-
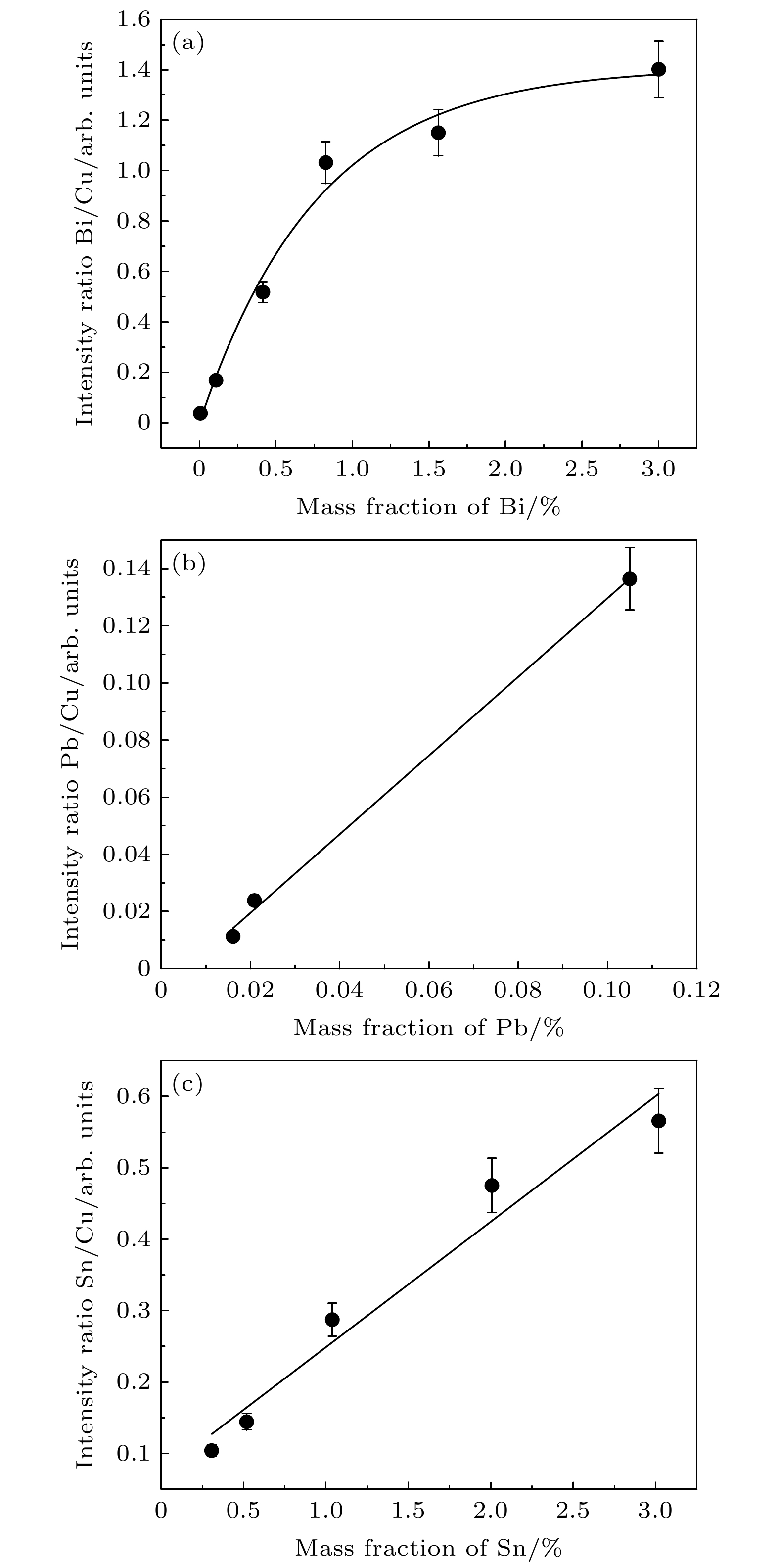
铋黄铜具有很好的机械加工性能且更为环保, 具有广泛的应用. 本文采用高重复频率激光剥离-火花诱导击穿光谱技术来实现铋黄铜中微量元素的快速和高灵敏分析. 实验采用小型化光纤激光器作为剥离光源, 采用小型化光纤光谱仪采集光谱, 对铋黄铜中的铋、铅和锡三元素开展了定量分析. 实验确定等离子体的温度和电子密度分别为7962 ± 300 K 和1.049 × 10–17 cm–3. 在该条件下建立了铋、铅和锡三元素的校正曲线, 并得到了较好的拟合优度. 现有条件下三元素的检测限分别达到了25.5 × 10–6, 64.2 × 10–6和316.5 × 10–6. 其中锡的检出限较高, 与锡的原子谱线强度较弱有关. 结果表明, 采用小型化的高重复频率激光剥离-火花诱导击穿光谱仪可以实现对铋黄铜中微量元素的便捷和高灵敏分析.Bismuth brass has very good mechanical properties and is friendly to environment. Therefore, it can be widely used in different fields. In order to realize the convenient, rapid and sensitive elemental analysis of trace elements in bismuth brass, fiber laser based high repetition rate laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectroscopy (HRR LA-SIBS) is developed. In the experiments, a compact fiber laser operated at 5 kHz pulse repetition rate is used to ablate the sample and produce plasma, and the spark discharge is used to further break down the ablated sample and enhance the plasma emission for sensitive elemental analysis. A compact fiber-optic spectrometer coupled with non-intensified charge-coupled device (CCD) is used to record the spectra. Bismuth, lead and tin in several bismuth brass standard samples are quantitatively analyzed. The plasma temperature is determined to be about 7962 ± 300 K by using the Boltzmann plots of copper, zinc and tin elements; the electron density is determined to be about 1.049 × 10–17 cm–3 based on the Stark broadening of Cu (I) 510.47 nm analytical line. The plasma is determined to be in local thermodynamic equilibrium (LTE) state according to McWhirter criterion as well as appended criteria for transient plasma. Under the present experimental condition, the calibration curves of bismuth, lead and tin in bismuth brass are built with fitting goodness of higher than 95%. The detection limits of bismuth, lead and tin are determined to be 25.5 ppm, 64.2 ppm and 316.5 ppm, respectively. The weak transition probability of tin atoms leads to worse detection limit of tin than the scenarios of bismuth and lead. The ways to further improve the analytical sensitivity and minimize system dimensions are discussed in this article. It is demonstrated that high repetition rate laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectrometer based on compact fiber laser as well as compact fiber-optic spectrometer can be used to realize the convenient, rapid and sensitive elemental analysis of trace elements in bismuth brass. This study is also helpful in analyzing the trace harmful elements, including bismuth, lead and tin in high temperature alloys with HRR LA-SIBS. In comparison with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), the HRR LA-SIBS technique has several intrinsic advantages, such as fast spectral data collection speed, cost-effective system and low continuum background and so on. This technique is very useful in implementing the elemental analysis of different alloy samples and can be potentially used in metallurgical industry in the future.
-
Keywords:
- laser-ablation /
- spark-induced breakdown spectroscopy /
- bismuth brass /
- elemental analysis /
- compact
[1] 肖来荣, 舒学鹏, 易丹青, 张路怀, 覃静丽, 胡加瑞 2009 中南大学学报 (自然科学版) 40 117
Xiao L R, Shu X P, Yi D Q, Zhang L H, Qin J L, Hu J R 2009 J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 40 117
[2] Thangavel S, Dash K, Dhavile S M, Sahayam A C 2015 Talanta 131 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu D, Wang X, Ni X W, Cheng J P, Lu J 2011 Plasma Sci. Technol. 13 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao T Z, Fan Z W, Lian F Q, Liu Y, Lin W R, Mo Z Q, Nie S Z, Wang P, Xiao H, Li X, Zhong Q X, Zhang H G 2017 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 137 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gojani A B 2012 ISRN Spectrosc. 2012 868561
[6] 崔执凤, 张先, 姚关心, 汪小丽, 许新胜, 郑贤锋, 凤尔银, 季学韩 2006 55 4506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Z F, Zhang X, Yao G X, Wang X L, Xu X S, Zheng X F, Feng E Y, Ji X H 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 4506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陈添兵, 姚明印, 刘木华, 林永增, 黎文兵, 郑美兰, 周华茂 2014 63 104213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen T B, Yao M Y, Liu M H, Lin Y Z, Li W B, Zheng M L, Zhou H M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 杜闯, 高勋, 邵妍, 宋晓伟, 赵振明, 郝作强, 林景全 2013 62 045202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du C, Gao X, Shao Y, Song X W, Zhao Z M, Hao Z Q, Lin J Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 045202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li C M, Hao Z Q, Zou Z M, Zhou R, Li J M, Guo L B, Li X Y, Lu Y F, Zeng X Y 2016 Opt. Express 24 7850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Laville S, Goueguel C, Loudyi H, Vidal F, Chaker M, Mohamad S 2009 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 64 347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y R, Kang J, Chen Y Q, Li R H 2019 J. Appl. Spectrosc. 86 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kang J, Chen Y Q, Li R H 2019 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 161 105711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jiang Y H, Li R H, Chen Y Q 2019 J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 34 1838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] He X Y, Li R H, Wang F J 2019 Plasma Sci. Technol. 21 034005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ciucci A, Corsi M, Palleschi V, Rastelli S, Tognoni E 1999 Appl. Spectrosc. 53 960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zmerli B, Ben Nessib N, Dimitrijevi M S, Sahal-Bréchot S 2010 Phys. Scr. 82 055301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao J K, Kang J, Li R H, Chen Y Q 2020 Appl. Opt. 59 4091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cristoforetti G, Giacomo A D, Dell’Aglio M, Legnaioli S, Tognoni E, Palleschi V, Omenetto N 2010 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 65 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Regemorter H V 1962 Astrophys. J. 136 906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Aragon C, Aguilera J A, Penalba F 1999 Appl. Spectrosc. 53 1259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen Z J, Li H K, Zhao F, Li R H 2008 J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 23 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 标准样品中铋、铅和锡元素的质量分数
Table 1. List of the mass fraction (%) of bismuth, lead and tin in standard samples.
Sample No. Bi Pb Sn 1 3.002 0.0054 1.038 2 0.414 0.105 0.306 3 1.561 0.0161 0.518 4 0.826 0.0209 2.007 5 0.108 0.0059 3.020 6 0.0058 — — 表 2 计算等离子体温度所选择的谱线及相应能级与跃迁参数列表
Table 2. List of the energy level and transition probability of the selected lines for plasma temperature calculation.
Species $\lambda $/nm A/s–1 gk Ek/eV Cu Ⅰ 261.83 3.07 × 107 4 6.120 Cu Ⅰ 282.43 0.78 × 107 6 5.780 Cu Ⅰ 306.34 1.55 × 106 4 5.688 Cu Ⅰ 319.40 1.55 × 106 4 5.523 Cu Ⅰ 333.78 0.38 × 106 8 5.102 Cu Ⅰ 406.26 2.10 × 107 6 6.868 Cu Ⅰ 510.55 0.20 × 107 4 3.820 Cu Ⅰ 515.32 0.60 × 108 4 6.190 Zn Ⅰ 307.58 0.38 × 106 3 4.030 Zn Ⅰ 328.23 9.00 × 107 3 7.780 Zn Ⅰ 330.25 1.20 × 108 5 7.783 Zn Ⅰ 334.50 1.70 × 108 7 7.783 Sn Ⅰ 242.94 1.50 × 108 7 5.527 Sn Ⅰ 270.65 6.60 × 107 5 4.789 Sn Ⅰ 283.99 1.70 × 108 5 4.789 Sn Ⅰ 286.33 5.40 × 107 3 4.329 Sn Ⅰ 300.91 3.80 × 107 3 4.329 Sn Ⅰ 303.41 2.00 × 108 1 4.295 Sn Ⅰ 317.50 1.00 × 108 3 4.329 Sn Ⅰ 326.23 2.70 × 108 3 4.867 表 3 铋黄铜中铋、铅、锡三元素的HRR LA-SIBS分析结果
Table 3. Analytical results of bismuth, lead and tin in bismuth brass with HRR LA-SIBS.
Analytical line S σB R2 LOD/10–6 Bi Ⅰ 306.77 nm 1.818 0.00155 0.98 25.5 Pb Ⅰ 405.78 nm 1.376 0.0029 0.98 64.2 Sn Ⅰ 326.23 nm 0.210 0.0022 0.96 316.5 -
[1] 肖来荣, 舒学鹏, 易丹青, 张路怀, 覃静丽, 胡加瑞 2009 中南大学学报 (自然科学版) 40 117
Xiao L R, Shu X P, Yi D Q, Zhang L H, Qin J L, Hu J R 2009 J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 40 117
[2] Thangavel S, Dash K, Dhavile S M, Sahayam A C 2015 Talanta 131 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu D, Wang X, Ni X W, Cheng J P, Lu J 2011 Plasma Sci. Technol. 13 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao T Z, Fan Z W, Lian F Q, Liu Y, Lin W R, Mo Z Q, Nie S Z, Wang P, Xiao H, Li X, Zhong Q X, Zhang H G 2017 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 137 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gojani A B 2012 ISRN Spectrosc. 2012 868561
[6] 崔执凤, 张先, 姚关心, 汪小丽, 许新胜, 郑贤锋, 凤尔银, 季学韩 2006 55 4506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Z F, Zhang X, Yao G X, Wang X L, Xu X S, Zheng X F, Feng E Y, Ji X H 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 4506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陈添兵, 姚明印, 刘木华, 林永增, 黎文兵, 郑美兰, 周华茂 2014 63 104213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen T B, Yao M Y, Liu M H, Lin Y Z, Li W B, Zheng M L, Zhou H M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 杜闯, 高勋, 邵妍, 宋晓伟, 赵振明, 郝作强, 林景全 2013 62 045202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du C, Gao X, Shao Y, Song X W, Zhao Z M, Hao Z Q, Lin J Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 045202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li C M, Hao Z Q, Zou Z M, Zhou R, Li J M, Guo L B, Li X Y, Lu Y F, Zeng X Y 2016 Opt. Express 24 7850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Laville S, Goueguel C, Loudyi H, Vidal F, Chaker M, Mohamad S 2009 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 64 347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y R, Kang J, Chen Y Q, Li R H 2019 J. Appl. Spectrosc. 86 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kang J, Chen Y Q, Li R H 2019 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 161 105711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jiang Y H, Li R H, Chen Y Q 2019 J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 34 1838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] He X Y, Li R H, Wang F J 2019 Plasma Sci. Technol. 21 034005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ciucci A, Corsi M, Palleschi V, Rastelli S, Tognoni E 1999 Appl. Spectrosc. 53 960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zmerli B, Ben Nessib N, Dimitrijevi M S, Sahal-Bréchot S 2010 Phys. Scr. 82 055301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao J K, Kang J, Li R H, Chen Y Q 2020 Appl. Opt. 59 4091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cristoforetti G, Giacomo A D, Dell’Aglio M, Legnaioli S, Tognoni E, Palleschi V, Omenetto N 2010 Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 65 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Regemorter H V 1962 Astrophys. J. 136 906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Aragon C, Aguilera J A, Penalba F 1999 Appl. Spectrosc. 53 1259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen Z J, Li H K, Zhao F, Li R H 2008 J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 23 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7832
- PDF下载量: 64
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: