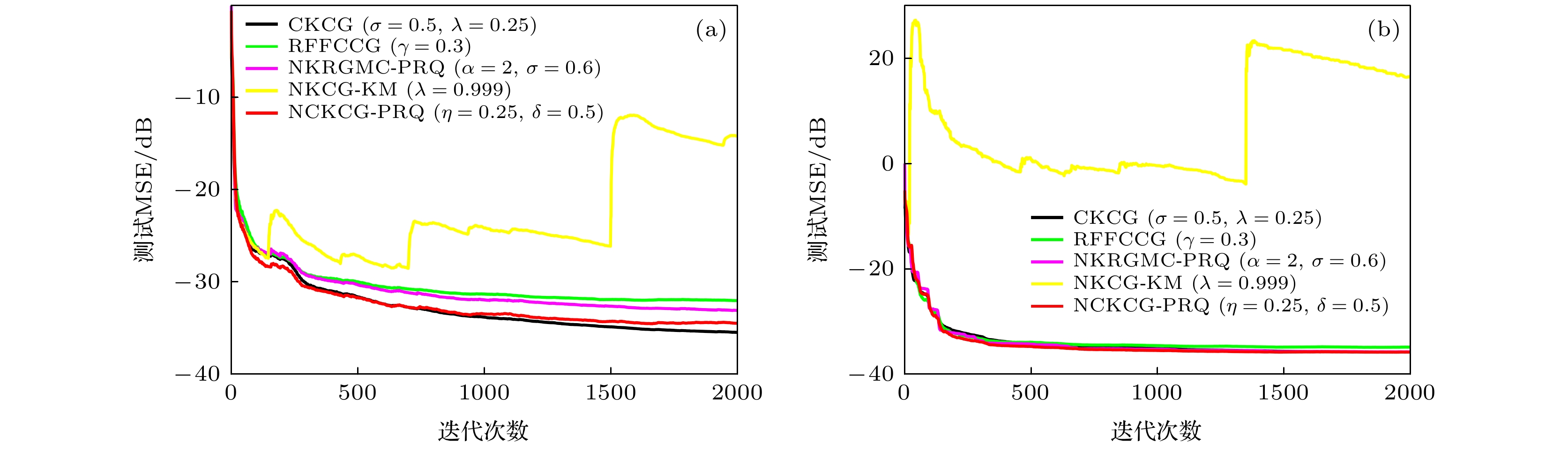
循环终止表 2 不同算法在MG混沌时间序列中的仿真结果
Table 2. Simulation results of different algorithms in MG chaotic time series.
实验模型 算法 字典数目 运算时间/s 稳态MSE/dB MG混沌时间序列 CKCG 2000 41.486 –35.443 RFFCCG 60 2.095 –32.006 NKRGMC-PRQ 60 2.383 –33.068 NKCG-KM 60 3.745 N/A NCKCG-PRQ 60 1.584 –34.446 表 3 不同算法在蔡氏电路混沌时间序列中的仿真结果
Table 3. Simulation results of different algorithms in chaotic time series based on Chua's circuit.
实验模型 算法 字典数目 运算时间/s 稳态MSE/dB 蔡氏混沌时间序列 CKCG 2000 42.618 –35.840 RFFCCG 13 1.128 –34.926 NKRGMC-PRQ 13 0.988 –35.819 NKCG-KM 13 1.146 N/A NCKCG-PRQ 13 0.957 –35.865 -
[1] 林毅, 刘文波, 沈骞 2018 67 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin Y, Liu W B, Shen Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王梦蛟, 吴中堂, 冯久超 2015 64 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M J, Wu Z T, Feng J C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 唐舟进, 任峰, 彭涛, 王文博 2014 63 050505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Z J, Ren F, Peng T, Wang W B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 050505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 梅英, 谭冠政, 刘振焘, 武鹤 2018 67 080502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mei Y, Tan G Z, Liu Z T, Wu H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 080502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王新迎, 韩敏, 王亚楠 2013 62 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Y, Han M, Wang Y N 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王世元, 史春芬, 钱国兵, 王万里 2018 67 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S Y, Shi C F, Qian G B, Wang W L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Peng L B, Li X F, Bi D J, Xie Y L 2018 Signal Process. Lett. 25 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 赵永平, 张丽艳, 李德才, 王立峰, 蒋洪章 2013 62 120511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Y P, Zhang L Y, Li D C, Wang L F, Jiang H Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 120511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张家树, 党建亮, 李恒超 2007 56 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J S, Dang J L, Li H C 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张洪宾, 孙小端, 贺玉龙 2014 63 040505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H B, Sun X D, He Y L 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 040505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 唐舟进, 彭涛, 王文博 2014 63 130504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Z J, Peng T, Wang W B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 130504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 火元莲, 王丹凤, 龙小强, 连培君, 齐永锋 2021 70 158401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huo Y L, Wang D F, Long X Q, Lian P J, Qi Y F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 158401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 火元莲, 王丹凤, 龙小强, 连培君, 齐永锋 2021 70 028401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huo Y L, Wang D F, Long X Q, Lian P J, Qi Y F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 028401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu Z, Shi J, Xie Z, Ma W 2015 Signal Process. 117 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu W F, Pokharel P P, Príncipe J C 2008 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56 543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R 2004 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52 2275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen B D, Príncipe J C 2012 Signal Process. Lett. 19 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li C G, Shen P C, Liu Y, Zhang Z Y 2013 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61 4011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen B D, Xing L, Zhao H Q, Zheng N N, Príncipe J C 2016 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64 3376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li X L, Lu Q M, Dong Y S, Tao D C 2019 Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30 2067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shi W, Xiong K, Wang S Y 2019 IEEE Access. 7 120548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lei Y W, Hu T, Li G Y, Tang K 2020 Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31 4394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang M, Wang X J, Chen X M, Zhang A X 2018 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66 4377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xiong K, Herbert H C, Wang S Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Cybern. 51 5497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen B D, Zhao S L, Zhu P P, Príncipe J C 2013 Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 24 1484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang T, Wang S Y, Huang X W, Jia L 2020 Signal Process. Lett. 27 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang T, He F L, Zheng Z, Wang S Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 67 2772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] He F L, Xiong K, Wang S Y 2020 IEEE Access. 8 18716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang T, Wang S Y 2020 Signal Process. Lett. 27 1535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qi L T, Shen M L, Wang D L, Wang S Y 2021 Signal Process. Lett. 28 1011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang H N, Yang B, Wang L, Wang S Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 69 1859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Xiong K, Wang S Y 2019 Signal Process. Lett. 26 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Qin Z D, Chen B D, GU Y T, Zheng N N, Príncipe J C 2020 IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31 3100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zheng Y F, Wang S Y, Feng J C, Tse C K 2016 Digit. Signal Process. 48 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Weng B W, Barner K E 2005 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53 2588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang X W, Wang S Y, Xiong K 2019 Symmetry 11 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6257
- PDF下载量: 71
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: