-
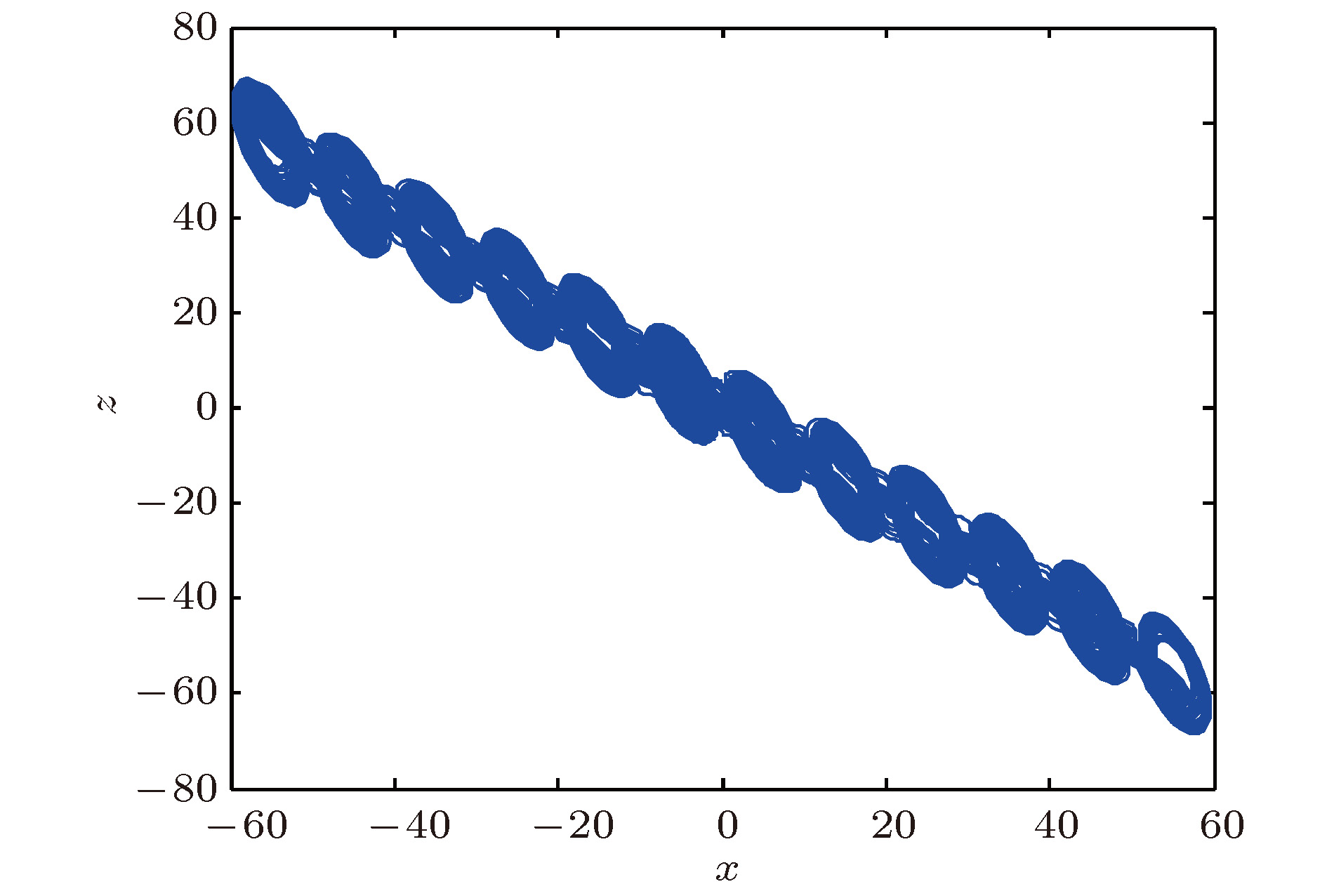
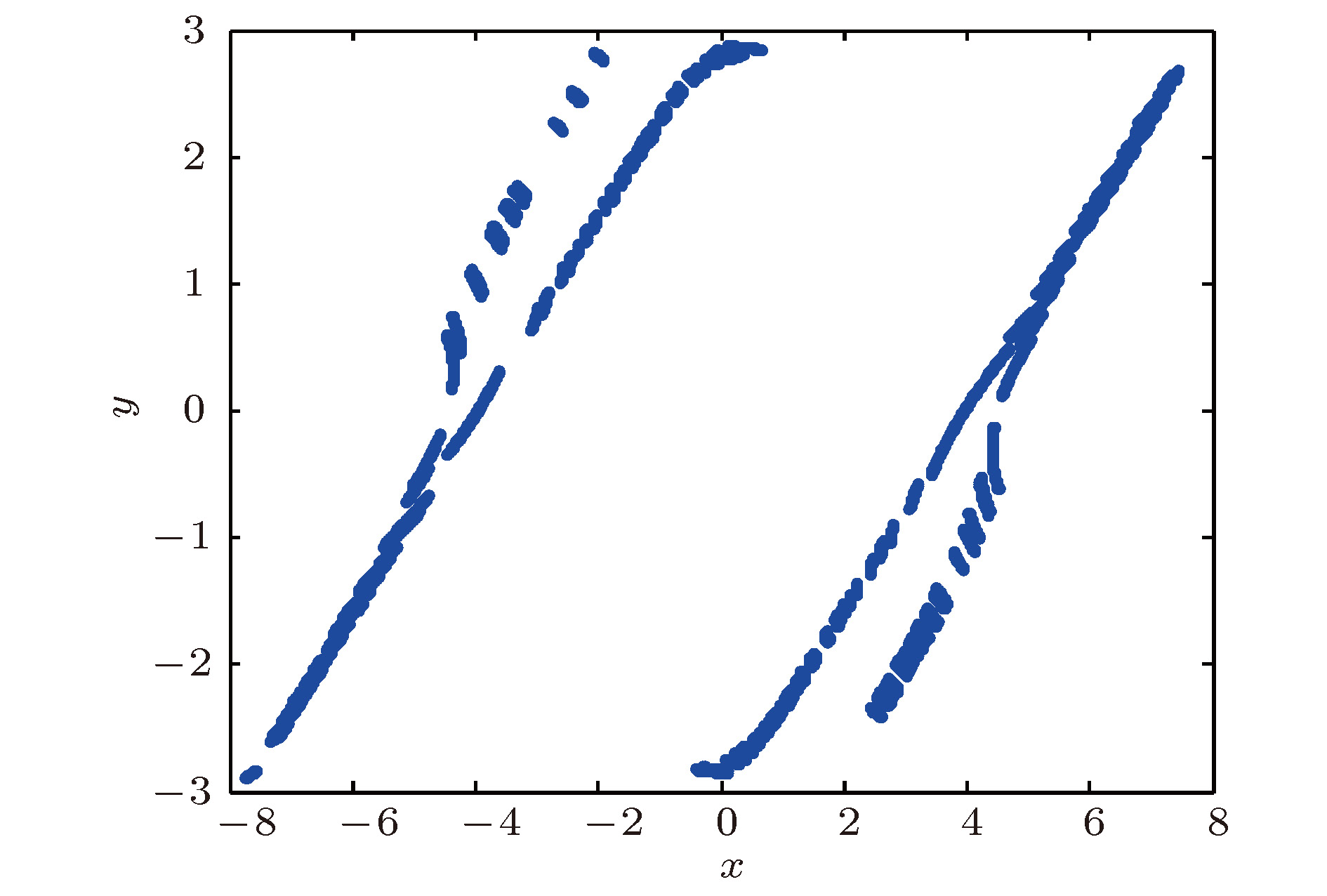
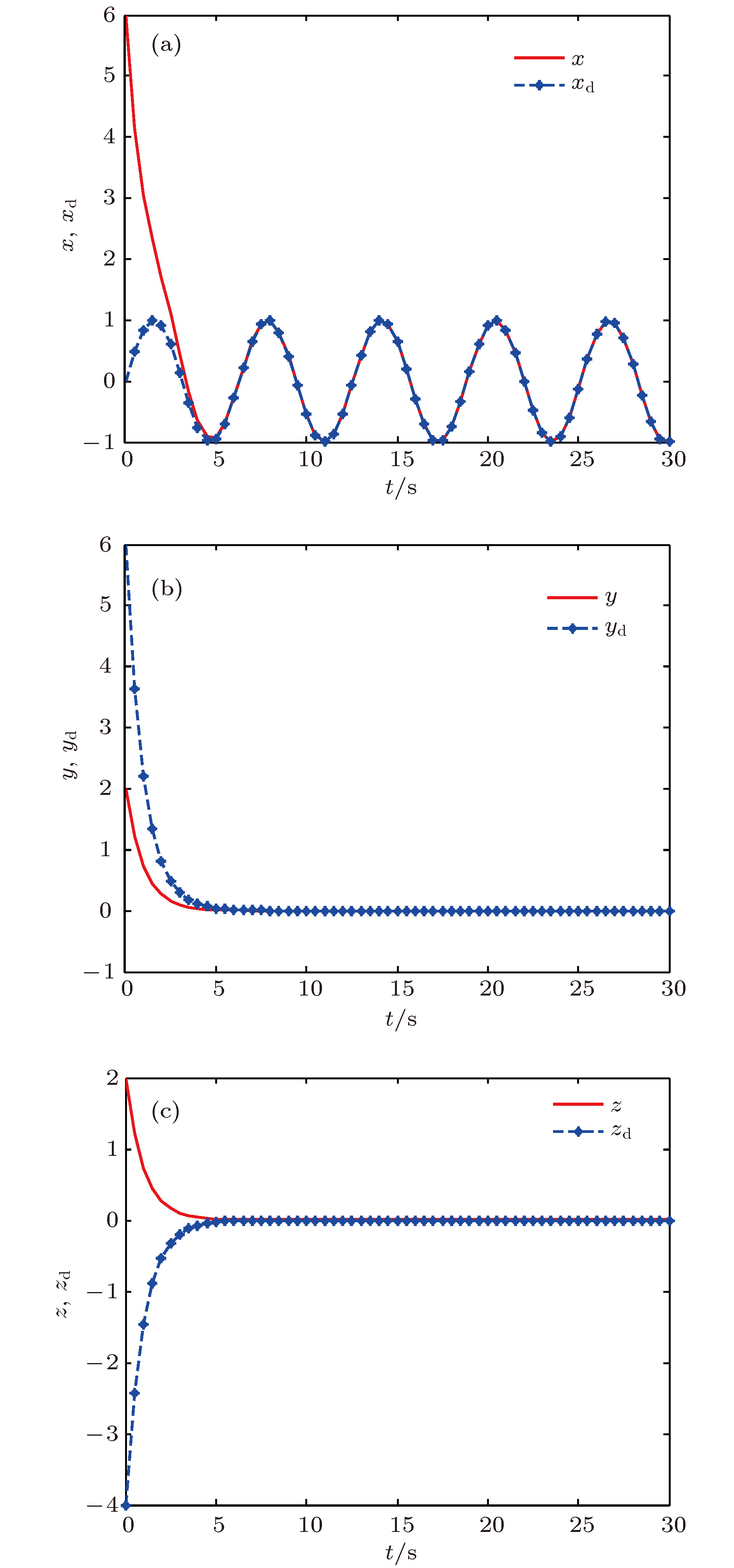
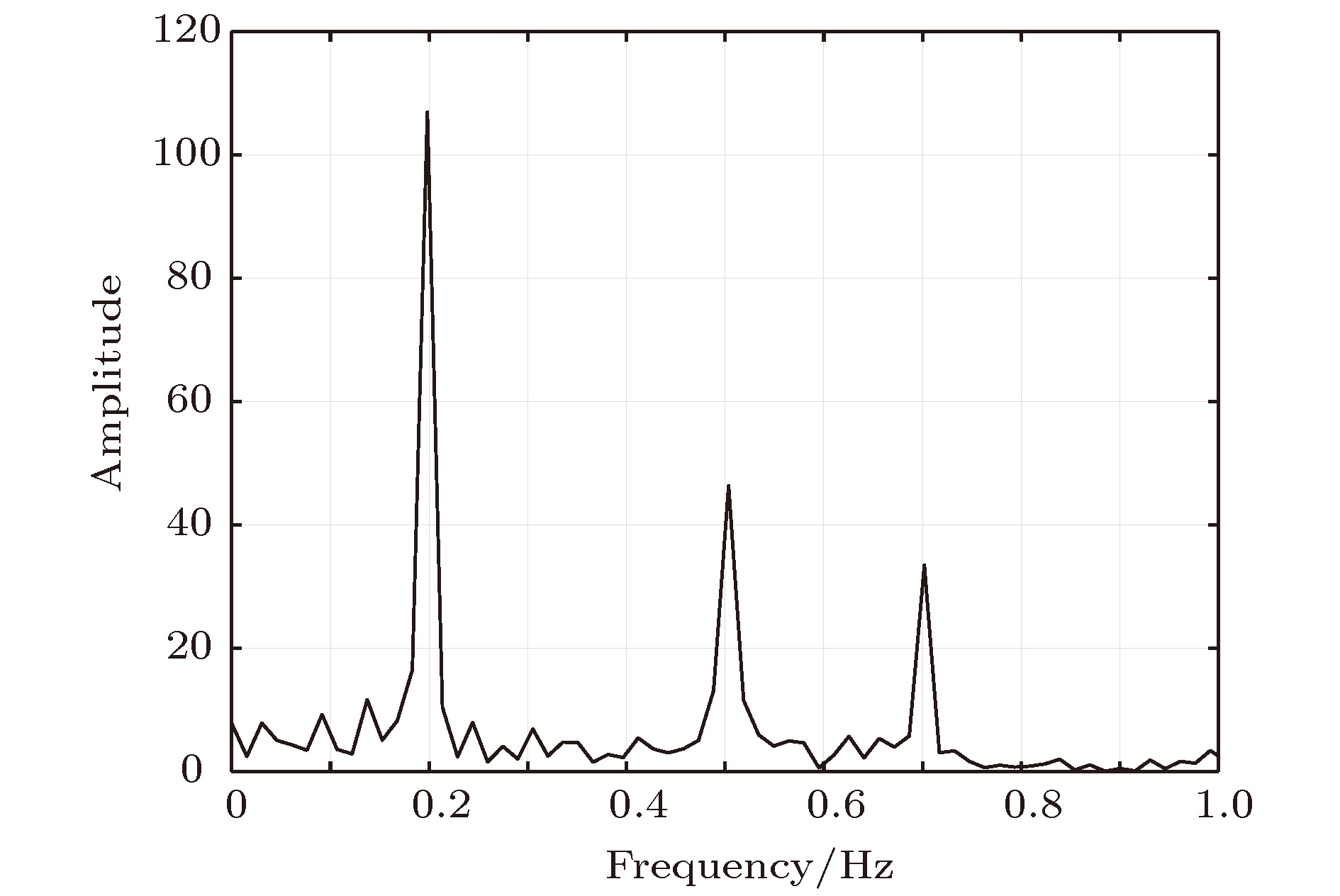
本文采用对数函数序列构造了一个新Chua多涡卷混沌系统, 分析了该系统的非线性动力学行为, 主要包括对称性、不变性、平衡点、最大李雅普诺夫指数等. 然后, 设计递归反步控制器控制Chua多涡卷混沌系统中的混沌行为. 最后, 利用Chua多涡卷混沌系统检测了多频微弱周期信号. 结果表明, 对数函数序列与新Chua双涡卷混沌系统相结合能够产生丰富的Chua多涡卷混沌吸引子. 产生机制为指标2的鞍焦平衡点用于产生涡卷, 指标1的鞍焦平衡点用于连接涡卷. 递归反步控制器能够将Chua多涡卷混沌系统控制到不动点或给定的正弦函数. Chua多涡卷混沌系统与递归反步控制器相结合的新微弱信号检测方法能够检测出淹没在高斯噪声背景下多频微弱周期信号的各频率.
-
关键词:
- Chua多涡卷混沌系统 /
- 对数函数序列 /
- 递归反步控制器 /
- 微弱信号检测
Chaos has great potential applications in engineering fields, such as secure communication and digital encryption. Since the double-scroll Chua’s circuit was developed first by Chua, it has quickly become a paradigm to study the double-scroll chaotic attractors. Compared with the conventional double-scroll chaotic attractors, the multi-scroll chaotic attractors have complex structures and rich nonlinear dynamical behaviors. The multi-scroll chaotic attractors have been applied to various chaos-based information technologies, such as secure communication and chaotic cryptanalysis. Hence, the generation of the multi-scroll chaotic attractors has become a hot topic in research field of chaos at present. In this paper, a novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system is constructed by using a logarithmic function series. The nonlinear dynamical behaviors of the novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system are analyzed, including symmetry, invariance, equilibrium points, the largest Lyapunov exponent, etc. The existence of chaos is confirmed by theoretical analyses and numerical simulations. The results show that the rich Chua multi-scroll chaotic attractors can be generated by combining the logarithmic function series with the novel Chua double-scroll chaotic system. The generation mechanism of the Chua multi-scroll chaotic attractors is that the saddle-focus equilibrium points of index 2 are used to generate the scrolls, and the saddle-focus equilibrium points of index 1 are used to connect these scrolls. Then, three recursive back-stepping controllers are designed to control the chaotic behavior in the novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system. The recursive back-stepping controllers can control the novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system to a fixed point or a given sinusoidal function. Finally, a new method of detecting a weak signal embedded in the Gaussian noise is proposed on the basis of the novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system and the recursive back-stepping controllers. The immunity of the novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system to the Gaussian noise with the zero mean is analyzed by using the stochastic differential equation theory. The results show that the proposed new method of detecting the weak signal can detect the frequencies of the multi-frequency weak periodic signal embedded in the Gaussian noise. In addition, the novel Chua multi-scroll chaotic system has strong immunity to any Gaussian noise with the zero mean. The proposed method provides a new thought for detecting the weak signal.-
Keywords:
- Chua multi-scroll chaotic system /
- logarithmic function series /
- recursive back-stepping controllers /
- weak signal detection
[1] Chua L O, Komuro M, Matsumoto T 1986 IEEE T. Circuits 33 1072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Suykens J A K, Van de walle J 1993 IEEE T. Circuits-I 40 861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lü J H, Chen G R, Yu X H, Leung H 2004 IEEE T. Circuits-I 51 2476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lü J H, Han F L, Yu X H, Chen G R 2004 Automatica 40 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 陈仕必, 曾以成, 徐茂林, 陈家胜 2011 60 020507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen S B, Zeng Y C, Xu M L, Chen J S 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 020507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 艾星星, 孙克辉, 贺少波 2014 63 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ai X X, Sun K H, He S B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hong Q H, Xie Q G, Xiao P 2017 Nonlinear Dyn. 87 1015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang G T, Wang F Q 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 018201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu F, Yu P 2010 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 362 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Z, Wen G L, Zhou H A, Chen J Y 2017 Optik 130 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang C H, Luo X W, Wan Z 2014 Optik 125 6716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lü J H, Murali K, Sinha S, Leung H, Aziz-Alaoui M A 2008 Phys. Lett. A 372 3234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yuan F, Wang G Y, Wang X W 2016 Chaos 26 073107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C H, Liu X M, Xia H 2017 Chaos 27 033114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hu X Y, Liu C X, Liu L, Yao Y P, Zheng G C 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang C H, Xia H, Zhou L 2017 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 27 1750091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 肖利全, 段书凯, 王丽丹 2018 67 090502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao L Q, Duan S K, Wang L D 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 090502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang G Y, Yuan F, Chen G R, Zhang Y 2018 Chaos 28 013125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ott E, Grebogi C, Yorke J A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 1196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang C H, Ge Z M, Chang C M, Li S Y 2010 Nonlinear Anal-real. 11 1977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Danaca M F, Fečkan M 2019 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 74 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Litak G, Syta A, Borowice M 2007 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 32 694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gamal Mahmoud M, Ayman A A, Tarek M A, Emad E M 2017 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 104 680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shen Y J, Wen S F, Yang S P, Guo S Q, Li L R 2018 Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 98 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mfoumou G S, Kenmoé G D, Kofané T C 2019 Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 119 399
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Harb A, Zaher A, Zohdy M 2002 Proceedings of the American Control Conference Anchorage, Ak, USA, May 8-10, 2002 p2251
[27] Laoye J A, Vincent U E, Kareem S O 2009 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 39 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Njah A N, Sunday O D 2009 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 41 2371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Njah A N 2010 Nonlinear Dyn. 61 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Birx D L, Pipenberg S J 1992 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks Baltimore, MD, USA, June 7-11, 1992 p881
[31] 徐艳春, 杨春玲 2010 哈尔滨工业大学学报 42 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Y C, Yang C L 2010 Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology 42 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Xu Y C, Yang C L, Qu X D 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 030516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li G Z, Zhang B 2017 IEEE T. Ind. Electron. 64 2255
[34] Zhong G Q, Man K F, Chen G R 2002 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 12 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yu S M, Lü J H, Chen G R 2007 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 17 1785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Christopher P S 1993 IEEE T. Circuits-I 40 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Cafagna D, Grassi G 2003 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 13 2889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] 李月, 杨宝俊, 石要武 2003 52 526
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Yang B J, Shi Y W 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 526
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 钱勇, 黄成军, 陈陈, 江秀臣 2007 中国电机工程学报 27 89
Qian Y, Huang C J, Chen C, Jiang X C 2007 Proceedings of the CSEE 27 89
-
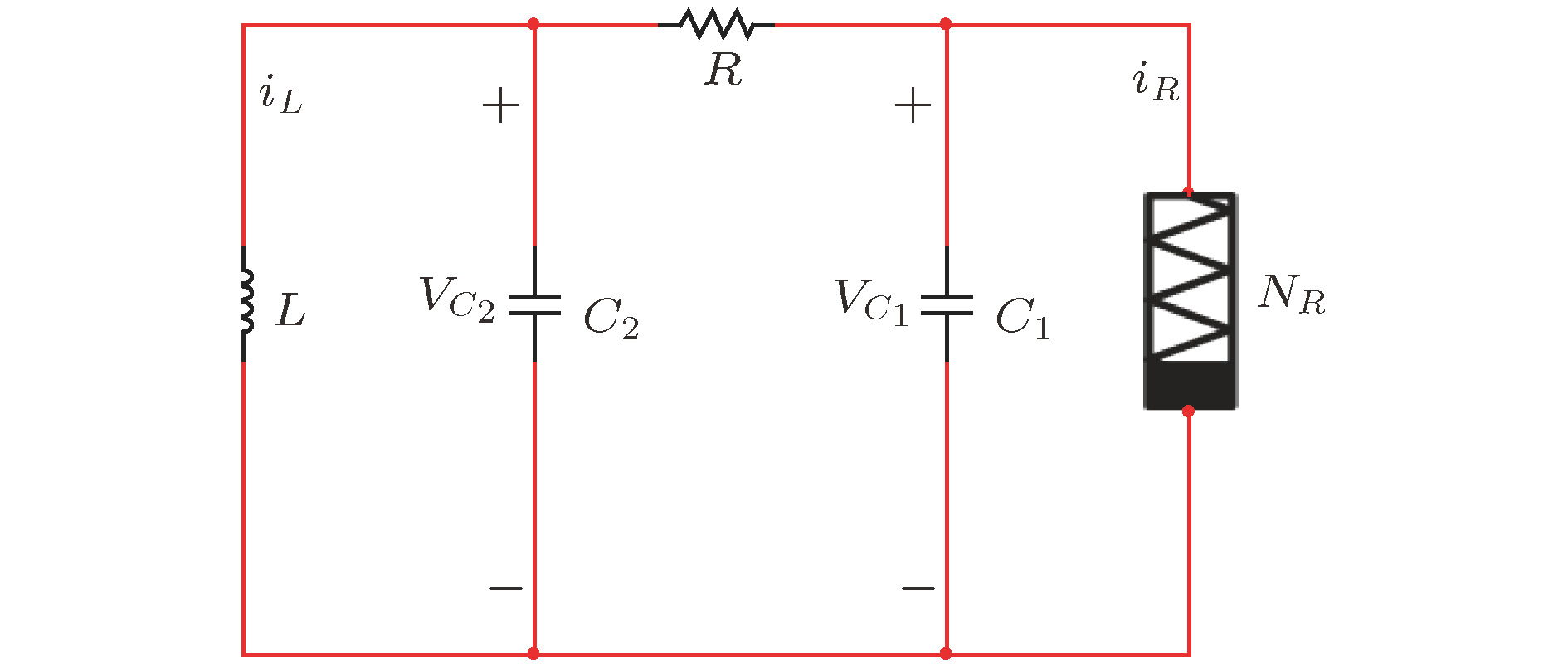
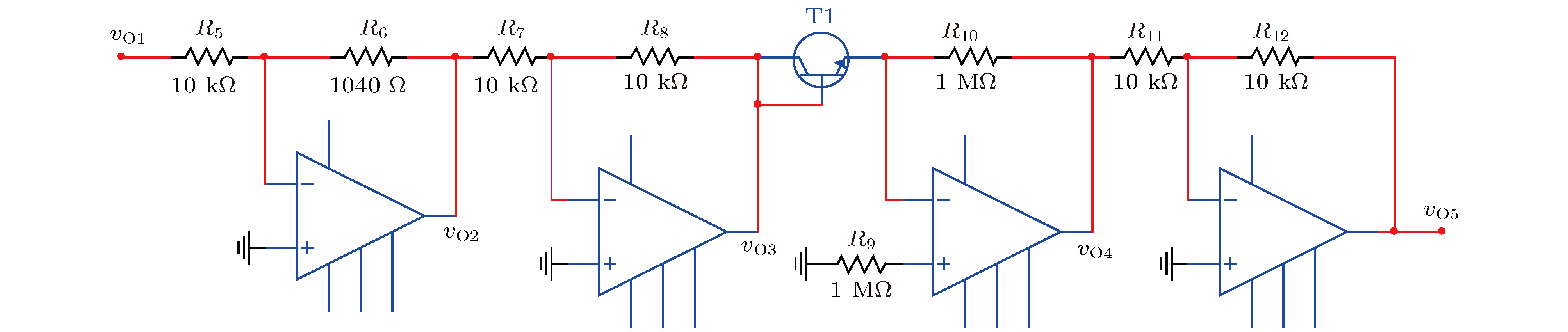
图 8
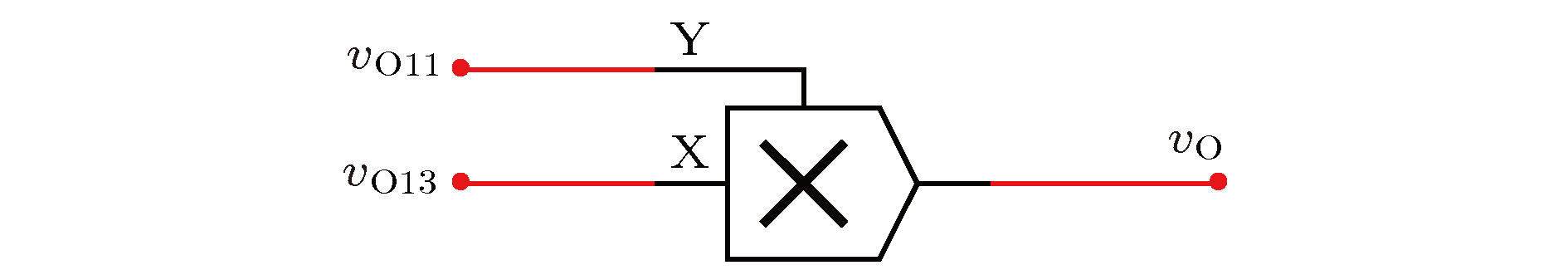
$g\left( {{v_{{C_1}}}} \right) = \log _2^{\frac{{{{\rm{e}}^{ - 4\left| {{v_{{C_1}}}} \right|}} + 1}}{2}} \cdot {\rm{sgn}} ( - {v_{{C_1}}})$ 的电路图Fig. 8. Circuit diagram of
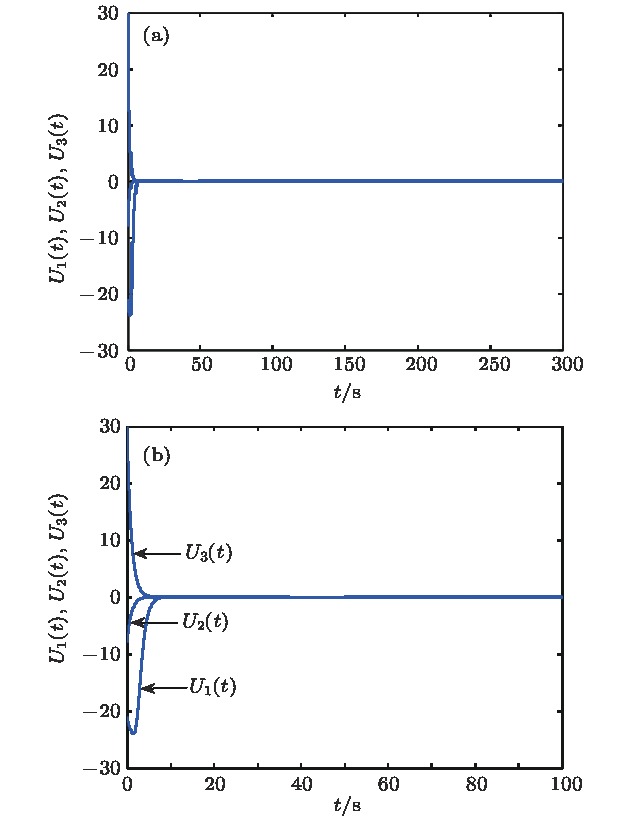
$g\left( {{v_{{C_1}}}} \right) = \log _2^{\frac{{{{\rm{e}}^{ - 4\left| {{v_{{C_1}}}} \right|}} + 1}}{2}}\times$ $ {\rm{sgn}} ( - {v_{{C_1}}})$ .图 22 控制信号
${U_1}\left( t \right)$ 、${U_2}\left( t \right)$ 、${U_3}\left( t \right)$ 的时域图 (a)原始图; (b)放大图,$ t = [0,100] {\rm{s}} $ Fig. 22. Time domain diagram of control signals
${U_1}\left( t \right)$ 、${U_2}\left( t \right)$ 、${U_3}\left( t \right)$ : (a) Original diagram (b) enlarging diagram,$t = [0,100]{\rm{ s}}$ .表 1 12-涡卷混沌吸引子的平衡点、特征值和平衡点的类型
Table 1. Equilibrium points, eigenvalues and types of equilibrium points for the 12-scroll chaotic attractor.
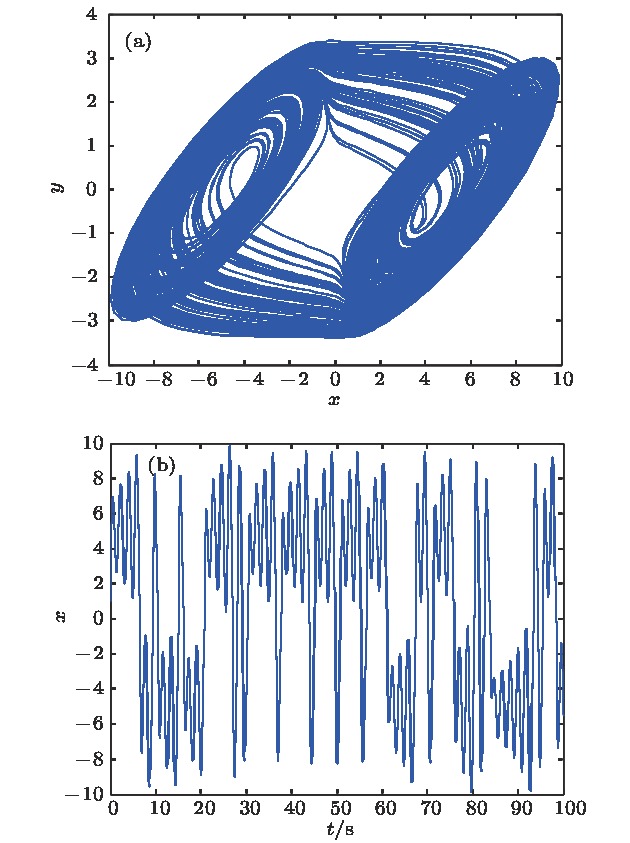
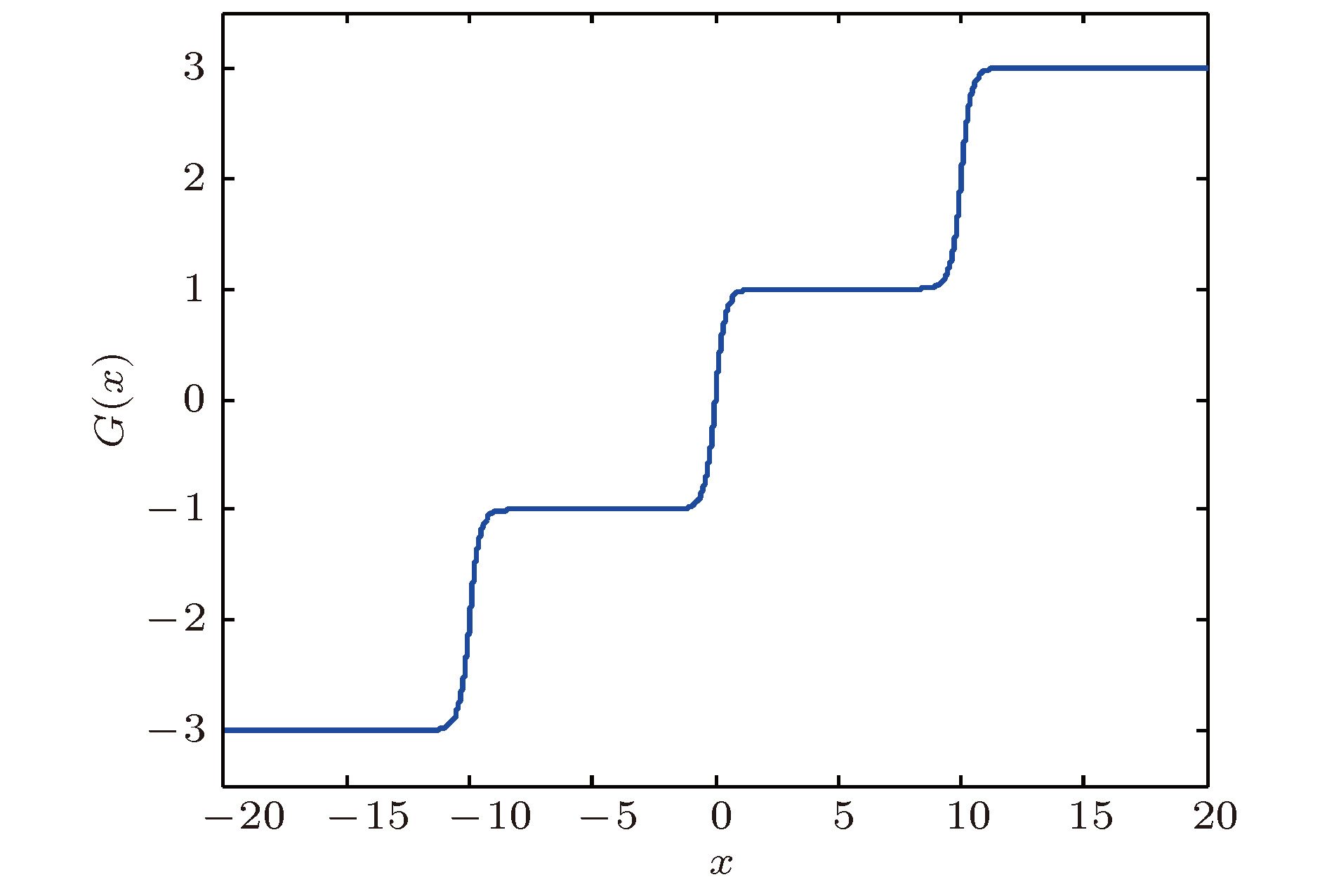
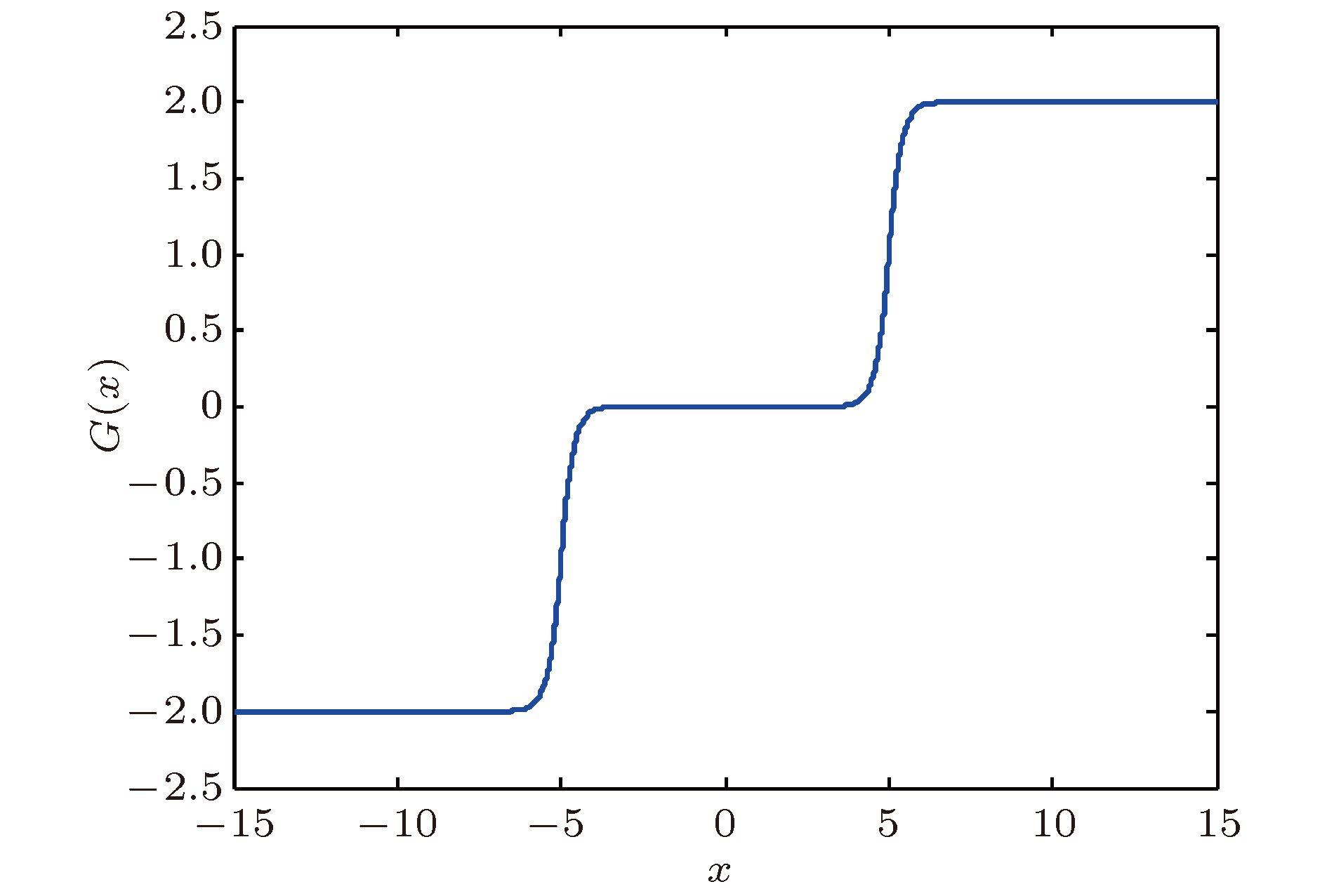
平衡点 特征值 平衡点的类型 ${Q_0}\left( {0,0,0} \right)$ $67.2809$,$ - 0.5730 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.9544}}$ Ⅰ ${Q_{1,2}}\left( { \pm 10,0,0} \right)$ $67.2809$,$ - 0.5730 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.9544}}$ Ⅰ ${Q_{3,4}}\left( { \pm 20,0,0} \right)$ $67.2809$,$ - 0.5730 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.9544}}$ Ⅰ ${Q_{5,6}}\left( { \pm 30,0,0} \right)$ $67.2809$,$ - 0.5730 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.9544}}$ Ⅰ ${Q_{7,8}}\left( { \pm 40,0,0} \right)$ $67.2809$,$ - 0.5730 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.9544}}$ Ⅰ ${Q_{9,10}}\left( { \pm 50,0,0} \right)$ $67.2809$,$ - 0.5730 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.9544}}$ Ⅰ ${Q_{11,12}}\left( { \pm 5,0,0} \right)$ $ - 6.2777$,$0.1389 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.5671}}$ Ⅱ ${Q_{13,14}}\left( { \pm 15,0,0} \right)$ $ - 6.2777$,$0.1389 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.5671}}$ Ⅱ ${Q_{15,16}}\left( { \pm 25,0,0} \right)$ $ - 6.2777$,$0.1389 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.5671}}$ Ⅱ ${Q_{17,18}}\left( { \pm 35,0,0} \right)$ $ - 6.2777$,$0.1389 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.5671}}$ Ⅱ ${Q_{19,20}}\left( { \pm 45,0,0} \right)$ $ - 6.2777$,$0.1389 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.5671}}$ Ⅱ ${Q_{2{\rm{1}},2{\rm{2}}}}\left( { \pm 55,0,0} \right)$ $ - 6.2777$,$0.1389 \pm {\rm{i3}}{\rm{.5671}}$ Ⅱ -
[1] Chua L O, Komuro M, Matsumoto T 1986 IEEE T. Circuits 33 1072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Suykens J A K, Van de walle J 1993 IEEE T. Circuits-I 40 861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lü J H, Chen G R, Yu X H, Leung H 2004 IEEE T. Circuits-I 51 2476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lü J H, Han F L, Yu X H, Chen G R 2004 Automatica 40 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 陈仕必, 曾以成, 徐茂林, 陈家胜 2011 60 020507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen S B, Zeng Y C, Xu M L, Chen J S 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 020507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 艾星星, 孙克辉, 贺少波 2014 63 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ai X X, Sun K H, He S B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hong Q H, Xie Q G, Xiao P 2017 Nonlinear Dyn. 87 1015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang G T, Wang F Q 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 018201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu F, Yu P 2010 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 362 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Z, Wen G L, Zhou H A, Chen J Y 2017 Optik 130 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang C H, Luo X W, Wan Z 2014 Optik 125 6716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lü J H, Murali K, Sinha S, Leung H, Aziz-Alaoui M A 2008 Phys. Lett. A 372 3234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yuan F, Wang G Y, Wang X W 2016 Chaos 26 073107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C H, Liu X M, Xia H 2017 Chaos 27 033114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hu X Y, Liu C X, Liu L, Yao Y P, Zheng G C 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang C H, Xia H, Zhou L 2017 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 27 1750091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 肖利全, 段书凯, 王丽丹 2018 67 090502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao L Q, Duan S K, Wang L D 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 090502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang G Y, Yuan F, Chen G R, Zhang Y 2018 Chaos 28 013125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ott E, Grebogi C, Yorke J A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 1196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang C H, Ge Z M, Chang C M, Li S Y 2010 Nonlinear Anal-real. 11 1977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Danaca M F, Fečkan M 2019 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 74 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Litak G, Syta A, Borowice M 2007 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 32 694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gamal Mahmoud M, Ayman A A, Tarek M A, Emad E M 2017 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 104 680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shen Y J, Wen S F, Yang S P, Guo S Q, Li L R 2018 Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 98 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mfoumou G S, Kenmoé G D, Kofané T C 2019 Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 119 399
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Harb A, Zaher A, Zohdy M 2002 Proceedings of the American Control Conference Anchorage, Ak, USA, May 8-10, 2002 p2251
[27] Laoye J A, Vincent U E, Kareem S O 2009 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 39 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Njah A N, Sunday O D 2009 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 41 2371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Njah A N 2010 Nonlinear Dyn. 61 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Birx D L, Pipenberg S J 1992 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks Baltimore, MD, USA, June 7-11, 1992 p881
[31] 徐艳春, 杨春玲 2010 哈尔滨工业大学学报 42 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Y C, Yang C L 2010 Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology 42 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Xu Y C, Yang C L, Qu X D 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 030516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li G Z, Zhang B 2017 IEEE T. Ind. Electron. 64 2255
[34] Zhong G Q, Man K F, Chen G R 2002 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 12 2907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yu S M, Lü J H, Chen G R 2007 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 17 1785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Christopher P S 1993 IEEE T. Circuits-I 40 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Cafagna D, Grassi G 2003 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 13 2889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] 李月, 杨宝俊, 石要武 2003 52 526
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Yang B J, Shi Y W 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 526
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 钱勇, 黄成军, 陈陈, 江秀臣 2007 中国电机工程学报 27 89
Qian Y, Huang C J, Chen C, Jiang X C 2007 Proceedings of the CSEE 27 89
计量
- 文章访问数: 21088
- PDF下载量: 224
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: