-
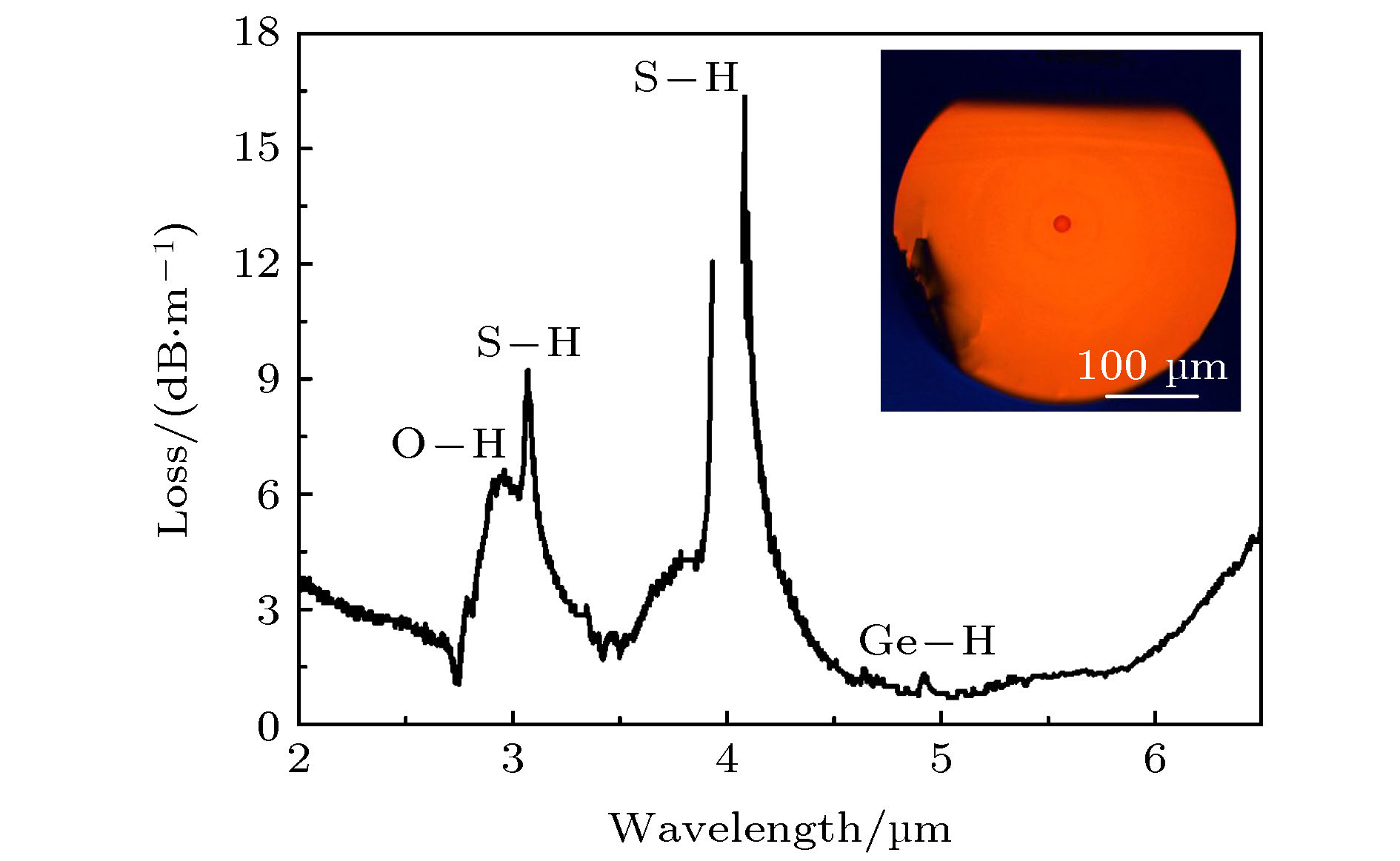
测量了Ge-As-S系列硫系玻璃在中红外波段的飞秒激光损伤阈值, 研究了它与玻璃化学组成的关系. 基于优化的玻璃组成, 采用棒管法制备了芯径为15 μm的阶跃折射率非线性光纤. 采用飞秒脉冲抽运光纤, 研究了光纤中超连续谱(supercontinuum, SC)的产生特性. 在研究的Ge-As-S硫系玻璃中, 具有化学计量配比的Ge0.25As0.1S0.65玻璃显示出最高的激光损伤阈值. 以该玻璃作为纤芯材料、以与其相匹配的Ge0.26As0.08S0.66玻璃作为包层材料制备的光纤的数值孔径约为0.24, 背景损耗 < 2 dB/m. 采用4.8 μm的飞秒激光抽运长度为10 cm的光纤, 获得了覆盖2.5—7.5 μm的SC. 这些结果表明, Ge-As-S硫系玻璃光纤是一种有潜力的中红外高亮度宽带SC产生的非线性介质.
High-brightness broadband mid-infrared supercontinuum sources are highly demanded for many applications such as remote sensing, environmental monitoring, manufacturing industry, medical surgery and thermal imaging. For fulfilling these applications, high average power output is required. Compared with all other mid-infrared glass fibers, chalcogenide glass fiber possesses low phonon energy, long wavelength transmission edge, and high Kerr nonlinearity, thereby becoming a uniquely ideal nonlinear optical material for generating broadband mid-infrared supercontinuum. Unfortunately, due to weak chemical bonds forming the glass network, the commonly used As-S chalcogenide glass has a relatively low laser damage threshold. Thus from the material aspect, it limits high power yielded from a chalcogenide fiber based mid-infrared supercontinuum source. A chalcogenide glass host with enhanced laser damage threshold is therefore needed for further power scaling up of such a mid-infrared fiber supercontinuum. In this work, we introduce germanium into a traditional As-S glass system. The laser damage threshold of Ge-As-S glass is investigated systematically. A 3.6-μm femtosecond laser is employed as an excitation source. The relationship between the laser damage threshold and the glass composition indicates that of the studied Ge-As-S chalcogenide glasses, stoichiometric Ge0.25As0.1S0.65 glass possesses the highest laser damage threshold. In the following fiber design and fabrication, the optimized stoichiometric Ge0.25As0.1S0.65 glass therefore is chosen as a core material of the designed fiber, while a compatible Ge0.26As0.08S0.66 glass is selected as a cladding material. A step-index nonlinear fiber with a core diameter of 15 μm is fabricated by the traditional rod-in-tube method. The numerical aperture and the background loss of the fabricated Ge0.25As0.1S0.65/Ge0.26As0.08S0.66 fiber are ~0.24 and < 2 dB/m, respectively. Broadband mid-infrared supercontinuum is generated in the fiber by using an anomalous-dispersion pumping scheme. A 4.8-μm femtosecond laser with a pulse duration of 170 femtosecond and a repetition rate of 100 kHz is adopted as a pump source. The guidance of the fundamental mode is confirmed under low pump power level. With the increase of the pump power, the supercontinuum shows to be significantly broadened. Broadband supercontinuum ranging from 2.5 μm to 7.5 μm is generated in an only 10-cm-long fiber, when the maximum coupled pump power is 15 mW, equivalent to a peak power of 882 kW. The power output of the supercontinuum is 5.5 mW. All in all, the results indicate that the Ge-As-S chalcogenide glass fiber is a promising nonlinear medium for broadband mid-infrared supercontinuum sources with high brightness. [1] Petersen C R, Moller U, Kubat I, Zhou B, Dupont S, Ramsay J, Benson T, Sujecki S, Abdel-Moneim N, Tang Z, Furniss D, Seddon A, Bang O 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yu Y, Gai X, Ma P, Vu K, Yang Z, Wang R, Choi D Y, Madden S, Luther-Davies B 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 958
[3] Cheng T, Nagasaka K, Tuan T H, Xue X, Matsumoto M, Tezuka H, Suzuki T, Ohishi Y 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shi H, Feng X, Tan F, Wang P, Wang P 2016 Opt. Mater. Express 6 3967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jiang X, Joly N Y, Finger M A, Babic F, Wong G K L, Travers J C, Russell P S J 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao Z, Chen P, Wang X, Xue Z, Tian Y, Jiao K, Wang X-g, Peng X, Zhang P, Shen X, Dai S, Nie Q, Wang R 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 5172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei H F, Chen S P, Hou J, Chen K K, Li J Y 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 64202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Boivin M, El-Amraoui M, Ledemi Y, Celarie F, Vallee R, Messaddeq Y 2016 Opt. Mater. Express 6 1653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rezvani S A, Nomura Y, Ogawa K, Fuji T 2019 Opt. Express 27 24499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li G, Peng X, Dai S, Wang Y, Xie M, Yang L, Yang C, Wei W, Zhang P 2018 J. Lightwave Technol. 37 1847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang B, Yu Y, Zhai C, Qi S, Wang Y, Yang A, Gai X, Wang R, Yang Z, Luther-Davies B 2016 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99 2565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao Z, Wu B, Wang X, Pan Z, Liu Z, Zhang P, Shen X, Nie Q, Dai S, Wang R 2017 Laser Photonics Rev. 11 1700005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dai S, Wang Y, Peng X, Zhang P, Wang X, Xu Y 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yao C, Jia Z, Li Z, Jia S, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Feng Y, Qin G, Ohishi Y, Qin W 2018 Optica 5 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gattass R R, Shaw L B, Nguyen V Q, Pureza P C, Aggarwal I D, Sanghera J S 2012 Opt. Fiber Technol. 18 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Robichaud L R, Duval S, Pleau L P, Fortin V, Bah S T, Chatigny S, Vallee R, Bernier M 2020 Opt. Express 28 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang M, Li T, Yang Y, Tao H, Zhang X, Yuan X, Yang Z 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] You C, Dai S, Zhang P, Xu Y, Wang Y, Xu D, Wang R 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 6497
[19] Zhu L, Yang D, Wang L, Zeng J, Zhang Q, Xie M, Zhang P, Dai S 2018 Opt. Mater. 85 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang Y, Xu Y, You C, Xu D, Tang J, Zhang P, Dai S 2017 Opt. Express 25 8886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Messaddeq S H, Vallee R, Soucy P, Bernier M, El-Amraoui M, Messaddeq Y 2012 Opt. Express 20 29882
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 李铜铜, 张鸣杰, 田康振, 张翔, 袁孝, 杨安平, 杨志勇 2019 光学学报 39 1016001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li T T, Zhang M J, Tian K Z, Zhang X, Yuan X, Yang A P, Yang Z Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 1016001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang M, Li L, Li T, Wang F, Tian K, Tao H, Feng X, Yang A, Yang Z 2019 Opt. Express 27 29287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun M, Yang A, Zhang X, Ma H, Zhang M, Tian K, Feng X, Yang Z 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 6600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang M, Yang Z, Zhao H, Yang A, Li L, Tao H 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 722 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lu X, Lai Z, Zhang R, Guo H, Ren J, Strizik L, Wagner T, Farrell G, Wang P 2019 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39 3373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 乔北京, 陈飞飞, 黄益聪, 戴世勋, 聂秋华, 徐铁峰 2015 64 154216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao B J, Chen F F, Huang Y C, Dai S X, Nie Q H, Xu T F 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 154216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu L, Zheng X, Xiao X, Xu Y, Cui X, Cui J, Guo C, Yang J, Guo H 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 3582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 杨艳, 陈云翔, 刘永华, 芮扬, 曹烽燕, 杨安平, 祖成奎, 杨志勇 2016 65 127801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Chen Y X, Liu Y H, Rui Y, Cao F Y, Yang A P, Zu C K, Yang Z Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 127801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang Y, Zhang B, Yang A, Yang Z, Lucas P 2015 J. Phys. Chem. B 119 5096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang B, Guo W, Yu Y, Zhai C, Qi S, Yang A, Li L, Yang Z, Wang R, Tang D, Tao G, Luther-Davies B 2015 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98 1389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Snopatin G E, Shiryaev V S, Plotnichenko V G, Dianov E M, Churbanov M F 2009 Inorg. Mater. 45 1439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Nguyen V Q, Sanghera J S, Kung F H, Aggarwal I D, Lloyd I K 1999 Appl. Opt. 38 3206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Dudley J M, Genty G, Coen S 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Biancalana F, Skryabin D V, Yulin A V 2004 Phys. Rev. E 70 016615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Eftekhar M A, Wright L G, Mills M S, Kolesik M, Correa R A, Wise F W, Christodoulides D N 2017 Opt. Express 25 9078
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 7 (a) Ge-As-S光纤输出光斑; (b) 采用4.8 μm激光(170 fs, 100 kHz)抽运芯径为15 μm的Ge0.25As0.1S0.65/Ge0.26As0.08S0.66玻璃光纤获得的SC输出
Fig. 7. (a) Measured light spot at the output end of the Ge-As-S fiber; (b) Measured SC generated in the Ge0.25As0.1S0.65/Ge0.26As0.08S0.66 fiber with a core diameter of 15 µm when pumped at 4.8 µm (170 fs, 100 kHz).
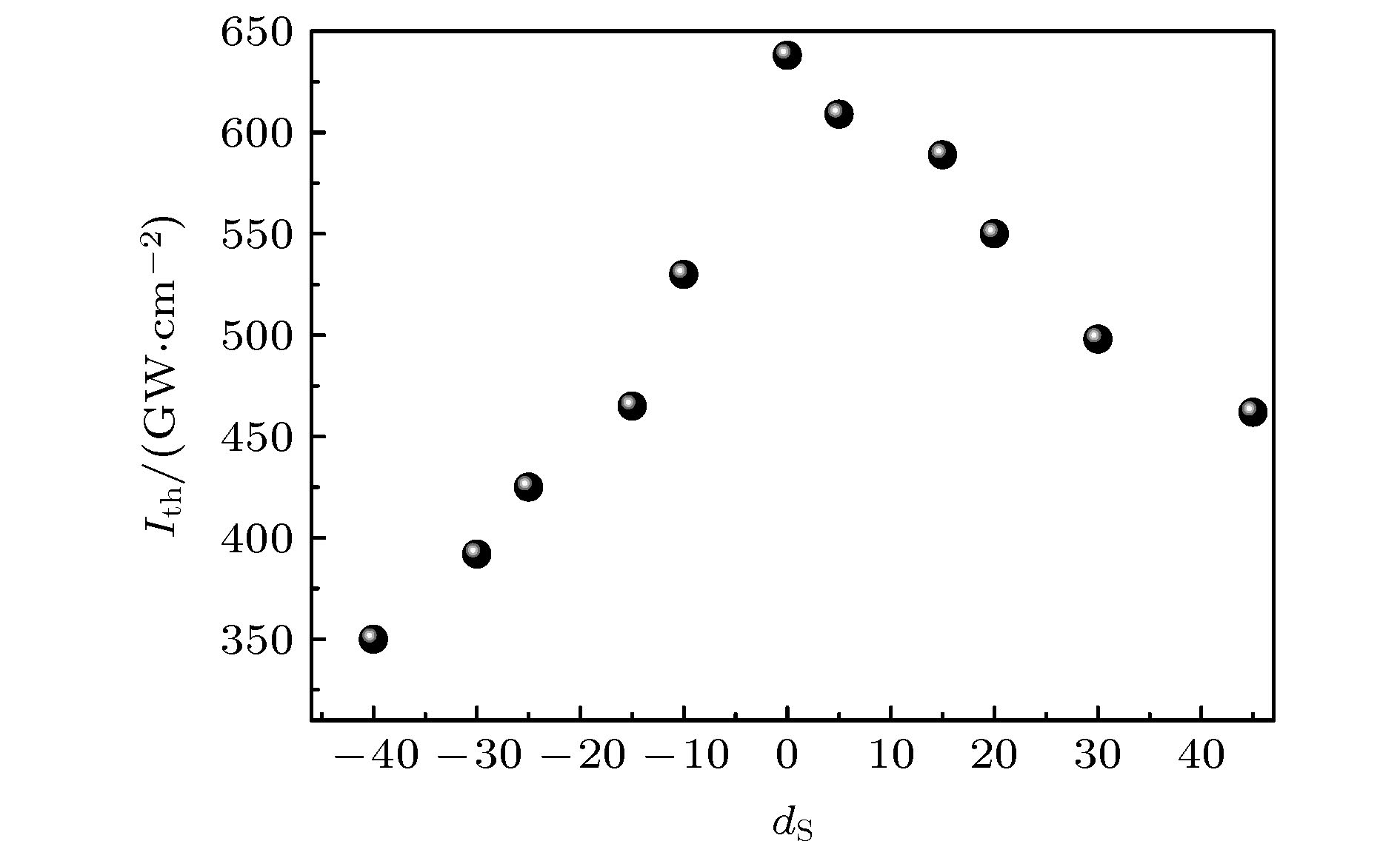
表 1 Ge-As-S玻璃在中心波长为3.6 μm、脉冲宽度为170 fs、重复频率为100 kHz激光辐照下的Ith
Table 1. Ith of Ge-As-S glasses under the irradiation of 170 fs pulses with the repetition rates of 100 kHz at 3.6 μm.
Composition dS /at. % Ith/GW·cm–2 Ge0.1As0.1S0.8 45 462 Ge0.15As0.1S0.75 30 498 Ge0.1As0.2S0.7 20 550 Ge0.2As0.1S0.7 15 589 Ge0.15As0.2S0.65 5 609 Ge0.25As0.1S0.65 0 638 Ge0.2As0.2S0.6 –10 530 Ge0.3As0.1S0.6 –15 465 Ge0.25As0.20S0.55 –25 425 Ge0.35As0.1S0.55 –30 392 Ge0.3As0.2S0.5 –40 350 -
[1] Petersen C R, Moller U, Kubat I, Zhou B, Dupont S, Ramsay J, Benson T, Sujecki S, Abdel-Moneim N, Tang Z, Furniss D, Seddon A, Bang O 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yu Y, Gai X, Ma P, Vu K, Yang Z, Wang R, Choi D Y, Madden S, Luther-Davies B 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 958
[3] Cheng T, Nagasaka K, Tuan T H, Xue X, Matsumoto M, Tezuka H, Suzuki T, Ohishi Y 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shi H, Feng X, Tan F, Wang P, Wang P 2016 Opt. Mater. Express 6 3967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jiang X, Joly N Y, Finger M A, Babic F, Wong G K L, Travers J C, Russell P S J 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao Z, Chen P, Wang X, Xue Z, Tian Y, Jiao K, Wang X-g, Peng X, Zhang P, Shen X, Dai S, Nie Q, Wang R 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 5172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei H F, Chen S P, Hou J, Chen K K, Li J Y 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 64202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Boivin M, El-Amraoui M, Ledemi Y, Celarie F, Vallee R, Messaddeq Y 2016 Opt. Mater. Express 6 1653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rezvani S A, Nomura Y, Ogawa K, Fuji T 2019 Opt. Express 27 24499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li G, Peng X, Dai S, Wang Y, Xie M, Yang L, Yang C, Wei W, Zhang P 2018 J. Lightwave Technol. 37 1847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang B, Yu Y, Zhai C, Qi S, Wang Y, Yang A, Gai X, Wang R, Yang Z, Luther-Davies B 2016 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99 2565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao Z, Wu B, Wang X, Pan Z, Liu Z, Zhang P, Shen X, Nie Q, Dai S, Wang R 2017 Laser Photonics Rev. 11 1700005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dai S, Wang Y, Peng X, Zhang P, Wang X, Xu Y 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yao C, Jia Z, Li Z, Jia S, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Feng Y, Qin G, Ohishi Y, Qin W 2018 Optica 5 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gattass R R, Shaw L B, Nguyen V Q, Pureza P C, Aggarwal I D, Sanghera J S 2012 Opt. Fiber Technol. 18 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Robichaud L R, Duval S, Pleau L P, Fortin V, Bah S T, Chatigny S, Vallee R, Bernier M 2020 Opt. Express 28 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang M, Li T, Yang Y, Tao H, Zhang X, Yuan X, Yang Z 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] You C, Dai S, Zhang P, Xu Y, Wang Y, Xu D, Wang R 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 6497
[19] Zhu L, Yang D, Wang L, Zeng J, Zhang Q, Xie M, Zhang P, Dai S 2018 Opt. Mater. 85 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang Y, Xu Y, You C, Xu D, Tang J, Zhang P, Dai S 2017 Opt. Express 25 8886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Messaddeq S H, Vallee R, Soucy P, Bernier M, El-Amraoui M, Messaddeq Y 2012 Opt. Express 20 29882
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 李铜铜, 张鸣杰, 田康振, 张翔, 袁孝, 杨安平, 杨志勇 2019 光学学报 39 1016001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li T T, Zhang M J, Tian K Z, Zhang X, Yuan X, Yang A P, Yang Z Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 1016001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang M, Li L, Li T, Wang F, Tian K, Tao H, Feng X, Yang A, Yang Z 2019 Opt. Express 27 29287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun M, Yang A, Zhang X, Ma H, Zhang M, Tian K, Feng X, Yang Z 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 6600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang M, Yang Z, Zhao H, Yang A, Li L, Tao H 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 722 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lu X, Lai Z, Zhang R, Guo H, Ren J, Strizik L, Wagner T, Farrell G, Wang P 2019 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39 3373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 乔北京, 陈飞飞, 黄益聪, 戴世勋, 聂秋华, 徐铁峰 2015 64 154216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao B J, Chen F F, Huang Y C, Dai S X, Nie Q H, Xu T F 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 154216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu L, Zheng X, Xiao X, Xu Y, Cui X, Cui J, Guo C, Yang J, Guo H 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 3582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 杨艳, 陈云翔, 刘永华, 芮扬, 曹烽燕, 杨安平, 祖成奎, 杨志勇 2016 65 127801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Chen Y X, Liu Y H, Rui Y, Cao F Y, Yang A P, Zu C K, Yang Z Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 127801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang Y, Zhang B, Yang A, Yang Z, Lucas P 2015 J. Phys. Chem. B 119 5096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang B, Guo W, Yu Y, Zhai C, Qi S, Yang A, Li L, Yang Z, Wang R, Tang D, Tao G, Luther-Davies B 2015 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98 1389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Snopatin G E, Shiryaev V S, Plotnichenko V G, Dianov E M, Churbanov M F 2009 Inorg. Mater. 45 1439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Nguyen V Q, Sanghera J S, Kung F H, Aggarwal I D, Lloyd I K 1999 Appl. Opt. 38 3206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Dudley J M, Genty G, Coen S 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Biancalana F, Skryabin D V, Yulin A V 2004 Phys. Rev. E 70 016615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Eftekhar M A, Wright L G, Mills M S, Kolesik M, Correa R A, Wise F W, Christodoulides D N 2017 Opt. Express 25 9078
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9472
- PDF下载量: 148
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: