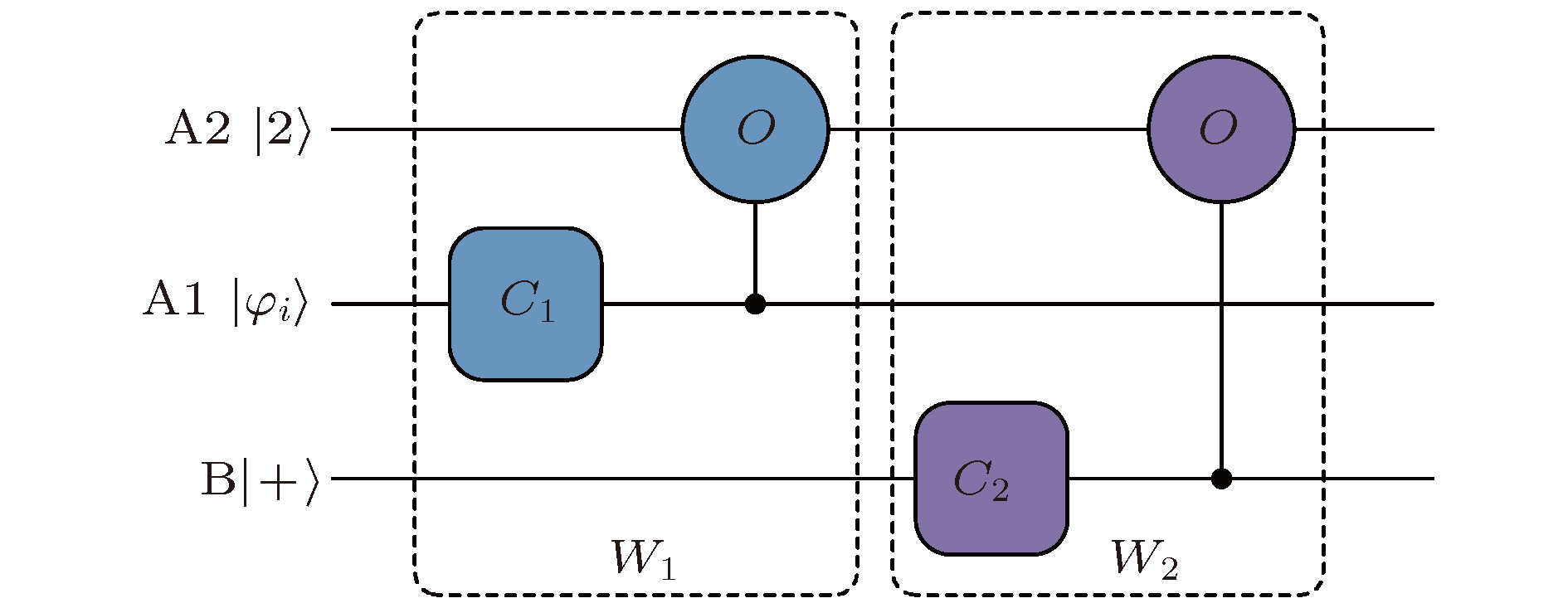
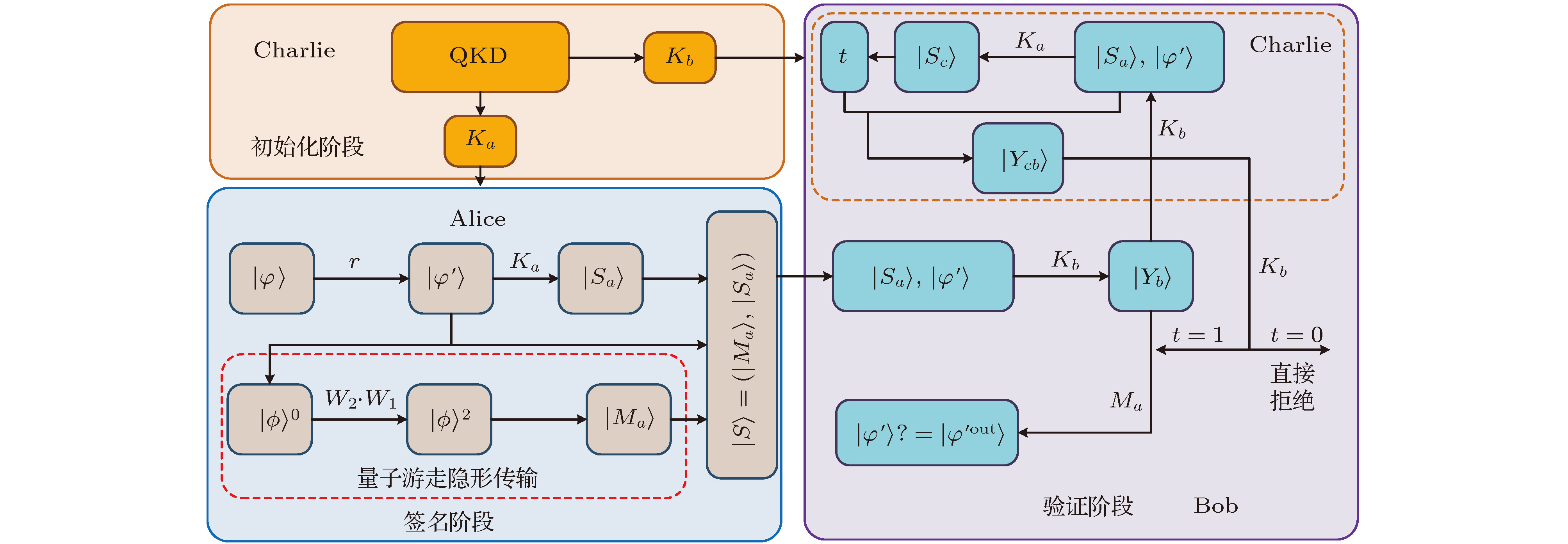
-
基于量子游走的量子隐形传输模型, 提出了一种仲裁量子签名方案. 发送者编码要签名的信息在硬币态上, 并应用硬币态和位置态之间的条件相移算符产生用于量子隐形传输必需的纠缠态. 对生成的纠缠态测量可作为签名设计和信息恢复依据. 然后, 接收者依据来自发送者的测量结果测量其量子态, 进而验证签名的有效性和信息的真实性、完整性. 由于量子游走的应用, 本签名方案的初始化阶段不需要提前制备必须的纠缠态. 安全性分析表明方案满足不可抵赖、不可伪造和不可否认特性, 讨论和比较展示了键控链式受控非加密算法和随机数的使用可以抵抗已有方案中的抵赖和存在性伪造攻击. 此外, 量子游走已经被证明可以在多种不同的物理系统中和实验上实现, 因此本签名方案未来也许是可实现的.
Quantum signature is quantum counterpart of classical digital signature, which has been widely applied to modern communication, such as electronic payment, electronic voting and electronic medical, owing to its great implication in ensuring the authenticity and the integrity of the message and the non-repudiation. Arbitrated quantum signature (AQS) is an important and practical type of quantum signature. The AQS algorithm is a symmetric key cryptography-based quantum signature algorithm, and its implementation requires the trusted arbitrator to be directly involved. In this paper, employing the key-controlled chained CNOT (KCCC) operation as the appropriate encryption (decryption) algorithm, we suggest an AQS scheme based on teleportation of quantum walks with two coins on a four-vertex cycle, which is used to transfer the message copy from the sender to the receiver. In light of the model of teleportation of quantum walks, the sender encodes the message to be signed into her or his coin state, and the necessary entangled states can be created as a result of the conditional shift between the coin state and the position state. The measurements performed on the generated entangled states are the bases of signature production and message recovery. Then according to the classical measurement results from the sender, the receiver performs the appropriate local unitary operations (i.e., Pauli operations) on his own coin state to recover the original message and further verifies the validity of the completed signature by using the appropriate verification algorithms under the aid of the trustworthy arbitrator. The suggested AQS scheme makes the following contributions: 1) the necessary entangled states for quantum teleportation of message copy do not need preparing in advance, and they can be produced automatically by the first step of quantum walks; 2) the scheme satisfies the features of non-repudiation, un-forgeability and non-disavowal due to the use of the KCCC operation; 3) the scheme may be achieved by linear optical elements such as beam splitters, wave plates, etc., because quantum walks have proven to be realizable in different physical systems and experiments. Analysis and discussion show that the proposed AQS scheme possesses the impossibility of disavowals by the signer and the receiver and impossibility of forgeries by anyone. Comparisons reveal that the designed AQS protocol is favorable. Furthermore, it provides an idea by employing the quantum computing model into quantum communication protocols with a possible improvement with respect to its favorable properties, for example, the automatic generation of entangled states via the first step of quantum walks on different models. In the near future, we will further investigate the production of entanglement by quantum walks and its applications with some improvements in designing the quantum communication protocols. -
Keywords:
- quantum cryptography /
- arbitrated quantum signature /
- quantum walk-based teleportation /
- key-controlled chained CNOT operation
[1] Meijer H, Akl S 1981 ACM SIGCOMM Comp. Com. 11 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zeng G, Keitel C H 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 042312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nielsen M A, Chuang I, Grover L K 2002 Am. J. Phys. 70 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Guo Y, Xie C L, Liao Q, Zhao W, Zeng G H, Huang D 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 022320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Guo Y, Liao Q, Wang Y, Wang Y J, Huang D, Huang P, Zeng G H 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 032304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xu G, Chen X B, Dou Z, Yang Y X, Li Z 2015 Quantum Inf. Process. 14 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen X B, Sun Y R, Xu G, Jia H Y, Qu Z, Yang Y X 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chen X B, Tang X, Xu G, Dou Z, Chen Y L, Yang Y X 2018 Quantum Inf. Process. 17 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Curty M, Lütkenhaus N 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 046301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zeng G 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 016301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li Q, Chan W H, Long D Y 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 054307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zou X, Qiu D 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 042325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gao F, Qin S J, Guo F Z, Wen Q Y 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 022344
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Choi J W, Chang K Y, Hong D 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 062330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张骏, 吴吉义 2013 北京邮电大学学报 36 113
Zhang J, Wu J Y 2013 J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. 36 113
[16] Li F G, Shi J H 2015 Quantum Inf. Process. 14 2171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang Y G, Lei H, Liu Z C, Zhou Y H, Shi W M 2016 Quantum Inf. Process. 15 2487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang L, Sun H W, Zhang K J, Jia H Y 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y, Zeng J 2018 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Guo Y, Feng Y Y, Huang D Z, Shi J J 2016 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55 2290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Feng Y Y, Shi R H, Guo Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 020302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Aharonov Y, Davidovich L, Zagury N 1993 Phys. Rev. A 48 1687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Venegas-Andraca S E 2012 Quantum Inf. Process. 11 1015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kempe J 2003 Contemp. Phys. 44 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Y, Shang Y, Xue P 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shang Y, Wang Y, Li M, Lu R Q 2019 EPL- Europhys. Lett. 124 60009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen X B, Wang Y L, Xu G, Yang Y X 2019 IEEE Access 7 13634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zou X, Dong Y, Guo G 2006 New J. Phys. 8 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bian Z H, Li J, Zhan X, Twamley J, Xue P 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 052338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tang H, Lin X F, Feng Z, Chen J Y, Gao J, Sun K, Wang C Y, Lai P C, Xu X Y, Wang Y, Qiao L F, Yang A L, Jin X M 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaat3174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Aharonov D, Ambainis A, Kempe J, Vazirani U 2001 Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing New York, USA, 2001 p50
[32] Xue P, Zhang R, Qin H, Zhan X, Bian Z H, Li J, Sanders Barry C 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 140502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 测量结果与对应的恢复操作
Table 1. Measurement outcomes and the corresponding recovery operations.
A2和A1的测量结果 幺正操作 2, 1 I 2, –1 Z 0, 1 X 0, –1 $ZX$ 表 2 协议比较
Table 2. Protocols comparison.
-
[1] Meijer H, Akl S 1981 ACM SIGCOMM Comp. Com. 11 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zeng G, Keitel C H 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 042312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nielsen M A, Chuang I, Grover L K 2002 Am. J. Phys. 70 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Guo Y, Xie C L, Liao Q, Zhao W, Zeng G H, Huang D 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 022320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Guo Y, Liao Q, Wang Y, Wang Y J, Huang D, Huang P, Zeng G H 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 032304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xu G, Chen X B, Dou Z, Yang Y X, Li Z 2015 Quantum Inf. Process. 14 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen X B, Sun Y R, Xu G, Jia H Y, Qu Z, Yang Y X 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chen X B, Tang X, Xu G, Dou Z, Chen Y L, Yang Y X 2018 Quantum Inf. Process. 17 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Curty M, Lütkenhaus N 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 046301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zeng G 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 016301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li Q, Chan W H, Long D Y 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 054307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zou X, Qiu D 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 042325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gao F, Qin S J, Guo F Z, Wen Q Y 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 022344
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Choi J W, Chang K Y, Hong D 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 062330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张骏, 吴吉义 2013 北京邮电大学学报 36 113
Zhang J, Wu J Y 2013 J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. 36 113
[16] Li F G, Shi J H 2015 Quantum Inf. Process. 14 2171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang Y G, Lei H, Liu Z C, Zhou Y H, Shi W M 2016 Quantum Inf. Process. 15 2487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang L, Sun H W, Zhang K J, Jia H Y 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y, Zeng J 2018 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Guo Y, Feng Y Y, Huang D Z, Shi J J 2016 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55 2290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Feng Y Y, Shi R H, Guo Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 020302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Aharonov Y, Davidovich L, Zagury N 1993 Phys. Rev. A 48 1687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Venegas-Andraca S E 2012 Quantum Inf. Process. 11 1015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kempe J 2003 Contemp. Phys. 44 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Y, Shang Y, Xue P 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shang Y, Wang Y, Li M, Lu R Q 2019 EPL- Europhys. Lett. 124 60009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen X B, Wang Y L, Xu G, Yang Y X 2019 IEEE Access 7 13634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zou X, Dong Y, Guo G 2006 New J. Phys. 8 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bian Z H, Li J, Zhan X, Twamley J, Xue P 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 052338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tang H, Lin X F, Feng Z, Chen J Y, Gao J, Sun K, Wang C Y, Lai P C, Xu X Y, Wang Y, Qiao L F, Yang A L, Jin X M 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaat3174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Aharonov D, Ambainis A, Kempe J, Vazirani U 2001 Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing New York, USA, 2001 p50
[32] Xue P, Zhang R, Qin H, Zhan X, Bian Z H, Li J, Sanders Barry C 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 140502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9352
- PDF下载量: 97
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: